Demographics of Ukraine
| Demographics of Ukraine | |
|---|---|
 Ukraine's population pyramid, 2024 | |
| Population | Including Russian occupied territory: 41,130,432 Excluding Russian occupied territory: 36,744,636 |
| Growth rate | −6.6 |
| Birth rate | 8.6 |
| Death rate | 15.2 |
| Life expectancy | 71.76 years |
| • male | 66.69 |
| • female | 76.72 |
| Fertility rate | 0.7 |
| Infant mortality rate | 7.0 deaths/1,000 |
| Net migration rate | −5.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015) |
| Age structure | |
| 0–14 years | |
| 15–64 years | |
| 65 and over | |
| Sex ratio | |
| At birth | 1.06 male(s)/female |
| Under 15 | 1.06 male(s)/female |
| 15–64 years | 0.92 male(s)/female |
| 65 and over | 0.51 male(s)/female |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | noun: Ukrainian(s) adjective: Ukrainian |
| Major ethnic | Ukrainians (77.8%) 2001 |
| Minor ethnic | Russians (17.3%) 2001, Other (4.9%) 2001 |
| Language | |
| Official | Ukrainian |
| Spoken | Ukrainian, Russian, others |


According to the United Nations, Ukraine has a population of 37.9 million as of 2024.[5]
This drop is in large part due to the ongoing Ukrainian refugee crisis and loss of territory caused by Russia's invasion of Ukraine. The most recent (and only) census of post-Soviet Ukraine occurred in 2001, and much of the information presented is potentially inaccurate and/or outdated.
In July 2023, Reuters reported that due to refugee outflows, the population of Ukrainian-controlled areas may have decreased to 28 million,[6] a steep decline from Ukraine's 2020 population of almost 42 million.[7][8]
History
The majority of the historical information is sourced from Demoscope.ru.[9]
The territory of Ukraine has shifted greatly throughout history. Until 1939, Western Ukraine, west of the Zbruch River, had mostly been part of the Kingdom of Galicia and later the Polish Republic. Detailed information for those territories is missing (for more information, see Demographics of Poland). Crimea changed hands as well; in 1897 it was a part of the Taurida Governorate, but after the October Revolution became part of the Russian SFSR, and in 1954 was brought under the administration of the Ukrainian SSR. The territory of Budjak (southern Bessarabia) became a part of the Ukrainian SSR in June 1940.
There were roughly four million Ukrainians at the end of the 17th century.[10]
The censuses of 1926 through 1989 were conducted in the Ukrainian SSR. The 1897 census is drawn from the statistics of nine governorates located in present-day Ukraine. The 1906 records are taken from Statoids.com, which provides a broad degree of historical context on imperial Russia. The 1931 census statistics were estimated by Professor Zenon Kuzelia,[11] whose calculations are as of 1 January 1931. The Encyclopedia of Ukraine mentions Kuzelia as one of the only ethnographic sources available, due to the lack of an official census.[12][page needed][13]
Famines and migration
The Ukrainian famines of the 1930s, followed by the devastation of World War II, created a demographic disaster for the country. In 1933, life expectancy at birth fell to levels as low as ten years of age for females and seven for males, and plateaued around 25 for females and 15 for males between 1941 and 1944.[14] According to The Oxford companion to World War II, "Over 7 million inhabitants of Ukraine, more than one-sixth of the pre-war population, were killed during the Second World War."[15]

Significant migration took place in the first years of Ukrainian independence. More than one million people moved into Ukraine in 1991–92, mostly from other former Soviet republics. Between 1991 and 2004, a total of 2.2 million immigrated to Ukraine (2 million of these from other former Soviet Union states), and 2.5 million emigrated from Ukraine (1.9 million of these to other former Soviet Union republics).[16] As of 2015, immigrants in Ukraine constituted an estimated 11.4% of the total population, or 4.8 million people.[17] In 2006, there were an estimated 1.2 million Canadians of Ukrainian ancestry,[18] giving Canada the world's third-largest Ukrainian population, behind Ukraine and Russia. Outside of these, there are also large Ukrainian diaspora communities in Poland, the United States, Brazil, Kazakhstan, and Argentina.
Since about 2015, a growing number of Ukrainians have worked in the European Union, particularly Poland. Eurostat reported that 662,000 Ukrainians received EU residence permits in 2017, 585,439 of them in Poland. In 2019, World Bank statistics showed that money remittances back to Ukraine roughly doubled from 2015 to 2018, and amounted to approximately 4% of Ukraine's GDP.[19][20] Ukraine only keeps records of its citizens who apply for foreign citizenship, not foreign residency[21]
With the Russian invasion of Ukraine, eight million people fled during the ensuing Ukrainian refugee crisis, Europe's biggest since World War II. Most have gone to Central Europe.
Population decline

According to estimates by the State Statistics Service of Ukraine, the population of Ukraine (excluding Crimea) on 1 May 2021 was 41,442,615.[1]
The country's population has been declining since the 1990s because of a high emigration rate, coupled with high death rates and low birth rates. The population has been shrinking by an average of over 300,000 annually since 1993.
In 2007, the country's rate of population decline was the fourth highest in the world.[24] But between 2008 and 2010, over 1.5 million children were born in Ukraine, compared with fewer than 1.2 million in 1999–2001. In 2008, Ukraine posted record-breaking birth rates not seen since its 1991 independence. Infant mortality rates also dropped from 10.4 deaths to 8.3 per 1,000 children under one year of age, a lower rate than in 153 other countries.[25]
In 2019, the Ukrainian government conducted an electronic census using multiple sources, including mobile phone and pension data, and estimated that Ukraine's population, excluding Crimea and parts of the Donbas, to be 37.3 million. About 20 million were of active working age.[26][27]
The Russian invasion considerably deepened the country's demographic crisis due to the illegal annexation of multiple oblasts, numerous civilians fleeing the country, and high casualties. A July 2023 study by the Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies stated the following:
"Regardless of how long the war lasts and whether or not there is further military escalation, Ukraine is unlikely to recover demographically from the consequences of the war. Even in 2040 it will have only about 35 million inhabitants, around 20% fewer than before the war (2021: 42.8 million) and the decline in the working-age population is likely to be the most severe and far-reaching."
The study examined different scenarios, from a "best case", in which the war ended in 2023 without significant further escalation, to a "worst case", ending in 2025 after further escalation. Flight from war particularly affects the southern and eastern regions and especially educated women of child-bearing age and their children. With an estimate of more than 20% of refugees not returning, study author Maryna Tverdostup concludes that this will lead to long-term shrinking and will significantly impair the conditions for reconstruction.[28]
Fertility and natalist policies
As of 2020, the birth rate in Ukraine was 8.1 live births/1,000 population, and the death rate 14.7 deaths/1,000 population.[4]
Lowest-low fertility, defined as total fertility below 1.3, is being encountered across Europe, attributed by many to postponement of the initiation of childbearing. Ukraine, where total fertility (1.1 in 2001), was one of the world's lowest, shows that there is more than one pathway to lowest-low fertility. Although Ukraine underwent immense political and economic transformations from 1991 to 2004, it maintained a young age at first birth and nearly universal childbearing. Analysis of official national statistics and the Ukrainian Reproductive Health Survey show that fertility declined to very low levels without a transition to a later pattern of childbearing. Findings from focus group interviews suggest that the early fertility pattern was explained by the persistence of traditional norms for childbearing and the roles of men and women, concerns about medical complications and infertility at a later age, and the link between early fertility and early marriage.[29] Ukraine subsequently has one of the oldest populations in the world, with an average age of 40.8 years.[30]
To help mitigate population decline, the government increased child support payments, providing one-time payments of 12,250 hryvnias for the first child, 25,000 hryvnias for the second and 50,000 hryvnias for the third and fourth, along with monthly payments of 154 hryvnias per child.[31][32] The demographic trend showed signs of improvement as the birth rate grew steadily from 2001 to 2013.[33] Five of the country's 24 provinces showed net population growth over the first nine months of 2007, and nationwide population decline showed signs of stabilization. In 2007, the highest birth rates were in the western oblasts.[34] In 2008, Ukraine emerged from lowest-low fertility, and the upward trend continued to 2012, with population decline slowing year after year. If early 2010s trends had persisted, the population could have returned to positive growth later that decade. Similar trends occurred in Russia and Belarus, which experienced population growth in the 2010s.
In 2014, the strong drop in births returned, and 2018 saw fewer than half the number of births of 1989 (see demographic tables). In 2020, the number of births decreased to 293,000, reaching rates not seen in a quarter century.
Mass emigration and property destruction caused by the Russian invasion led Ukraine's birth to drop still further: it was 28% lower in the first half of 2023 than the first half of 2021.[35] However, a small but meaningful increase in births may have occurred, with a potential fertility rate increase to 1.60 children per woman, higher than the 2012 peak of 1.53.[36]
Population


Life expectancy

- total population: 71.37
 years
years - male: 66.34
 years
years - female: 76.22
 years (2013 official)
years (2013 official)
Average life expectancy at birth of the total population.[37]
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 61.83 |
| 1955–1960 | |
| 1960–1965 | |
| 1965–1970 | |
| 1970–1975 | |
| 1975–1980 | |
| 1980–1985 | |
| 1985–1990 | |
| 1990–1995 | |
| 1995–2000 | |
| 2000–2005 | |
| 2005–2010 | |
| 2010–2015 |

Total fertility rate
- 1.12
 children born/woman (2000)
children born/woman (2000) - 1.44
 children born/woman (2010)
children born/woman (2010) - 1.22
 children born/women (2020)
children born/women (2020)
Vital statistics
Notable events in Ukrainian demographics:
- 1932–33 – South Soviet Famine in Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
- 1939 – Addition of western oblasts to Ukraine with the end of the Second Polish Republic due to German–Soviet invasion of Poland at the beginning of Second World War
- 1991 – Independence from the USSR
- 2004–2005 – Orange Revolution
- 2014 – Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
- 2022 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
Ukrainian provinces of the Russian Empire
The figures below refer to the nine governorates of the Russian Empire (Volhynia, Katerynoslav, Kyiv, Podilia, Poltava, Tauryda, Kharkiv, Kherson and Chernihiv) with a Ukrainian majority.[41]
| Average population | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Total fertility rates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 24,969,000 | 1,203,334 | 660,723 | 542,611 | 48.2 | 26.5 | 21.7 | |
| 1901 | 25,505,000 | 1,123,519 | 657,883 | 465,636 | 44.1 | 25.8 | 18.3 | |
| 1902 | 25,935,000 | 1,207,512 | 681,580 | 525,932 | 46.6 | 26.3 | 20.3 | |
| 1903 | 26,449,000 | 1,188,404 | 663,067 | 525,337 | 44.9 | 25.1 | 19.9 | |
| 1904 | 26,961,000 | 1,228,116 | 682,068 | 546,048 | 45.6 | 25.3 | 20.3 | |
| 1905 | 27,210,000 | 1,160,308 | 779,107 | 381,201 | 41.1 | 27.6 | 14.0 | |
| 1906 | 27,949,000 | 1,225,951 | 724,045 | 501,906 | 43.9 | 25.9 | 18.0 | |
| 1907 | 28,418,000 | 1,279,027 | 701,451 | 577,576 | 45.0 | 24.7 | 20.3 | |
| 1908 | 29,069,000 | 1,232,862 | 692,624 | 540,238 | 42.4 | 23.8 | 18.6 | |
| 1909 | 29,700,000 | 1,226,155 | 744,818 | 481,337 | 41.3 | 25.1 | 16.2 | |
| 1910 | 30,297,000 | 1,225,658 | 839,491 | 386,167 | 40.5 | 27.7 | 12.7 | |
| 1911 | 30,858,000 | 1,240,985 | 670,742 | 570,243 | 40.2 | 21.7 | 18.5 | |
| 1912 | 30,580,000 | 1,245,358 | 654,157 | 591,201 | 40.7 | 21.4 | 19.3 | |
| 1913 | 31,142,000 | 1,222,277 | 715,924 | 506,353 | 39.2 | 23.0 | 16.3 | 6.00 |
| 1914 | 30,973,000 | 1,240,114 | 716,875 | 523,239 | 40.0 | 23.1 | 16.9 |
Between WWI and WWII
| [42] | Average population | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | Life Expectancy (male) | Life Expectancy (female) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1924 | 27,400,000 | 1,211,000 | 484,880 | 726,120 | 43.3 | 17.3 | 25.9 | |||
| 1925 | 28,000,000 | 1,246,000 | 531,819 | 714,181 | 43.4 | 18.5 | 24.9 | 5.39 | ||
| 1926 | 28,700,000 | 1,258,000 | 518,656 | 739,344 | 42.5 | 17.5 | 25.0 | |||
| 1927 | 29,589,000 | 1,228,000 | 579,000 | 649,000 | 40.6 | 19.1 | 21.5 | 43.3 | 46.8 | |
| 1928 | 30,251,000 | 1,178,000 | 575,000 | 603,000 | 38.1 | 18.6 | 19.5 | 44.6 | 48.7 | |
| 1929 | 30,894,000 | 1,115,000 | 585,000 | 530,000 | 35.5 | 18.6 | 16.9 | 42.8 | 46.7 | |
| 1930 | 31,436,000 | 1,053,000 | 580,000 | 473,000 | 33.0 | 18.2 | 14.8 | 42.5 | 46.9 | |
| 1931 | 31,882,000 | 1,001,000 | 553,000 | 448,000 | 31.0 | 17.1 | 13.9 | 43.5 | 47.9 | |
| 1932 | 32,342,000 | 801,000 | 746,000 | 55,000 | 24.7 | 23.0 | 1.7 | 34.5 | 39.4 | |
| 1933 | 32,456,000 | 564,000 | 2,104,000 | −1,540,000 | 17.4 | 64.8 | −47.4 | |||
| 1934 | 30,916,000 | 562,000 | 508,000 | 54,000 | 18.1 | 16.4 | 1.7 | 37.6 | 42.1 | |
| 1935 | 31,006,000 | 770,000 | 381,000 | 389,000 | 24.5 | 12.1 | 12.4 | 46.3 | 52.7 | |
| 1936 | 31,423,000 | 905,000 | 403,000 | 502,000 | 28.3 | 12.6 | 15.7 | 47.6 | 53.0 | |
| 1937 | 31,957,000 | 1,227,000 | 450,000 | 777,000 | 37.5 | 13.7 | 23.7 | 46.2 | 51.9 | |
| 1938 | 32,742,000 | 1,123,000 | 451,000 | 672,000 | 33.6 | 13.5 | 20.1 | 47.9 | 52.7 | |
| 1939 | 33,425,000 | 1,080,000 | 412,600 | 667,400 | 31.7 | 12.1 | 19.6 | 47.7 | 52.5 | |
| 1940(b) | 40,649,000 | 1,243,000 | 30.6 | 3.80 | 47.4 | 52.4 |
(a) Information is given for Ukraine's territory within its old boundaries up to 17 September 1939 (b) Information is given for Ukraine's territory within its present-day boundaries, after the Soviet annexation of Eastern Galicia and Volhynia in September 1939
After WWII
Source: State Statistics Service of Ukraine[43]
| Average population |
Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Fertility rates | Urban fertility | Rural fertility | Abortions, reported | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945 | 435,230 | ||||||||||
| 1946 | 753,493 | ||||||||||
| 1947 | 712,994 | ||||||||||
| 1948 | 757,783 | ||||||||||
| 1949 | 911,641 | ||||||||||
| 1950 | 36,905,000 | 844,585 | 315,300 | 529,300 | 22.9 | 8.5 | 14.3 | 2.81 | |||
| 1951 | 37,569,000 | 858,052 | 327,500 | 530,600 | 22.8 | 8.7 | 14.1 | 2.76 | |||
| 1952 | 38,141,000 | 846,434 | 325,700 | 520,700 | 22.2 | 8.5 | 13.7 | 2.64 | |||
| 1953 | 38,678,000 | 795,652 | 326,800 | 468,900 | 20.6 | 8.4 | 12.1 | 2.41 | |||
| 1954 | 39,131,000 | 845,128 | 318,500 | 526,600 | 21.6 | 8.1 | 13.5 | 2.48 | |||
| 1955 | 39,506,000 | 792,696 | 296,200 | 496,500 | 20.1 | 7.5 | 12.6 | 2.70 | |||
| 1956 | 40,082,000 | 822,569 | 293,000 | 529,600 | 20.5 | 7.3 | 13.2 | 2.29 | |||
| 1957 | 40,800,000 | 847,781 | 304,800 | 543,000 | 20.8 | 7.5 | 13.3 | 2.29 | |||
| 1958 | 41,512,000 | 873,483 | 286,700 | 586,800 | 21.0 | 6.9 | 14.1 | 2.30 | |||
| 1959 | 42,155,000 | 880,552 | 316,800 | 563,800 | 20.9 | 7.5 | 13.4 | 2.29 | |||
| 1960 | 42,469,000 | 878,768 | 296,171 | 582,597 | 20.7 | 7.0 | 13.7 | 2.24 | |||
| 1961 | 43,097,000 | 843,482 | 304,346 | 539,136 | 19.6 | 7.1 | 12.5 | 2.17 | |||
| 1962 | 43,559,000 | 823,151 | 331,454 | 491,697 | 18.9 | 7.6 | 11.3 | 2.14 | |||
| 1963 | 44,088,000 | 794,969 | 323,556 | 471,413 | 17.9 | 7.3 | 10.6 | 2.06 | |||
| 1964 | 44,664,000 | 741,668 | 315,340 | 426,328 | 16.5 | 7.0 | 9.5 | 1.96 | |||
| 1965 | 45,133,000 | 692,153 | 342,717 | 349,436 | 15.3 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 1.99 | |||
| 1966 | 45,548,000 | 713,492 | 344,850 | 368,642 | 15.6 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 2.02 | |||
| 1967 | 45,997,000 | 699,381 | 368,573 | 330,808 | 15.1 | 8.0 | 7.2 | 2.01 | |||
| 1968 | 46,408,000 | 693,064 | 374,440 | 318,624 | 14.9 | 8.0 | 6.9 | 1.99 | |||
| 1969 | 46,778,000 | 687,991 | 404,151 | 283,840 | 14.7 | 8.6 | 6.1 | 2.04 | |||
| 1970 | 47,127,000 | 719,213 | 418,679 | 300,534 | 15.2 | 8.9 | 6.4 | 2.10 | 1,130,315 | ||
| 1971 | 47,507,000 | 736,691 | 424,717 | 311,974 | 15.4 | 8.9 | 6.6 | 2.12 | |||
| 1972 | 47,903,000 | 745,696 | 443,038 | 302,658 | 15.5 | 9.2 | 6.3 | 2.08 | |||
| 1973 | 48,274,000 | 719,560 | 449,351 | 270,209 | 14.9 | 9.3 | 5.6 | 2.04 | |||
| 1974 | 48,571,000 | 736,616 | 455,970 | 280,646 | 15.1 | 9.4 | 5.8 | 2.04 | |||
| 1975 | 48,881,000 | 738,857 | 489,550 | 249,307 | 15.1 | 10.0 | 5.1 | 2.02 | 1,110,223 | ||
| 1976 | 49,151,000 | 747,069 | 500,584 | 246,485 | 15.2 | 10.2 | 5.0 | 1.99 | |||
| 1977 | 49,388,000 | 726,217 | 517,967 | 208,250 | 14.7 | 10.5 | 4.2 | 1.94 | |||
| 1978 | 49,578,000 | 732,187 | 529,681 | 202,506 | 14.7 | 10.7 | 4.1 | 1.96 | |||
| 1979 | 49,755,000 | 735,188 | 552,019 | 183,169 | 14.7 | 11.1 | 3.7 | 1.96 | |||
| 1980 | 50,044,000 | 742,489 | 568,243 | 174,246 | 14.8 | 11.4 | 3.5 | 1.95 | 1,197,000 | ||
| 1981 | 50,222,000 | 733,183 | 568,789 | 164,394 | 14.6 | 11.3 | 3.3 | 1.93 | 1,112,734 | ||
| 1982 | 50,388,000 | 745,591 | 568,231 | 177,360 | 14.8 | 11.3 | 3.5 | 1.94 | 1,131,437 | ||
| 1983 | 50,573,000 | 807,111 | 583,496 | 223,615 | 16.0 | 11.6 | 4.4 | 2.11 | 1,125,686 | ||
| 1984 | 50,768,000 | 792,035 | 610,338 | 181,697 | 15.6 | 12.0 | 3.6 | 2.08 | 1,127,627 | ||
| 1985 | 50,941,000 | 762,775 | 617,548 | 145,227 | 15.0 | 12.1 | 2.9 | 2.02 | 1,179,000 | ||
| 1986 | 51,143,000 | 792,574 | 565,150 | 227,424 | 15.5 | 11.1 | 4.4 | 2.13 | 1,166,039 | ||
| 1987 | 51,373,000 | 760,851 | 586,387 | 174,464 | 14.8 | 11.4 | 3.4 | 2.07 | 1,168,136 | ||
| 1988 | 51,593,000 | 744,056 | 600,725 | 143,331 | 14.4 | 11.6 | 2.8 | 2.04 | 1,080,029 | ||
| 1989 | 51,770,000 | 690,981 | 600,590 | 90,391 | 13.3 | 11.6 | 1.7 | 1.92 | 1.78 | 2.33 | 1,058,414 |
| 1990 | 51,838,500 | 657,202 | 629,602 | 27,600 | 12.7 | 12.1 | 0.5 | 1.84 | 1.69 | 2.27 | 1,019,038 |
| 1991 | 51,944,400 | 630,813 | 669,960 | −39,147 | 12.1 | 12.9 | −0.8 | 1.78 | 1.60 | 2.29 | 957,022 |
| 1992 | 52,056,600 | 596,785 | 697,110 | −100,325 | 11.4 | 13.4 | −1.9 | 1.67 | 1.48 | 2.23 | 932,272 |
| 1993 | 52,244,100 | 557,467 | 741,662 | −184,195 | 10.7 | 14.2 | −3.5 | 1.56 | 1.37 | 2.08 | 860,996 |
| 1994 | 52,114,400 | 521,545 | 764,669 | −243,124 | 10.0 | 14.7 | −4.7 | 1.47 | 1.28 | 1.98 | 798,538 |
| 1995 | 51,728,400 | 492,861 | 792,587 | −299,726 | 9.6 | 15.4 | −5.8 | 1.40 | 1.21 | 1.88 | 740,172 |
| 1996 | 51,297,100 | 467,211 | 776,717 | −309,506 | 9.2 | 15.2 | −6.0 | 1.34 | 1.16 | 1.79 | 687,035 |
| 1997 | 50,818,400 | 442,581 | 754,151 | −311,570 | 8.7 | 14.9 | −6.1 | 1.27 | 1.10 | 1.70 | 596,740 |
| 1998 | 50,370,800 | 419,238 | 719,954 | −300,716 | 8.4 | 14.4 | −6.0 | 1.21 | 1.05 | 1.64 | 525,329 |
| 1999 | 49,918,100 | 389,208 | 739,170 | −349,962 | 7.8 | 14.9 | −7.0 | 1.13 | 0.97 | 1.53 | 495,760 |
| 2000 | 49,429,800 | 385,126 | 758,082 | −372,956 | 7.8 | 15.4 | −7.6 | 1.12 | 0.97 | 1.51 | 434,223 |
| 2001 | 48,923,200 | 376,478 | 745,952 | −369,474 | 7.7 | 15.3 | −7.6 | 1.08 | 0.95 | 1.41 | 369,750 |
| 2002 | 48,457,102 | 390,688 | 754,911 | −364,223 | 8.1 | 15.7 | −7.6 | 1.10 | 0.97 | 1.43 | 345,967 |
| 2003 | 48,003,463 | 408,589 | 765,408 | −356,819 | 8.5 | 16.0 | −7.4 | 1.17 | 1.07 | 1.45 | 315,835 |
| 2004 | 47,622,434 | 427,259 | 761,261 | −334,002 | 9.0 | 16.0 | −7.0 | 1.22 | 1.13 | 1.46 | 289,065 |
| 2005 | 47,280,817 | 426,086 | 781,961 | −355,875 | 9.0 | 16.6 | −7.5 | 1.21 | 1.12 | 1.46 | 263,950 |
| 2006 | 46,929,525 | 460,368 | 758,092 | −297,724 | 9.8 | 16.2 | −6.3 | 1.31 | 1.21 | 1.59 | 229,618 |
| 2007 | 46,646,046 | 472,657 | 762,877 | −290,220 | 10.2 | 16.4 | −6.2 | 1.35 | 1.24 | 1.63 | 210,454 |
| 2008 | 46,372,664 | 510,589 | 754,460 | −243,871 | 11.0 | 16.3 | −5.3 | 1.46 | 1.35 | 1.75 | 217,413 |
| 2009 | 46,143,714 | 512,525 | 706,739 | −194,214 | 11.1 | 15.3 | −4.2 | 1.47 | 1.35 | 1.78 | 194,845 |
| 2010 | 45,962,947 | 497,689 | 698,235 | −200,546 | 10.8 | 15.2 | −4.4 | 1.44 | 1.31 | 1.77 | 176,774 |
| 2011 | 45,778,534 | 502,595 | 664,588 | −161,993 | 11.0 | 14.5 | −3.5 | 1.46 | 1.32 | 1.80 | 169,131 |
| 2012 | 45,633,637 | 520,705 | 663,139 | −142,434 | 11.4 | 14.5 | −3.1 | 1.53 | 1.39 | 1.87 | 153,147 |
| 2013 | 45,553,047 | 503,657 | 662,368 | −158,711 | 11.1 | 14.6 | −3.5 | 1.51 | 1.37 | 1.83 | 147,736 |
| 2014 | 45,426,249 | 465,882 | 632,296 | −166,414 | 10.3 | 14.0 | −3.7 | 1.50 | 1.35 | 1.83 | 116,104 |
| 2015 | 42,929,298 | 411,781 | 594,796 | −183,015 | 9.6 | 13.9 | −4.3 | 1.51 | 1.39 | 1.71 | 106,357 |
| 2016 | 42,760,516 | 397,037 | 583,631 | −186,594 | 9.3 | 13.6 | −4.3 | 1.47 | 1.36 | 1.64 | 101,121 |
| 2017 | 42,584,542 | 363,987 | 574,123 | −210,136 | 8.5 | 13.5 | −5.0 | 1.37 | 1.28 | 1.52 | 94,665 |
| 2018 | 42,386,403 | 335,874 | 587,665 | −251,791 | 7.9 | 13.9 | −6.0 | 1.30 | 1.22 | 1.43 | 46,552 |
| 2019 | 42,153,201 | 308,817 | 581,114 | −272,297 | 7.3 | 13.8 | −6.5 | 1.23 | 1.16 | 1.34 | 74,606 |
| 2020 | 41,902,416 | 293,457 | 616,835 | −323,378 | 7.0 | 14.7 | −7.7 | 1.22 | 1.13 | 1.36 | |
| 2021 | 41,167,336 | 271,983 | 714,263 | −442,280 | 6.6 | 17.4 | −10.8 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 1.29 | |
| 2022[44] | 35,100,000(e) | 206,032 | 541,739 | −335,707 | 6.0 | 15.4 | −9.4 | ||||
| 2023 | 32,544,634 | 187,387 | 496,200 | –308,813 | 5.4 | 15.2 | –9.8 | 1.00 | |||
| 2024 | 31,293,500 |
| Urban live births | Urban deaths | Urban natural change | Urban crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Urban crude death rate (per 1,000) | Urban natural change (per 1,000) | Rural live births | Rural deaths | Rural natural change | Rural crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Rural crude death rate (per 1,000) | Rural natural change (per 1,000) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 442,869 | 357,114 | 85,755 | 12.7 | 10.2 | 2.5 | 214,333 | 272,488 | −58,155 | 12.7 | 16.1 | −3.4 |
| 1991 | 419,205 | 380,988 | 38,217 | 11.9 | 10.8 | 1.1 | 211,608 | 288,972 | −77,364 | 12.6 | 17.2 | −4.6 |
| 1992 | 387,696 | 401,849 | −14,153 | 11.0 | 11.4 | −0.4 | 209,089 | 295,261 | −86,172 | 12.5 | 17.6 | −5.1 |
| 1993 | 356,833 | 432,462 | −75,629 | 10.1 | 12.2 | −2.1 | 200,634 | 309,200 | −108,566 | 12.0 | 18.5 | −6.5 |
| 1994 | 328,522 | 450,823 | −122,301 | 9.3 | 12.8 | −3.5 | 193,023 | 313,846 | −120,823 | 11.6 | 18.8 | −7.2 |
| 1995 | 308,408 | 476,434 | −168,026 | 8.8 | 13.6 | −4.8 | 184,453 | 316,153 | −131,700 | 11.1 | 19.1 | −8.0 |
| 1996 | 291,121 | 460,805 | −169,684 | 8.4 | 13.3 | −4.9 | 176,090 | 315,912 | −139,822 | 10.7 | 19.2 | −8.5 |
| 1997 | 274,961 | 444,446 | −169,485 | 8.0 | 13.0 | −5.0 | 167,620 | 309,705 | −142,085 | 10.2 | 18.9 | −8.7 |
| 1998 | 258,724 | 425,521 | −166,797 | 7.6 | 12.6 | −5.0 | 160,514 | 294,433 | −133,919 | 9.9 | 18.1 | −8.2 |
| 1999 | 239,408 | 439,986 | −200,578 | 7.1 | 13.1 | −6.0 | 149,800 | 299,184 | −149,384 | 9.3 | 18.5 | −9.2 |
| 2000 | 238,014 | 457,069 | −219,055 | 7.2 | 13.8 | −6.6 | 147,112 | 301,013 | −153,901 | 9.2 | 18.8 | −9.6 |
| 2001 | 237,228 | 450,329 | −213,101 | 7.2 | 13.8 | −6.6 | 139,250 | 295,623 | −156,373 | 8.7 | 18.6 | −9.9 |
| 2002 | 248,877 | 454,406 | −205,529 | 7.7 | 14.0 | −6.3 | 141,811 | 300,505 | −158,694 | 9.0 | 19.1 | −10.1 |
| 2003 | 266,415 | 459,965 | −193,550 | 8.3 | 14.3 | −6.0 | 142,174 | 305,443 | −163,269 | 9.1 | 19.6 | −10.5 |
| 2004 | 284,361 | 460,492 | −176,131 | 8.9 | 14.4 | −5.5 | 142,898 | 300,769 | −157,871 | 9.3 | 19.6 | −10.3 |
| 2005 | 284,257 | 471,561 | −187,304 | 8.9 | 14.8 | −5.9 | 141,829 | 310,400 | −168,571 | 9.4 | 20.5 | −11.1 |
| 2006 | 306,635 | 461,774 | −155,139 | 9.6 | 14.5 | −4.9 | 153,733 | 296,318 | −142,585 | 10.3 | 19.8 | −9.5 |
| 2007 | 314,065 | 466,253 | −152,188 | 9.9 | 14.7 | −4.8 | 158,592 | 296,624 | −138,032 | 10.7 | 20.1 | −9.4 |
| 2008 | 340,594 | 462,897 | −122,303 | 10.8 | 14.6 | −3.8 | 169,995 | 291,563 | −121,568 | 11.6 | 19.9 | −8.3 |
| 2009 | 339,497 | 432,294 | −92,797 | 10.8 | 13.7 | −2.9 | 173,028 | 274,445 | −101,417 | 11.9 | 18.9 | −7.0 |
| 2010 | 326,587 | 431,130 | −104,543 | 10.4 | 13.7 | −3.3 | 171,102 | 267,105 | −96,003 | 11.9 | 18.6 | −6.7 |
| 2011 | 328,934 | 411,025 | −82,091 | 10.5 | 13.1 | −2.6 | 173,661 | 253,563 | −79,902 | 12.1 | 17.7 | −5.6 |
| 2012 | 341,599 | 411,787 | −70,188 | 10.9 | 13.1 | −2.2 | 179,106 | 251,352 | −72,246 | 12.6 | 17.7 | −5.1 |
| 2013 | 330,284 | 412,553 | −82,269 | 10.5 | 13.2 | −2.7 | 173,373 | 249,815 | −76,442 | 12.3 | 17.7 | −5.4 |
| 2014 | 304,190 | 391,739 | −87,549 | 10.2 | 13.2 | −3.0 | 161,692 | 240,557 | −78,865 | 12.2 | 18.1 | −5.9 |
| 2015 | 266,082 | 358,749 | −92,667 | 10.4 | 13.2 | −2.8 | 145,699 | 236,047 | −90,348 | 11.3 | 18.0 | −6.7 |
| 2016 | 258,688 | 354,634 | −95,946 | 10.0 | 13.2 | −3.2 | 138,349 | 228,997 | −90,648 | 10.8 | 17.6 | −6.8 |
| 2017 | 237,874 | 350,549 | −112,675 | 9.2 | 13.0 | −3.8 | 126,113 | 223,574 | −97,461 | 9.9 | 17.3 | −7.4 |
| 2018 | 220,102 | 363,732 | −143,630 | 8.5 | 13.4 | −4.9 | 115,772 | 223,933 | −108,161 | 9.2 | 17.5 | −8.3 |
| 2019 | 202,646 | 362,660 | −160,014 | 7.9 | 13.4 | −5.5 | 106,171 | 218,454 | −112,283 | 8.5 | 17.2 | −8.7 |
Note: Data excludes Crimea starting in 2014.[45]
Current vital statistics
| Period | Live births | Deaths | Natural increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| January-June 2023 | 96,755 | 258,055 | −161,300 |
| January-June 2024 | 87,600 | 250,972 | −163,372 |
| Difference |
Note: Russia occupied and later annexed the Crimean Peninsula in 2014. The annexation is internationally recognized only by a small number of nations. Following the occupation, the Ukrainian statistics service could no longer provide accurate data on Crimea. Thus, as of 2014, the territories of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol are not included in the Demographics of Ukraine but in the Demographics of Russia. All data from State Statistics Service of Ukraine.
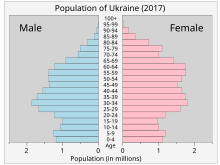
Structure of the population
| Age Group | Male | Female | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 19 195 376 | 22 223 341 | 41 418 717 | 100 |
| 0–4 | 871 807 | 817 549 | 1 689 356 | 4.08 |
| 5–9 | 1 184 223 | 1 113 485 | 2 297 708 | 5.55 |
| 10–14 | 1 179 905 | 1 112 800 | 2 292 705 | 5.54 |
| 15–19 | 978 279 | 923 149 | 1 901 428 | 4.59 |
| 20–24 | 1 029 297 | 969 836 | 1 999 133 | 4.83 |
| 25–29 | 1 323 862 | 1 255 946 | 2 579 808 | 6.23 |
| 30–34 | 1 705 251 | 1 646 672 | 3 351 923 | 8.09 |
| 35–39 | 1 758 922 | 1 739 010 | 3 497 932 | 8.45 |
| 40–44 | 1 533 807 | 1 583 673 | 3 117 480 | 7.53 |
| 45–49 | 1 420 874 | 1 541 601 | 2 962 475 | 7.15 |
| 50–54 | 1 269 395 | 1 447 927 | 2 717 322 | 6.56 |
| 55–59 | 1 285 999 | 1 603 824 | 2 889 823 | 6.98 |
| 60–64 | 1 225 350 | 1 685 084 | 2 910 434 | 7.03 |
| 65–69 | 921 671 | 1 454 610 | 2 376 281 | 5.74 |
| 70–74 | 656 532 | 1 190 134 | 1 846 666 | 4.46 |
| 75–79 | 323 037 | 740 699 | 1 063 736 | 2.57 |
| 80–84 | 335 863 | 874 371 | 1 210 234 | 2.92 |
| 85–89 | 113 869 | 308 482 | 422 351 | 1.02 |
| 90–94 | 54 945 | 164 392 | 219 337 | 0.53 |
| 95–99 | 15 892 | 37 973 | 53 865 | 0.13 |
| 100+ | 6 596 | 12 124 | 18 720 | 0.05 |
| Age group | Male | Female | Total | Percent |
| 0–14 | 3 235 935 | 3 043 834 | 6 279 769 | 15.16 |
| 15–64 | 13 531 036 | 14 396 722 | 27 927 758 | 67.43 |
| 65+ | 2 428 405 | 4 782 785 | 7 211 190 | 17.41 |
Regional data
Population by oblast

| Name of Oblast | Population as of Dec 2021 | According to the electronic census on December 1, 2019 |
|---|---|---|
| 4,062,839 | 1,981,200 | |
| 3,100,320 | 3,230,000 | |
| 2,952,577 | 3,703,100 | |
| 2,602,207 | 2,795,000 | |
| 2,480,137 | 2,290,100 | |
| 2,352,648 | 2,347,900 | |
| 2,104,531 | 1,127,500 | |
| 1,795,099 | 2,286,400 | |
| 1,640,876 | 1,656,700 | |
| 1,511,574 | 1,331,400 | |
| 1,354,444 | 1,337,000 | |
| 1,352,973 | 1,125,700 | |
| 1,245,491 | 924,700 | |
| 1,230,507 | 1,024,700 | |
| 1,180,638 | 1,062,600 | |
| 1,162,439 | 1,088,100 | |
| 1,142,599 | 943,600 | |
| 1,093,492 | 1,053,200 | |
| 1,037,237 | 932,500 | |
| 1,022,625 | 763,600 | |
| 1,022,107 | 903,600 | |
| 1,002,923 | 913,700 | |
| 961,054 | 912,600 | |
| 905,715 | 826,800 | |
| 891,054 | 727,500 | |
| 41,208,106 | 37,289,400 |
Birth data by oblast
Note: Recent data for Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts have been affected by the war in Donbas, and may only include births within the government-held parts of the oblasts.[47]
| Number of births by oblast for January–November | Birth/2016 | Birth/2015 | Death/2016 | Death/2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33416 |
32382 |
27772 |
27767 | |
| 28473 |
30620 |
47934 |
49258 | |
| 25708 |
25007 |
29247 |
30010 | |
| 24246 |
25182 |
30479 |
31512 | |
| 21992 |
22864 |
38502 |
38965 | |
| 17772 |
15608 |
33464 |
36883 | |
| 17559 |
18485 |
25623 |
26046 | |
| 14862 |
15525 |
13880 |
14164 | |
| 14454 |
14809 |
13261 |
13426 | |
| 14430 |
15140 |
25533 |
25657 | |
| 14153 |
15126 |
22521 |
23237 | |
| 13547 |
14412 |
15616 |
16144 | |
| 12047 |
12307 |
12311 |
12602 | |
| 11958 |
12526 |
18301 |
19085 | |
| 11793 |
12768 |
18097 |
18702 | |
| 11503 |
12381 |
22084 |
22440 | |
| 9904 |
10626 |
15834 |
16316 | |
| 9877 |
10476 |
14891 |
15055 | |
| 9721 |
10560 |
18437 |
18315 | |
| 9461 |
9851 |
10399 |
10738 | |
| 9177 |
9912 |
13584 |
13962 | |
| 8189 |
8662 |
14810 |
14809 | |
| 8169 |
8959 |
16982 |
17322 | |
| 7816 |
8359 |
17515 |
18199 | |
| 5960 |
4978 |
12689 |
13401 |
| Number of births by oblast | Birth/2014 | Birth/2013 | Birth/2012 | Birth/2011 | Death/2014 | Death/2013 | Death/2012 | Death/2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36497 |
36134 |
37087 |
36116 |
52722 |
51134 |
51486 |
52106 | |
| 35595 |
41034 |
42839 |
41720 |
71799 |
69345 |
70496 |
71042 | |
| 34821 |
33305 |
33887 |
32068 |
29992 |
28003 |
27840 |
27050 | |
| 30270 |
29542 |
30220 |
28904 |
32450 |
31666 |
31667 |
31162 | |
| 29465 |
29075 |
30384 |
29225 |
34155 |
33523 |
33648 |
33688 | |
| 27690 |
26700 |
27244 |
26317 |
41891 |
39465 |
40130 |
40079 | |
| 20900 |
20511 |
20966 |
20083 |
28264 |
27198 |
27161 |
26847 | |
| 18713 |
18134 |
18882 |
18198 |
27773 |
26498 |
26406 |
27033 | |
| 18377 |
18490 |
18968 |
18460 |
14808 |
14801 |
14813 |
14588 | |
| 17547 |
17437 |
18339 |
17894 |
25567 |
25453 |
25158 |
25376 | |
| 17169 |
17445 |
18316 |
17697 |
14714 |
14556 |
14302 |
14168 | |
| 16886 |
16716 |
17101 |
16497 |
17670 |
17358 |
16801 |
16657 | |
| 15115 |
15001 |
15486 |
15154 |
21185 |
20859 |
20685 |
20417 | |
| 14668 |
14700 |
15346 |
14620 |
13748 |
13666 |
13710 |
13842 | |
| 14631 |
14548 |
14881 |
14492 |
20408 |
20581 |
20362 |
20116 | |
| 14504 |
14296 |
14635 |
14167 |
24784 |
24358 |
24223 |
24384 | |
| 13076 |
13043 |
13515 |
13029 |
17750 |
17353 |
17277 |
17441 | |
| 12351 |
12100 |
12798 |
12473 |
20800 |
20477 |
20667 |
20848 | |
| 12308 |
12300 |
12643 |
12085 |
16141 |
16048 |
15904 |
15828 | |
| 11717 |
11807 |
12202 |
11964 |
15180 |
14682 |
14838 |
14829 | |
| 11679 |
11465 |
11592 |
11281 |
11619 |
11520 |
11321 |
11192 | |
| 11442 |
20531 |
21743 |
21320 |
22755 |
35822 |
36316 |
37256 | |
| 10576 |
10562 |
11029 |
10578 |
16716 |
16513 |
16521 |
16697 | |
| 10344 |
10411 |
11093 |
10473 |
19452 |
19219 |
19002 |
18833 | |
| 9552 |
9852 |
10222 |
10134 |
20324 |
19909 |
20208 |
20179 |
| Birth rate by oblast | Birth/2014 | Birth/2013 | Birth/2012 | Birth/2011 | Death/2014 | Death/2013 | Death/2012 | Death/2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.8 |
15.1 |
15.9 |
15.3 |
12.7 |
12.6 |
12.4 |
12.3 | |
| 14.6 |
14.7 |
15.1 |
14.8 |
11.8 |
11.8 |
11.8 |
11.7 | |
| 14.1 |
14.1 |
14.8 |
14.1 |
13.2 |
13.1 |
13.2 |
13.3 | |
| 12.9 |
12.6 |
12.8 |
12.5 |
12.8 |
12.7 |
12.5 |
12.4 | |
| 12.3 |
12.1 |
12.7 |
12.2 |
14.3 |
14.0 |
14.1 |
14.1 | |
| 12.2 |
12.1 |
12.4 |
12.0 |
12.8 |
12.6 |
12.2 |
12.1 | |
| 12.1 |
11.9 |
12.2 |
11.7 |
16.4 |
15.8 |
15.8 |
15.6 | |
| 12.1 |
11.7 |
12.0 |
11.4 |
10.4 |
9.8 |
9.8 |
9.6 | |
| 12.0 |
11.9 |
12.2 |
11.9 |
16.8 |
16.5 |
16.3 |
16.0 | |
| 11.9 |
11.6 |
11.9 |
11.4 |
12.8 |
12.4 |
12.5 |
12.3 | |
| 11.5 |
11.4 |
11.7 |
11.1 |
15.1 |
14.9 |
14.7 |
14.6 | |
| 11.2 |
11.1 |
11.5 |
11.0 |
15.2 |
14.8 |
14.7 |
14.8 | |
| 11.2 |
11.1 |
11.3 |
11.0 |
15.6 |
15.7 |
15.5 |
15.2 | |
| 11.1 |
11.0 |
11.2 |
10.9 |
16.0 |
15.5 |
15.5 |
15.7 | |
| 10.9 |
10.8 |
11.2 |
10.9 |
15.9 |
15.7 |
15.4 |
15.5 | |
| 10.9 |
11.0 |
11.3 |
11.1 |
14.2 |
13.7 |
13.8 |
13.7 | |
| 10.8 |
10.7 |
11.0 |
10.5 |
17.0 |
16.7 |
16.5 |
16.6 | |
| 10.6 |
10.2 |
10.6 |
10.1 |
15.7 |
14.9 |
14.8 |
15.0 | |
| 10.1 |
9.8 |
9.9 |
9.6 |
15.3 |
14.4 |
14.6 |
14.6 | |
| 10.0 |
9.8 |
9.9 |
9.5 |
17.1 |
16.7 |
16.5 |
16.4 | |
| 9.8 |
9.6 |
10.1 |
9.8 |
16.5 |
16.2 |
16.2 |
16.3 | |
| 9.2 |
9.2 |
9.7 |
9.1 |
17.2 |
16.9 |
16.6 |
16.3 | |
| 9.0 |
9.2 |
9.4 |
9.3 |
19.2 |
18.6 |
18.7 |
18.5 | |
| 8.2 |
9.4 |
9.8 |
9.5 |
16.6 |
15.9 |
16.1 |
16.1 | |
| 5.1 |
9.1 |
9.6 |
9.3 |
10.2 |
15.9 |
16.0 |
16.3 |
Year in review 2013
Compared to 2012, the amount of attrition increased in 2013 by 16,278 persons, or 3.1 to 3.5 persons per 1,000 inhabitants (real). Natural decreases were observed in 23 oblasts of the country, while natural increases were recorded only in Kyiv and in the Zakarpattya, Rivne and Volyn oblasts (5,302, 3,689, 2,889 and 1,034 people, respectively).
Some regions registered a low natural decline, such as Chernivtsi, Ivano-Frankivsk, Sevastopol, Lviv, Ternopil, Crimea, Kherson and Odesa (−55, −642, −863, −2,124, −2,875, −2,974, −3,748 and −4,448 people, respectively). The largest declines were recorded in Donetsk, Luhansk, Dnipro, Kharkiv, Poltava and Chernihiv (−28,311, −15,291, −15,007, −12,765, −10,062 and −10,057, respectively), regions which share a low birth rate and high mortality of a large urban population and rapid aging of the rural population.
Net migration rate
−5.4 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015).
Infant mortality rate
- 9.1
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,564 deaths (2010)
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,564 deaths (2010) - 9.0
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,511 deaths (2011)
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,511 deaths (2011) - 8.4
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,371 deaths (2012)
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,371 deaths (2012) - 8.0
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,030 deaths (2013)
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 4,030 deaths (2013) - 8.9
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 2,193 death for January–June 2011
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 2,193 death for January–June 2011 - 8.6
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 2,190 death for January–June 2012
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 2,190 death for January–June 2012 - 7.8
 deaths/1,000 infants live births for 1,993 deaths for January–June 2013[48]
deaths/1,000 infants live births for 1,993 deaths for January–June 2013[48]
| Infant mortality by oblast | Death/2012 | Death/2011 | Death/2010 | Death/2009 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 540 |
473 |
497 |
533 | |
| 370 |
343 |
347 |
329 | |
| 267 |
268 |
263 |
280 | |
| 262 |
255 |
233 |
244 | |
| 233 |
272 |
266 |
238 | |
| 203 |
234 |
243 |
252 | |
| 168 |
195 |
199 |
238 | |
| 166 |
186 |
148 |
149 | |
| 165 |
188 |
199 |
252 | |
| 154 |
169 |
182 |
174 | |
| 147 |
156 |
158 |
164 | |
| 134 |
89 |
109 |
174 | |
| 124 |
134 |
135 |
127 | |
| 122 |
101 |
125 |
132 | |
| 119 |
143 |
140 |
146 | |
| 109 |
145 |
170 |
157 | |
| 106 |
116 |
123 |
118 | |
| 103 |
139 |
112 |
119 | |
| 100 |
120 |
116 |
136 | |
| 97 |
97 |
104 |
112 | |
| 97 |
96 |
98 |
93 | |
| 94 |
80 |
82 |
103 | |
| 92 |
96 |
90 |
91 | |
| 85 |
86 |
87 |
105 | |
| 76 |
78 |
97 |
91 |
| Infant mortality per 1,000 by Oblast | Death/2012 | Death/2011 | Death/2010 | Death/2009 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12.7 |
11.4 |
12.0 |
12.3 | |
| 10.0 |
9.5 |
9.7 |
8.8 | |
| 9.6 |
8.1 |
10.0 |
10.5 | |
| 9.4 |
13.2 |
10.6 |
10.9 | |
| 9.2 |
7.9 |
8.1 |
9.9 | |
| 9.1 |
10.4 |
8.4 |
8.3 | |
| 9.0 |
6.2 |
7.5 |
11.8 | |
| 8.9 |
10.6 |
10.9 |
13.1 | |
| 8.8 |
9.2 |
9.2 |
9.7 | |
| 8.2 |
9.3 |
10.1 |
9.4 | |
| 8.1 |
8.9 |
9.2 |
9.4 | |
| 8.0 |
9.9 |
9.4 |
11.0 | |
| 8.0 |
8.9 |
9.1 |
8.5 | |
| 8.0 |
8.5 |
8.2 |
8.2 | |
| 8.0 |
8.0 |
8.2 |
7.5 | |
| 7.8 |
9.4 |
9.2 |
8.0 | |
| 7.8 |
8.0 |
7.3 |
7.5 | |
| 7.6 |
8.8 |
9.4 |
11.6 | |
| 7.5 |
8.9 |
9.2 |
9.3 | |
| 7.3 |
7.5 |
8.1 |
8.5 | |
| 7.0 |
7.9 |
8.2 |
7.7 | |
| 6.9 |
7.5 |
9.3 |
8.5 | |
| 6.4 |
8.8 |
10.3 |
9.1 | |
| 5.8 |
6.1 |
6.1 |
7.1 | |
| 5.7 |
7.2 |
7.0 |
7.1 |
Total fertility rate by oblast

None of the oblasts in 2013 recorded a higher fertility rate than 2.10 children per woman, though rural areas saw higher rates in the Rivne Oblast (2.50) and Volyn Oblast (2.20). While close-to-generational renewal rates were achieved in the Odesa (2.04), Zakarpattia (2.00), Mykolaiv (1.95), Chernivtsi (1.93) and Zhytomyr (1.91) oblasts, they were weaker in the Luhansk (1.41), Sumy (1.47) and Cherkasy (1.53) oblasts.
The highest urban fertility rates were recorded in the Zakarpattia Oblast (1.80), city of Sevastopol (1.57), Volyn Oblast (1.56), Kyiv Oblast (1.56) and Rivne Oblast (1.54). The lowest were in the Sumy (1.23), Kharkiv (1.26), Cherkasy (1.28), Chernihiv (1.28), Chernivtsi (1.28), Luhansk (1.28), Poltava (1.29), Donetsk (1.29) and Zaporizhzhia (1.32) oblasts.
| Children born per woman by oblast | Total fertility rate/2020 | Total fertility rate/2012 | Total fertility rate/2011 | Total fertility rate/2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.54 |
2.08 |
1.99 |
1.93 | |
| 1.60 |
1.95 |
1.90 |
1.83 | |
| 1.51 |
1.92 |
1.81 |
1.85 | |
| 1.20 |
1.71 |
1.65 |
1.61 | |
| 1.34 |
1.71 |
1.62 |
1.58 | |
| 1.18 |
1.67 |
1.58 |
1.58 | |
| 1.30 |
1.64 |
1.58 |
1.53 | |
| 1.26 |
1.62 |
1.56 |
1.55 | |
| 1.27 |
1.63 |
1.55 |
1.58 | |
| 1.20 |
1.61 |
1.51 |
1.51 | |
| 1.10 |
1.61 |
1.51 |
1.50 | |
| 1.24 |
1.58 |
1.49 |
1.50 | |
| 1.11 |
1.57 |
1.47 |
1.44 | |
| 1.20 |
1.59 |
1.53 |
1.50 | |
| 1.22 |
1.53 |
1.46 |
1.45 | |
| 1.09 |
1.52 |
1.44 |
1.43 | |
| 1.13 |
1.50 |
1.45 |
1.46 | |
| 1.03 |
1.46 |
1.37 |
1.34 | |
| 1.04 |
1.41 |
1.33 |
1.34 | |
| 1.01 |
1.43 |
1.37 |
1.36 | |
| 1.02 |
1.40 |
1.36 |
1.36 | |
| 1.44 |
1.38 |
1.29 |
1.30 | |
| 1.34 |
1.27 |
1.26 | ||
| 0.98 |
1.32 |
1.25 |
1.24 | |
| 0.93 |
1.36 |
1.25 |
1.23 | |
| 1.33 |
1.27 |
1.23 |
Other demographics statistics







Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2019[49]
- One birth every 1 minute
- One death every 48 seconds
- Net loss of one person every 2 minutes
- One net migrant every 30 minutes
Demographic statistics according to the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated[30]
- Age structure:
- 0–314 years: 15.95% (male 3,609,386/female 3,400,349)
- 15–24 years: 9.57% (male 2,156,338/female 2,047,821)
- 25–54 years: 44.03% (male 9,522,108/female 9,831,924)
- 55–64 years: 13.96% (male 2,638,173/female 3,499,718)
- 65 years and over: 16.49% (male 2,433,718/female 4,812,764) (2018 est.)
- 0–14 years: 15.76% (male 3,571,358/female 3,366,380)
- 15–24 years: 9.86% (male 2,226,142/female 2,114,853)
- 25–54 years: 44.29% (male 9,579,149/female 9,921,387)
- 55–64 years: 13.8% (male 2,605,849/female 3,469,246)
- 65 years and over: 16.3% (male 2,409,049/female 4,770,461) (2017 est.)
- 0–14 years: 15.1% = 6,449,171 (2015 official)
- 15–64 years: 69.3% = 29,634,710
- 65 years and over: 15.6% = 6,675,780
- 0–14 years: 14.8% = 6,989,802
- 15–64 years: 69.2% = 32,603,475
- 65 years and over: 16.0% = 7,507,185 (2005 official)
- 0–14 years: 21.6% = 11,101,469
- 15–64 years: 66.7% = 34,320,742
- 65 years and over: 11.7% = 6,022,934 (1989 official)
- Median age
- total: 40.8 years. Country comparison to the world: 47th
- male: 37.7 years
- female: 43.9 years (2018 est.)
- total: 40.6 years
- male: 37.4 years
- female: 43.7 years (2017 est.)
- total: 39.8 years
- male: 39.7 years
- female: 40.1 years (2014 official)
- total: 39.7 years
- male: 39.5 years
- female: 40.1 years (2013 official)
- total: 34.8 years
- male: 31.9 years
- female: 37.7 years (1989 official)
- Birth rate
- 10.1 births/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 190th
- 10.3 births/1,000 population (2017 est.)
- Death rate
- 14.3 deaths/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 6th
- 14.4 deaths/1,000 population (2017 est.)
- Total fertility rate
- 1.55 children born/woman (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 190th
- 1.54 children born/woman (2017 est.)
- Net migration rate
- 4.6 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 29th
- 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2017 est.)
- Mother's mean age at first birth
- 24.9 years (2014 est.)
- Population growth rate
- 0.04% (2018 est.) Country comparison to the world: 187th
- −0.41% (2017 est.)
- Life expectancy at birth
- total population: 72.4 years. Country comparison to the world: 148th
- male: 67.7 years
- female: 77.4 years (2018 est.)
- Ethnic groups
Ukrainian 77.8%, Russian 17.3%, Belarusian 0.6%, Moldovan 0.5%, Crimean Tatar 0.5%, Bulgarian 0.4%, Hungarian 0.3%, Romanian 0.3%, Polish 0.3%, Jewish 0.2%, other 1.8% (2001 est.)
- Languages
Ukrainian (official) 67.5%, Russian (regional language) 29.6%, other (includes small Crimean Tatar-, Moldovan/Romanian-, and Hungarian-speaking minorities) 2.9% (2001 est.)
Note: in February 2018, the Constitutional Court ruled that 2012 language legislation entitling a language spoken by at least 10% of an oblast's population to be given the status of "regional language" – allowing for its use in courts, schools, and other government institutions – was unconstitutional, thus making the law invalid; Ukrainian remains the country's only official nationwide language.
- Religions
Orthodox (includes Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox (UAOC), Ukrainian Orthodox – Kyiv Patriarchate (UOC-KP), Ukrainian Orthodox – Moscow Patriarchate (UOC-MP)), Ukrainian Greek Catholic, Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim, Jewish
Note: Ukraine's population is overwhelmingly Christian; the vast majority – up to two-thirds – identify themselves as Orthodox, but many do not specify a particular branch; the UOC-KP and the UOC-MP each represent less than a quarter of the country's population, the Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church accounts for 8–10%, and the UAOC accounts for 1–2%; Muslim and Jewish adherents each compose less than 1% of the total population (2013 est.).
- Dependency ratios
- total dependency ratio: 44.8 (2015 est.)
- youth dependency ratio: 21.8 (2015 est.)
- elderly dependency ratio: 23 (2015 est.)
- potential support ratio: 4.3 (2015 est.)
- Note: data include Crimea
- Urbanization
- urban population: 69.4% of total population (2018)
- rate of urbanization: −0.33% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
- Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2015 est.)
- total population: 99.8%
- male: 99.8%
- female: 99.7% (2015 est.)
- School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
- total: 15 years
- male: 15 years
- female: 16 years (2014)
- Unemployment, youth ages 15–24
- total: 23%. Country comparison to the world: 53rd
- male: 24%
- female: 21.5% (2016 est.)
Birth and death rates of regional capitals
| Birth rate in
regional centers |
Birth/2012 | Birth/2011 | Birth/2010 | Birth/2009 | Birth/2007 | Birth/2005 | Birth/2003 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simferopol | 13.6 |
12.8 |
11.8 |
11.8 |
11.0 |
9.5 |
9.2 |
| Lutsk | 12.6 |
12.3 |
12.6 |
13.9 |
12.6 |
11.7 |
10.0 |
| Rivne | 12.6 |
12.0 |
11.8 |
12.3 |
10.9 |
10.1 |
9.4 |
| Uzhhorod | 12.1 |
11.9 |
12.0 |
12.4 |
12.8 |
12.6 |
10.8 |
| Kyiv | 12.0 |
11.4 |
11.5 |
11.7 |
10.4 |
9.8 |
8.8 |
| Khmelnytskyi | 12.0 |
11.2 |
11.8 |
11.5 |
10.4 |
10.2 |
9.2 |
| Sevastopol | 12.0 |
11.1 |
11.0 |
11.2 |
10.5 |
9.6 |
8.7 |
| Kherson | 11.9 |
11.1 |
10.1 |
10.5 |
9.6 |
8.6 |
8.5 |
| Ternopil | 11.8 |
12.2 |
11.7 |
12.3 |
11.9 |
11.6 |
10.4 |
| Ivano-Frankivsk | 11.6 |
11.6 |
10.1 |
10.8 |
11.3 |
10.7 |
9.3 |
| Vinnytsia | 11.5 |
11.2 |
10.9 |
11.1 |
10.1 |
9.4 |
9.1 |
| Kropyvnytskyi | 11.5 |
11.1 |
10.5 |
11.3 |
10.5 |
8.9 |
8.4 |
| Zhytomyr | 11.4 |
11.5 |
10.8 |
11.7 |
10.6 |
9.5 |
8.7 |
| Sumy | 11.3 |
10.3 |
10.0 |
10.3 |
9.6 |
8.2 |
7.8 |
| Lviv | 11.0 |
10.4 |
10.0 |
10.5 |
9.7 |
9.3 |
9.0 |
| Ukraine Urban | 10.9 |
10.5 |
10.4 |
10.8 |
9.9 |
8.9 |
8.3 |
| Dnipro | 10.5 |
10.2 |
10.0 |
10.5 |
9.4 |
8.5 |
7.9 |
| Luhansk | 10.5 |
9.8 |
8.8 |
9.2 |
8.2 |
7.4 |
6.8 |
| Chernivtsi | 10.2 |
10.3 |
10.1 |
10.2 |
9.2 |
9.6 |
8.3 |
| Odesa | 10.1 |
9.8 |
9.6 |
9.9 |
9.0 |
8.3 |
7.5 |
| Cherkasy | 9.9 |
9.4 |
9.4 |
9.4 |
8.7 |
7.8 |
7.4 |
| Poltava | 9.9 |
9.1 |
8.8 |
9.7 |
8.4 |
7.8 |
7.3 |
| Zaporizhzhia | 9.5 |
9.2 |
9.2 |
9.3 |
8.9 |
8.2 |
7.5 |
| Mykolaiv | 9.4 |
9.3 |
9.1 |
9.4 |
8.7 |
8.0 |
7.9 |
| Chernihiv | 9.3 |
9.2 |
9.1 |
9.6 |
8.4 |
8.0 |
7.6 |
| Kharkiv | 9.2 |
8.9 |
8.8 |
9.2 |
8.4 |
7.6 |
7.1 |
| Donetsk | 9.1 |
8.7 |
8.6 |
9.0 |
8.2 |
7.5 |
6.6 |
| Death rate in
regional centers |
Death/2012 | Death/2011 | Death/2010 | Death/2009 | Death/2007 | Death/2005 | Death/2003 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kherson | 15.2 |
15.6 |
14.0 |
14.2 |
14.9 |
14.8 |
14.5 |
| Luhansk | 14.2 |
14.3 |
13.6 |
13.4 |
13.8 |
14.2 |
14.1 |
| Simferopol | 14.0 |
14.8 |
13.6 |
13.8 |
15.3 |
15.3 |
15.2 |
| Sevastopol | 13.7 |
14.1 |
14.7 |
14.5 |
15.5 |
15.4 |
14.1 |
| Kropyvnytskyi | 13.7 |
13.7 |
13.8 |
14.0 |
14.4 |
14.1 |
14.1 |
| Dnipro | 13.5 |
13.7 |
14.1 |
13.8 |
15.1 |
15.1 |
16.0 |
| Donetsk | 13.4 |
13.5 |
14.0 |
13.9 |
15.2 |
15.4 |
14.7 |
| Zaporizhzhia | 13.2 |
13.4 |
14.2 |
13.8 |
15.0 |
14.7 |
14.2 |
| Ukraine Urban | 13.1 |
13.1 |
13.7 |
13.7 |
14.7 |
14.8 |
14.3 |
| Mykolaiv | 12.8 |
12.8 |
13.8 |
13.8 |
14.5 |
14.5 |
14.9 |
| Poltava | 12.8 |
12.6 |
13.2 |
13.0 |
13.7 |
13.6 |
13.6 |
| Sumy | 12.1 |
11.9 |
12.4 |
12.6 |
13.0 |
13.1 |
11.9 |
| Kharkiv | 12.0 |
11.8 |
12.4 |
12.2 |
13.1 |
13.1 |
13.0 |
| Odesa | 11.9 |
12.2 |
13.0 |
12.5 |
13.9 |
14.1 |
14.0 |
| Cherkasy | 11.2 |
10.7 |
11.3 |
11.2 |
11.7 |
11.7 |
11.0 |
| Chernihiv | 11.4 |
11.1 |
12.0 |
11.8 |
12.5 |
12.4 |
12.0 |
| Lviv | 11.0 |
10.8 |
10.5 |
10.8 |
11.5 |
11.4 |
11.5 |
| Zhytomyr | 10.7 |
10.9 |
11.2 |
11.1 |
12.0 |
12.2 |
11.4 |
| Uzhhorod | 10.3 |
10.2 |
10.5 |
11.3 |
12.0 |
12.4 |
10.3 |
| Kyiv | 9.8 |
9.6 |
10.3 |
10.2 |
11.4 |
11.2 |
10.7 |
| Lutsk | 9.6 |
9.4 |
9.6 |
9.1 |
10.4 |
10.2 |
10.5 |
| Chernivtsi | 9.5 |
9.4 |
9.9 |
10.3 |
11.0 |
11.0 |
10.8 |
| Khmelnytskyi | 9.4 |
8.8 |
9.0 |
9.5 |
9.8 |
9.8 |
9.2 |
| Vinnytsia | 9.1 |
9.0 |
9.2 |
9.2 |
10.2 |
10.2 |
10.0 |
| Ivano-Frankivsk | 9.1 |
8.7 |
8.2 |
8.5 |
9.1 |
9.3 |
9.3 |
| Ternopil | 8.1 |
7.6 |
8.1 |
7.7 |
8.5 |
8.5 |
7.7 |
| Rivne | 7.9 |
7.8 |
8.7 |
8.6 |
9.0 |
9.2 |
8.8 |
Ethnic groups

In 2001, the ethnic composition of Ukraine was: Ukrainian 77.8%, Russian 17.3%, Romanian 1.1% (including Moldovan 0.8%), Belarusian 0.6%, Crimean Tatar 0.5%, Bulgarian 0.4%, Hungarian 0.3%, Polish 0.3%, Jewish 1.0%, Pontic Greek 0.2% and other 1.6% (including Armenians, Germans, Romas, Georgians, Slovaks, Albanians, Crimean Karaites, as well as Muslim Bulgarians, otherwise known as Torbesh, and a microcosm of Swedes of Gammalsvenskby).[50] It is also estimated that there are about 49,817 ethnic Koreans (0.12%) in Ukraine that belong to the Koryo-saram group. Their number may be as high as 100,000 as many ethnic Koreans were assimilated into the majority population.[51][52] Rusyns are also not recognised by the Ukrainian government as a distinct ethnic group and are instead treated as a sub-group of Ukrainians.[53]
According to the 2021 law “On the Indigenous Peoples of Ukraine”, the Crimean Tatars, Crimean Karaites and Krymchaks are the indigenous peoples of Ukraine.[54]

Before World War II
| Ethnic group |
census 19261 | census 19392 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |
| Ukrainians | 23,218,860 | 80.0 | 23,667,509 | 76.5 |
| Russians | 2,677,166 | 9.2 | 4,175,299 | 13.5 |
| Jewish | 1,574,428 | 5.4 | 1,532,776 | 5.0 |
| Germans | 393,924 | 1.4 | 392,458 | 1.3 |
| Polish | 476,435 | 1.6 | 357,710 | 1.2 |
| Moldavians / Romanians | 257,794 | 0.9 | 230,698 | 0.8 |
| Belarusians | 75,842 | 0.3 | 158,174 | 0.5 |
| Pontic Greeks | 104,666 | 0.4 | 107,047 | 0.4 |
| Bulgarians | 99,278 | 0.3 | 83,838 | 0.3 |
| Tatars | 22,281 | 0.1 | 55,456 | 0.2 |
| Roma | 13,578 | 0.0 | 10,443 | 0.0 |
| Others | 103,935 | 0.4 | 174,810 | 0.6 |
| Total | 29,018,187 | 30,946,218 | ||
| 1 Source:.[55] | ||||
After World War II
| Ethnic group |
census 19591 | census 19702 | census 19793 | census 19894 | census 20015 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Ukrainians | 32,158,493 | 76.8 | 35,283,857 | 74.9 | 36,488,951 | 73.6 | 37,419,053 | 72.7 | 37,541,693 | 77.5 |
| Russians | 7,090,813 | 16.9 | 9,126,331 | 19.4 | 10,471,602 | 21.1 | 11,355,582 | 22.1 | 8,334,141 | 17.2 |
| Romanians / Moldovans | 391,753 | 1.1 | 378,043 | 1.1 | 415,371 | 1.1 | 459,350 | 1.2 | 409,608 | 1.1 |
| Belarusians | 290,890 | 0.7 | 385,847 | 0.8 | 406,098 | 0.8 | 440,045 | 0.9 | 275,763 | 0.6 |
| Crimean Tatars | 193 | 0.0 | 3,554 | 0.0 | 6,636 | 0.0 | 46,807 | 0.1 | 248,193 | 0.5 |
| Bulgarians | 219,419 | 0.5 | 234,390 | 0.5 | 238,217 | 0.5 | 233,800 | 0.5 | 204,574 | 0.4 |
| Hungarians | 149,229 | 0.4 | 157,731 | 0.3 | 164,373 | 0.3 | 163,111 | 0.3 | 156,566 | 0.3 |
| Poles | 363,297 | 0.9 | 295,107 | 0.6 | 258,309 | 0.5 | 219,179 | 0.4 | 144,130 | 0.3 |
| Jewish | 840,311 | 2.0 | 777,126 | 1.7 | 634,154 | 1.3 | 486,628 | 1.0 | 103,591 | 0.2 |
| Armenians | 28,024 | 0.1 | 33,439 | 0.1 | 38,646 | 0.1 | 54,200 | 0.1 | 99,894 | 0.2 |
| Greeks | 104,359 | 0.3 | 106,909 | 0.2 | 104,091 | 0.2 | 98,594 | 0.2 | 91,548 | 0.2 |
| Tatars | 61,334 | 0.2 | 72,658 | 0.2 | 83,906 | 0.2 | 86,875 | 0.2 | 73,304 | 0.2 |
| Roma | 22,515 | 0.1 | 30,091 | 0.1 | 34,411 | 0.1 | 47,917 | 0.1 | 47,587 | 0.1 |
| Azerbaijanis | 6,680 | 0.0 | 10,769 | 0.0 | 17,235 | 0.0 | 36,961 | 0.1 | 45,176 | 0.1 |
| Georgians | 11,574 | 0.0 | 14,650 | 0.0 | 16,301 | 0.0 | 23,540 | 0.1 | 34,199 | 0.1 |
| Germans | 23,243 | 0.1 | 29,871 | 0.1 | 34,139 | 0.1 | 37,849 | 0.1 | 33,302 | 0.1 |
| Gagauz | 23,530 | 0.1 | 26,464 | 0.1 | 29,398 | 0.1 | 31,967 | 0.1 | 31,923 | 0.1 |
| Karaites | 3,301 | 0.0 | 2,596 | 0.0 | 1,845 | 0.0 | 1,404 | 0.0 | 1,196 | 0.0 |
| Others | 129,338 | 0.3 | 157,084 | 0.3 | 165,650 | 0.3 | 209,172 | 0.4 | 363,821 | 1.1 |
| Total | 41,869,046 | 47,126,517 | 49,609,333 | 51,452,034 | 48,240,902 | |||||
| 1 Source:.[56] 2 Source:.[57] 3 Source:.[58] 4 Source:.[59] 5 Source: [1]. | ||||||||||
Ethnic Groups in Ukraine, 2001[60]
Languages
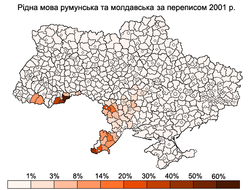
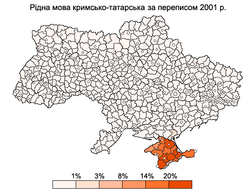
According to the 2001 census, the following languages are common in Ukraine: Ukrainian 67.5%, Russian 29.6%, Crimean Tatar, Urum (Turkic Greeks), Bulgarian, Moldovan/Romanian, Polish, Hungarian. The table below lists the total population of various ethnic groups in Ukraine and their primary language, according to the 2001 census.[50]
| Ethnic group | Population | Native | Ukrainian | Russian | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ukrainians | 37,541,693 | 31,970,728 | – | 5,544,729 | 532 |
| Russians | 8,334,141 | 7,993,832 | 328,152 | – | 402 |
| Moldovans | 258,619 | 181,124 | 27,775 | 45,607 | 1242 |
| Belarusians | 275,763 | 54,573 | 48,202 | 172,251 | |
| Crimean Tatars | 248,193 | 228,373 | 184 | 15,208 | 43 |
| Bulgarians | 204,574 | 131,237 | 10,277 | 62,067 | 9 |
| Hungarians | 156,566 | 149,431 | 5,367 | 1,513 | 14 |
| Romanians | 150,989 | 138,522 | 9,367 | 2,297 | 170 |
| Polish | 144,130 | 18,660 | 102,268 | 22,495 | 390 |
| Hebrew | 103,591 | 3,213 | 13,924 | 85,964 | 16 |
| Armenians | 99,894 | 50,363 | 5,798 | 43,105 | 11 |
| Greeks | 91,548 | 5,829 | 4,359 | 80,992 | 9 |
| Tatars | 73,304 | 25,770 | 3,310 | 43,060 | 6 |
| Koreans | 49,817 | 2,223 | 37,932 | 9,662 | 0 |
| Roma | 47,587 | 21,266 | 10,039 | 6,378 | 6 |
| Azerbaijanis | 45,176 | 23,958 | 3,224 | 16,968 | 36 |
| Georgians | 34,199 | 12,539 | 2,818 | 18,589 | 15 |
| Germans | 33,302 | 4,056 | 7,360 | 21,549 | 20 |
| Gagauz | 31,923 | 22,822 | 1,102 | 7,232 | 2 |
| Uzbeks | 12,353 | 3,604 | 1,818 | 5,996 | 0 |
| Chuvash | 10,593 | 2,268 | 564 | 7,636 | 1 |
| Mordvinians | 9,331 | 1,473 | 646 | 7,168 | 0 |
| Turks | 8,844 | 7,923 | 133 | 567 | 0 |
| Lithuanians | 7,207 | 1,932 | 1,029 | 4,182 | 4 |
| Arabs | 6,575 | 4,071 | 897 | 1,235 | 0 |
| Slovaks | 6,397 | 2,633 | 2,665 | 335 | 0 |
| Czechs | 5,917 | 1,190 | 2,503 | 2,144 | 2 |
| Kazakhs | 5,526 | 1,041 | 822 | 3,470 | 11 |
| Latvians | 5,079 | 957 | 872 | 3,188 | 1 |
| Ossetians | 4,834 | 1,150 | 401 | 3,110 | 4 |
| Udmurts | 4,712 | 729 | 380 | 3,515 | 0 |
| Lezghinians | 4,349 | 1,507 | 330 | 2,341 | 4 |
| Tadjiks | 4,255 | 1,521 | 488 | 1,983 | 0 |
| Bashkirs | 4,253 | 843 | 336 | 2,920 | 0 |
| Mari people | 4,130 | 1,059 | 264 | 2,758 | 7 |
| Thai | 3,850 | 3,641 | 29 | 164 | 0 |
| Turkmens | 3,709 | 719 | 1,079 | 1,392 | 0 |
| Albanians | 3,308 | 1,740 | 301 | 1,181 | 0 |
| Assyrians | 3,143 | 883 | 408 | 1,730 | 0 |
| Chechens | 2,877 | 1,581 | 212 | 977 | 0 |
| Estonians | 2,868 | 416 | 321 | 2,107 | 4 |
| Chinese people | 2,213 | 1,817 | 73 | 307 | 0 |
| Kurds | 2,088 | 1,173 | 236 | 396 | 0 |
| Darghins | 1,610 | 409 | 199 | 955 | 0 |
| Komis | 1,545 | 330 | 127 | 1,046 | 0 |
| Karelians | 1,522 | 96 | 145 | 1,244 | 1 |
| Avars | 1,496 | 582 | 121 | 761 | 0 |
| Peoples of India and Pakistan | 1,483 | 1,092 | 26 | 192 | 0 |
| Abkhazians | 1,458 | 317 | 268 | 797 | 0 |
| Karaites | 1,196 | 72 | 160 | 931 | 0 |
| Komi-Permians | 1,165 | 160 | 79 | 898 | 1 |
| Kyrgyz people | 1,128 | 208 | 221 | 617 | 19 |
| Laks | 1,019 | 199 | 271 | 514 | 13 |
| Afghans | 1,008 | 551 | 60 | 213 | 0 |
| other | 3,228 | 1,027 | 144 | 790 | 0 |
| NA | 188,639 | 0 | 1,108 | 1,844 | 1 |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Ukrainian | Russian | Romanian and Moldovan |
 |
 |
 |
|||
| Crimean Tatar | Bulgarian | Hungarian |
Religion
A 2018 survey conducted by the Razumkov Centre found that 71.7% of the population declared themselves believers in any religion, while 4.7% declared themselves non-believers, and 3.0% declared themselves atheists.[61] Of the total Ukrainian population, 87.4% declared they were Christians, comprising 67.3% who declared themselves Eastern Orthodox, 10.2% Catholics (split into 9.4% Ukrainian Greek Catholics and 0.8% Latin Catholics), 7.7% "Christians", and 2.2% Protestants. Judaism comprises 0.4% of the population. In earlier surveys, between 1 and 2% of the population stated that it adhered to Islam.
According to data from 2018, among those Ukrainians declaring themselves Orthodox Christians, 28.7% said they were members of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Kyivan Patriarchate (incorporated as of 5 January 2019 into the Orthodox Church of Ukraine), while 12.8% said they were members of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscovian Patriarchate (an autonomous Eastern Orthodox church under the Russian Orthodox Church). A further 0.3% said they were members of the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Church, which, like the Kyivan Patriarchate, was incorporated in 2019 into the Orthodox Church of Ukraine. Among the remaining Orthodox Ukrainians, 23.4% declared themselves "simply Orthodox", without affiliation to any patriarchate, while a further 1.9% declared that they "did not know" which patriarchate or Orthodox church they belonged to.[61]
Regional differences
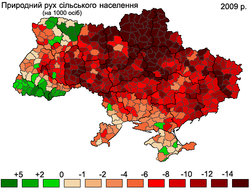
Regional differences in population change

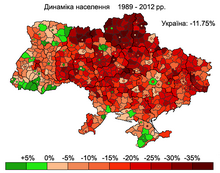
Between the Soviet census of 1989 and the Ukrainian census of 2001, Ukraine's population declined from 51,706,600 to 48,457,020,[62] a loss of 2,926,700 people, or 5.7% of the 1989 population. However, this trend was quite uneven and subject to regional variation. Two oblasts in western Ukraine, Rivne and Zakarpattia, saw slight population increases of 0.3% and 0.5%, respectively. A third western Ukrainian oblast, Volyn, lost less than 0.1% of its population between 1989 and 2001.[62] Collectively, between 1989 and 2001, the seven westernmost Ukrainian oblasts lost 167,500 people, or 1.7% of their 1989 population. The total population of these oblasts in 2001 was 9,593,800.[62]
Between 1989 and 2001, the population of Kyiv City increased by 0.3%[62] due to positive net migration.[citation needed] Outside Kyiv, the central, southern and eastern oblasts experienced a severe population declines. Between 1989 and 2001, the Donetsk Oblast lost 491,300 people, or 9.2% of its 1989 population, while the neighbouring Luhansk Oblast lost 11% of its population.[62] Chernihiv Obast, in central Ukraine (northeast of Kyiv), lost 170,600 people, or 12% of its 1989 population, the highest percentage loss in of any Ukrainian oblast. In southern Ukraine, Odesa Oblast lost 173,600 people, or 6.6% of its 1989 population.
By 2001, Crimea's population declined by 29,900, representing only a 1.4% loss of its 1989 population.[62] This however was due to the influx of approximately 200,000 Crimean Tatars – equivalent to approximately 10% of Crimea's 1989 population – who arrived in Crimea after 1989 and whose population in that region increased by a factor of 6.4 (from 38,000 to 243,400 between 1989 and 2001).[63] Collectively, the net population loss in Ukraine outside the westernmost oblasts was 2,759,200, or 6.6% of the 1989 population. The total population of these regions in 2001 was 39,186,100.[62]
Overall in 1989–2001, the pattern of population change was one of slight growth in Kyiv, slight declines in western Ukraine, large declines in eastern, central and southern Ukraine, and a relatively small decline in Crimea due to a large influx of Crimean Tatars.
 |
 |
 |
|||
| All population, 2012 | Urban population, 2009 | Rural population, 2009 |
Regional differences in birth and fertility rates
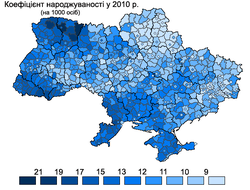
Ukraine's total fertility rate is one of the lowest in Europe.[64][65] However, significant regional differences in birth rates may account for some of the demographic differences. In the third quarter of 2007, for instance, the highest birth rate among Ukrainian oblasts occurred in Volyn Oblast, with a birth rate of 13.4/1,000 people, compared to the Ukrainian countrywide average of 9.6/1,000 people.[66] Volyn's birthrate was higher than the average birth rate of any European country except Iceland and Albania.[67]
In 2007, for the first time since 1990, five Ukrainian oblasts (Zakarpattia, Rivne, Volyn, Lviv, and Kyiv oblasts) experienced more births than deaths.[68] This demonstrated a positive trend of increasing birthrates in the preceding years throughout Ukraine. The ratio of births to deaths in those oblasts in 2007 was 119%, 117%, 110%, 100.7%, and 108%, respectively.[68]
With the exception of the Kyiv Oblast, all of the oblasts with more births than deaths were in the less-industrially developed oblasts of western Ukraine. According to a spokesperson for Ukraine's Ministry of Justice, the overall ratio of births to deaths in Ukraine improved from 1 to 1.7 in 2004–2005 to 1 to 1.4 in 2008. However, the worst birth-to-death ratios in the country were in the eastern and central oblasts of Donetsk, Luhansk, Cherkasy and Poltava. These areas saw 2.1 deaths for every birth.[69]
Notably, western Ukraine never experienced the Holodomor, as Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Romania ruled it at the time, helping to understand the more favorable demographic trends there, as the rural population was never devastated. Specifically, during the Holodomor, Poland ruled Ivano-Frankivsk, Lviv, Rivne, Ternopil, and Volyn oblasts, whereas Zakarpattia Oblast was under Czechoslovak rule, and Romania controlled Chernivtsi Oblast and the Budjak section of Odesa Oblast.
While abortion rates in the North, South, East and Center of Ukraine are relatively homogeneous, the Western region differs greatly. Overall, the abortion rate in western Ukraine is three times lower than in other regions. This is not due to increased use of modern contraceptive methods in the West, but to the fact that pregnant women in the Western regions are more likely to keep their babies.[70] Donetsk and Dniproptrovsk oblasts in eastern and central Ukraine have the country's highest abortion rate.[71]
 |
 |
 |
|||
| The birth rate in Ukraine, 2003. | The birth rate in Ukraine, 2010. | The death rate in Ukraine, 2010. |
Regional differences in death rates and health

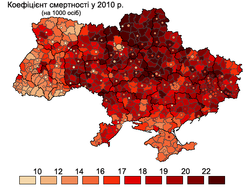
Death rates also vary widely by region; eastern and southern Ukraine have the highest death rates in the country, and the life expectancy for children born in Chernihiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Donetsk, Kherson, Kropyvnytskyi, Luhansk, Mikolaiv, and Odesa oblasts is 1.5 years lower than the national average.[72]
Ukraine had a suicide rate of 16.5 per 100,000 population in 2017, a significant decrease from the suicide rate of 29.6 per 100,000 in 1998. Suicides were more frequent in the central part of the country (the highest suicide rate was in Kirovohrad Oblast; in western Ukraine, the suicide rate was lower than the national average. Lviv Oblast had the lowest suicide rate (5.3).[73]
Southern and eastern Ukraine also suffered from the highest rates of HIV and AIDS, which impacts life expectancy. In late 2000, 60% of all AIDS cases in Ukraine were concentrated in the Odesa, Dnipropetrovsk, and Donetsk oblasts.[74] A major reason behind the higher rates was that the urbanized and industrialized oblasts in the East and South of Ukraine suffered most from the economic crisis in the 1990s, leading to the increased spread of unemployment, alcoholism, and drug abuse, setting the conditions for a wider spread of the epidemic.[75]
Regional differences in income

The western and central oblasts of Ukraine had lower GDP per capita than Kyiv and the industrialized eastern oblasts of Ukraine. In December 2019, the average monthly salary in Ukraine was 12,264 hryvnias (519 US dollars). Chernihiv Oblast (northern Ukraine) and Kirovohrad Oblast (central Ukraine) had the lowest monthly salary of 8,851 and 9,450 hryvnias, respectively. In contrast, the monthly wage in the city of Kyiv was 18,869 hryvnias per month, and in Kyiv Oblast, 13,259 per month.[76] In 2013, outside of the capital city of Kyiv, the wealthiest oblast was Donetsk with an annual income of 31,048 hryvnias. But as of 2017, it ranked second poorest after Luhansk Oblast, with annual incomes 25,278 hryvnias and 16,416 hryvnias, respectively.[77] Both are in eastern Ukraine and sustained direct losses as a consequence of military actions.
Ukraine recorded one of the sharpest declines in poverty of any transition economy in 2001–2016. The poverty rate, measured against an absolute poverty line (below $1.25 per day, based on World Bank numbers) fell from a high of 32 percent in 2001 to 8 percent in 2005. In terms of poverty rates, the central and northern oblasts have the country's highest poverty rates: 10.0%. The western and southern oblasts are 9.1% and 9%, respectively. Kyiv City had the lowest poverty rate: 1.4%.[78] The percent of the population living under $5.50 a day was 19% in 2005 and dropped to 4.0 percent in 2018.[79][80]
Urbanization
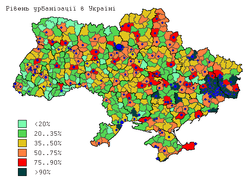 |
 |
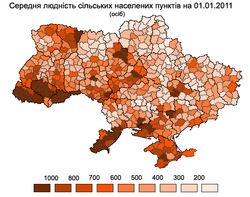 | ||
| Urbanization rate, 2011 | Population density, 2013 | Median population of rural settlements, 2011 |
Migration

Emigration
Ukraine is the major source of migrants for many EU member states. In the 1990s and early 2000s, Ukraine's sputtering economy and political instability contributed to rising emigration, especially to nearby Poland and Hungary, but also to other countries such as Italy, Portugal, Spain, Israel and Canada. Although estimates vary, approximately two to three million Ukrainian citizens were working abroad, in construction, service, housekeeping, and agriculture industries.
Between 1991 and 2004, the government counted 2,537,400 individuals who emigrated; 1,897,500 moved to other post-Soviet states, and 639,900 moved to other, mainly Western, states.[81]
By the early 2000s, Ukrainian embassies reported that 300,000 Ukrainian citizens were working in Poland, 200,000 in Italy, approximately 200,000 in the Czech Republic, 150,000 in Portugal, 100,000 in Spain, 35,000 in Turkey, 20,000 in the United States and smaller but significant numbers in Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Greece, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom. The largest number of Ukrainian workers abroad, about one million, were in Russia. Since 1992, 232,072 persons born in Ukraine have emigrated to the United States.
Yet absolute numbers are less relevant to the economic impact on host countries than the volume of immigration as a proportion of the native population. Italy had the highest rate of Ukrainian emigrants as a proportion of the native population, while the far more populous Russia had the largest absolute confirmed number of Ukrainian emigrants (excluding Poland, Portugal and the Czech Republic, for which there was conflicting data).
Immigration
Between 1991 and 2003, about 100,000 illegal immigrants were detained at the western borders of Ukraine.[82] As of 2005, about 5,000 illegal immigrants were being detained yearly, mostly from China, India, Pakistan and Afghanistan.[82] At the time, about 3,000 officially registered refugees resided in Ukraine, of whom most were Afghans.[82]
Ukraine accepted some 62,000 refugees from Transnistria following its war in 1992.[82] That same decade, thousands more were also accepted from other post-Soviet conflict zones in Abkhazia, Chechnya and Tajikistan.[82]
Between the 1989 Soviet census and the 2001 census, an increased number of former CIS residents moved to Ukraine from war zones. The number of Armenians in Ukraine almost doubled to 99,900 people during this period, while the number of Georgians and Azerbaijanis also increased substantially.[82]
As of April 2020, 1.4 million Ukrainians were internally displaced due to the war in Donbas.[83]
See also
General:
Notes
- ^ Note: Crude migration change (per 1000) is a trend analysis, an extrapolation based average population change (current year minus previous) minus natural change of the current year (see table vital statistics). As average population is an estimate of the population in the middle of the year and not end of the year.
References
- ^ a b "Population of Ukraine". www.ukrstat.gov.ua. State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ "Total Population by sex - Ukraine - 1990 to 2030". population.un.org/wpp/. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook database". 11 October 2024.
- ^ a b c "Population estimate as of February 1, 2022". www.ukrcensus.gov.ua/eng. State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ^ "World Population Dashboard -Ukraine". United Nations Population Fund. Retrieved 6 March 2024.
- ^ Harmash, Olena (7 July 2023). "Ukrainian refugees: how will the economy recover with a diminished population?". Reuters. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine – Emigration and Displacement in Past and Present". 8 July 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine Population 1950-2023". macrotrends.net. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "ru:Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета 'Высшая школа экономики'" [Institute of Demography of the National Research University "Graduate School of Economics']. Demoscope.ru (in Russian). 21 March 2013. ISSN 1726-2887. Retrieved 10 December 2016.
- ^ Ukraine, Orest Subtelny, page 152, 2000
- ^ Mirchuk, I. (December 1952). "Zenon Kuzela (1882-1952)". The Slavonic and East European Review. 31 (76). Modern Humanities Research Association: 249–251. JSTOR 4204419. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ Ukraine: A Concise Encyclopedia Vol. 1, Book by Volodymyr Kubiyovych; University of Toronto Press, 1963
- ^ "Posted availability of the book".[permanent dead link]
- ^ Vallin, Jacques; Meslé, France; Adamets, Serguei; Pyrozhkov, Serhii (2002). "A New Estimate of Ukrainian Population Losses During the Crises of the 1930s and 1940s". Population Studies. 56 (3): 249–264. doi:10.1080/00324720215934. JSTOR 3092980. PMID 12553326. S2CID 21128795.
- ^ Ian Dear, Michael Richard Daniell Foot (2001). The Oxford companion to World War II. Oxford University Press. p. 909. ISBN 0-19-860446-7
- ^ Malynovska, Olena (January 2006). "Caught Between East and West, Ukraine Struggles with Its Migration Policy". National Institute for International Security Problems, Kyiv. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ "United Nations Population Division". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^ "Ethnic origins, 2006 counts, for Canada, provinces and territories – 20% sample data" Archived 18 August 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Statistics Canada.
- ^ Bershidsky, Leonid (20 February 2019). "Eastern Europe Feeds on a Shrinking Ukraine". Bloomberg. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ Kiryukhin, Denys (14 May 2019). "Losing Brains and Brawn: Outmigration from Ukraine". Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ Tyshchuk, Tetyana (20 June 2018). "The Great Migration: No One in Ukraine Knows How Many of Our Compatriots Have Moved Abroad". vox ukraine. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ State Statistics Committee of Ukraine Retrieved 18 September 2009
- ^ Demoscope Retrieved 18 September 2009
- ^ "Field Listing – Population growth rate". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 5 July 2008.
- ^ "Infant mortality rate, Ukraine". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 26 January 2014.
- ^ "Ukraine's Population Shrinks By Nearly A Quarter". Radio Free Europe. 23 January 2020. Retrieved 24 August 2020.
- ^ "The government has estimated Ukraine's population at 37.3 million". empr.media. Archived from the original on 6 October 2023. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Knapp, Andreas (13 July 2023). "Ukraine: Population loss endangers reconstruction". WIIW. Retrieved 19 July 2023.
- ^ Perelli-Harris, Brienna (2005). "The Path to Lowest-low Fertility in Ukraine". Population Studies. 59 (1): 55–70. doi:10.1080/0032472052000332700. JSTOR 30040436. PMID 15764134. S2CID 21769928.
- ^ a b "The World FactBook – Ukraine", The World Factbook, 12 July 2018
- ^ "Bohdan Danylyshyn at the Economic ministry". Economic Ministry. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ "President meets with business bosses". Press office of President Victor Yushchenko. Archived from the original on 14 December 2007. Retrieved 1 February 2008.
- ^ (in Ukrainian) The demographic situation in Ukraine in January–September 2009, State Statistics Committee of Ukraine
- ^ "Ukraine's birth rate shows first positive signs in decade". Ukrainian Independent Information Agency (UNIAN). 5 October 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2008.
- ^ "Ukraine's birth rate plummets in aftermath of Russian invasion, data shows". The Guardian. 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Because of the war: How Ukraine's population will change by 2030". english.nv.ua. Retrieved 22 July 2023.
- ^ "World Population Prospects – Population Division – United Nations". esa.un.org. Retrieved 26 August 2018.
- ^ Demographic yearbook, 2001 (PDF). New York: United Nations. 2003. ISBN 978-92-1-051094-3. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ Общий коэффициент смертности (на 1000 населения): Украина: 1950–2013 [Crude death rate (per 1,000 people): Ukraine: 1950–2013]. Demoscope Weekly (in Russian). Archived from the original on 21 March 2016. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- ^ Державна служба статистикі України [State Statistics Committee of Ukraine]. State Statistics Committee of Ukraine (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 15 September 2002. Retrieved 14 December 2009.
- ^ "Statistical Yearbooks of the Russian Empire". Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "The Crisis of the 1930s" (PDF).
- ^ a b "Державна служба статистики України". ukrstat.gov.ua. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine's population". 19 June 2023.
- ^ "Table: 0301. Number of live births, deaths and natural increase (decrease) of the population (0,1)". Databank. State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Archived from the original on 23 January 2017. Retrieved 9 July 2019.
- ^ "UNSD — Demographic and Social Statistics". unstats.un.org. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Населення та міграція 2016".
- ^ State Statistics Committee of Ukraine – Natural increase in population in 2010 Retrieved on 20 May 2011
- ^ "Ukraine Population 2018", World Population Review
- ^ a b "Population census 2001: Population by nationality". Archived from the original on 15 March 2007. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ "Державна служба статистики України". www.ukrstat.gov.ua. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- ^ "Phantom Syndrome: Ethnic Koreans in Ukraine". Bird In Flight. 18 July 2017. Retrieved 15 April 2019.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Rusyn history and culture. Toronto, Ont.: University of Toronto Press. 2002. ISBN 0802035663.
- ^ "The Law on the Indigenous Peoples of Ukraine. What does it bring to national minorities?". Culturico. 20 December 2021. Retrieved 3 November 2023.
- ^ "Демоскоп Weekly – Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". Demoscope.ru. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Демоскоп Weekly – Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". Demoscope.ru. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Демоскоп Weekly – Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". Demoscope.ru. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Демоскоп Weekly – Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". Demoscope.ru. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Демоскоп Weekly – Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". Demoscope.ru. 21 March 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
- ^ "Ukraine People 2017 Source: 2017 CIA World Factbook and Other Sources".
- ^ a b Особливості Релігійного І Церковно-Релігійного Самовизначення Українських Громадян: Тенденції 2010–2018 [Features of Religious and Church – Religious Self-Determination of Ukrainian Citizens: Trends 2010–2018] (PDF) (in Ukrainian), Kyiv: Razumkov Center in collaboration with the All-Ukrainian Council of Churches, 22 April 2018, pp. 12, 13, 16, 31, archived (PDF) from the original on 26 April 2018
Sample of 2,018 respondents aged 18 years and over, interviewed 23–28 March 2018 in all regions of Ukraine except Crimea and the occupied territories of the Donetsk and Lugansk regions. - ^ a b c d e f g "All-Ukrainian population census of 2001". State Statistics Committee of Ukraine. 2003. Archived from the original on 14 June 2007.
- ^ "About number and composition population of Autonomous Republic of Crimea by data All-Ukrainian population census". Archived from the original on 4 December 2007. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ Рождаемость в Украине самая низкая в Европе, Demoscope.ru, 16–29 April 2007 (in Russian)
- ^ United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2007). "United Nations World Population Prospects: 2006 revision, Table A.15" (PDF). New York: UN. Retrieved 26 September 2010.
- ^ MIGnews: Volyn Region – Fertility Leader in Ukraine Archived 12 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine, 10 October 2007. Retrieved 19 October 2007.
- ^ "CIA world factbook". Archived from the original on 9 March 2013. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ a b Ukrainian News: Birth Rate Exceeds Death Rate in Five Regions of Ukraine First Since 1990s Archived 18 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine 4 October 2007. Retrieved 19 October 2007.
- ^ Inna Filipenko. The Day. Births and deaths: A record-breaking half million children were born in Ukraine last year. #3. 3 February 2009. Retrieved 8 December 2009.
- ^ Natalia LEvchuk, Brienna Perelli-Harris. (2009). Declining Fertility in UKraine: What is the role of abortion and contraception? Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research
- ^ "World Bank Report, Chapter 3: Demographic Forecast Under the HIV/AIDS Epidemic" (PDF).
- ^ Unicef. (2004). The Situation of Children and Young People at the Regional Level in Ukraine Prepared by Ukraine Country Statistical Team Co-ordinator: Iryna Kalachova State Statistic Committee, Kyiv
- ^ "Home". ukrstat.gov.ua.
- ^ The International Encyclopedia of Sexuality of the Kinsey Institute. Tamara V. Hovorun, Ph.D., and Borys M. Vornyk, Ph.D. (Medicine). Rewritten and updated in 2003 by T. V. Hovorun and B. M. Vornyk(2003) Ukraine Archived 23 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vulnerability Assessment of People Living With HIV (PLHIV) in Ukraine Archived 24 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine United Nations Development Programme, page 24 – Retrieved on 8 December 2009
- ^ "Average Monthly Salary".
- ^ "Average Income in Ukraine Per Region, 2017 State Statistics Committee of Ukraine" (PDF). Archived from the original on 18 December 2019. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- ^ "UKRAINE: Poverty Update" (PDF).
- ^ "Ukraine poverty rate".
- ^ "World Bank, Poverty & Equity and M acroeconomics, Trade & Investment Global Update-Spring-2019" (PDF).
- ^ By Olena Malynovska, National Institute for International Security Problems, Kyiv Caught Between East and West, Ukraine Struggles with Its Migration Policy
- ^ a b c d e f "Caught Between East and West, Ukraine Struggles with Its Migration Policy". Migration Policy Institute. January 2006.
- ^ "National Monitoring System Report on the Situation of Internally Displaced Persons – March 2020 – Ukraine | ReliefWeb". Reliefweb.int. 21 January 2021. Retrieved 14 March 2022.
External links
 Media related to Demographics of Ukraine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Demographics of Ukraine at Wikimedia Commons- State Committee for Statistics of Ukraine, official website at the Library of Congress Web Archives (archived 2002-09-15)
- Ukraine Situation Flash Update #47 (19 May 2023) May 2023 updated UNHCR numbers of Ukrainian population (8,240,289) displaced into other countries of the European Union.
- Trafficking in and enslavement of women Archived 22 February 2006 at the Wayback Machine Follow-up to the Fourth World Conference on Women, 2–13 March 1998
- Migration News, 2001 University of California, Davis
- The demographic situation in Ukraine: present state. tendencies, and predictions Archived 23 February 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Razumkov Centre
- On the status of observance and protection of the rights of Ukrainian citizens abroad the Special Report of the Ukrainian Parliament Commissioner for Human Rights
- News on Trafficking of Ukrainian Women, 2000–01 Trafficking in Women from Ukraine Research Project, University of Rhode Island
- Caught Between East and West, Ukraine Struggles with Its Migration Policy By Olena Malynovska, National Institute for International Security Problems, Kyiv, January 2006
- Emigration from Ukraine, 23 October 2003 The Economist (subscription required)
- Meslé, France; Pison, Gilles; Vallin, Jacques (2005). "France-Ukraine: Demographic Twins Separated by History" (PDF). Population and Societies (413): 1–4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 May 2011.
- Vallin, Jacques; Meslé, France; Adamets, Serguei; Pyrozhkov, Serhii (2002). "A New Estimate of Ukrainian Population Losses during the Crises of the 1930s and 1940s" (PDF). Population Studies. 56 (3): 249–264. doi:10.1080/00324720215934. PMID 12553326. S2CID 21128795. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2022. Retrieved 22 April 2016.
- Mortality and Causes of Death in 20th-Century Ukraine MPIDR - Publications
- Rapawy, Stephen (August 1997). "ETHNIC REIDENTIFICATION IN UKRAINE" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau.
- Pirie, Paul S. (November 1996). "National Identity and Politics in Southern and Eastern Ukraine". Europe-Asia Studies. 48 (7). Taylor & Francis, Ltd.: 1079–1104. doi:10.1080/09668139608412401. JSTOR 153099.
