States of Nigeria
| States of Nigeria | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Federated states |
| Location | Federal Republic of Nigeria |
| Number | 36 |
| Populations | 1,704,358 (Bayelsa State) – 9,401,288 (Lagos State) Mean: 5,300,000 |
| Areas | 3,580 km2 (1,381 sq mi) (Lagos State) – 76,360 km2 (29,484 sq mi) (Niger State) Mean: 25,660 km2 (9,907 sq mi) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions |
|
 |
|---|
|
|
Nigeria is a federation of 36 states, each of which is a semi-autonomous political unit that shares power with the federal government as enumerated under the Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. In addition to the states, there is the Federal Capital Territory (FCT), in which the capital city of Abuja is located.[1] The FCT is not a state, but a territory of the federal government, governed by an administration headed by a minister. Each state is subdivided into local government areas (LGAs). There are 774 local governments in Nigeria.[2] Under the Nigerian Constitution, the 36 states enjoy substantial autonomy but are not sovereign entities, as ultimate authority lies with the federal government. Amendments to the constitution can be proposed by the National Assembly, but for an amendment to be valid, it must be approved by a two-third majority of the 36 state legislatures, as required under Section 9 of the 1999 Constitution of Nigeria.[3]
Current states and the Federal Capital Territory
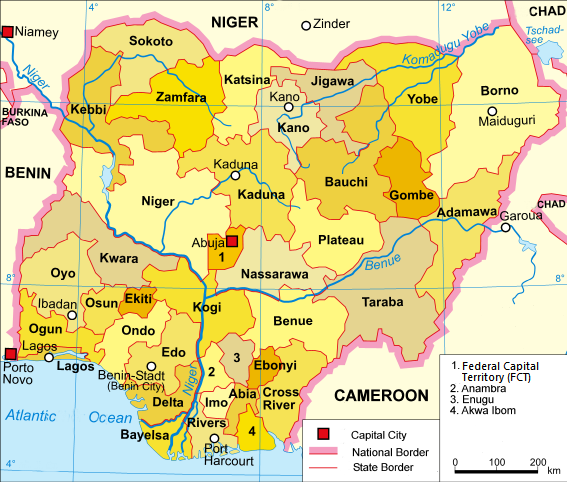
| ||||||||||||
| Name | ISO 3166-2 code |
Seal | Location | City | Geopolitical zone |
Area | Population (2019 estimate)[4] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital | Largest | |||||||
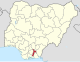
| Abia | AB | 
|
|
Umuahia | Aba | South East | 6,320 km2 (2,440 sq mi) | 3,841,943 |
| Adamawa | AD | 
|

|
Yola | North East | 36,917 km2 (14,254 sq mi) | 4,536,948 | |
| Akwa Ibom | AK | 
|

|
Uyo | South South | 7,081 km2 (2,734 sq mi) | 4,780,581 | |
| Anambra | AN | 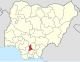
|
Awka | Onitsha | South East | 4,844 km2 (1,870 sq mi) | 5,599,910 | |
| Bauchi | BA | 
|

|
Bauchi | North East | 45,893 km2 (17,719 sq mi) | 7,540,663 | |
| Bayelsa | BY | 
|
Yenagoa | South South | 10,773 km2 (4,159 sq mi) | 2,394,725 | ||
| Benue | BE | 
|

|
Makurdi | North Central | 34,059 km2 (13,150 sq mi) | 5,787,706 | |
| Borno | BO | 
|

|
Maiduguri | North East | 70,898 km2 (27,374 sq mi) | 5,751,590 | |
| Cross River | CR | 
|
Calabar | South South | 20,156 km2 (7,782 sq mi) | 4,175,020 | ||
| Delta | DE | 
|
Asaba | South South | 17,698 km2 (6,833 sq mi) | 5,307,543 | ||
| Ebonyi | EB | 
|
Abakaliki | South East | 6,400 km2 (2,500 sq mi) | 3,007,155 | ||
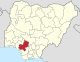
| Edo | ED | 
|
|
Benin City | South South | 19,559 km2 (7,552 sq mi) | 4,461,137 | |
| Ekiti | EK | 
|
Ado Ekiti | South West | 6,353 km2 (2,453 sq mi) | 3,350,401 | ||
| Enugu | EN | 
|

|
Enugu | South East | 13,161 km2 (5,081 sq mi) | 4,396,098 | |
| Federal Capital Territory | FC | 
|
Abuja | North Central | 7,315 km2 (2,824 sq mi) | 1,406,239 | ||
| Gombe | GO | 
|
Gombe | North East | 18,768 km2 (7,246 sq mi) | 3,623,462 | ||
| Imo | IM | 
|

|
Owerri | South East | 5,530 km2 (2,140 sq mi) | 5,167,722 | |
| Jigawa | JI | 
|
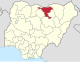
|
Dutse | North West | 23,154 km2 (8,940 sq mi) | 6,779,080 | |
| Kaduna | KD | 
|
Kaduna | North West | 46,053 km2 (17,781 sq mi) | 8,324,285 | ||
| Kano | KN | 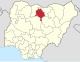
|
Kano | North West | 20,131 km2 (7,773 sq mi) | 14,253,549 | ||
| Katsina | KT | 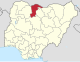
|
Katsina | North West | 24,192 km2 (9,341 sq mi) | 9,300,382 | ||
| Kebbi | KE | 
|
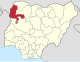
|
Birnin Kebbi | North West | 36,800 km2 (14,200 sq mi) | 5,001,610 | |
| Kogi | KO | 
|
Lokoja | North Central | 29,833 km2 (11,519 sq mi) | 4,153,734 | ||
| Kwara | KW | 
|
Ilorin | North Central | 36,825 km2 (14,218 sq mi) | 3,259,613 | ||
| Lagos | LA | 
|

|
Ikeja | Lagos | South West | 3,577 km2 (1,381 sq mi) | 12,772,884 |
| Nasarawa | NA | 
|
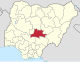
|
Lafia | North Central | 26,256 km2 (10,137 sq mi) | 2,632,239 | |
| Niger | NI | 
|
Minna | North Central | 76,363 km2 (29,484 sq mi) | 6,220,617 | ||
| Ogun | OG | 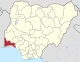
|
Abeokuta | South West | 16,981 km2 (6,556 sq mi) | 5,945,275 | ||
| Ondo | ON | 
|
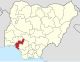
|
Akure | South West | 15,500 km2 (6,000 sq mi) | 4,969,707 | |
| Osun | OS | 
|
Osogbo | South West | 9,251 km2 (3,572 sq mi) | 4,237,396 | ||
| Oyo | OY | 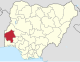
|
Ibadan | South West | 28,454 km2 (10,986 sq mi) | 7,512,855 | ||
| Plateau | PL | 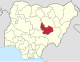
|
Jos | North Central | 30,913 km2 (11,936 sq mi) | 4,400,974 | ||
| Rivers | RI | 
|
Port Harcourt | South South | 11,077 km2 (4,277 sq mi) | 7,034,973 | ||
| Sokoto | SO | 
|
Sokoto | North West | 25,973 km2 (10,028 sq mi) | 5,863,187 | ||
| Taraba | TA | 
|
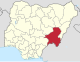
|
Jalingo | North East | 54,473 km2 (21,032 sq mi) | 3,331,885 | |
| Yobe | YO | 
|

|
Damaturu | Potiskum | North East | 45,502 km2 (17,568 sq mi) | 3,398,177 |
| Zamfara | ZA | 
|

|
Gusau | North West | 39,762 km2 (15,352 sq mi) | 5,317,793 | |
Evolution of Nigerian administrative divisions
| Date | Events | Map |
|---|---|---|
| 1960–1963 | At the time of independence in 1960, Nigeria was a federal state of three regions: Northern, Western, and Eastern. Additionally, provinces, which were a legacy of colonial and protectorate times, remained extant until they were abolished in 1976. | 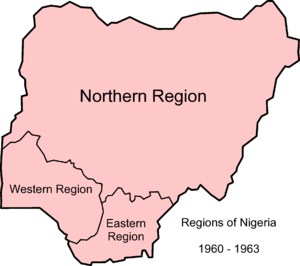 |
| 1963–1967 | In 1963, a new region, the Mid-Western Region, was created from the Western Region. |  |
| 1967–1976 | In 1967, the regions were replaced by 12 states by military decree. From 1967 to 1970 the Eastern Region attempted to secede, as a nation called Biafra during the Nigerian civil war. The Mid-Western Region was renamed to the State of Bendel during this period. | 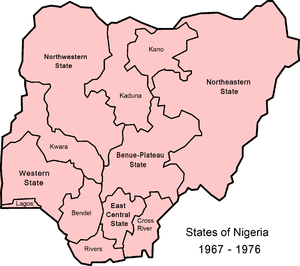 |
| 1976–1987 | In 1976, seven new states were created, making 19 altogether.[5] | 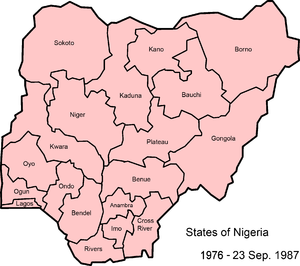 |
| 1987–1991 | During this period, there were 21 states and the Federal Capital Territory. |  |
| 1991–1996 | During this period, there were 30 states and the Federal Capital Territory. The Federal Capital Territory was established in 1991. In 1987 two new states were established, followed by another nine in 1991, bringing the total to 30. The latest change, in 1996, resulted in the present number of 36 states. |  |
Government
States of Nigeria have the right to organize and structure their individual governments in any way within the parameters set by the Constitution of Nigeria.
Legislature
At the state level, the legislature is unicameral, with the number of its members equal to three times the number of legislators it has in the Federal House of Representatives. It has the power to legislate on matters on the concurrent list.
Executive
At the state level, the head of the executive is the governor, who has the power to appoint people to the state executive council, subject to the advice and consent of the state house of assembly (legislature). The head of a ministry at the state level is the commissioner, who is assisted by a permanent secretary, who is also a senior civil servant of the state.
Judiciary
The Judiciary is one of the co-equal arms of the state government concerned with the interpretation of the laws of the state government. The judiciary is headed by the chief justice of the state appointed by the president subject to the approval of the state house of assembly.[6]
Chronology
| Regions | States | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 1963 | 1967 | 1976 | 1987 | 1991 | 1996 |
| Eastern | South-Eastern | Cross River | Akwa Ibom | |||
| Cross River | ||||||
| East Central | Imo | Imo | ||||
| Abia | ||||||
| Anambra | Enugu | Ebonyi | ||||
| Enugu | ||||||
| Anambra | ||||||
| Rivers | Bayelsa | |||||
| Rivers | ||||||
| Western | Mid-Western | Bendel | Delta | |||
| Edo | ||||||
| Western | Lagos | |||||
| Western | Ogun | |||||
| Ondo | Ekiti | |||||
| Ondo | ||||||
| Oyo | Osun | |||||
| Oyo | ||||||
| Northern | Benue-Plateau | Plateau | Nasarawa | |||
| Plateau | ||||||
| Benue | Benue | |||||
| Kogi | ||||||
| Kwara | ||||||
| Kwara | ||||||
| Kano | Jigawa | |||||
| Kano | ||||||
| North Central | Kaduna | Kaduna | ||||
| Katsina | ||||||
| North Western | Niger | |||||
| Sokoto | Kebbi | |||||
| Sokoto | Sokoto | |||||
| Zamfara | ||||||
| North Eastern | Bauchi | Bauchi | ||||
| Gombe | ||||||
| Borno | Borno | |||||
| Yobe | ||||||
| Gongola | Adamawa | |||||
| Taraba | ||||||
See also
Notes
- ^ "Federal Capital Territory (FCT) | Location & Geography | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 7 June 2023.
- ^ "USAID Nigeria mission: Nigeria administrative divisions" Archived 2007-01-13 at the Wayback Machine United States Agency for International Development, October 2004, last accessed 21 April 2010
- ^ "1999 Constitution of Nigeria" (PDF). Retrieved 20 September 2024.
- ^ Demographic Statistics Bulletin 2020
- ^ Kraxberger, Brennan (2005) "Strangers, Indigenes and Settlers: Contested Geographies of Citizenship in Nigeria" Space and Polity 9(1): pp. 9–27, pages 10, 11, & 15
- ^ Shetreet, Shimon; Deschênes, Jules (1 January 1985). Judicial Independence: The Contemporary Debate. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 978-90-247-3182-4.
Sources
- Gboyega Ajayi (2007). The military and the Nigerian state, 1966–1993: a study of the strategies of political power control. Trenton, New Jersey: Africa World Press. ISBN 978-1-59221-568-3.
- Solomon Akhere Benjamin (1999). The 1996 state and local government reorganizations in Nigeria. Ibadan: Nigerian Institute of Social and Economic Research. ISBN 978-181-238-9.
- Rotimi T. Suberu (1994). 1991 state and local government reorganizations in Nigeria. Ibadan: Institute of African Studies, University of Ibadan. ISBN 978-2015-28-8.
External links
- "New States of Nigeria". Statoids.
- Headline News in Nigeria Archived 2018-08-20 at the Wayback Machine States
States And Capital In Nigeria, Their Slogans & Current Governors A comprehensive list of all states in Nigeria and their current governors.
