Complemented lattice

In the mathematical discipline of order theory, a complemented lattice is a bounded lattice (with least element 0 and greatest element 1), in which every element a has a complement, i.e. an element b satisfying a ∨ b = 1 and a ∧ b = 0. Complements need not be unique.
A relatively complemented lattice is a lattice such that every interval [c, d], viewed as a bounded lattice in its own right, is a complemented lattice.
An orthocomplementation on a complemented lattice is an involution that is order-reversing and maps each element to a complement. An orthocomplemented lattice satisfying a weak form of the modular law is called an orthomodular lattice.
In bounded distributive lattices, complements are unique. Every complemented distributive lattice has a unique orthocomplementation and is in fact a Boolean algebra.
Definition and basic properties
A complemented lattice is a bounded lattice (with least element 0 and greatest element 1), in which every element a has a complement, i.e. an element b such that
- a ∨ b = 1 and a ∧ b = 0.
In general an element may have more than one complement. However, in a (bounded) distributive lattice every element will have at most one complement.[1] A lattice in which every element has exactly one complement is called a uniquely complemented lattice[2]
A lattice with the property that every interval (viewed as a sublattice) is complemented is called a relatively complemented lattice. In other words, a relatively complemented lattice is characterized by the property that for every element a in an interval [c, d] there is an element b such that
- a ∨ b = d and a ∧ b = c.
Such an element b is called a complement of a relative to the interval.
A distributive lattice is complemented if and only if it is bounded and relatively complemented.[3][4] The lattice of subspaces of a vector space provide an example of a complemented lattice that is not, in general, distributive.
Orthocomplementation
An orthocomplementation on a bounded lattice is a function that maps each element a to an "orthocomplement" a⊥ in such a way that the following axioms are satisfied:[5]
- Complement law
- a⊥ ∨ a = 1 and a⊥ ∧ a = 0.
- Involution law
- a⊥⊥ = a.
- Order-reversing
- if a ≤ b then b⊥ ≤ a⊥.
An orthocomplemented lattice or ortholattice is a bounded lattice equipped with an orthocomplementation. The lattice of subspaces of an inner product space, and the orthogonal complement operation, provides an example of an orthocomplemented lattice that is not, in general, distributive.[6]
- Some complemented lattices
- In the pentagon lattice N5, the node on the right-hand side has two complements.
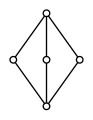
- The diamond lattice M3 admits no orthocomplementation.
- The lattice M4 admits 3 orthocomplementations.
- The hexagon lattice admits a unique orthocomplementation, but it is not uniquely complemented.
Boolean algebras are a special case of orthocomplemented lattices, which in turn are a special case of complemented lattices (with extra structure). The ortholattices are most often used in quantum logic, where the closed subspaces of a separable Hilbert space represent quantum propositions and behave as an orthocomplemented lattice.
Orthocomplemented lattices, like Boolean algebras, satisfy de Morgan's laws:
- (a ∨ b)⊥ = a⊥ ∧ b⊥
- (a ∧ b)⊥ = a⊥ ∨ b⊥.
Orthomodular lattices
A lattice is called modular if for all elements a, b and c the implication
- if a ≤ c, then a ∨ (b ∧ c) = (a ∨ b) ∧ c
holds. This is weaker than distributivity; e.g. the above-shown lattice M3 is modular, but not distributive.
A natural further weakening of this condition for orthocomplemented lattices, necessary for applications in quantum logic, is to require it only in the special case b = a⊥. An orthomodular lattice is therefore defined as an orthocomplemented lattice such that for any two elements the implication
- if a ≤ c, then a ∨ (a⊥ ∧ c) = c
holds.
Lattices of this form are of crucial importance for the study of quantum logic, since they are part of the axiomisation of the Hilbert space formulation of quantum mechanics. Garrett Birkhoff and John von Neumann observed that the propositional calculus in quantum logic is "formally indistinguishable from the calculus of linear subspaces [of a Hilbert space] with respect to set products, linear sums and orthogonal complements" corresponding to the roles of and, or and not in Boolean lattices. This remark has spurred interest in the closed subspaces of a Hilbert space, which form an orthomodular lattice.[7]
See also
Notes
- ^ Grätzer (1971), Lemma I.6.1, p. 47. Rutherford (1965), Theorem 9.3 p. 25.
- ^ Stern, Manfred (1999), Semimodular Lattices: Theory and Applications, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, Cambridge University Press, p. 29, ISBN 9780521461054.
- ^ Grätzer (1971), Lemma I.6.2, p. 48. This result holds more generally for modular lattices, see Exercise 4, p. 50.
- ^ Birkhoff (1961), Corollary IX.1, p. 134
- ^ Stern (1999), p. 11.
- ^ The Unapologetic Mathematician: Orthogonal Complements and the Lattice of Subspaces.
- ^ Ranganathan Padmanabhan; Sergiu Rudeanu (2008). Axioms for lattices and boolean algebras. World Scientific. p. 128. ISBN 978-981-283-454-6.
References
- Birkhoff, Garrett (1961). Lattice Theory. American Mathematical Society.
- Grätzer, George (1971). Lattice Theory: First Concepts and Distributive Lattices. W. H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 978-0-7167-0442-3.
- Grätzer, George (1978). General Lattice Theory. Basel, Switzerland: Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-0-12-295750-5.
- Rutherford, Daniel Edwin (1965). Introduction to Lattice Theory. Oliver and Boyd.
External links
|