Battle of France
| Battle of France | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of World War II | |||||||||
 Clockwise from top left: | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Units involved | |||||||||
Axis armies
| Allied armies | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
Germany: 141 divisions 7,378 guns[2] 2,445 tanks[2] 5,638 aircraft[3][c] 3,300,000 troops[4] Italians in the Alps 22 divisions 3,000 guns 300,000 troops Total: 3,600,000 troops |
Allies: 135 divisions 13,974 guns 3,383–4,071 French tanks[2][5] <2,935 aircraft[3][d] 3,300,000 troops French in the Alps 5 divisions ~150,000 troops Total: 3,450,000 troops | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
Germany: Total: 162,587 |
73,000 killed 240,000 wounded 15,000 missing[g] 1,756,000 captured 2,233 aircraft lost[24] 1,749 French tanks lost[h] 689 British tanks lost[i] | ||||||||
The Battle of France (French: bataille de France; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (German: Westfeldzug), the French Campaign (Frankreichfeldzug, campagne de France) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands) and France. The invasion plan for the Low Countries and France was called Case Yellow (German, Fall Gelb). Fall Rot (Case Red) was planned to finish off the French and British after the evacuation at Dunkirk. The Low Countries and France were defeated and occupied by Axis troops down to the Demarcation line. In November 1942, Wehrmacht troops also occupied Vichy France ending land operations on the Western Front until the Normandy landings began on 6 June 1944.
On 3 September 1939, France and Britain declared war on Nazi Germany, over the German invasion of Poland on 1 September. In early September 1939, France began the limited Saar Offensive but by mid-October had withdrawn to their start lines. Starting 10 May 1940, Wehrmacht armies invaded Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and parts of France.
In Fall Gelb ("Case Yellow"), German armoured units made a surprise push through the Ardennes and then along the Somme valley, cutting off and surrounding the Allied units that had advanced into Belgium to meet the German armies there. British, Belgian and French forces were pushed back to the sea by the Germans where the British and French navies evacuated the encircled elements of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French and Belgian armies from Dunkirk in Operation Dynamo.
German forces began Fall Rot ("Case Red") on 5 June 1940. The remaining Allied divisions in France, sixty French and two British, made a determined stand on the Somme and Aisne rivers but were defeated by the German combination of air superiority and armoured mobility. Italy entered the war on the German side on 10 June 1940 and began the Italian invasion of France. German armies outflanked the Maginot Line and pushed deep into France, occupying Paris unopposed on 14 June. After the flight of the French government and the collapse of the French Army, German commanders met with French officials on 18 June to negotiate an end to hostilities.
On 22 June 1940, the Second Armistice at Compiègne was signed by France and Germany. The neutral Vichy government led by Marshal Philippe Pétain replaced the Third Republic and German military occupation began along the French North Sea and Atlantic coasts and their hinterlands. The Italian invasion of France over the Alps took a small amount of ground and after the armistice, Italy occupied a small area in the south-east. The Vichy regime retained the zone libre (free zone) in the south. Following the Allied invasion of French North Africa in November 1942, in Case Anton, the Germans and Italians took control of the zone until France was liberated by the Allies in 1944.
Background
Maginot Line

During the 1930s, the French built the Maginot Line, fortifications along the border with Germany.[26][page needed] The line was intended to economise on manpower and deter a German invasion across the Franco–German border by diverting it into Belgium, which could then be met by the best divisions of the French Army. The war would take place outside French territory, avoiding the destruction of the First World War.[27][28] The main section of the Maginot Line ran from the Swiss border and ended at Longwy; the hills and woods of the Ardennes region were thought to cover the area to the north.[29] General Philippe Pétain declared the Ardennes to be "impenetrable" as long as "special provisions" were taken to destroy an invasion force as it emerged from the Ardennes by a pincer attack. The French commander-in-chief, Maurice Gamelin, also believed the area to be safe from attack, noting it "never favoured large operations". French war games, held in 1938, of a hypothetical German armoured attack through the Ardennes, left the army with the impression that the region was still largely impenetrable and that this, along with the obstacle of the Meuse River, would allow the French time to bring up troops into the area to counter any attack.[30]
German invasion of Poland
In 1939, the United Kingdom and France offered military support to Poland in the likely case of a German invasion.[31] At dawn on 1 September 1939, the German invasion of Poland began. France and the United Kingdom declared war on 3 September, after an ultimatum for German forces immediately to withdraw their forces from Poland was not answered.[32] Australia and New Zealand also declared war on 3 September, South Africa on 6 September and Canada on 10 September. While British and French commitments to Poland were met politically, the Allies failed to fulfil their military obligations to Poland, later called the Western betrayal by the Poles. The possibility of Soviet assistance to Poland had ended with the Munich Agreement of 1938, after which the Soviet Union and Germany eventually negotiated the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, which included an agreement to partition Poland. The Allies settled on a long-war strategy in which they would complete the rearmament plans of the 1930s while fighting a defensive land war against Germany and weakening its war economy with a trade blockade, ready for an eventual invasion of Germany.[33]
Phoney War

On 7 September, in accordance with the Franco-Polish alliance, France began the Saar Offensive with an advance from the Maginot Line 5 km (3 mi) into the Saar. France had mobilised 98 divisions (all but 28 of them reserve or fortress formations) and 2,500 tanks against a German force consisting of 43 divisions (32 of them reserves) and no tanks. The French advanced until they met the thin and undermanned Siegfried Line. On 17 September, Gamelin gave the order to withdraw French troops to their starting positions; the last of them left Germany on 17 September, the day of the Soviet invasion of Poland. Following the Saar Offensive, a period of inaction called the Phoney War (the French Drôle de guerre, joke war or the German Sitzkrieg, sitting war) set in between the belligerents. Adolf Hitler had hoped that France and Britain would acquiesce in the conquest of Poland and quickly make peace. On 6 October, in a speech to the Reichstag he made a peace offer to the Western powers.[34][35][36]
German strategy
Fall Gelb (Case Yellow)
On 9 October 1939, Hitler issued Führer-Directive Number 6 (Führer-Anweisung N°6).[34] Hitler recognised the necessity of military campaigns to defeat the Western European nations, preliminary to the conquest of territory in Eastern Europe, to avoid a two-front war but these intentions were absent from Directive N°6.[37] The plan was based on the seemingly more realistic assumption that German military strength would have to be built up for several years. Only limited objectives could be envisaged and were aimed at improving Germany's ability to survive a long war in the west.[38] Hitler ordered a conquest of the Low Countries to be executed at the shortest possible notice to forestall the French and prevent Allied air power from threatening the industrial area of the Ruhr.[39] It would also provide the basis for a long-term air and sea campaign against Britain. There was no mention in the directive of a consecutive attack to conquer the whole of France, although the directive read that as much as possible of the border areas in northern France should be occupied.[37][40]
On 10 October 1939, Britain refused Hitler's offer of peace and on 12 October, France did the same. The pre-war German codename of plans for a campaign in the Low Countries was Aufmarschanweisung N°1, Fall Gelb (Deployment Instruction No. 1, Case Yellow). Colonel-General Franz Halder (Chief of the General Staff Oberkommando des Heeres [OKH]), presented the first plan for Fall Gelb on 19 October.[41] Fall Gelb entailed an advance through the middle of Belgium; Aufmarschanweisung N°1 envisioned a frontal attack, at a cost of half million German soldiers to attain the limited goal of throwing the Allies back to the River Somme. German strength in 1940 would then be spent and only in 1942 could the main attack against France begin.[42] When Hitler raised objections to the plan and wanted an armoured breakthrough, as had happened in the invasion of Poland, Halder and Brauchitsch attempted to dissuade him, arguing that while the fast-moving mechanised tactics were effective against a "shoddy" Eastern European army, they would not work against a first-rate military like the French.[43]
Hitler was disappointed with Halder's plan and initially reacted by deciding that the Army should attack early, ready or not, hoping that Allied unreadiness might bring about an easy victory. Hitler proposed an invasion on 25 October 1939 but accepted that the date was probably unrealistic. On 29 October, Halder presented Aufmarschanweisung N°2, Fall Gelb, with a secondary attack on the Netherlands.[44] On 5 November, Hitler informed Walther von Brauchitsch that he intended the invasion to begin on 12 November. Brauchitsch replied that the military had yet to recover from the Polish campaign and offered to resign; this was refused but two days later Hitler postponed the attack, giving poor weather as the reason for the delay.[45][46] More postponements followed, as commanders persuaded Hitler to delay the attack for a few days or weeks, to remedy some defect in the preparations or to wait for better weather. Hitler also tried to alter the plan, which he found unsatisfactory; his weak understanding of how poorly prepared Germany was for war and how it would cope with losses of armoured vehicles were not fully considered. Though Poland had been quickly defeated, many armoured vehicles had been lost and were hard to replace. This led to the German effort becoming dispersed; the main attack would remain in central Belgium, secondary attacks would be undertaken on the flanks. Hitler made such a suggestion on 11 November, pressing for an early attack on unprepared targets.[47]
Halder's plan satisfied no-one; General Gerd von Rundstedt, the commander of Army Group A (Heeresgruppe A) recognised that it did not adhere to the classic principles of Bewegungskrieg (war of manoeuvre) that had guided German strategy since the 19th century. A breakthrough was needed to encircle and destroy the main body of Allied forces. The most practical place to achieve this would be in the region of Sedan, which lay in the sector of Army Group A. On 21 October, Rundstedt agreed with his chief of staff, Generalleutnant Erich von Manstein, that an alternative operational plan to reflect these principles was needed, by making Army Group A as strong as possible at the expense of Army Group B to the north.[48]
Manstein plan

While Manstein was formulating new plans in Koblenz, Generalleutnant Heinz Guderian, commander of the XIX Army Corps, was lodged in a nearby hotel.[49] Manstein was initially considering a move north from Sedan, directly in the rear of the main Allied mobile forces in Belgium. When Guderian was invited to contribute to the plan during informal discussions, he proposed that most of the Panzerwaffe should be concentrated at Sedan. This concentration of armour would advance to the west to the English Channel, without waiting for the main body of infantry divisions. This might lead to a strategic collapse of the enemy, avoiding the relatively high number of casualties normally caused by a Kesselschlacht (cauldron battle).[50]
Such a risky independent use of armour had been widely discussed in Germany before the war but OKH doubted such an operation could work.[50] Manstein's general operational ideas won immediate support from Guderian, who understood the terrain, having experienced the conditions with the German Army in 1914 and 1918.[51] Manstein wrote his first memorandum outlining the alternative plan on 31 October. In it he avoided mentioning Guderian and played down the strategic part of the armoured units, to avoid unnecessary resistance.[52] Six more memoranda followed between 31 October 1939 and 12 January 1940, each becoming more radical. All were rejected by OKH and nothing of their content reached Hitler.[51]
Mechelen incident
On 10 January 1940, a German aircraft, carrying a staff officer with the Luftwaffe plans for an offensive through central Belgium to the North Sea, force-landed near Maasmechelen (Mechelen) in Belgium. The documents were captured but Allied intelligence doubted that they were genuine. In the full moon period in April 1940, another Allied alert was called for a possible attack on the Low Countries or Holland, an offensive through the Low Countries to outflank the Maginot Line from the north, an attack on the Maginot Line or an invasion through Switzerland. None of the contingencies anticipated the German attack through the Ardennes but after the loss of the Luftwaffe plans, the Germans assumed that the Allied appreciation of German intentions would have been reinforced. Aufmarschanweisung N°3, Fall Gelb, an amendment to the plan on 30 January, was only a revision of details. On 24 February, the main German effort was moved south to the Ardennes.[53] Twenty divisions (including seven panzer and three motorised divisions) were transferred from Heeresgruppe B opposite Holland and Belgium to Heeresgruppe A facing the Ardennes. French military intelligence uncovered a transfer of German divisions from the Saar to the north of the Moselle but failed to detect the redeployment from the Dutch frontier to the Eifel–Moselle area.[54]
Adoption of the Manstein plan

On 27 January, Manstein was sacked as Chief of Staff of Army Group A and appointed commander of an army corps in East Prussia. To silence Manstein, Halder had instigated his transfer to Stettin on 9 February. Manstein's staff brought his case to Hitler, who had independently suggested an attack at Sedan, against the advice of OKH. On 2 February, Hitler was told of Manstein's plan and on 17 February, Hitler summoned Manstein, General Rudolf Schmundt (Chief of Personnel of the German Army) and General Alfred Jodl, the Chief of Operations of Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (OKW, Supreme Command of the Armed Forces), to a conference.[55] The next day, Hitler ordered Manstein's thinking to be adopted, because it offered the possibility of decisive victory.[56] Hitler recognised the breakthrough at Sedan only in tactical terms, whereas Manstein saw it as a means to an end. He envisaged an operation to the English Channel and the encirclement of the Allied armies in Belgium; if the plan succeeded, it could have a strategic effect.[57]
Halder then went through an "astonishing change of opinion", accepting that the Schwerpunkt should be at Sedan. He had no intention of allowing an independent strategic penetration by the seven Panzer divisions of Army Group A. Much to the dismay of Guderian, this element was absent from the new plan, Aufmarschanweisung N°4, Fall Gelb, issued on 24 February.[44] The bulk of the German officer corps was appalled and called Halder the "gravedigger of the Panzer force". Even when adapted to more conventional methods, the new plan provoked a storm of protest from the majority of German generals. They thought it utterly irresponsible to create a concentration of forces in a position impossible to adequately resupply, along routes that could be cut easily by the French. If the Allies did not react as expected, the German offensive could end in catastrophe. Their objections were ignored and Halder argued that, as Germany's strategic position seemed hopeless anyway, even the slightest chance of decisive victory should be grasped.[58] Shortly before the invasion, Hitler, who had spoken to forces on the Western Front and who was encouraged by the success in Norway, confidently predicted the campaign would take only six weeks. He was most excited over the planned military glider attack on Fort Eben-Emael.[59]
Allied strategy
Escaut plan/Plan E
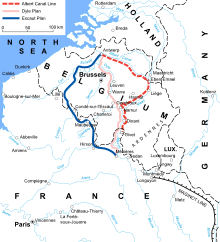
On 3 September 1939, French military strategy had been settled, taking in analyses of geography, resources and manpower. The French Army would defend in the east (right flank) and attack on the west (left flank) by advancing into Belgium, to fight forward of the French frontier. The extent of the forward move was dependent on events, which were complicated when Belgium ended the Franco-Belgian Accord of 1920 after the German Remilitarisation of the Rhineland on 7 March 1936. The neutrality of the Belgian state was reluctant openly to co-operate with France but information was communicated about Belgian defences. By May 1940, there had been an exchange of the general nature of French and Belgian defence plans but little co-ordination against a German offensive to the west, through Luxembourg and eastern Belgium. The French expected Germany to breach Belgian neutrality first, providing a pretext for French intervention or that the Belgians would request support when an invasion was imminent. Most of the French mobile forces were assembled along the Belgian border, ready to forestall the Germans.[60]
An early appeal for help might give the French time to reach the German–Belgian frontier but if not, there were three feasible defensive lines further back. A practicable line existed from Givet to Namur, across the Gembloux Gap (la trouée de Gembloux), Wavre, Louvain and along the Dyle river to Antwerp, which was 70–80 km (43–50 mi) shorter than the alternatives. A second possibility was a line from the French border to Condé, Tournai, along the Escaut (Scheldt) to Ghent and thence to Zeebrugge on the North Sea coast, possibly further along the Scheldt (Escaut) to Antwerp, which became the Escaut plan/Plan E. The third possibility was along field defences of the French border from Luxembourg to Dunkirk. For the first fortnight of the war, Gamelin favoured Plan E, because of the example of the fast German advances in Poland. Gamelin and the other French commanders doubted that they could move any further forward before the Germans arrived. In late September, Gamelin issued a directive to Général d'armée Gaston Billotte, commander of the 1st Army Group,
...assuring the integrity of the national territory and defending without withdrawing the position of resistance organised along the frontier....
— Gamelin[61]
giving the 1st Army Group permission to enter Belgium, to deploy along the Escaut according to Plan E. On 24 October, Gamelin directed that an advance beyond the Escaut was only feasible if the French moved fast enough to forestall the Germans.[62]
Dyle plan/Plan D
By late 1939, the Belgians had improved their defences along the Albert Canal and increased the readiness of the army; Gamelin and Grand Quartier Général (GQG) began to consider the possibility of advancing further than the Escaut. By November, GQG had decided that a defence along the Dyle Line was feasible, despite the doubts of General Alphonse Georges, commander of the North-Eastern Front, about reaching the Dyle before the Germans. The British had been lukewarm about an advance into Belgium, but Gamelin persuaded them; on 9 November, the Dyle plan was adopted. On 17 November, a session of the Supreme War Council deemed it essential to occupy the Dyle Line and Gamelin issued a directive that day detailing a line from Givet to Namur, the Gembloux Gap, Wavre, Louvain and Antwerp. For the next four months, the Dutch and Belgian armies laboured over their defences, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) expanded and the French army received more equipment and training. Gamelin also considered a move towards Breda in the Netherlands; if the Allies prevented a German occupation of Holland, the ten divisions of the Dutch army would join the Allied armies, control of the North Sea would be enhanced and the Germans would be denied bases for attacks on Britain.[63]

By May 1940, the 1st Army Group was responsible for the defence of France from the Channel coast south to the Maginot Line. The Seventh Army (Général d'armée Henri Giraud), BEF (General Lord Gort), First Army (Général d'armée Georges Maurice Jean Blanchard) and Ninth Army (Général d'armée André Corap) were ready to advance to the Dyle Line, by pivoting on the right (southern) Second Army. The Seventh Army would take over west of Antwerp, ready to move into Holland and the Belgians were expected to delay a German advance, then retire from the Albert Canal to the Dyle, from Antwerp to Louvain. On the Belgian right, the BEF was to defend about 20 km (12 mi) of the Dyle from Louvain to Wavre with nine divisions and the First Army, on the right of the BEF, was to hold 35 km (22 mi) with ten divisions from Wavre across the Gembloux Gap to Namur. The gap from the Dyle to Namur north of the Sambre, with Maastricht and Mons on either side, had few natural obstacles and was a traditional route of invasion, leading straight to Paris. The Ninth Army would take post south of Namur, along the Meuse to the left (northern) flank of the Second Army.[64]
The Second Army was the right (eastern) flank army of the 1st Army Group, holding the line from Pont à Bar 6 km (3.7 mi) west of Sedan to Longuyon. GQG considered that the Second and Ninth armies had the easiest task of the army group, dug in on the west bank of the Meuse on ground that was easily defended and behind the Ardennes, a considerable obstacle, the traversing of which would give plenty of warning of a German attack in the centre of the French front. After the transfer from the strategic reserve of the Seventh Army to the 1st Army Group, seven divisions remained behind the Second and Ninth armies and more could be moved from behind the Maginot Line. All but one division were either side of the junction of the two armies, GQG being more concerned about a possible German attack past the north end of the Maginot Line and then south-east through the Stenay Gap, for which the divisions behind the Second Army were well placed.[65]
Breda variant

If the Allies could control the Scheldt Estuary, supplies could be transported to Antwerp by ship and contact established with the Dutch Army along the river. On 8 November, Gamelin directed that a German invasion of the Netherlands must not be allowed to progress around the west of Antwerp and gain the south bank of the Scheldt. The left flank of the 1st Army Group was reinforced by the Seventh Army, containing some of the best and most mobile French divisions, which moved from the general reserve by December. The role of the army was to occupy the south bank of the Scheldt and be ready to move into Holland and protect the estuary by holding the north bank along the Beveland Peninsula (now the Walcheren–Zuid-Beveland–Noord-Beveland peninsula) in the Holland Hypothesis.[66]
On 12 March 1940, Gamelin discounted dissenting opinion at GQG and decided that the Seventh Army would advance as far as Breda, to link with the Dutch. Georges was told that the role of the Seventh Army on the left flank of the Dyle manoeuvre would be linked to it and Georges notified Billotte that if it were ordered to cross into the Netherlands, the left flank of the army group was to advance to Tilburg if possible and certainly to Breda. The Seventh Army was to take post between the Belgians and Dutch by passing the Belgians along the Albert Canal and then turning east, a distance of 175 km (109 mi), when the Germans were only 90 km (56 mi) distant from Breda. On 16 April, Gamelin also made provision for a German invasion of the Netherlands but not Belgium, by changing the deployment area to be reached by the Seventh Army; the Escaut plan would only be followed if the Germans forestalled the French move into Belgium.[66]
Allied intelligence
In the winter of 1939–40, the Belgian consul-general in Cologne had anticipated the angle of advance that Manstein was planning. Through intelligence reports, the Belgians deduced that German forces were concentrating along the Belgian and Luxembourg frontiers. In March 1940, Swiss intelligence detected six or seven Panzer divisions on the German-Luxembourg-Belgian border and more motorised divisions were detected in the area. French intelligence were informed through aerial reconnaissance that the Germans were constructing pontoon bridges about halfway over the Our River on the Luxembourg–German border. On 30 April, the French military attaché in Bern warned that the centre of the German assault would come on the Meuse at Sedan, sometime between 8 and 10 May. These reports had little effect on Gamelin, as did similar reports from neutral sources such as the Vatican and a French sighting of a 100 km-long (60 mi) line of German armoured vehicles on the Luxembourg border trailing back inside Germany.[67][68]
Prelude
German Army
Germany had mobilised 4,200,000 men of the Heer (German Army), 1,000,000 of the Luftwaffe (German Air Force), 180,000 of the Kriegsmarine (German Navy) and 100,000 of the Waffen-SS (military arm of the Nazi Party). When consideration is made for those in Poland, Denmark and Norway, the Army had 3,000,000 men available for the offensive starting on 10 May 1940. These manpower reserves were formed into 157 divisions. Of these, 135 were earmarked for the offensive, including 42 reserve divisions. The German forces in the west in May and June deployed some 2,439 tanks and 7,378 guns.[69] In 1939–40, 45 per cent of the army was at least 40 years old and 50 per cent of all the soldiers had just a few weeks' training. The German Army was far from motorised; ten per cent of their army was motorised in 1940 and could muster only 120,000 vehicles, compared with the 300,000 of the French Army. All of the British Expeditionary Force was motorised.[70] Most of the German logistical transport consisted of horse-drawn vehicles.[71] Only 50 per cent of the German divisions available in 1940 were fit for operations, often being worse equipped than the German army of 1914 or their equivalents in the British and French Armies. In the spring of 1940, the German Army was semi-modern; a small number of the best-equipped and "elite divisions were offset by many second and third rate divisions".[72]
Army Group A, commanded by Gerd von Rundstedt, comprised 45+1⁄2 divisions, including seven Panzer and was to execute the main movement effort through the Allied defences in the Ardennes. The manoeuvre carried out by the Germans is sometimes referred to as a "Sichelschnitt", the German translation of the phrase "sickle cut" coined by Winston Churchill after the event. It involved three armies (the 4th, 12th and 16th) and had three Panzer corps. The XV had been allocated to the 4th Army but the XLI (Reinhardt) and the XIX (Guderian) were united with the XIV Army Corps of two motorised infantry divisions on a special independent operational level in Panzergruppe Kleist (XXII Corps).[73] Army Group B (Fedor von Bock), comprised 29+1⁄2 divisions including three armoured, was to advance through the Low Countries and lure the northern units of the Allied armies into a pocket. It was composed of the 6th and 18th Armies. Army Group C, (General Wilhelm Ritter von Leeb) comprising 18 divisions of the 1st and 7th Armies, was to prevent a flanking movement from the east and with launching small holding attacks against the Maginot Line and the upper Rhine.[74]
Communications
Wireless proved essential to German success in the battle. German tanks had radio receivers that allowed them to be directed by platoon command tanks, which had voice communication with other units. Wireless allowed tactical control and far quicker improvisation than the opponent. Some commanders regarded the ability to communicate to be the primary method of combat and radio drills were considered to be more important than gunnery. Radio allowed German commanders to co-ordinate their formations, bringing them together for a mass firepower effect in attack or defence. The French numerical advantage in heavy weapons and equipment, which was often deployed in "penny-packets" (dispersed as individual support weapons) was offset. Most French tanks also lacked radio and orders between infantry units were typically passed by telephone or verbally.[75]
The German communications system permitted a degree of communication between air and ground forces. Attached to Panzer divisions were the Fliegerleittruppen (Tactical Air Control Party troops) in wheeled vehicles. There were too few Sd.Kfz. 251 command vehicles for all of the army but the theory allowed the army in some circumstances to call Luftwaffe units to support an attack. Fliegerkorps VIII, equipped with Junkers Ju 87 dive-bombers (Stukas), was to support the dash to the Channel if Army Group A broke through the Ardennes and kept a Ju 87 and a fighter group on call. On average, they could arrive to support armoured units within 45–75 minutes of orders being issued.[76]
Tactics

The German army conducted combined arms operations of mobile offensive formations, with well-trained artillery, infantry, engineer and tank formations, integrated into Panzer divisions. The elements were united by wireless communication, which enabled them to work together at a quick tempo and exploit opportunities faster than the Allies. Panzer divisions could conduct reconnaissance, advance to contact or defend and attack vital positions and weak spots. Captured ground would be occupied by infantry and artillery as pivot points for further attacks. Although many German tanks were outgunned by their opponents, they could lure Allied tanks onto the divisional anti-tank guns.[77] The avoidance of tank-versus-tank engagements conserved German tanks for the next stage of the offensive, units carrying supplies for three to four days' operations. The Panzer divisions were supported by motorised and infantry divisions.[78]
German tank battalions (Panzer-Abteilungen) were to be equipped with the Panzerkampfwagen III and Panzerkampfwagen IV tanks but shortages led to the use of light Panzerkampfwagen II and even lighter Panzerkampfwagen I instead.[citation needed] The German Army lacked a heavy tank like the French Char B1; French tanks were better designs, more numerous, with superior armour and armament but slower and with inferior mechanical reliability than the German designs.[79][80] Although the German Army was outnumbered in artillery and tanks, it possessed some advantages over its opponents. The newer German Panzers had a crew of five: commander, gunner, loader, driver, and mechanic. Having a trained individual for each task allowed a logical division of labour. French tanks had smaller crews; the commander had to load the main gun, distracting him from observation and tactical deployment.[75] The Germans enjoyed an advantage through the theory of Auftragstaktik (mission command) by which officers, NCOs and men were expected to use their initiative and had control over supporting arms, rather than the slower, top-down methods of the Allies.[81]
Luftwaffe
Army Group B had the support of 1,815 combat aircraft, 487 transport aircraft and 50 gliders; 3,286 combat aircraft supported Army Groups A and C. The Luftwaffe was the most experienced, well-equipped and well-trained air force in the world. The combined Allied total was 2,935 aircraft, about half the size of the Luftwaffe.[82] The Luftwaffe could provide close support with dive-bombers and medium bombers but was a broadly based force, intended to support national strategy and could carry out operational, tactical and strategic bombing operations. Allied air forces were mainly intended for army co-operation but the Luftwaffe could fly air superiority missions, medium-range interdiction, strategic bombing and close air support operations, depending on circumstances. It was not a Panzer spearhead arm, since in 1939 fewer than 15 per cent of Luftwaffe aircraft were designed for close support as this was not its main role.[83][84]
Flak
The Germans had an advantage in anti-aircraft guns (Fliegerabwehrkanone [Flak]), with 2,600 88 mm (3.46 in) heavy Flak guns and 6,700 37 mm (1.46 in) and 20 mm (0.79 in). Light Flak refers to the number of guns in the German armed forces, including the anti-aircraft defence of Germany and the equipment of training units. (A 9,300-gun Flak component with the field army would have needed more troops than the British Expeditionary Force.) The 88 mm Flak had an elevation of −3° to +85° and could be used as artillery i.e. against panzers.[85] The armies which invaded the west had 85 heavy and 18 light batteries belonging to the Luftwaffe, 48 companies of light Flak integral to divisions of the army and 20 companies of light Flak allocated as army troops, a reserve in the hands of HQs above corps, about 700 88 mm (3.46 in) and 180 37 mm (1.46 in) guns manned by Luftwaffe ground units and 816 20 mm (0.79 in) guns manned by the army.[86]
Allies
France had spent a higher percentage of its GNP from 1918 to 1935 on its military than other great powers[example needed] and the government had added a large rearmament effort in 1936.[citation needed] France mobilised about one-third of the male population between the ages of 20 and 45, bringing the strength of its armed forces to 5,000,000.[87] Only 2,240,000 of these served in army units in the north. The British contributed a total strength of 897,000 men in 1939, rising to 1,650,000 by June 1940.[dubious – discuss] Dutch and Belgian manpower reserves amounted to 400,000 and 650,000, respectively.[88]
Armies

The French Army had 117 divisions, of which 104 (including 11 in reserve) were for the defence of the north. The British contributed 13 divisions in the BEF, three of which were untrained and poorly-armed labour divisions. Twenty-two Belgian, ten Dutch and two Polish divisions were also part of the Allied order of battle. British artillery strength amounted to 1,280 guns, Belgium fielded 1,338 guns, the Dutch 656 guns and France 10,700 guns, giving an Allied total of about 14,000 guns, 45 per cent more than the Germans. The French Army was also more motorised than its opponent, which still relied on horses. Although the Belgians, British and Dutch had few tanks, the French had 3,254, outnumbering the Germans.[89][90]
Despite several partial mobilisations since 1936, during the full mobilisation in September 1939, officers were unfamiliar with their duties, technical experts were simultaneously expected to hand over their vehicles, report to recruitment centres and were also exempt from service as essential workers. Reservists flooded the depots leading to shortages of beds and poor sanitary conditions. The army lacked 150,000 pairs of trousers, 350,000 blankets, 415,000 tents and 600,000 pairs of boots. Recruits often left their centres and returned home or drank excessively as they waited around for someone to take charge and integrate them. This was a disastrous process not too dissimilar from that of 1870, though the main German blow fell on Poland initially and not France.[91]
The French mechanised light and heavy armoured divisions (DLM and DCr) were new and not thoroughly trained. Reserve B Divisions were composed of reservists above 30 years old and ill-equipped. A serious qualitative deficiency was a lack of anti-aircraft artillery, mobile anti-tank artillery and wireless, despite the efforts of Gamelin to produce mobile artillery units.[87][92] Only 0.15 per cent of military spending between 1923 and 1939 had been on radio and other communications equipment; to maintain signals security, Gamelin used telephones and couriers to communicate with field units.[93]
French tactical deployment and the use of mobile units at the operational level of war was also inferior to that of the Germans.[87] The French had 3,254 tanks on the north-eastern front on 10 May, against 2,439 German tanks. Much of the armour was distributed for infantry support, each army having a tank brigade (groupement) of about ninety light infantry tanks. With so many tanks available, the French could still concentrate a considerable number of light, medium and heavy tanks in armoured divisions, which in theory were as powerful as German panzer divisions.[94] Only French heavy tanks generally carried wireless but these were unreliable, hampering communication and making tactical manoeuvre difficult, compared to German units. In 1940, French military theorists still mainly considered tanks as infantry support vehicles and French tanks were slow (except for the SOMUA S35) compared to their German rivals, enabling German tanks to offset their disadvantages by out-manoeuvring French tanks. On several occasions, the French were not able to achieve the same tempo as German armoured units.[87] The state of training was also unbalanced, with the majority of personnel trained only to man static fortifications. Very little training for mobile action was carried out between September 1939 and May 1940.[95]
Deployment

The French Army comprised three army groups; the 2nd and 3rd Army Groups defended the Maginot Line to the east; the 1st Army Group (General Gaston Billotte) was on the western (left) flank, ready to move into the Low Countries. Initially positioned on the left flank near the coast, the Seventh Army, reinforced by a Division Légère Mécanique (DLM, mechanised light division), was intended to move to the Netherlands via Antwerp. To the south of the Seventh Army were the motorised divisions of the BEF, which would advance to the Dyle Line on the right flank of the Belgian army, from Leuven (Louvain) to Wavre. The First Army, reinforced by two DLM and with a Division Cuirassée (DCR, Armoured Division) in reserve, would defend the Gembloux Gap between Wavre and Namur. The southernmost army involved in the move forward into Belgium was the French Ninth Army, which had to cover the Meuse sector between Namur to the north of Sedan.[27]
Gort expected to have two or three weeks to prepare for the Germans to advance 100 km (60 mi) to the Dyle but the Germans arrived in four days.[96] The Second Army was expected to form the "hinge" of the movement and remain entrenched. It was to face the elite German armoured divisions in their attack at Sedan. It was given low priority for manpower, anti-aircraft and anti-tank weapons and air support, consisting of five divisions; two were over-age reservist Serie B divisions and the 3rd North African Division.[97][98] Considering their training and equipment, they had to cover a long front and formed a weak point of the French defence system. GQG had anticipated that the Ardennes Forest would be impassable to tanks, even though Belgian army and French intelligence warned them of long armour and transport columns crossing the Ardennes and being stuck in a huge traffic-jam for some time. French war games in 1937 and 1938 had shown that the Germans could penetrate the Ardennes; Corap called it "idiocy" to think that the enemy could not get through. Gamelin ignored the evidence, as it was not in line with his strategy.[99]
Air forces

The Armée de l'Air had 1,562 aircraft, RAF Fighter Command 680 and RAF Bomber Command could contribute about 392 aircraft.[82] Some Allied types, like the Fairey Battle, were approaching obsolescence. In the fighter force, only the British Hawker Hurricane, the US Curtiss Hawk 75 and the Dewoitine D.520 were a match for the German Messerschmitt Bf 109, the D.520 being more manoeuvrable although being slightly slower.[100][101] On 10 May 1940, only 36 D.520s had been delivered. The Allies outnumbered the Germans in fighter aircraft, with 81 Belgian, 261 British and 764 French fighters (1,106) against 836 German Bf 109s. The French and British had more aircraft in reserve.[102]
In early June 1940, the French aviation industry was producing a considerable number of aircraft, with an estimated reserve of nearly 2,000 but a chronic lack of spare parts crippled this fleet. Only about 599 (29 per cent) were serviceable, of which 170 were bombers.[103] The Germans had six times more medium bombers than the French.[93][102] Despite its disadvantages, the Armée de l'Air performed far better than expected, destroying 916 enemy aircraft in air-to-air combat, a kill ratio of 2.35:1. Almost a third of the French victories were accomplished by French pilots flying the Curtiss Hawk 75, which accounted for 12.6 per cent of the French single-seat fighter force.[104]
Anti-aircraft defence

In addition to 580 13 mm (0.5 in) machine guns assigned to civilian defence, the French Army had 1,152 25 mm (0.98 in) anti-aircraft guns, with 200 20 mm (0.79 in) auto-cannon in the process of delivery and 688 75 mm (2.95 in) guns and 24 90 mm (3.54 in) guns, the latter having problems with barrel wear. There were also forty First World War-vintage 105 mm (4.1 in) anti-aircraft guns available.[105] The BEF had ten regiments of QF 3.7-inch (94 mm) heavy anti-aircraft guns, the most advanced in the world and 7+1⁄2 regiments of Bofors 40 mm light anti-aircraft guns, about 300 heavy and 350 light anti-aircraft guns.[106] The Belgians had two heavy anti-aircraft regiments and were introducing Bofors guns for divisional anti-aircraft troops. The Dutch had 84 75 mm (2.95 in), 39 elderly 60 mm (2.36 in), seven 100 mm (3.9 in), 232 20 mm (0.79 in) 40 mm (1.57 in) anti-aircraft guns and several hundred First World War-vintage Spandau M.25 machine guns on anti-aircraft mountings.[86]
Battle
Northern front
At 21:00 on 9 May, the code word Danzig was relayed to all German army divisions, beginning Fall Gelb. Security was so tight that many officers, due to the constant delays, were away from their units when the order was sent.[59] German forces occupied Luxembourg virtually unopposed.[107] Army Group B launched its feint offensive during the night into the Netherlands and Belgium. On the morning of 10 May, Fallschirmjäger (paratroopers) from the 7th Flieger Division and 22nd Luftlande Division (Kurt Student) executed surprise landings at The Hague, on the road to Rotterdam and against the Belgian Fort Eben-Emael which helped the advance of Army Group B.[108] The French command reacted immediately, sending the 1st Army Group north in accordance with Plan D. This move committed their best forces, diminishing their fighting power by the partial disorganisation it caused and their mobility by depleting their fuel stocks. By the time the French Seventh Army crossed the Dutch border, they found the Dutch already in full retreat and withdrew into Belgium to protect Antwerp.[109]
Invasion of the Netherlands
The Luftwaffe effort over the Netherlands comprised 247 medium bombers, 147 fighters, 424 Junkers Ju 52 transports and 12 Heinkel He 59 seaplanes. The Dutch Air Force, (Militaire Luchtvaartafdeling, ML), had a strength of 144 combat aircraft, half of which were destroyed on the first day. The remainder of the ML was dispersed and accounted for only a handful of Luftwaffe aircraft shot down. The ML managed 332 sorties, losing 110 aircraft.[110] The German 18th Army captured bridges during the Battle of Rotterdam, bypassing the New Water Line from the south and penetrating Fortress Holland. A separate operation organised by the Luftwaffe, the Battle for The Hague, failed.[111] Airfields around (Ypenburg, Ockenburg and Valkenburg) were captured in a costly success, with many transport aircraft lost but the Dutch army re-captured the airfields by the end of the day.[112] Ninety-six aircraft in all were lost to Dutch artillery-fire.[111] Luftwaffe Transportgruppen operations had cost 125 Ju 52s destroyed and 47 damaged, a 50 per cent loss. The airborne operation also cost 50 per cent of the German paratroopers: 4,000 men, including 20 per cent of its NCOs and 42 per cent of its officers; of these casualties, 1,200 were made prisoners of war and evacuated to Britain.[113]

The French Seventh Army failed to block the German armoured reinforcements from the 9th Panzer Division, which reached Rotterdam on 13 May. That same day in the east, following the Battle of the Grebbeberg, in which a Dutch counter-attack to contain a German breach failed, the Dutch retreated from the Grebbe line to the New Water Line. The Dutch Army, still largely intact, surrendered in the evening of 14 May after the Bombing of Rotterdam by Heinkel He 111 medium bombers of Kampfgeschwader 54 (Bomber Wing 54); an act which has remained controversial. The Dutch Army considered its strategic situation to have become hopeless and feared destruction of other Dutch cities. The capitulation document was signed on 15 May but Dutch forces continued fighting in the Battle of Zeeland with Seventh Army and in the colonies. Queen Wilhelmina established a government in exile in Britain.[114] Dutch casualties amounted to 2,157 army, 75 air force and 125 Navy personnel; 2,559 civilians were also killed.[115]
Invasion of Belgium

The Germans quickly established air superiority over Belgium. Having completed thorough photographic reconnaissance, they destroyed 83 of the 179 aircraft of the Aeronautique Militaire within the first 24 hours of the invasion. The Belgians flew 77 operational missions but this contributed little to the air campaign. The Luftwaffe was assured air superiority over the Low Countries.[116] Because Army Group B's composition had been so weakened compared to the earlier plans, the feint offensive by the 6th Army was in danger of stalling immediately, since the Belgian defences on the Albert Canal position were very strong. The main approach route was blocked by Fort Eben-Emael, a large fortress then generally considered the most modern in Europe, which controlled the junction of the Meuse and the Albert Canal.[117]
Delay might endanger the outcome of the entire campaign, because it was essential that the main body of Allied troops be engaged before Army Group A established bridgeheads. To overcome this difficulty, the Germans resorted to unconventional means in the Battle of Fort Eben-Emael. In the early hours of 10 May, DFS 230 gliders landed on top of the fort and unloaded assault teams that disabled the main gun cupolas with hollow charges. The bridges over the canal were seized by German paratroopers. The Belgians launched considerable counterattacks which were broken up by the Luftwaffe. Shocked by a breach in its defences just where they had seemed the strongest, the Belgian Supreme Command withdrew its divisions to the KW-line five days earlier than planned. Similar operations against the bridges in the Netherlands, at Maastricht, failed. All were blown up by the Dutch and only one railway bridge was taken, which held up the German armour on Dutch territory for a short time.[118][119]

The BEF and the French First Army were not yet entrenched and the news of the defeat on the Belgian border was unwelcome. The Allies had been convinced Belgian resistance would have given them several weeks to prepare a defensive line at the Gembloux Gap. The XVI Panzerkorps (General Erich Hoepner) consisting of the 3rd Panzer Division and the 4th Panzer Division, was launched over the newly captured bridges in the direction of the Gembloux Gap. This seemed to confirm the expectations of the French Supreme Command that the German Schwerpunkt (point of main effort, centre of gravity) would be at that point. Gembloux was located between Wavre and Namur, on flat, ideal tank terrain. It was also an unfortified part of the Allied line. To gain time to dig in there, René Prioux, commanding the Cavalry Corps of the French First Army, sent the 2nd DLM and 3rd DLM towards the German armour at Hannut, east of Gembloux. They would provide a screen to delay the Germans and allow sufficient time for the First Army to dig in.[120]
Battles of Hannut and Gembloux

The Battle of Hannut (12–13 May) was the largest tank battle yet fought, with about 1,500 armoured fighting vehicles involved. The French knocked out about 160 German tanks for a loss of 105 machines including 30 Somua S35 tanks.[121] The Germans were left in control of the battlefield after the French made a planned withdrawal and were able to repair many of their knocked-out tanks. The net German loss amounted to 20 tanks of the 3rd Panzer Division and 29 of the 4th Panzer Division.[122] Prioux had achieved a tactical and operational success for the French by fulfilling his objective of delaying the panzer divisions until the First Army had time to arrive and dig in.[123][121] The German attack had engaged the First Army to the north of Sedan, which was the most important objective that Hoepner had to achieve but had failed to forestall the French advance to the Dyle or to destroy the First Army. On 14 May, having been held up at Hannut, Hoepner attacked again, against orders, in the Battle of Gembloux. This was the only occasion when German tanks frontally attacked a fortified position during the campaign. The 1st Moroccan Division repulsed the attack and another 42 tanks of the 4th Panzer Division were knocked out, 26 being written off. This second French defensive success was nullified by events further south at Sedan.[124]
Central front
Ardennes

The advance of Army Group A was to be delayed by Belgian motorised infantry and French mechanised cavalry divisions (DLC, Divisions Légères de Cavalerie) advancing into the Ardennes. The main resistance came from the Belgian 1st Chasseurs Ardennais, the 1st Cavalry Division, reinforced by engineers and the French 5e Division Légère de Cavalerie (5th DLC).[125] The Belgian troops blocked roads, held up the 1st Panzer Division at Bodange for about eight hours and then retired northwards too quickly for the French, who had not arrived. The Belgian barriers proved ineffective when not defended; German engineers were not disturbed as they dismantled the obstacles. The French had insufficient anti-tank capacity to block the surprisingly large number of German tanks they encountered and quickly gave way, withdrawing behind the Meuse.[126]
The German advance was hampered by the number of vehicles trying to force their way along the poor road network. Panzergruppe Kleist had more than 41,140 vehicles, which had only four march routes through the Ardennes.[126] French reconnaissance aircrews had reported German armoured convoys by the night of 10/11 May but this was assumed to be secondary to the main attack in Belgium. On the next night, a reconnaissance pilot reported that he had seen long vehicle columns moving without lights; another pilot sent to check reported the same and that many of the vehicles were tanks. Later that day, photographic reconnaissance and pilot reports were of tanks and bridging equipment. On 13 May, Panzergruppe Kleist caused a traffic jam about 250 km (160 mi) long from the Meuse to the Rhine on one route. While the German columns were sitting targets, the French bomber force attacked the Germans in northern Belgium during the Battle of Maastricht and had failed with heavy losses. In two days, the bomber force had been reduced from 135 to 72.[127]

On 11 May, Gamelin ordered reserve divisions to begin reinforcing the Meuse sector. Because of the danger the Luftwaffe posed, movement over the rail network was limited to night-time, slowing the reinforcement. The French felt no sense of urgency, as they believed the build-up of German divisions would be correspondingly slow; the French Army did not conduct river crossings unless assured of heavy artillery support. While they were aware that the German tank and infantry formations were strong, they were confident in their strong fortifications and artillery superiority. The capabilities of the French units in the area were dubious; in particular, their artillery was designed for fighting infantry and they were short of anti-aircraft and anti-tank guns.[128] The German advance forces reached the Meuse line late in the afternoon of 12 May. To allow each of the three armies of Army Group A to cross, three bridgeheads were to be established, at Sedan in the south, Monthermé to the north-west and Dinant further north.[129] The first German units to arrive hardly had local numerical superiority; the German artillery had an average of 12 rounds per gun per day, while French artillery had 30 rounds per gun per day.[130][131]
Battle of Sedan
At Sedan, the Meuse Line consisted of a strong defensive belt 6 km (3+1⁄2 mi) deep, laid out according to the modern principles of zone defence on slopes overlooking the Meuse valley. It was strengthened by 103 pillboxes, manned by the 147th Fortress Infantry Regiment. Deeper positions were held by the 55th Infantry Division, a grade "B" reserve division. On the morning of 13 May, the 71st Infantry Division was inserted to the east of Sedan, allowing the 55th Infantry Division to narrow its front by a third and deepen its position to over 10 km (6 mi). The division had a superiority in artillery to the German units present.[130] On 13 May, Panzergruppe Kleist forced three crossings near Sedan, executed by the 1st Panzer Division, 2nd Panzer Division and 10th Panzer Division. These groups were reinforced by the elite Infantry Regiment Großdeutschland. Instead of slowly massing artillery as the French expected, the Germans concentrated most of their air power (lacking artillery) on smashing a hole in a narrow sector of the French lines by carpet bombing and dive bombing. Guderian had been promised extraordinarily heavy air support during a continual eight-hour air attack, from 08:00 am until dusk.[132]

The Luftwaffe executed the heaviest air bombardment the world had yet witnessed and the most intense by the Germans during the war.[133] Two Sturzkampfgeschwader (dive bomber wings) attacked, flying 300 sorties against French positions.[134] A total of 3,940 sorties were flown by nine Kampfgeschwader (Bomber Groups).[135] Some of the forward pillboxes were undamaged and the garrisons repulsed the crossing attempts of the 2nd Panzer Division and 10th Panzer Division. The morale of the troops of the 55th Infantry Division further back was broken by the air attacks and French gunners fled. The German infantry, at a cost of a few hundred casualties, penetrated up to 8 km (5.0 mi) into the French defensive zone by midnight. Even by then, most of the infantry had not crossed. Much of this success was due to the actions of just six German platoons, mainly assault engineers.[136]
The disorder that had begun at Sedan spread further. At 19:00 on 13 May, troops of the 295th Regiment of the 55th Infantry Division were holding the last prepared defensive line at the Bulson ridge 10 km (6 mi) behind the river. They were panicked by alarmist rumours that German tanks were already behind them and fled, creating a gap in the French defences before any tanks had crossed the river. This "Panic of Bulson" also involved the divisional artillery. The Germans had not attacked their position and would not do so until 12 hours later, at 07:20 on 14 May.[137] Recognising the gravity of the defeat at Sedan, General Gaston-Henri Billotte, commander of the 1st Army Group, whose right flank pivoted on Sedan, urged that the bridges across the Meuse be destroyed by air attack. He was convinced that "over them will pass either victory or defeat!" That day, every available Allied light bomber was employed in an attempt to destroy the three bridges but lost about 44 per cent of the Allied bomber strength for no result.[135][138]
Collapse on the Meuse

Guderian had indicated on 12 May that he wanted to enlarge the bridgehead to at least 20 km (12 mi). His superior, General Ewald von Kleist, ordered him, on behalf of Hitler, to limit his moves to a maximum of 8 km (5.0 mi) before consolidation. At 11:45 on 14 May, Rundstedt confirmed this order, which implied that the tank units should now start to dig in.[139] Guderian was able to get Kleist to agree on a form of words for a "reconnaissance in force", by threatening to resign and behind-the-scenes intrigues. Guderian continued the advance, despite the halt order.[140] In the original Manstein plan, as Guderian had suggested, secondary attacks would be carried out to the south-east, in the rear of the Maginot Line. This would confuse the French command and occupy ground where French counter-offensive forces would assemble. This element had been removed by Halder but Guderian sent the 10th Panzer Division and Infantry Regiment Großdeutschland south over the Stonne plateau.[141]
The commander of the French Second Army, General Charles Huntziger, intended to carry out a counter-attack at the same spot by the 3e Division Cuirassée (3e DCR, 3rd Armoured Division). The intended attack would eliminate the bridgehead. Both sides attacked and counter-attacked from 15 to 17 May. Huntziger considered this at least a defensive success and limited his efforts to protecting the flank. Success in the Battle of Stonne and the recapture of Bulson would have enabled the French to defend the high ground overlooking Sedan and bombard the bridgehead with observed artillery-fire, even if they could not take it. Stonne changed hands 17 times and fell to the Germans for the last time on the evening of 17 May.[142] Guderian turned the 1st Panzer Division and the 2nd Panzer Division westwards on 14 May, which advanced swiftly down the Somme valley towards the English Channel.[143]
On 15 May, Guderian's motorised infantry fought their way through the reinforcements of the new French Sixth Army in their assembly area west of Sedan, undercutting the southern flank of the French Ninth Army. The Ninth Army collapsed and surrendered en masse. The 102nd Fortress Division, its flanks unsupported, was surrounded and destroyed on 15 May at the Monthermé bridgehead by the 6th Panzer Division and 8th Panzer Division without air support.[144][145] The French Second Army had also been seriously damaged. The Ninth Army was also giving way because they did not have time to dig in, as Erwin Rommel had broken through French lines within 24 hours of the battle's beginning. The 7th Panzer Division raced ahead. Rommel refused to allow the division rest and they advanced by day and night. The division advanced 30 mi (48 km) in 24 hours.[146]

Rommel lost contact with General Hermann Hoth, having disobeyed orders by not waiting for the French to establish a new line of defence. The 7th Panzer Division continued to advance north-west to Avesnes-sur-Helpe, just ahead of the 1st and 2nd Panzer divisions.[147] The French 5th Motorised Infantry Division had bivouacked in the path of the German division, with its vehicles neatly lined up along the roadsides and the 7th Panzer Division dashed through them.[148] The slow speed, overloaded crews and lack of battlefield communications undid the French. The 5th Panzer Division joined in the fight. The French inflicted many losses on the division. However, they could not cope with the speed of the German mobile units, which closed fast and destroyed the French armour at close range.[149] The remaining elements of the 1st DCR, resting after losing all but 16 of its tanks in Belgium, were also engaged and defeated. The 1st DCR retired with three operational tanks, while defeating only 10 per cent of the 500 German tanks.[150][151]
By 17 May, Rommel claimed to have taken 10,000 prisoners while suffering only 36 losses.[148] Guderian was delighted with the fast advance and encouraged XIX Korps to head for the channel, continuing until fuel was exhausted.[152] Hitler worried that the German advance was moving too fast. Halder recorded in his diary on 17 May,
Führer is terribly nervous. Frightened by his own success, he is afraid to take any chance and so would pull the reins on us ... [he] keeps worrying about the south flank. He rages and screams that we are on the way to ruin the whole campaign.
Through deception and different interpretations of orders to stop from Hitler and Kleist, the front line commanders ignored Hitler's attempts to stop the westward advance to Abbeville.[140]
French leaders

The French High Command, slow to react because of its strategy of "methodical warfare", reeled from the shock of the German offensive and was overtaken by defeatism. On the morning of 15 May, the French Prime Minister, Paul Reynaud, telephoned the new British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill and said, "We have been defeated. We are beaten; we have lost the battle." Churchill, attempting to offer some comfort to Reynaud, reminded him of all the times the Germans had broken through the Allied lines in the First World War only to be stopped but Reynaud was inconsolable.[153]
Churchill flew to Paris on 16 May. He immediately recognised the gravity of the situation when he observed that the French government was already burning its archives and was preparing for an evacuation of the capital. In a sombre meeting with the French commanders, Churchill asked General Gamelin, "Where is the strategic reserve?" referring to the reserve that had saved Paris in the First World War. Gamelin replied:
"Aucune" [None]
— Gamelin, according to Churchill
After the war, Gamelin claimed he said "There is no longer any."[154] Churchill later described hearing this as the most shocking moment in his life. Churchill asked Gamelin where and when the general proposed to launch a counter-attack against the flanks of the German bulge. Gamelin simply replied "inferiority of numbers, inferiority of equipment, inferiority of methods."[155]
Allied counter-attacks
Some of the best Allied units in the north had seen little fighting. Had they been kept in reserve, they might have been used in a counter-attack. Pre-war General Staff Studies had concluded that the main reserves were to be kept on French soil to resist an invasion of the Low Countries. They could also deliver a counterattack or "re-establish the integrity of the original front".[156] Despite having a numerically superior armoured force, the French failed to use it properly or to deliver an attack on the vulnerable German bulge. The Germans combined their fighting vehicles in divisions and used them at the point of main effort. The bulk of French armour was scattered along the front in tiny formations. Most of the French reserve divisions had by now been committed. The 1st DCr had been wiped out when it had run out of fuel and the 3rd DCr had failed to take its opportunity to destroy the German bridgeheads at Sedan. The only armoured division still in reserve, the 2nd DCr, was to attack on 16 May west of Saint-Quentin, Aisne. The division commander could locate only seven of its twelve companies, which were scattered along a 49 mi × 37 mi (79 km × 60 km) front. The formation was overrun by the 8th Panzer Division while still forming up and was destroyed as a fighting unit.[157]

The 4th DCr, led by de Gaulle, attempted to launch an attack from the south at Montcornet, where Guderian had his Korps headquarters and the 1st Panzer Division had its rear services. During the Battle of Montcornet, the French would manage to brush aside the unsuspecting Germans, catching Guderian offguard. Faced with such a threat, a hastily improvised defence was established while Guderian rushed up the 10th Panzer Division to threaten de Gaulle's flank. This flank pressure and dive-bombing by Fliegerkorps VIII (General Wolfram von Richthofen) broke up the attack. French losses on 17 May amounted to 32 tanks and armoured vehicles but the French had inflicted much greater casualties on the Germans. On 19 May, after receiving reinforcements and commandeering nearby units, de Gaulle attacked again. In spite of the 10th Panzer Division's arrival, the French would pierce the German defence, coming to within a mile of Guderian's headquarters before being checked; having lost 80 out of 155 vehicles.[158] Fliegerkorps VIII relentlessly attacked the French Armour, preventing them from capitalizing on their success and overruning the Germans. Faced with increasingly stiffening German resistance, de Gaulle would ask for further reinforcements, requesting that two Infantry Divisions be brought forward to support his tanks. However, this plea was refused. With no help forthcoming, de Gaulle would finally be forced to retreat on the 20th of May, largely due to heavy German aerial attacks. The defeat of the 4th DCr and the disintegration of the French Ninth Army was caused mainly by the Fliegerkorps, rather than German infantry and armour.[159] The 4th DCr had achieved a measure of success, causing considerable delays to the German timetable and tying up enemy units, but the attacks on 17 and 19 May had only local effect.[160]
Channel coast
On 19 May, General Edmund Ironside, the British Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS), conferred with General Lord Gort, commander of the BEF, at his headquarters near Lens. He urged Gort to save the BEF by attacking south-west toward Amiens. Gort replied that seven of his nine divisions were already engaged on the Scheldt River and he had only two divisions left to mount such an attack. He then said that he was under the orders of General Billotte, the commander of the French 1st Army Group but that Billotte had issued no orders for eight days. Ironside confronted Billotte, whose own headquarters was nearby and found him apparently incapable of taking action. He returned to Britain, concerned that the BEF was doomed and ordered urgent anti-invasion measures.[161]
The German land forces could not remain inactive any longer, since it would allow the Allies to reorganise their defence or escape. On 19 May, Guderian was permitted to start moving again and smashed through the weak 12th (Eastern) Infantry Division and the 23rd (Northumbrian) Division (both Territorial divisions) on the Somme river. The German units occupied Amiens and secured the westernmost bridge over the river at Abbeville. This move isolated the British, French, Dutch and Belgian forces in the north from their supplies.[162] On 20 May, a reconnaissance unit from the 2nd Panzer Division reached Noyelles-sur-Mer, 100 km (62 mi) to the west of their positions on 17 May. From Noyelles, they were able to see the Somme estuary and the English Channel. A huge pocket, containing the Allied 1st Army Group (the Belgian, British and French First, Seventh and Ninth armies), was created.[163]
Fliegerkorps VIII covered the dash to the channel coast. Heralded as the finest hour of the Ju 87 (Stuka), these units responded via an extremely efficient communications system to requests for support, which blasted a path for the army. The Ju 87s were particularly effective at breaking up attacks along the flanks of the German forces, breaking fortified positions and disrupting supply routes.[164][165] Radio-equipped forward liaison officers could call upon the Stukas and direct them to attack Allied positions along the axis of advance. In some cases, the Luftwaffe responded to requests within 10 to 20 minutes. Oberstleutnant Hans Seidemann, the Fliegerkorps vIII Chief of Staff, said that "never again was such a smoothly functioning system for discussing and planning joint operations achieved". Closer examination reveals the army had to wait 45–75 minutes for Ju 87 units and ten minutes for Henschel Hs 123s.[166]
Weygand plan
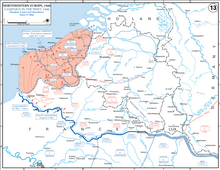
On the morning of 20 May, Gamelin ordered the armies trapped in Belgium and northern France to fight their way south and link up with French forces attacking northwards from the Somme river.[167] On the evening of 19 May, the French Prime Minister, Paul Reynaud, had sacked Gamelin and replaced him with Maxime Weygand, who claimed his first mission as Commander-in-Chief would be to get a good night's sleep.[168] Gamelin's orders were cancelled and Weygand took several days during the crisis to make courtesy visits in Paris. Weygand proposed a counter-offensive by the armies trapped in the north combined with an attack by French forces on the Somme front, the new French 3rd Army Group (General Antoine-Marie-Benoît Besson).[167][169]
The corridor through which Panzergruppe von Kleist had advanced to the coast was narrow and to the north were the three DLMs and the BEF; to the south was the 4th DCR. Allied delays caused by the French change of command gave the German infantry divisions time to follow up and reinforce the panzer corridor. Their tanks had also pushed further along the channel coast. Weygand flew into the pocket on 21 May and met Billotte, the commander of the 1st Army Group and King Leopold III of Belgium. Leopold announced that the Belgian Army could not conduct offensive operations, as it lacked tanks and aircraft and that unoccupied Belgium had enough food for only two weeks. Leopold did not expect the BEF to endanger itself to keep contact with the Belgian Army but warned that if it persisted with the southern offensive, the Belgian army would collapse.[170] Leopold suggested the establishment of a beach-head covering Dunkirk and the Belgian channel ports.[171]
Gort doubted that the French could prevail. On 23 May, the situation was worsened by Billotte being killed in a car crash, leaving the 1st Army Group leaderless for three days. He was the only Allied commander in the north briefed on the Weygand plan. That day, the British decided to evacuate from the Channel ports. Only two local offensives, by the British and French in the north at Arras on 21 May and by the French from Cambrai in the south on 22 May, took place. Frankforce (Major-General Harold Franklyn) consisting of two divisions, had moved into the Arras area. Franklyn was not aware of a French push north toward Cambrai and the French were ignorant of a British attack towards Arras. Franklyn assumed he was to relieve the Allied garrison at Arras and cut German communications in the vicinity. He was reluctant to commit the 5th Infantry Division and 50th (Northumbrian) Infantry Division, with the 3rd DLM providing flank protection, in a limited objective attack. Only two British infantry battalions and two battalions of the 1st Army Tank Brigade, with 58 Matilda I and 16 Matilda II tanks and an attached motorcycle battalion, took part in the main attack.[172]
The Battle of Arras achieved surprise and initial success against overstretched German forces but failed in its objective. Radio communication between tanks and infantry was poor and there was little combined arms co-ordination as practised by the Germans. German defences (including 88 mm (3.46 in) FlaK guns and 105 mm (4.1 in) field guns) eventually stopped the attack. The French knocked out many German tanks as they retired but the Luftwaffe broke up the counter-attacks and 60 British tanks were lost. The southern attack at Cambrai also failed, because V Corps had been too disorganised after the fighting in Belgium to make a serious effort.[173][174] OKH panicked at the thought of hundreds of Allied tanks smashing the best forces but Rommel wanted to continue the pursuit. Early on 22 May, OKH recovered and ordered the XIX Panzerkorps to press north from Abbeville to the Channel ports. The 1st Panzer Division advanced to Calais, the 2nd Panzer Division to Boulogne and the 10th Panzer Division to Dunkirk (later, the 1st and 10th Panzer divisions' roles were reversed).[175][176] South of the German salient, limited French attacks occurred on 23 May near Peronne and Amiens. French and British troops fought the Battle of Abbeville from 27 May to 4 June but failed to eliminate the German bridgehead south of the Somme.[citation needed]
BEF and the Channel ports
Siege of Calais

In the early hours of 23 May, Gort ordered a retreat from Arras. By now, he had no faith in the Weygand plan, nor in Weygand's proposal at least to try to hold a pocket on the Flemish coast, a so-called Réduit de Flandres. Gort knew that the ports needed to supply such a foothold were already being threatened. That same day, the 2nd Panzer Division had assaulted Boulogne. The remaining French and British there surrendered on 25 May, although 4,286 men were evacuated by Royal Navy ships. The RAF also provided air cover, denying the Luftwaffe an opportunity to attack the shipping.[177]
The 10th Panzer Division (Ferdinand Schaal) attacked Calais on 24 May. British reinforcements (the 3rd Royal Tank Regiment, equipped with cruiser tanks and the 30th Motor Brigade; the latter constituted much of the infantry force that was to have served with British 1st Armoured Division) had been hastily landed 24 hours before the Germans attacked. The defenders held on to the port as long as possible, aware that an early capitulation would free up German forces to advance on Dunkirk. The British and French held the town despite the best efforts of Schaal's division to break through. Frustrated, Guderian ordered that, if Calais had not fallen by 14:00 on 26 May, he would withdraw the 10th Panzer Division and ask the Luftwaffe to destroy the town. Eventually, the French and British ran out of ammunition and the Germans were able to break into the fortified city at around 13:30 on 26 May, 30 minutes before Schaal's deadline was up.[178] Despite the French surrender of the main fortifications, the British held the docks until the morning of 27 May. Around 440 men were evacuated. The siege lasted for four crucial days.[179][180] The delaying action came at a price, about 60 per cent of Allied personnel were killed or wounded.[181]
Halt orders

Frieser wrote that the Franco-British counter-attack at Arras had a disproportionate effect on the Germans because the German higher commanders were apprehensive about flank security. Kleist, the commander of Panzergruppe von Kleist, perceived a "serious threat" and informed Halder that he had to wait until the crisis was resolved before continuing. Colonel-General Günther von Kluge, the 4th Army commander ordered the tanks to halt, with the support of Rundstedt. On 22 May, when the attack had been repulsed, Rundstedt ordered that the situation at Arras must be restored before Panzergruppe von Kleist moved on Boulogne and Calais. At OKW, the panic was worse and Hitler contacted Army Group A on 22 May, to order that all mobile units were to operate either side of Arras and infantry units were to operate to the east.[182]
The crisis among the higher staffs of the German army was not apparent at the front and Halder formed the same conclusion as Guderian, that the real threat was that the Allies would retreat to the channel coast too quickly and a race for the channel ports began. Guderian ordered the 2nd Panzer Division to capture Boulogne, the 1st Panzer Division to take Calais and the 10th Panzer division to seize Dunkirk. Most of the BEF and the French First Army were still 100 km (60 mi) from the coast but despite delays, British troops were sent from England to Boulogne and Calais just in time to forestall the XIX Corps panzer divisions on 22 May. Frieser wrote that had the panzers advanced at the same speed on 21 May as they had on 20 May, before the halt order stopped their advance for 24 hours, Boulogne and Calais would have fallen. (Without a halt at Montcornet on 15 May and the second halt on 21 May after the Battle of Arras, the final halt order of 24 May would have been irrelevant, because Dunkirk would have already been captured by the 10th Panzer Division.)[183]
Operation Dynamo

The British launched Operation Dynamo, which evacuated the encircled British, French and Belgian troops from the northern pocket in Belgium and Pas-de-Calais, beginning on 26 May. About 28,000 men were evacuated on the first day. The French First Army – the bulk of which remained in Lille – fought the Siege of Lille owing to Weygand's failure to pull it back along with other French forces to the coast. The 50,000 men involved capitulated on 31 May. While the First Army was mounting its sacrificial defence at Lille, it drew German forces away from Dunkirk, allowing 70,000 Allied soldiers to escape. Total Allied evacuation stood at 165,000 on 31 May. The Allied position was complicated by Belgian King Leopold III's surrender on 27 May, which was postponed until 28 May. The gap left by the Belgian Army stretched from Ypres to Dixmude. A collapse was averted at the Battle of Dunkirk and 139,732 British and 139,097 French soldiers were evacuated by sea across the English Channel in Operation Dynamo. Between 31 May and 4 June, another 20,000 British and 98,000 French were saved; about 30,000 to 40,000 French soldiers of the rearguard remained to be captured.[184] The total evacuated was 338,226, including 199,226 British and 139,000 French.[185]
During the Dunkirk battle, the Luftwaffe did its best to prevent the evacuation. It flew 1,882 bombing missions and 1,997 fighter sorties. British losses at Dunkirk made up 6 per cent of their total losses during the French campaign, including 60 precious fighter pilots. The Luftwaffe failed in its task of preventing the evacuation but inflicted serious losses on the Allied forces. 89 merchantmen (of 126,518 grt) were lost; the navy lost 29 of its 40 destroyers sunk or seriously damaged. The Germans lost around 100 aircraft; the RAF lost 106 fighters.[186] Other sources put Luftwaffe losses in the Dunkirk area at 240.[187] Confusion still reigned. After the evacuation at Dunkirk, while Paris was enduring a short-lived siege, part of the 1st Canadian Infantry Division was sent to Brittany but was withdrawn after the French capitulation.[188] The 1st Armoured Division under General Evans arrived in France in June and fought in the Battle of Abbeville. It did so without some of its infantry, which had earlier been diverted to the defence of Calais. At the end of the campaign, Erwin Rommel praised the staunch resistance of British forces, despite being under-equipped and without ammunition for much of the fighting.[189][j]
Fall Rot
By the end of May 1940, the best and most modern French armies had been sent north and lost in the resulting encirclement; the French had also lost much of their heavy weaponry and their best armoured formations. Overall, the Allies had lost 61 divisions in Fall Gelb. Weygand was faced with the prospect of defending a long front (from Sedan to the channel), with a greatly depleted French Army now lacking significant Allied support. Weygand had only 64 French divisions and the 51st (Highland) Infantry Division available. Weygand lacked the reserves to counter a breakthrough or to replace frontline troops, should they become exhausted from a prolonged battle on a front of 965 km (600 mi). The Germans had 142 divisions and air supremacy, except over the English Channel.[191] The French also had to deal with millions of civilian refugees fleeing the war in what became known as L'Exode (the Exodus). Automobiles and horse-drawn carts carrying possessions clogged roads. As the government had not foreseen such a rapid military collapse, there were few plans to cope. Between six and ten million French fled, sometimes so quickly that they left uneaten meals on tables, even while officials stated that there was no need to panic and that civilians should stay. The population of Chartres dropped from 23,000 to 800 and Lille from 200,000 to 20,000, while cities in the south such as Pau and Bordeaux rapidly grew in population.[192]
Weygand line

The Germans began their second offensive on 5 June on the Somme and the Aisne. During the next three weeks, far from the easy advance the Wehrmacht expected, they encountered strong resistance from a rejuvenated French Army.[193] The French armies had fallen back on their lines of supply and communications and were closer to repair shops, supply dumps and stores. About 112,000 French soldiers from Dunkirk were repatriated via the Normandy and Brittany ports, a partial substitute for the lost divisions in Flanders. The French were also able to make good a significant amount of their armoured losses and raised the 1st and 2nd DCR (heavy armoured divisions). The 4th DCR also had its losses replaced. Morale rose and was very high by the end of May 1940. Most French soldiers that joined the line only knew of German success by hearsay.[194]
French officers had gained tactical experience against German mobile units and had more confidence in their weapons after seeing that their artillery and tanks performed better than German armour. The French tanks were now known to have better armour and armament. Between 23 and 28 May, the French Seventh and Tenth armies were reconstituted. Weygand decided to implement defence in depth and use delaying tactics to inflict maximum attrition on German units. Small towns and villages were fortified for all-round defence as tactical hedgehogs. Behind the front line, the new infantry, armoured and half-mechanised divisions formed up, ready to counter-attack and relieve the surrounded units, which were to hold out at all costs.[195]
The 47 divisions of Army Group B attacked either side of Paris with the majority of the mobile units.[191] After 48 hours, the German offensive had not broken through.[196] On the Aisne, the XVI Panzerkorps employed over 1,000 AFVs in two Panzer divisions and a motorised division against the French. German offensive tactics were crude and Hoepner soon lost 80 out of 500 AFVs in the first attack. The 4th Army captured bridgeheads over the Somme but the Germans struggled to get over the Aisne.[197][198] At Amiens, the Germans were repeatedly driven back by French artillery-fire and realised that French tactics were much improved.[199]
The German Army relied on the Luftwaffe to silence French artillery, to enable German infantry to inch forward.[199] German progress was made only late on the third day of operations, finally forcing crossings. The French Air Force (Armée de l'Air) attempted to bomb them but failed. German sources acknowledged the battle was "hard and costly in lives, the enemy putting up severe resistance, particularly in the woods and tree lines continuing the fight when our troops had pushed past the point of resistance".[200] South of Abbeville, the French Tenth Army (General Robert Altmayer) was forced to retreat to Rouen and then south over the Seine.[201] The 7th Panzer Division forced the surrender of the British 51st (Highland) Division and the French IX Corps on 12 June at Saint-Valery-en-Caux, then crossed the Seine river to race through Normandy, capturing the port of Cherbourg on 18 June.[202][11] German spearheads were overextended and vulnerable to counter-attack but the Luftwaffe denied the French the ability to concentrate and the fear of air attack negated their mass and mobility.[203]

On 10 June, Reynaud declared Paris an open city.[204] The German 18th Army then deployed against Paris. The French resisted the approaches to the capital strongly but the line was broken in several places. Weygand asserted it would not take long for the French Army to disintegrate.[205] On 13 June, Churchill attended a meeting of the Anglo-French Supreme War Council at Tours and suggested a Franco-British Union but this was refused.[206] On 14 June, Paris fell.[11] Parisians who stayed in the city found that in most cases the Germans were extremely well mannered.[207]
The Luftwaffe gained air supremacy as the Armée de l'Air was brought to the verge of collapse.[208] The French had only just begun to make the majority of bomber sorties; between 5 and 9 June (during Operation Paula), over 1,815 sorties, 518 by bombers, were flown. The number of sorties declined as losses became impossible to replace. After 9 June, French aerial resistance virtually ceased; some surviving aircraft withdrew to French North Africa. The Luftwaffe exploited its dominance, concentrating on the direct and indirect support of the Wehrmacht. The Luftwaffe attacked lines of resistance, which then quickly collapsed under armoured attack.[209] The RAF attempted to divert the attention of the Luftwaffe with 660 sorties flown against targets over the Dunkirk area but suffered many losses. On 21 June, 37 Bristol Blenheims were destroyed.[citation needed]
Collapse of the Maginot line

To the east, Army Group C was to help Army Group A encircle and capture the French forces on the Maginot line. The goal of the operation was to envelop the Metz region with its fortifications, to prevent a French counter-offensive from the Alsace region against the German line on the Somme. XIX Korps (Guderian) was to advance to the French border with Switzerland and trap the French forces in the Vosges Mountains while the XVI Korps attacked the Maginot Line from the west, into its vulnerable rear, to take the cities of Verdun, Toul and Metz. The French had moved the 2nd Army Group from Alsace and Lorraine to the 'Weygand line' on the Somme, leaving only small forces guarding the Maginot line. After Army Group B had begun its offensive against Paris and into Normandy, Army Group A began its advance into the rear of the Maginot line. On 15 June, Army Group C launched Operation Tiger, a frontal assault across the Rhine and into France.[210]
German attempts to break open or into the Maginot line prior to Tiger had failed. One assault lasted for eight hours on the extreme north of the line, costing the Germans 46 dead and 251 wounded for two French killed (one at Ferme-Chappy and one at Fermont fortress). On 15 June, the last well-equipped French forces, including the Fourth Army, were preparing to leave as the Germans struck. The French force now holding the line was exiguous; the Germans greatly outnumbered the French. They could call upon the I Armeekorps of seven divisions and 1,000 artillery pieces, although most were First World War vintage and could not penetrate the thick armour of the fortresses. Only 88 mm (3.5 in) guns could do the job and 16 were allocated to the operation. To bolster this, 150 mm (5.9 in) and eight railway batteries were also employed. The Luftwaffe deployed the Fliegerkorps V.[211]
The battle was difficult and slow progress was made against strong French resistance. Each fortress was overcome one by one.[212] One fortress (Schoenenbourg) fired 15,802 75 mm (3.0 in) rounds at attacking German infantry. It was the most heavily shelled of all the French positions but its armour protected it from fatal damage. On the day that Tiger was launched, Unternehmen Kleiner Bär (Operation Little Bear) began. Five divisions of the VII Armeekorps crossed the Rhine into the Colmar area with a view to advancing to the Vosges Mountains. The force had 400 artillery pieces, reinforced by heavy artillery and mortars. The French 104th Division and 105th Division were forced back into the Vosges Mountains on 17 June. On the same day, XIX Korps reached the Swiss border the Maginot defences were cut off from the rest of France. Most units surrendered on 25 June and the Germans claimed to have taken 500,000 prisoners. Some main fortresses continued the fight, despite appeals for surrender. The last only capitulated on 10 July, after a request from Georges and only then under protest. Of the 58 main fortifications on the Maginot Line, ten were captured by the Wehrmacht.[213]
Second BEF evacuation

The evacuation of the second BEF took place during Operation Aerial between 15 and 25 June. The Luftwaffe, with air supremacy, was determined to prevent more Allied evacuations after the Dunkirk débâcle. Fliegerkorps 1 was assigned to the Normandy and Brittany sectors. On 9 and 10 June, the port of Cherbourg was subject to 15 long tons (15 t) of German bombs, while Le Havre received 10 bombing attacks that sank 2,949 GRT of Allied shipping. On 17 June, Junkers Ju 88s – mainly from Kampfgeschwader 30 – sank a "10,000 tonne ship", the 16,243 GRT liner RMS Lancastria off St Nazaire, killing about 4,000 Allied troops and civilians. This was nearly double the British killed in the Battle of France, yet the Luftwaffe failed to prevent the evacuation of 190,000–200,000 Allied personnel.[214]
Battle of the Alps
Italy declared war on France and Britain on 10 June but it was not prepared for war and made little impact during the last two weeks of fighting in the Italian invasion of France. The Italian dictator, Benito Mussolini, sought to profit from the German success.[215] Mussolini felt the conflict would soon end and he reportedly said to the army Chief-of-Staff, Marshal Pietro Badoglio, "I only need a few thousand dead so that I can sit at the peace conference as a man who has fought".[216] Opposite the Italians was the French Army of the Alps (General Rene Olry). In two weeks of fighting, the Italian 1st Army and 4th Army advanced a few kilometres intro French territory against determined French resistance but the offensive was halted on the negotiation of the Franco-Italian Armistice. Only the city of Menton and few Alpine towns had been captured by Italian forces.[citation needed]
Armistice

Discouraged by his cabinet's hostile reaction to a British proposal for a Franco-British union to avoid defeat and believing that his ministers no longer supported him, Reynaud resigned on 16 June. He was succeeded by Pétain, who delivered a radio address to the French people announcing his intention to ask for an armistice with Germany. When Hitler received word from the French government that they wished to negotiate an armistice, he selected the Forest of Compiègne as the site for the negotiations.[217] Compiègne had been the site of the 1918 Armistice, which ended the First World War with a humiliating defeat for Germany; Hitler viewed the choice of location as a supreme moment of revenge for Germany over France.[218]
On 21 June 1940, Hitler visited the site to start the negotiations, which took place in the same railway carriage in which the 1918 Armistice was signed. It had just been removed from a museum building and placed on the spot where it was located in 1918. Hitler sat in the same chair in which Marshal Ferdinand Foch had sat when he faced the defeated German representatives.[219] After listening to the reading of the preamble, Hitler left the carriage in a calculated gesture of disdain for the French delegates and negotiations were turned over to Wilhelm Keitel, the chief of staff of OKW. The armistice was signed on the next day at 18:36 (French time), by General Keitel for Germany and Huntziger for France. The armistice and cease-fire went into effect two days and six hours later, at 00:35 on 25 June, once the Franco-Italian Armistice had also been signed, at 18:35 on 24 June, near Rome.[220] On 27 June, German troops occupied the coast of the Basque Country between France and Spain.[citation needed]
Aftermath
Analysis
The title of Ernest May's book Strange Victory: Hitler's Conquest of France (2000) nods to an earlier analysis, Strange Defeat (written 1940; published 1946) by the historian Marc Bloch (1886–1944), a participant in the battle. May wrote that Hitler had better insight into the French and British governments than vice-versa and knew that they would not go to war over Austria and Czechoslovakia, because he concentrated on politics rather than the state and national interest. From 1937 to 1940, Hitler gave his views on events, their importance and his intentions, then defended them against contrary opinion from the likes of the former Chief of the General Staff Ludwig Beck and Ernst von Weizsäcker. Hitler sometimes concealed aspects of his thinking but he was unusually frank about priority and his assumptions. May referred to John Wheeler-Bennett (1964),
Except in cases where he had pledged his word, Hitler always meant what he said.[221]
May asserted that in Paris, London and other capitals, there was an inability to believe that someone might want another world war. He wrote that, given public reluctance to contemplate another war and a need to reach consensus about Germany, the rulers of France and Britain were reticent (to resist German aggression), which limited dissent at the cost of enabling assumptions that suited their convenience. In France, Édouard Daladier withheld information until the last moment and in September 1938 presented the Munich Agreement to the French cabinet as a fait accompli, thus avoiding discussions over whether Britain would follow France into war or if the military balance was really in Germany's favour or how significant it was. The decision for war in September 1939 and the plan devised in the winter of 1939–1940 by Daladier for war with the USSR followed the same pattern.[222]
Hitler had miscalculated Franco-British reactions to the invasion of Poland in September 1939, because he had not realised that a shift in public opinion had occurred in mid-1939. May wrote that the French and British could have defeated Germany in 1938 with Czechoslovakia as an ally and also in late 1939, when German forces in the West were incapable of preventing a French occupation of the Ruhr, which would have forced a capitulation or a futile German resistance in a war of attrition. France did not invade Germany in 1939 because it wanted British lives to be at risk too and because of hopes that a blockade might force a German surrender without a bloodbath. The French and British also believed that they were militarily superior, which guaranteed victory. The run of victories enjoyed by Hitler from 1938 to 1940 could only be understood in the context of defeat being inconceivable to French and British leaders.[223]
May wrote that when Hitler demanded a plan to invade France in September 1939, the German officer corps thought that it was foolhardy and discussed a coup d'état, only backing down when doubtful of the loyalty of the soldiers to them. With the deadline for the attack on France being postponed so often, OKH had time to revise Fall Gelb (Case Yellow) for an invasion over the Belgian Plain several times. In January 1940, Hitler came close to ordering the invasion but was prevented by bad weather. Until the Mechelen incident in January forced a fundamental revision of Fall Gelb, the main effort (schwerpunkt) of the German army in Belgium would have been confronted by first-rate French and British forces, equipped with more and better tanks and with a great advantage in artillery. After the Mechelen Incident, OKH devised an alternative and hugely risky plan to make the invasion of Belgium a decoy, switch the main effort to the Ardennes, cross the Meuse and reach the Channel coast. May wrote that although the alternative plan was called the Manstein plan, Guderian, Manstein, Rundstedt, Halder and Hitler had been equally important in its creation.[224]
War games held by Generalmajor (Major-General) Kurt von Tippelskirch, the chief of army intelligence and Oberst Ulrich Liss of Fremde Heere West (FHW, Foreign Armies West), tested the concept of an offensive through the Ardennes. Liss thought that swift reactions could not be expected from the "systematic French or the ponderous English" and used French and British methods, which made no provision for surprise and reacted slowly when one was sprung. The results of the war games persuaded Halder that the Ardennes scheme could work, even though he and many other commanders still expected it to fail. May wrote that without the reassurance of intelligence analysis and the results of the war games, the possibility of Germany adopting the ultimate version of Fall Gelb would have been remote. The French Dyle-Breda variant of the Allied deployment plan was based on an accurate prediction of German intentions, until the delays caused by the winter weather and shock of the Mechelen Incident, led to the radical revision of Fall Gelb. The French sought to assure the British that they would act to prevent the Luftwaffe using bases in the Netherlands and the Meuse valley and to encourage the Belgian and Dutch governments. The politico-strategic aspects of the plan ossified French thinking, the Phoney War led to demands for Allied offensives in Scandinavia or the Balkans and the plan to start a war with the USSR. French generals thought that changes to the Dyle-Breda variant might lead to forces being taken from the Western Front.[225]
French and British intelligence sources were better than the German equivalents, which suffered from too many competing agencies but Allied intelligence analysis was not as well integrated into planning or decision-making. Information was delivered to operations officers but there was no mechanism like the German system of allowing intelligence officers to comment on planning assumptions about opponents and allies. The insularity of the French and British intelligence agencies meant that had they been asked if Germany would continue with a plan to attack across the Belgian plain after the Mechelen Incident, they would not have been able to point out how risky the Dyle-Breda variant was. May wrote that the wartime performance of the Allied intelligence services was abysmal. Daily and weekly evaluations had no analysis of fanciful predictions about German intentions. A May 1940 report from Switzerland that the Germans would attack through the Ardennes was marked as a German spoof. More items were obtained about invasions of Switzerland or the Balkans, while German behaviour consistent with an Ardennes attack, such as the dumping of supplies and communications equipment on the Luxembourg border or the concentration of Luftwaffe air reconnaissance around Sedan and Charleville-Mézières, was overlooked.[226]
According to May, French and British rulers were at fault for tolerating poor performance by the intelligence agencies; that the Germans could achieve surprise in May 1940, showed that even with Hitler, the process of executive judgement in Germany had worked better than in France and Britain. May referred to Strange Defeat that the German victory was a "triumph of intellect", which depended on Hitler's "methodical opportunism". May further asserted that, despite Allied mistakes, the Germans could not have succeeded but for outrageous good luck. German commanders wrote during the campaign and after, that often only a small difference had separated success from failure. Prioux thought that a counter-offensive could still have worked up to 19 May but by then, roads were crowded with Belgian refugees when they were needed for redeployment and the French transport units, which performed well in the advance into Belgium, failed for lack of plans to move them back. Gamelin had said "It is all a question of hours." but the decision to sack Gamelin and appoint Weygand, caused a two-day delay.[227]
Occupation

France was divided into a German occupation zone in the north and west and a zone libre (free zone) in the south. Both zones were nominally under the sovereignty of the French rump state headed by Pétain that replaced the Third Republic; this rump state is often referred to as Vichy France. De Gaulle, who had been made an Undersecretary of National Defence by Reynaud in London at the time of the armistice, refused to recognise Pétain's Vichy government as legitimate. He delivered the Appeal of 18 June, the beginning of Free France.[228]
The British doubted Admiral François Darlan's promise not to allow the French fleet at Toulon to fall into German hands by the wording of the armistice conditions. They feared the Germans would seize the fleet, docked at ports in Vichy France and North Africa and use them in an invasion of Britain (Operation Sea Lion). Within a month, the Royal Navy conducted the Attack on Mers-el-Kébir against French ships at Oran.[229] The British Chiefs of Staff Committee had concluded in May 1940 that if France collapsed, "we do not think we could continue the war with any chance of success" without "full economic and financial support" from the United States. Churchill's desire for American aid led in September to the Destroyers for Bases agreement that began the Atlantic Charter, the wartime Anglo-American partnership.[230]
The occupation of the various French zones continued until November 1942, when the Allies began Operation Torch, the invasion of Western North Africa. To safeguard southern France, the Germans enacted Case Anton and occupied Vichy France.[231] In June 1944, the Western Allies launched Operation Overlord, followed by the Operation Dragoon on the French Mediterranean coast on 15 August. This threatened to cut off German troops in western and central France and most began to retire toward Germany (The fortified French Atlantic U-boat bases remained as pockets until the German capitulation.). On 24 August 1944, Paris was liberated and by September 1944 most of the country was in Allied hands.[232]
The Free French provisional government declared the re-establishment of a provisional French Republic to ensure continuity with the defunct Third Republic. It set about raising new troops to participate in the advance to the Rhine and the Western Allied invasion of Germany by using the French Forces of the Interior as military cadres and manpower pools of experienced fighters to allow a very large and rapid expansion of the French Liberation Army (Armée française de la Libération). It was well equipped and well supplied despite the economic disruption brought by the occupation thanks to Lend-Lease and grew from 500,000 men in the summer of 1944 to over 1,300,000 by V-E day, making it the fourth largest Allied army in Europe.[233]

The 2e Division Blindée (2nd Armoured Division), part of the Free French forces that had participated in the Normandy Campaign and had liberated Paris, went on to liberate Strasbourg on 23 November 1944, fulfilling the Oath of Kufra made by General Leclerc almost four years earlier. The unit under his command, barely above company size when it had captured the Italian fort, had grown into an armoured division. The I Corps was the spearhead of the Free French First Army that had landed in Provence as a part of Operation Dragoon. Its leading unit, the 1re Division Blindée, was the first Western Allied unit to reach the Rhône (25 August), the Rhine (19 November) and the Danube (21 April 1945). On 22 April, it captured the Sigmaringen enclave in Baden-Württemberg, where the last Vichy regime exiles were hosted by the Germans in one of the ancestral castles of the Hohenzollern dynasty.[citation needed]
By the end of the war, some 580,000 French citizens had died (40,000 of these were killed by the western Allied forces during the bombardments of the first 48 hours of Operation Overlord).[citation needed] Military deaths were 55,000–60,000 in 1939–40.[234] Some 58,000 were killed in action from 1940 to 1945 fighting in the Free French forces. Some 40,000 malgré-nous ("against our will", citizens of the re-annexed Alsace-Lorraine province drafted into the Wehrmacht) became casualties. Civilian casualties amounted to around 150,000 (60,000 by aerial bombing, 60,000 in the resistance and 30,000 murdered by German occupation forces). Prisoners of war and deportee totals were around 1,900,000; of these, around 240,000 died in captivity. An estimated 40,000 were prisoners of war, 100,000 racial deportees, 60,000 political prisoners and 40,000 died as slave labourers.[235]
Casualties

German casualties are hard to determine but commonly accepted figures are: 27,074 killed, 111,034 wounded and 18,384 missing.[6][7][8] German deaths may have been as high as 45,000 men, due to non-combat causes, such as death from wounds and missing who were later listed as dead.[6] The battle cost the Luftwaffe 28 per cent of its front line strength; some 1,236–1,428 aircraft were destroyed (1,129 to enemy action, 299 in accidents), 323–488 were damaged (225 to enemy action, 263 in accidents), making 36 per cent of the Luftwaffe strength lost or damaged.[6][236][24] Luftwaffe casualties amounted to 6,653 men, including 4,417 airmen; of these 1,129 were killed and 1,930 were reported missing or captured, many of whom were liberated from French prison camps upon the French capitulation.[9] Italian casualties amounted to 631 or 642 men killed, 2,631 wounded and 616 reported missing. A further 2,151 men suffered from frostbite during the campaign. The official Italian numbers were compiled for a report on 18 July 1940, when many of the fallen still lay under snow and it is probable that most of the Italian missing were dead. Units operating in more difficult terrain had higher ratios of missing to killed but probably most of the missing had died.[237]
According to the French Defence Historical Service, 85,310 French military personnel were killed (including 5,400 Maghrebis); 12,000 were reported missing, 120,000 were wounded and 1,540,000 prisoners (including 67,400 Maghrebis) were taken.[16] Some recent French research indicates that the number of killed was between 55,000 and 85,000, a statement of the French Defence Historical Service tending to the lower end.[7][k] In August 1940, 1,540,000 prisoners were taken into Germany, where roughly 940,000 remained until 1945, when they were liberated by advancing Allied forces. At least 3,000 Senegalese Tirailleurs were murdered after being taken prisoner.[239] While in captivity, 24,600 French prisoners died; 71,000 escaped; 220,000 were released by various agreements between the Vichy government and Germany; several hundred thousand were paroled because of disability and/or sickness.[240] Air losses are estimated at 1,274 aircraft destroyed during the campaign.[24] French tank losses amount to 1,749 tanks (43 per cent of tanks engaged), of which 1,669 were lost to gunfire, 45 to mines and 35 to aircraft. Tank losses are amplified by the large numbers that were abandoned or scuttled and then captured.[5]

The BEF suffered 66,426 casualties, 11,014 killed or died of wounds, 14,074 wounded and 41,338 men missing or taken prisoner.[241] About 64,000 vehicles were destroyed or abandoned and 2,472 guns were destroyed or abandoned. RAF losses from 10 May – 22 June, amounted to 931 aircraft and 1,526 casualties. The Allied naval forces also lost 243 ships to Luftwaffe bombing in Dynamo.[242] Belgian losses were 6,093 killed, 15,850 wounded and more than 500 missing.[21][20] Those captured amounted to 200,000 men, of whom 2,000 died in captivity.[21][243] The Belgians also lost 112 aircraft.[244] The Dutch Armed forces lost 2,332 killed and 7,000 wounded.[245] Polish losses were around 5,500 killed or wounded and 16,000 prisoners, nearly 13,000 troops of the 2nd Infantry Division were interned in Switzerland for the duration of the war.[246][citation needed]
Popular reaction in Germany
Hitler had expected a million Germans to die in conquering France; instead, his goal was accomplished in just six weeks with only 27,000 Germans killed, 18,400 missing and 111,000 wounded, little more than a third of the German casualties in the Battle of Verdun during World War I.[247] The unexpectedly swift victory resulted in a wave of euphoria among the German population and a strong upsurge in war-fever.[248] Hitler's popularity reached its peak with the celebration of the French capitulation on 6 July 1940.
"If an increase in feeling for Adolf Hitler was still possible, it has become reality with the day of the return to Berlin", commented one report from the provinces. "In the face of such greatness," ran another, "all pettiness and grumbling are silenced." Even opponents to the regime found it hard to resist the victory mood. Workers in the armaments factories pressed to be allowed to join the army. People thought final victory was around the corner. Only Britain stood in the way. For perhaps the only time during the Third Reich there was genuine war-fever among the population.
— Kershaw[249]
On 19 July, during the 1940 Field Marshal Ceremony at the Kroll Opera House in Berlin, Hitler promoted 12 generals to the rank of field marshal.
- Walther von Brauchitsch, Commander in Chief of the Army
- Wilhelm Keitel, Chief of the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (OKW)
- Gerd von Rundstedt, Commander in chief of Army Group A
- Fedor von Bock, Commander in chief of Army Group B
- Wilhelm von Leeb, Commander in chief of Army Group C
- Günther von Kluge, Commander of the 4th Army
- Wilhelm List, Commander of the 12th Army
- Erwin von Witzleben, Commander of the 1st Army
- Walther von Reichenau, Commander of the 6th Army
- Albert Kesselring, Commander of Luftflotte 2 (Air Fleet 2)
- Erhard Milch, Inspector General of the Luftwaffe
- Hugo Sperrle, Commander of the Luftflotte 3 (Air Fleet 3)
This number of promotions to what had previously been the highest rank in the Wehrmacht (Hermann Göring, Commander in chief of the Luftwaffe and already a Field Marshal, was elevated to the new rank of Reichsmarschall) was unprecedented. In the First World War, Kaiser Wilhelm II had promoted only five generals to Field Marshal.[250][251]
Witness accounts
- From Lemberg to Bordeaux (Von Lemberg bis Bordeaux), written by Leo Leixner, a journalist and war correspondent, is a witness account of the battles that led to the fall of Poland and France. In August 1939, Leixner joined the Wehrmacht as a war reporter, was promoted to sergeant and in 1941 published his recollections. The book was originally issued by Franz Eher Nachfolger, the central publishing house of the Nazi Party.[252]
- Tanks Break Through! (Panzerjäger Brechen Durch!), written by Alfred-Ingemar Berndt, a journalist and close associate of propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels, is a witness account of the battles that led to the fall of France. When the 1940 attack was in the offing, Berndt joined the Wehrmacht, was sergeant in an anti-tank division and afterward published his recollections.[253] The book was originally issued by Franz Eher Nachfolger, the central publishing house of the Nazi Party, in 1940.[254]
- Escape via Berlin (De Gernika a Nueva York), written by José Antonio Aguirre, president of the Basque Country, describes his passage through occupied France and Belgium on his way to exile. Aguirre supported the loyalist side during the Spanish Civil war and was forced to exile in France, where the German invasion took him by surprise. He joined the wave of refugees trying to flee France and finally managed to escape to the United States through a long journey involving disguise.
- Berlin Diary, published in 1941 by William L. Shirer, a foreign correspondent for CBS World News Roundup in the prewar period, gives a day-by-day account of his reporting before, during, and after the Battle of France, including conversations with military and political leaders – as well as ordinary soldiers and civilians – on both the Allied and Axis sides. Unable to continue reporting the war honestly from Berlin due to increasing German censorship, Shirer returned to the United States in December 1940.
See also
- British Expeditionary Force order of battle (1940)
- Polish Army in France (1939–40)
- Historiography of the Battle of France
- Military history of France during World War II
- List of French World War II military equipment
- List of British military equipment of World War II
- List of Belgian military equipment of World War II
- List of Dutch military equipment of World War II
- List of German military equipment of World War II
- Timeline of the Battle of France
- Western Front (World War II)
Notes
- ^ a b Until 17 May
- ^ From 17 May
- ^ Hooton uses the Bundesarchiv, Militärarchiv in Freiburg. Luftwaffe strength included gliders and transports used in the assaults on the Netherlands and Belgium.[3]
- ^ Hooton used the National Archives in London for RAF records, including "Air 24/679 Operational Record Book: The RAF in France 1939–1940", "Air 22/32 Air Ministry Daily Strength Returns", "Air 24/21 Advanced Air Striking Force Operations Record" and "Air 24/507 Fighter Command Operations Record". For the Armée de l'Air Hooton used "Service Historique de Armée de l'Air (SHAA), Vincennes".[3]
- ^ Steven Zaloga wrote, "Of the 2,439 panzers originally committed 822, or about 34 per cent, were total losses after five weeks of fighting.... Detailed figures for the number of mechanical breakdowns are not available and are not relevant as in the French case, since, as the victors, the Wehrmacht could recover damaged or broken-down tanks and put them back into service".[12]
- ^ Official Italian report on 18 July 1940: Italian casualties amounted to 631 or 642 men killed, 2,631 wounded and 616 reported missing. A further 2,151 men suffered from frostbite during the campaign.[13][14][15]
- ^ French:
≈60,000 killed
200,000 wounded
12,000 missing[16][17]
British:
3,500–5,000 dead
16,815 wounded
47,959 missing or captured[6][18][19]
Belgian:
6,093 killed
15,850 wounded
500 missing[20][21]
Dutch:
2,332 killed
7,000 wounded
Polish:
5,500 killed or wounded[22]
Luxembourg:
7 wounded[23] - ^ Steven Zaloga notes that "According to a postwar French Army study, French tank losses in 1940 amounted to 1,749 tanks lost out of 4,071 engaged, of which 1,669 were lost to gunfire, 45 to mines and 35 to aircraft. This amounts to about 43 per cent. French losses were substantially amplified by the large numbers of tanks that were abandoned or scuttled by their crews".[5]
- ^ Jonathan Fennell notes "Losses 'included 180,000 rifles, 10,700 Bren guns, 509 two-pounder anti-tank guns, 509 cruiser tanks and 180 infantry tanks'."[25]
- ^ On 26 February 1945, Hitler claimed he had let the BEF escape as a "sporting" gesture, in the hope Churchill would come to terms. Few historians accept Hitler's word in light of Directive No. 13, which called for "the annihilation of French, British and Belgian forces in the Dunkirk pocket".[190]
- ^ "Combat losses amounted in reality to 58,829 deaths, excluding marine however, whose deaths were registered under different procedures."[238]
Footnotes
- ^ a b c d e f Scheck 2010, p. 426.
- ^ a b c Umbreit 2015, p. 279.
- ^ a b c d Hooton 2007, pp. 47–48.
- ^ Publishing, D. K. (1 October 2009). War: The Definitive Visual History. Penguin. p. 467. ISBN 978-0-7566-6817-4. Retrieved 14 June 2024.
- ^ a b c Zaloga 2011, p. 73.
- ^ a b c d e f Frieser 1995, p. 400.
- ^ a b c L'Histoire, No. 352, April 2010 France 1940: Autopsie d'une défaite, p. 59.
- ^ a b Sheppard 1990, p. 88.
- ^ a b Hooton 2010, p. 73.
- ^ Murray 1983, p. 40.
- ^ a b c Healy 2007, p. 85.
- ^ Zaloga 2011, p. 76.
- ^ Sica 2012, p. 374.
- ^ Porch 2004, p. 43.
- ^ Rochat 2008, para. 19.
- ^ a b Gorce 1988, p. 496.
- ^ Quellien 2010, pp. 262–263.
- ^ French 2001, p. 156.
- ^ Archives, The National. "The National Archives | World War II | Western Europe 1939–1945: Invasion | How worried was Britain about invasion 1940–41?". archive.wikiwix.com. Archived from the original on 6 March 2023. Retrieved 14 January 2023.
- ^ a b Dear & Foot 2005, p. 96.
- ^ a b c Ellis 1993, p. 255.
- ^ Jacobson, 2015, nopp
- ^ "Inauguration du Monument érigé à la Mémoire des Morts de la Force Armée de la guerre de 1940–1945" (PDF). Grand Duché de Luxembourg Ministére D'État Bulletin D'Information (in French). Vol. 4, no. 10. Luxembourg: Service information et presse. 31 October 1948. p. 147. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 January 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- ^ a b c Hooton 2007, p. 90.
- ^ Fennell 2019, p. 115.
- ^ Donnell 2017.
- ^ a b Jackson 2003, p. 33.
- ^ Roth 2010, p. 6.
- ^ Kaufmann & Kaufmann 2007, p. 23.
- ^ Jackson 2003, pp. 32–33.
- ^ Baliszewski 2004.
- ^ Viscount Halifax to Sir N. Henderson (Berlin) Archived 2 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine Cited in the British Blue book
- ^ "Chronology 1939". indiana.edu. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ^ a b Shirer 1990, p. 715.
- ^ Full text of the speech Archived 26 September 2022 at the Wayback Machine (in German, pdf)
- ^ archive.org: Video of his speech (77 min)
- ^ a b Frieser 2005, p. 61.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 32.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 74.
- ^ "Directive No. 6 Full Text". Archived from the original on 29 July 2016. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- ^ Shirer 1990, p. 717.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 67.
- ^ Megargee 2000, p. 76.
- ^ a b Shirer 1990, p. 718.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 25.
- ^ Atkin 1990, pp. 42–43.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 62.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 63.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 79.
- ^ a b Frieser 2005, p. 60.
- ^ a b Frieser 2005, p. 65.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 87.
- ^ Frieser 1995, p. 76.
- ^ Hinsley et al. 1979, pp. 114, 128, 130.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 65–67.
- ^ Bond 1990, pp. 43–44.
- ^ Melvin 2010, pp. 148, 154–155.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 88, 94–95, 113, 116.
- ^ a b Beevor 2013, p. 97.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, p. 7.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, pp. 6–7.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, pp. 7–8.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, p. 11.
- ^ Doughty 2014a, p. 12.
- ^ a b Doughty 2014a, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Bond 1990, pp. 36, 46.
- ^ Atkin 1990, p. 53.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 35–37.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 29.
- ^ DiNardo & Bay 1988, pp. 131–132.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 29–30.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 71, 101.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 323.
- ^ a b Healy 2007, p. 23.
- ^ Corum 1995, p. 70.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 37–42.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 861.
- ^ Citino 1999, p. 249.
- ^ Corum 1992, p. 203.
- ^ French 2001, pp. 16–24.
- ^ a b Hooton 2007, p. 47.
- ^ Buckley 1998, pp. 126–127.
- ^ Corum 1995, p. 54.
- ^ For details see de:8,8-cm-Flak 18/36/37#Die 8,8 als Panzerabwehrkanone.
- ^ a b Harvey 1990, p. 449.
- ^ a b c d Dear & Foot 2005, p. 316.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 35.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 36–37.
- ^ Christofferson & Christofferson 2006, pp. 18–19.
- ^ Porch 2022, pp. 72–76.
- ^ Blatt 1997, p. 23.
- ^ a b Christofferson & Christofferson 2006, p. 18.
- ^ Tooze 2006, p. 372.
- ^ Corum 1992, pp. 204–205.
- ^ Atkin 1990, p. 58.
- ^ Citino 2005, p. 284.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 90, 153.
- ^ Schuker 2014, pp. 111–112.
- ^ Stout 2010, p. 19.
- ^ Taylor & Mayer 1974, p. 72.
- ^ a b Harvey 1990, p. 448.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 81.
- ^ Facon 1996, pp. 54–62.
- ^ Belgium 1941, p. 32.
- ^ Ellis 2004, pp. 359–371.
- ^ Weinberg 1994, p. 122.
- ^ Hooton 2007, pp. 49–54.
- ^ Evans 2000, pp. 33–38.
- ^ Hooton 2007, pp. 48–49.
- ^ a b Hooton 1994, p. 244.
- ^ de Jong 1970.
- ^ Hooton 2007, pp. 244, 50, 52.
- ^ Shirer 1990, p. 723.
- ^ Evans 2000, p. 38.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 48.
- ^ Dunstan 2005, pp. 31–32.
- ^ Dunstan 2005, pp. 45–54.
- ^ Gunsburg 1992, p. 215.
- ^ Gunsburg 1992, pp. 209–210, 218.
- ^ a b Healy 2007, p. 38.
- ^ Gunsburg 1992, pp. 207–244 [236–237, 241].
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 246–248.
- ^ Gunsburg 2000, pp. 97–140, 242, 249.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 137.
- ^ a b Frieser 2005, pp. 137–142.
- ^ Jackson 1974, p. 56.
- ^ Mansoor 1988, p. 68.
- ^ Citino 1999, p. 250.
- ^ a b Frieser 2005, p. 192.
- ^ Mansoor 1988, p. 69.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 64.
- ^ Frieser 1995, p. 193.
- ^ Weal 1997, p. 46.
- ^ a b Hooton 2007, p. 65.
- ^ Frieser 1995, pp. 216, 244.
- ^ Krause & Phillips 2006, p. 172.
- ^ Weal 1997, p. 22.
- ^ Frieser 1995, p. 258.
- ^ a b Strawson 2003, p. 108.
- ^ Frieser 1995, p. 259.
- ^ Healy 2007, p. 67.
- ^ Taylor & Mayer 1974, p. 55.
- ^ Evans 2000, p. 70.
- ^ Citino 2002, p. 270.
- ^ Evans 2000, pp. 70, 72.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 271.
- ^ a b Krause & Phillips 2006, p. 176.
- ^ Healy 2007, p. 75.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 269, 273.
- ^ Evans 2000, pp. 66–67, 69, 72.
- ^ Evans 2000, p. 73.
- ^ Shirer 1990, p. 720.
- ^ L'Aurore 1949.
- ^ Churchill 1949, pp. 42–49.
- ^ Blatt 1997, p. 326.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 262–263.
- ^ Evans 2000, pp. 75–76.
- ^ Corum 1997, p. 278.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 265.
- ^ Neave 2003, pp. 31–32.
- ^ Bond 1990, p. 69.
- ^ Sheppard 1990, p. 81.
- ^ Weal 1997, p. 47.
- ^ Corum 1997, pp. 73, 277–280.
- ^ Hooton 2007, pp. 67, 70.
- ^ a b Gardner 2000, p. 10.
- ^ Bond 1990, pp. 66, 69.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 278–280.
- ^ Ellis 2004, p. 105.
- ^ Bond 1990, p. 70.
- ^ Ellis 2004, p. 89.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 283–286.
- ^ Bond 1990, p. 71.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 286–287, 36.
- ^ Healy 2007, p. 81.
- ^ Gardner 2000, pp. 9–10.
- ^ Sebag-Montefiore 2006, pp. 234, 236–237.
- ^ Longden 2008, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Sebag-Montefiore 2006, pp. 238–239.
- ^ Longden 2008, p. 89.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 287.
- ^ Frieser 2005, pp. 287–288.
- ^ Bond 1990, pp. 89–98, 106–107, 115.
- ^ Umbreit 2015, p. 293.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 74.
- ^ Murray 1983, p. 39.
- ^ Chappel 1985, p. 21.
- ^ Harman 1980, p. 82.
- ^ Bond 1990, p. 105.
- ^ a b Healy 2007, p. 84.
- ^ Jackson 2001, pp. 119–120.
- ^ Alexander 2007, p. 219.
- ^ Alexander 2007, pp. 225–226.
- ^ Alexander 2007, pp. 227, 231, 238.
- ^ Alexander 2007, p. 248.
- ^ Alexander 2007, p. 245.
- ^ Umbreit 2015, p. 297.
- ^ a b Alexander 2007, p. 249.
- ^ Alexander 2007, p. 250.
- ^ Alexander 2007.
- ^ David 2018, chpt. 13.
- ^ Alexander 2007, p. 240.
- ^ Shirer 1990, p. 738.
- ^ Umbreit 2015, p. 300.
- ^ Umbreit 2015, p. 301.
- ^ Shirer, William (1941). Berlin Diary. Alfred A. Knopf.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 86.
- ^ Hooton 2007, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Romanych & Rupp 2010, p. 52.
- ^ Romanych & Rupp 2010, p. 56.
- ^ Romanych & Rupp 2010, pp. 56–80.
- ^ Romanych & Rupp 2010, pp. 90–91.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 88.
- ^ Taylor & Mayer 1974, p. 63.
- ^ De Waal 1990, p. 244.
- ^ Evans 2000, p. 156.
- ^ Taylor & Mayer 1974, p. 57.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 326.
- ^ Frieser 2005, p. 317.
- ^ May 2000, p. 453.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 453–454.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 454–455.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 455–456.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 456–457.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 457–458.
- ^ May 2000, pp. 458–460.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, pp. 336–339.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 317.
- ^ Reynolds 1993, pp. 248, 250–251.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 635.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 634.
- ^ Imlay & Toft 2007, p. 227.
- ^ Carswell 2019, p. 92.
- ^ Dear & Foot 2005, p. 321.
- ^ Murray 1983.
- ^ Sica 2012, p. 374; Porch 2004; Rochat 2008, p. 43, para. 19.
- ^ servicehistorique (20 November 2017)
- ^ Scheck 2010, p. 58.
- ^ Durand 1981, p. 21.
- ^ Sebag-Montefiore 2006, p. 506.
- ^ Churchill 1949, p. 102.
- ^ Keegan 2005, p. 96.
- ^ Hooton 2007, p. 52.
- ^ Goossens, Balance Sheet, waroverholland.nl Archived 17 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jacobson.
- ^ Atkin 1990, pp. 233–234.
- ^ Neitzel & Welzer 2012, pp. 193, 216.
- ^ Kershaw 2002, p. 407.
- ^ Deighton 2008, pp. 7–9.
- ^ Ellis 1993, p. 94.
- ^ Leixner, Leo; Lehrer, Steven (2 March 2017). "From Lemberg to Bordeaux: a German war correspondent's account of battle in Poland, the low countries and France, 1939–40". SF Tafel Publishers. Archived from the original on 20 August 2017. Retrieved 2 June 2017 – via catalog.loc.gov Library Catalog.
- ^ Berndt, Alfred-Ingemar (2016). Tanks Break Through!: A German Soldier's Account of War in the Low Countries and France, 1940. SF Tafel. ISBN 9781539810971. Archived from the original on 10 May 2024. Retrieved 18 November 2018 – via Google Books.
- ^ Berndt, Alfred-Ingemar (2 March 2016). "Tanks break through! a German soldier's account of war in the Low Countries and France, 1940". SF Tafel. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 2 June 2017 – via catalog.loc.gov Library Catalog.
References
Books
- Atkin, Ronald (1990). Pillar of Fire: Dunkirk 1940. Edinburgh: Birlinn. ISBN 1-84158-078-3.
- Beevor, Antony (2013). The Second World War. London: Phoenix (Orion Books). ISBN 978-0-7538-2824-3.
- Belgium: The Official Account of What Happened 1939–1940 [Belgian Ministry of Foreign Affairs] (in French). London: Ministère des Affaires Étrangères de la Belge. 1941. OCLC 4025429. LCOC 42016037. Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- Blatt, Joel, ed. (1997). The French Defeat of 1940: Reassessments. Providence, RI: Berghahn. ISBN 1-57181-109-5.
- Bond, Brian (1990). Britain, France and Belgium, 1939–1940. London: Brassey's. ISBN 0-08-037700-9.
- Buckley, John (1998). Air Power in the Age of Total War. London: UCL Press. ISBN 1-85728-589-1.
- Carswell, Richard (2019). The Fall of France in the Second World War: History and Memory. London: Palgrave MacMillan. ISBN 978-3-030-03954-7.
- Chappel, Michael "Mike" (1985). The Canadian Army at War. Men at Arms. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-0-85045-600-4.
- Christofferson, Thomas R.; Christofferson, Michael S. (2006). France during World War II: From Defeat to Liberation. Fordham University Press. ISBN 0-8232-2562-3.
- Churchill, Winston S. (1949). Their Finest Hour. The Second World War. Vol. II. Cambridge: Houghton Mifflin. OCLC 396145.
- Citino, Robert Michael (1999). The Path to Blitzkrieg: Doctrine and Training in the German Army, 1920–1939. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. ISBN 1-55587-714-1.
- Citino, Robert M. (2002). Quest for Decisive Victory: From Stalemate to Blitzkrieg in Europe, 1899–1940. Modern War Studies. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-1176-2.
- Citino, Robert M. (2005). The German Way of War: From the Thirty Years' War to the Third Reich. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-1624-4.
- Corum, James (1992). The Roots of Blitzkrieg: Hans von Seeckt and German Military Reform. Modern War Studies. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 0-7006-0541-X.
- Corum, James (1997). The Luftwaffe: Creating the Operational Air War, 1918–1940. Lawrence: University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-0836-2.
- David, Saul (2018) [1994]. After Dunkirk: Churchill's Sacrifice of the Highland Division (Kindle ed.). Sharpe Book. ISBN 978-1-911445-44-9.
- de Jong, Loe (1970). Het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden in de Tweede Wereldoorlog 1939–1945 Deel 3 Mei '40 [The Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Second World War 1939–1945 Part 3 May '40] (PDF) (in Dutch). Amsterdam: Rijksinstituut Voor Oorlogsdocumentatie. OCLC 926786827. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 April 2022. Retrieved 27 May 2022.
- Donnell, Clayton (2017). The Battle for the Maginot Line, 1940. Barnsley: Pen and Sword. ISBN 978-1-4738-7728-3.
- Gorce, Paul-Marie de la (1988). L'aventure coloniale de la France – L'Empire écartelé, 1936–1946 [The French Colonial Adventure] (in French). Paris: Denoël. ISBN 978-2-207-23520-1.
- De Waal, Frans (1990). Peacemaking Among Primates. New York: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-65921-X.
- Dear, Ian; Foot, M. (2005). The Oxford Companion to World War II. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280666-6.
- Deighton, Len (2008). Fighter: The True Story of the Battle of Britain (illus. ed.). Random House. ISBN 978-1-84595-106-1.
- Doughty, R. A. (2014a) [1985]. The Seeds of Disaster: The Development of French Army Doctrine, 1919–1939 (Stackpole, Mechanicsburg, PA ed.). Hamden, CT: Archon Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-1460-0.
- Dunstan, Simon (2005). Fort Eben Emael: The Key to Hitler's Victory in the West. Bloomsbury USA. ISBN 1-84176-821-9.
- Durand, Yves (1981). La Captivité, Histoire des prisonniers de guerre francais 1939–1945 [The Captivity: History of the French War Prisoners] (in French) (2nd revue et corrigée ed.). Paris: F.N.C.P.G.-C.A.T.M. OCLC 417568776.
- Ellis, John (1993). The World War II Data Book. Aurum Press. ISBN 978-1-85410-254-6.
- Ellis, Major L. F. (2004) [1st. pub. HMSO 1954]. Butler, J. R. M. (ed.). The War in France and Flanders 1939–1940. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series. Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-056-6. Archived from the original on 17 December 2020. Retrieved 11 September 2016.
- Evans, Martin Marix (2000). The Fall of France: Act of Daring. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 1-85532-969-7.
- Fennell, Jonathan (2019). Fighting the People's War. The British and Commonwealth Armies and the Second World War. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-03095-4.
- French, David (2001). Raising Churchill's Army: The British Army and the War against Germany, 1919–1945. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-924630-4.
- Frieser, Karl-Heinz (1995). Blitzkrieg-Legende: Der Westfeldzug 1940, Operationen des Zweiten Weltkrieges [The Blitzkrieg Myth: The Western Campaign in 1940, Operations of the Second World War] (in German). München: R. Oldenbourg. ISBN 3-486-56124-3.
- Frieser, Karl-Heinz (2005). The Blitzkrieg Legend: The 1940 Campaign in the West. Translated by Greenwood, J. T. (eng. trans. ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-294-2.
- Gardner, W. J. R. (2000). The evacuation from Dunkirk: Operation Dynamo, 26 May – 4 June 1940. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-7146-8150-4.
- Harman, Nicholas (1980). Dunkirk: The Necessary Myth. London: Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 0-340-24299-X.
- Haslam, J.; Urbach, K., eds. (2014). Secret Intelligence in the European States System, 1918–1989. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-8891-5.
- Schuker, S. A. "Seeking a Scapegoat: Intelligence and Grand Strategy in France". In Haslam & Urbach (2014).
- Healy, Mark (2007). Prigent, John (ed.). Panzerwaffe: The Campaigns in the West 1940. Vol. I. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 978-0-7110-3239-2.
- Hinsley, F. H.; et al. (1979). British Intelligence in the Second World War: Its Influence on Strategy and Operations. Vol. I. London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-630933-4.
- Hooton, E. R. (1994). Phoenix Triumphant: The Rise and Rise of the Luftwaffe. London: Brockhampton Press. ISBN 1-86019-964-X.
- Hooton, E. R. (2007). Luftwaffe at War; Blitzkrieg in the West. London: Chevron/Ian Allan. ISBN 978-1-85780-272-6.
- Hooton, E. R. (2010). The Luftwaffe: A Study in Air Power 1933–1945. Classic. ISBN 978-1-906537-18-0.
- Imlay, Talbot C.; Toft, Monica Duffy (2007). The Fog of Peace and War Planning: Military and Strategic Planning Under Uncertainty. Cass: Strategy and History. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-21088-6.
- Jackson, Robert (1974). Air War Over France, 1939–1940. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 978-0-7110-0510-5.
- Jackson, Julian (2003). The Fall of France: The Nazi Invasion of 1940. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-192-80550-8.
- Jackson, Julian (2001). France: The Dark Years, 1940–1944. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-820706-9.
- Kaufmann, J. E.; Kaufmann, H. W. (2007). Fortress France: The Maginot Line and French Defenses in World War II. Stackpole Military History. Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-811-73395-3.
- Keegan, John (2005). The Second World War. New York: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-303573-2.
- Kershaw, Ian (2002). Hitler, 1936–1945. Munich: Pantheon.
- Krause, M.; Phillips, C. (2006). Historical Perspectives of Operational Art. Fort McNair, Washington DC: Center of Military History. ISBN 978-0-16-072564-7.
- Longden, Sean (2008). Dunkirk: The Men They Left Behind. London: Constable. ISBN 978-1-84529-520-2.
- Maier, Klaus A.; Rohde, Horst; Stegemann, Bernd; Umbreit, Hans (2015) [1991]. Falla, P. S. (ed.). Germany and the Second World War: Germany's Initial Conquests in Europe. Vol. II. Translated by McMurry, Dean S.; Osers, Ewald (trans. pbk. Clarendon Press, Oxford ed.). Freiburg im Breisgau: Militärgeschichtliches Forschungsamt [Research Institute for Military History]. ISBN 978-0-19-873834-3.
- Umbreit, B. "German Victory in Western Europe". In Maier et al. (2015).
- Maier, K. "Die Errichtung der Hegemonie auf dem europäischen Kontinent (The establishment of hegemony on the European continent)". In Maier et al. (2015).
- May, Ernest R. (2000). Strange Victory: Hitler's Conquest of France. London: I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-85043-329-3. online
- Megargee, Geoffrey P. (2000). Inside Hitler's High Command. Lawrence: Kansas University Press. ISBN 0-7006-1015-4.
- Melvin, Mungo (2010). Manstein: Hitler's Most Controversial General. W&N. ISBN 978-0-297-84561-4.
- Murray, Williamson (1983). Strategy for Defeat: The Luftwaffe 1933–1945 (online ed.). Maxwell Air Force Base, AL: Air University Press (US National Government Publication). ISBN 978-1-4294-9235-5.
- Neave, Airey (2003) [1972]. The Flames of Calais: A Soldiers Battle 1940 (Pen & Sword, Barnsley ed.). London: Hodder & Stoughton. ISBN 978-0-85052-997-5.
- Neitzel, Sönke; Welzer, Harald (2012). Soldaten: On Fighting, Killing and Dying: The Secret World War II Tapes of German POWs. London: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1-84983-948-8.
- Porch, Douglas (2004). The Path to Victory: The Mediterranean Theater in World War II (1st ed.). New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 978-0-374-20518-8.
- Porch, Douglas (2022). Defeat and Division: France at War, 1939–1942. Armies of the Second World War. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-04746-4.
- Quellien, Jean (2010). "Les pertes humaines". La France pendant la Seconde Guerre mondiale – Atlas historique (in French) (online scan ed.). éd. Fayard, ministère de la Défense. OCLC 812049413.
- Reynolds, David (1993). "Churchill in 1940: The Worst and Finest Hour". In Blake, Robert B.; Louis, William Roger (eds.). Churchill. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-820626-7.
- Roth, Ariel Ilan (2010). Leadership in International Relations: The Balance of Power and the Origins of World War II. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-10690-1.
- Romanych, M.; Rupp, M. (2010). Maginot Line 1940: Battles on the French Frontier. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84603-499-2.
- Sebag-Montefiore, Hugh (2006). Dunkirk: Fight to the Last Man. New York: Viking. ISBN 978-0-670-91082-3.
- Sheppard, Alan (1990). France, 1940: Blitzkrieg in the West. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-0-85045-958-6.
- Shirer, William L. (1990). The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich: A History of Nazi Germany. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-72868-7.
- Strawson, John (2003). Hitler as Military Commander. Military Classics. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-0-85052-956-2.
- Stout, Jay. A (2010). The Men Who Killed the Luftwaffe: The U.S Army Air Forces against Germany (1st ed.). Mechanicsburg PA: Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-0659-9.
- Taylor, A. J. P.; Mayer, S. L., eds. (1974). A History of World War Two. London: Octopus Books. ISBN 0-7064-0399-1.
- Tooze, Adam (2006). The Wages of Destruction: The Making and Breaking of the Nazi Economy. Allen Lane. ISBN 0-7139-9566-1.
- Weal, John (1997). Junkers Ju 87 Stukageschwader 1937–41. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 1-85532-636-1.
- Weinberg, Gerhard (1994). A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-44317-3.
- Zaloga, Steven J. (2011). Panzer IV vs Char B1 bis: France 1940. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84908-378-2.
Journals
- Alexander, Martin (2007). "After Dunkirk: The French Army's Performance Against 'Case Red', 25 May to 25 June 1940". War in History. 14 (2): 219–264. doi:10.1177/0968344507075873. ISSN 1477-0385. S2CID 153751513.
- Baliszewski, Dariusz (19 September 2004). "Most honoru". Wprost (in Polish) (1138). ISSN 0209-1747. Archived from the original on 14 May 2007. Retrieved 24 March 2005.
- Corum, James (January 1995). "The Luftwaffe's Army Support Doctrine, 1918–1941". The Journal of Military History. 59 (1): 53–76. doi:10.2307/2944364. ISSN 1543-7795. JSTOR 2944364.
- DiNardo, R. L.; Bay, Austin (January 1988). "Horse-Drawn Transport in the German Army". Journal of Contemporary History. 23 (1): 129–142. doi:10.1177/002200948802300108. ISSN 0022-0094. S2CID 159871841.
- Facon, Patrick (March 1996). "Slowing Down Blitzkrieg: A Curtiss Fighter Ace in the Battle of France". Air Fan International. Publitek. ISSN 1083-2548.
- Gunsburg, Jeffery A. (April 1992). "The Battle of the Belgian Plain, 12–14 May 1940: The First Great Tank Battle". The Journal of Military History. 56 (2): 207–244. doi:10.2307/1985797. ISSN 0899-3718. JSTOR 1985797.
- ——— (January 2000). "The Battle of Gembloux, 14–15 May 1940: The 'Blitzkrieg' Checked". The Journal of Military History. 64 (1): 97–140. doi:10.2307/120789. JSTOR 120789.
- Harvey, D. (October 1990). "The French Armée de l'Air in May–June 1940: A Failure of Conception". Journal of Contemporary History. 25 (4): 447–465. doi:10.1177/002200949002500404. ISSN 0022-0094. S2CID 159795712.
- Mansoor, Peter R. (June 1988). Childress, P. W. (ed.). "The Second Battle of Sedan, May 1940". Military Review. LXVIII (6). Fort Leavenworth, KS: United States Army Combined Arms Center: 64–75. ISSN 0026-4148. PB-100-88-6. Archived from the original on 25 August 2020. Retrieved 6 October 2016.
- Rochat, Giorgio (1 January 2008). "La campagne italienne de juin 1940 dans les Alpes occidentales". Revue historique des armées. 250. Translator: Anne Pilloud. Vincennes: Service historique de la défense: 77–84. doi:10.3917/rha.250.0077. ISSN 0035-3299. S2CID 161280892. Archived from the original on 1 September 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- Sica, Emanuele (2012). "June 1940: The Italian Army and the Battle of the Alps". Canadian Journal of History. 47 (2). Saskatoon, SK: University of Toronto Press: 355–378. doi:10.3138/cjh.47.2.355. ISSN 0008-4107.
- Scheck, Raffael (2010). "French Colonial Soldiers in German Prisoner-of-War Camps (1940–1945)". French History. XXIV (3): 426. doi:10.1093/fh/crq035.
Websites
- Jacobson, Douglas. "Article 9: Polish Army in France". Douglas W. Jacobson. Archived from the original on 11 December 2015. Retrieved 9 December 2015.
Newspapers
- "Communications Secretes du G.Q.G." [Secret Communications from G.Q.G.]. L'Aurore (in French). Paris. 21 November 1949. p. 4. Retrieved 27 May 2022.
Further reading
Books
- d'Avout, Aurélien (2023). La France en éclats. Écrire la débâcle de 1940, d'Aragon à Claude Simon. Bruxelles: Les Impressions Nouvelles. ISBN 978-2-39070-025-8.
- Bloch, Marc (1968) [1946]. Strange Defeat: A Statement of Evidence Written in 1940. New York, NY: Norton. ISBN 0-393-31911-3.
- Cooper, M. (1978). The German Army 1933–1945, Its Political and Military Failure. Briarcliff Manor, NY: Stein and Day. ISBN 0-8128-2468-7.
- Doughty, R. A. (2014) [1990]. The Breaking Point: Sedan and the Fall of France, 1940. Stackpole Military History (pbk. repr. Stackpole, Mechanicsburg, PA ed.). Hamden, CN: Archon Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-1459-4.
- Fantom, Paul (2021). A Forgotten Campaign: The British Armed Forces in France, 1940 – From Dunkirk to the Armistice. Warwick: Helion. ISBN 978-1-914059-01-8.
- Martin, J.; Martin, P. (2001). Ils étaient là: l'armée de l'Air septembre 39 – juin 40 [They Were There: The Air Force September 39 – June 40] (in French). Aero-Editions. ISBN 2-9514567-2-7.
- Jowett, Philip S. (2000). The Italian Army 1940–45: Europe 1940–1943. Vol. I. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-85532-864-8.
- Kershaw, Ian (2008). Fateful Choices: Ten Decisions That Changed the World, 1940–1941. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-101418-0.
- Nord, Philip (2015). France 1940: Defending the Republic. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-19068-7.
- Raffael, Scheck (2005). Hitler's African Victims: The German Army Massacres of Black French Soldiers in 1940. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-85799-6.
- Winchester, Charles (1998). Ostfront: Hitler's War on Russia 1941–45. Oxford: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84176-066-7.
Theses
- Connors, Joseph David (1977). "Bibliography". Paul Reynaud and French National Defense, 1933–1939 (PhD thesis) (online scan ed.). Loyola University of Chicago. pp. 265–283. OCLC 10499727.
- de Konkoly Thege, Michel (2015). "Bibliography". Paul Reynaud and the Reform of France's Economic, Military and Diplomatic Policies of the 1930s (MALS/MPhil thesis) (online scan ed.). Graduate Liberal Studies Works. pp. 171–176. doi:10.14418/wes01.4.6. Docket Paper 6.
External links
- Brooke, Alan (1946). Despatch on Operations of the British Expeditionary Force in From 12th June, 1940 to 19th June, 1940. London: War Office. In "No. 37573". The London Gazette (Supplement). 22 May 1946. pp. 2433–2439.
- The Battle of France 1940 (Official Nazi propaganda account of the Battle of France)
- The invasion of Holland in May 1940
- Gort, John (10 October 1941). "Viscount Gort's Despatch on Operations of the British Expeditionary Force in France and Belgium, 1939–1940". Supplement to the London Gazette, Number 35305. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
