Lockheed YF-22
| YF-22 | |
|---|---|
 A YF-22 during a test flight | |
| General information | |
| Type | Stealth fighter technology demonstrator |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed / Boeing / General Dynamics |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary user | United States Air Force |
| Number built | 2 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1989–1990 |
| First flight | 29 September 1990 |
| Developed into | Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor |
The Lockheed/
In the 1980s, the USAF began looking for a replacement for its fighter aircraft to counter emerging threats such as the advanced Soviet Su-27 and MiG-29. A number of companies submitted their proposals, with the competition narrowing down to two teams for demonstration/validation. Northrop and McDonnell Douglas submitted the YF-23. Lockheed, Boeing and General Dynamics proposed and built the YF-22, which, although marginally slower and having a larger radar cross-section, was more agile than the YF-23. The Lockheed team was picked by the Air Force as the winner of the ATF in April 1991. The U.S. Navy considered adopting a naval version of the ATF, but these plans were later canceled due to cost.
Following the selection, the first prototype was retired as an exhibit at the Air Force Flight Test Museum, while the second continued flight testing until an accident relegated it to the role of an antenna test vehicle and it was later stored.
Development
Concept definition
In 1981, the U.S. Air Force (USAF) began developing requirements for an Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) that would eventually become a new air superiority fighter to replace the F-15 Eagle and F-16 Fighting Falcon. This was made more crucial by the emerging worldwide threats, including development and proliferation of Soviet MiG-29 "Fulcrum" and Su-27 "Flanker"-class fighter aircraft, A-50 "Mainstay" airborne warning and control system (AWACS), and more advanced surface-to-air missile systems. The ATF would take advantage of the new technologies in fighter design on the horizon including composite materials, lightweight alloys, advanced avionics and flight-control systems, more powerful propulsion systems and stealth technology.[1]
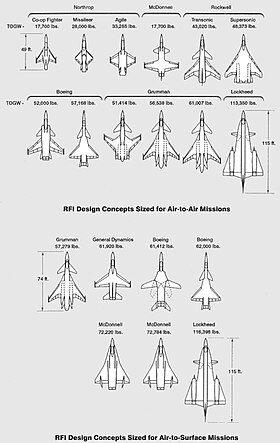
The USAF sent out the ATF request for information (RFI) to the aerospace industry in May 1981 to explore what the future fighter aircraft could look like, and subsequently established a Concept Development Team (CDT) to analyze the results.[2] Eventually code-named "Senior Sky", the ATF at this time was still in the midst of requirements definition with both air-to-air and air-to-ground missions in consideration, and consequently there was substantial variety in the responses from the industry. Lockheed's initial concept was a particularly large aircraft called CL-2016, nicknamed "battlecruiser" for its size, that resembled its SR-71/YF-12 with large delta wings and engines mounted in nacelles spaced away from the fuselage and would have had similarly high operating speed and altitude as a missile platform (or "missileer" per Lockheed).[3][4]
In 1983, the ATF Concept Development Team became the System Program Office (SPO) at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base. After discussions with aerospace companies and Tactical Air Command (TAC), the CDT/SPO narrowed the requirements to an air superiority fighter with outstanding kinematic performance in speed and maneuverability to replace the F-15.[5] Additionally, the SPO began to increasingly emphasize stealth for increasing survivability due to the Air Force's experience from "black world" projects such as the Have Blue/F-117 ("Senior Trend") and the Advanced Technology Bomber (ATB) program (which would result in the B-2, or "Senior Ice").[6] With stealth becoming a core requirement, Lockheed's design team, led by Bart Osborne from its Skunk Works division at Burbank, California, migrated away from its initial SR-71-like "battlecruiser" concept and instead began drafting a design that resembled the company's F-117. However, the faceted shape, resulting from Lockheed using the same "Echo" computer program that it had used to design the F-117, gave the design very poor aerodynamic performance that would be unsuitable for a fighter. Lockheed would perform poorly throughout the concept exploration phase, placing among the bottom of the competing contractors.[3]
Demonstration and validation

By November 1984, the SPO had further narrowed the requirements and released the Statement of Operational Need (SON), with requirements calling for a 50,000 lb (22,700 kg) takeoff weight fighter that places strong emphasis on stealth, maneuver, and supersonic cruise without afterburners, or supercruise.[7] In September 1985, the Air Force sent out technical request for proposals (RFP) to a number of aircraft manufacturing teams for demonstration and validation (Dem/Val). In addition to the ATF's demanding technical requirements, Dem/Val also placed a great deal of importance on systems engineering, technology development plans, and risk mitigation. The top four proposals, later reduced to two to reduce program costs, would proceed with Dem/Val as finalists. At the time, the Air Force anticipated procuring 750 ATFs at a unit flyaway cost of $35 million in fiscal year (FY) 1985 dollars (~$84.2 million in 2023).[3][7][8] Furthermore, under Congressional pressure to combine efforts with the Air Force to reduce costs, the U.S. Navy joined the ATF program initially as an observer and eventually announced in 1988 that it would use a variant/derivative of the winning design to replace its F-14 Tomcat as the Navy Advanced Tactical Fighter (NATF); the service called for the procurement of 546 aircraft.[9]

Having performed poorly during ATF concept exploration while also losing the ATB to Northrop who had a curved surface design, Lockheed abandoned faceting in 1984 and began incorporating curved shapes and surfaces. Although its analytical tools were initially not able to calculate for such shapes, good empirical results from radar range testing at Helendale, California, gave Lockheed confidence in designing a stealthy aircraft with smooth, curved surfaces, thus greatly improving its aerodynamic characteristics. As Lockheed gradually became able to analyze curved shapes,[N 2] the final design submitted for Dem/Val, designated Configuration 090P, would have an arrowhead-like forward fuselage shape, swept trapezoidal wings, four empennage surfaces, S-shaped inlet ducts obscuring the engine face, and an internal rotary missile launcher.[3] In addition to the change in aircraft design, Lockheed also shifted much more engineering talent and manpower to its ATF effort, appointing Sherman Mullin as the program manager, and had its draft proposals aggressively red-teamed by a group led by retired Air Force general Alton D. Slay.[10] The resulting proposal improvements were substantial, particularly the systems engineering volume.[11]
The ATF RFP would see some alterations after its first release; the SPO drastically increased all-aspect stealth requirements in December 1985 after discussions with Lockheed and Northrop regarding their experiences with the Have Blue/F-117 and ATB/B-2, and the requirement for flying technology demonstrator prototypes was added in May 1986 due to recommendations from the Packard Commission, a federal commission by President Ronald Reagan to study Department of Defense procurement practices.[12][13] Seven companies submitted bids in July 1986.[N 3] Owing to the immense investments companies were expected to make on their own, teaming was encouraged by the SPO. Following proposal submissions, Lockheed, Boeing, and General Dynamics formed a team to develop whichever of their proposed designs was selected, if any. Northrop and McDonnell Douglas formed a team with a similar agreement.[15]
On 31 October 1986, Lockheed and Northrop, the two industry leaders in stealth aircraft, were selected as the first and second place respectively; Sherman Mullin would credit the Lockheed proposal's system engineering volume for the top rank, an area other contractors had not emphasized. The two teams, Lockheed/Boeing/General Dynamics and Northrop/McDonnell Douglas, were awarded $691 million contracts in FY 1985 dollars (~$1.66 billion in 2023) and would undertake a 50-month demonstration phase, culminating in the flight test of the two teams' prototypes, the YF-22 and the YF-23; Pratt & Whitney and General Electric had earlier been awarded contracts to develop the competing prototype propulsion systems with the designations YF119 and YF120 respectively.[16][17][18] Because the requirement for flying prototypes was a late addition due to political pressure, the prototypes were to be "best-effort" vehicles not meant to perform a competitive flyoff or represent a production aircraft, but to demonstrate the viability of its concept and to mitigate risk.[N 4][20]
Design evolution

Work would be divided roughly equally among the team. Because Lockheed's submission was selected as one of the winners, the company assumed leadership of the program partners. It would be responsible for the forward fuselage and cockpit at Burbank as well as final assembly at Palmdale, California. Meanwhile, the wings and aft fuselage would be built by Boeing at Seattle, Washington, and the center fuselage, weapons bays, tail and landing gear would be built by General Dynamics at Fort Worth, Texas.[21] The team would also invest $675 million (~$1.5 billion in 2023) combined into their ATF effort during Dem/Val in addition to the government contract awards.[22] The partners brought their design experience and proposals with them. Boeing's design was large and long with a chin-mounted inlet, trapezoid wings, V-tail empennage surfaces (deemed sufficient due to the high operating speed), and palletized internal weapons. General Dynamics' design was smaller with fuselage and delta wings optimized for maneuver and supercruise, shoulder-mounted inlets, a large single vertical tail as the only empennage surface which compromised all-aspect stealth, and weapon bays in the center fuselage. However, much of the team's scrutiny fell on Lockheed's Configuration 090P, which was problematic due to being highly immature as a result of Lockheed's greater focus on systems engineering rather than a point design. Nevertheless, 090P was the initial starting point that the team worked to refine.[23]
Throughout Dem/Val, the SPO held System Requirement Reviews (SRR) with contractor teams and used the results of their performance and cost trade studies to adjust ATF requirements and delete ones that were significant weight and cost drivers while having marginal value.[24] For instance, the requirement for eight internal missiles (represented by the baseline AIM-120A)[N 5] was reduced to six. The team continually refined the design, making extensive use of analytical and empirical methods such as wind tunnel testing (18,000 hours by the end of Dem/Val), pole testing at radar ranges, and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and computer-aided design (CAD) software. By early 1987, the design had evolved into Configuration 095, which replaced the rotary launcher with a flatter weapons bay to reduce volume and drag, and the shapes of the forward fuselage and leading-edge root extensions were recontoured to prevent uncontrollable pitch-up moments. Around this time, the design had split into two families, the 500 prefix that represents the full system design – or Preferred System Concept (PSC) — to be carried forward for full-scale development and the 1000 prefix that represents the same external shape but designed to be built as prototype air vehicles instrumented for flight testing; Configuration 095 thus became 595 and 1095 respectively.[23]

By mid-1987, detailed weight analysis of Configuration 595/1095 revealed that it was overweight by 9,000 lb (4,100 kg) even if it could still nominally meet maneuver parameters.[23] With weight likely to increase and compromises not forthcoming, the team chose to completely start over with a new design in July 1987, with Lockheed bringing a new director of design engineering, Richard Cantrell.[N 6][27] Various different layouts were explored and after an intensive three-month effort, the team chose a new design, Configuration 614/1114, as the starting point in late 1987 with shoulder-mounted inlets and diamond-like delta wings similar to General Dynamics' design, and four empennage surfaces; notably, the diamond-like delta's aerodynamic characteristics approached the original swept trapezoidal profile's while offering much lower structural weight due to the longer root chord. The design evolved through the rest of 1987 and into May 1988, when Configuration 632/1132 was frozen as the YF-22. Changes include the shapes of the empennage surfaces to diamond-like and recontouring of the fore and aft fuselage to reduce wave drag following the deletion of the thrust reverser requirement after another SRR;[28][29] the prototype thrust vectoring nozzles still retained some thrust reversing hardware provisions however, resulting in the prototype aft fuselage being bulkier than needed. Ultimately, the 50,000-lb takeoff weight still proved to be unachievable for both teams and was adjusted to 60,000 lb (27,200 kg), resulting in engine thrust increasing from 30,000 lbf (133 kN) to 35,000 lbf (156 kN) class.[30] While the YF-22 configuration was frozen at an immature state relatively soon after the redesign to begin construction of the prototypes, the team continued evolving the configuration and PSC design into the F-22 for full-scale development.[23]
In addition to the advanced air vehicle and propulsion design, the ATF required an integrated avionics system for sensor fusion to increase the pilot's situational awareness and decrease workload; this demanded a leap in sensor and avionics capability. Avionics development was marked by extensive testing and prototyping and supported by ground and flying laboratories, with Boeing being responsible for avionics integration. As the YF-22 was a technology demonstrator for the airframe and engines, it would not have any of the mission systems avionics. Boeing would build the Avionics Ground Prototype (AGP) and also provide a Boeing 757 modified with the mission systems as a flying laboratory for avionics development; this aircraft would later be named the Flying Test Bed.[31][32] The SPO would similarly adjust avionics requirements as a result of SRRs with contractors. Side-looking radar and infrared search and track (IRST) were deleted from the baseline requirement and became provisions for potential future addition, and a $9 million cap in FY 1985 dollars (~$21.7 million in 2023) for avionics per aircraft was placed by the SPO in 1989 on the baseline proposal for full-scale development.[23]
Formally designated as the YF-22A, the first aircraft (PAV-1, serial number 87-0700, N22YF), with the GE YF120 engine,[33][34] was rolled out on 29 August 1990[21][35] and first flew on 29 September 1990, taking off from Palmdale piloted by David L. Ferguson.[21][36] The second YF-22A (PAV-2, s/n 87-0701, N22YX) with the P&W YF119 made its maiden flight on 30 October at the hands of chief test pilot Thomas A. Morgenfeld.[21] The aircraft was given the unofficial name "Lightning II" after Lockheed's World War II-era fighter, the P-38 Lightning, which persisted until the mid-1990s when the USAF officially named the production F-22 "Raptor".[37] The F-35 later received the "Lightning II" name in 2006.[38]
Naval variant
Because the NATF, which was to replace the F-14 Tomcat, required a lower landing speed than the ATF for aircraft carrier recovery while still attaining Mach 2-class speeds, the Lockheed team's NATF design group went through several configurations to arrive at a design that would achieve acceptable characteristics for carrier operations. Boeing had advocated for a fixed-wing design while General Dynamics favored variable-sweep wings. After an internal competition and extensive wind tunnel testing, the team chose to incorporate variable-sweep wings in August 1989.[39] The resulting aircraft would have been heavier, more complex, and more expensive than the Air Force ATF counterpart.[40] The Lockheed team would submit its NATF design along with its ATF full-scale development proposal in December 1990, although the Navy would withdraw from the program shortly afterwards due to cost.[39]
Design

The YF-22 (internally designated Configuration 1132) was a prototype air vehicle intended to demonstrate the viability of the ATF air vehicle and propulsion design, which was ultimately meant to meet USAF requirements for survivability, supercruise, stealth, and ease of maintenance.[41] The airframe has large diamond-like delta wings with leading edge swept back 48°, shoulder-mounted inlets, three internal weapons bays, and four empennage surfaces: canted vertical tails with rudders and all moving horizontal stabilizers. All major edges were aligned at a common set of angles for stealth. It had a tricycle landing gear, an aerial refueling receptacle centered on its spine, and an airbrake between the vertical tails.[42] The cockpit had a completely frameless bubble canopy. Compared with its Northrop/McDonnell Douglas counterpart, the YF-22 has a more conventional design – its wings have larger control surfaces, such as full-span leading edge,[43] and, whereas the YF-23 had two tail surfaces, the YF-22 had four, which made it more maneuverable than its counterpart.[44]

The YF-22 was powered by two engines, with the General Electric YF120 mounted on the first aircraft and the second with the Pratt & Whitney YF119.[1][45] The fixed-geometry caret engine inlets were spaced away from the forward fuselage to divert the boundary layer and generate oblique shocks with the upper inboard corner for efficient supersonic compression; the serpentine inlet ducts fully shield the engine faces from any exterior view. The two-dimensional thrust vectoring nozzles reduce the infrared signature by flattening the exhaust plume and facilitating its mixing with ambient air.[46][47] Chines run from the nose along the sides of the forward fuselage where they eventually meet the upper edge of the inlets; those then transition to sharp leading edge root extensions of the wings further aft. These produce vortices that improved high angle-of-attack characteristics. To reduce supersonic drag for supercruise, area rule was applied to the airframe shape and most of the fuselage volume lies ahead of the wing's trailing edge, although the late configuration redesign meant that the prototype shaping was immature and not quite refined.[28]
The aircraft had relaxed static stability and was controlled via fly-by-wire, integrated into the vehicle management system (VMS). The cockpit had a throttle and sidestick arrangement similar to the F-16 and simulated an operational fighter layout with a heads-up display (HUD), two 6 in × 6 in (15 cm × 15 cm) primary multifunction displays (MFD) and three 4 in × 6 in (10 cm × 15 cm) secondary MFDs. Some of the MFDs could be replaced by instrument panels as needed for specific flight test events. The prototype avionics incorporated a software-controlled stores management system (SMS) to test missile launching from internal weapons bays and its integration into the VMS; the weapons bays were also instrumented to measure vibration and acoustics.[48][49]
NATF-22

The Lockheed team's design for the Navy Advanced Tactical Fighter (NATF), sometimes referred to as "NATF-22" or "F-22N" (the design was never formally designated), would have differed from the Air Force version in many ways. Because the NATF needed lower landing speeds than the F-22 for aircraft carrier operations while still attaining Mach 2-class speeds, the design would have incorporated variable-sweep wings; furthermore, the Navy placed greater emphasis on loiter time for fleet air defense rather than supercruise, so the variable-sweep wings also improved endurance.[39][40] The fuselage shaping was similar, while the landing gears and arresting hook were strengthened for aircraft carrier landings; all of these changes would have resulted in a heavier, more complex, and more expensive aircraft. It retained four empennage surfaces and thrust vectoring nozzles, and the avionics would initially have been largely common with the F-22, although additional sensors and mission avionics had also been planned for maritime missions. The design would have had a similar weapons bay arrangement but with expanded weapons carriage, including the AIM-152 AAAM, AGM-88 HARM, and AGM-84 Harpoon.[50][51]

While the Lockheed team would submit the NATF-22 design with its F-22 full-scale development proposal in December 1990, the Navy began backing out of the NATF program in late 1990 to early 1991 and fully abandoned NATF by FY 1992 due to escalating cost and thus the design never progressed beyond Dem/Val to full-scale development, or engineering and manufacturing development (EMD). Lockheed and Boeing would leverage aspects of the design, such as the variable-sweep wings, for several concepts for the Navy's Advanced-Attack (A-X) program, which later became the Advanced Attack/Fighter (A/F-X) program with added fighter capability, the successor to the canceled A-12 Avenger II; however, A/F-X would also be canceled as a result of the 1993 Bottom-Up Review due to post-Cold War budget pressure.[52][53]
Operational history
Evaluation

Testing began with the first flight of PAV-1 on 29 September 1990. During the 18-minute flight, PAV-1 reached a maximum speed of 250 knots (460 km/h; 290 mph) and a height of 12,500 feet (3,800 m), before landing at Edwards AFB.[34] Following the flight, test pilot Dave Ferguson said that the remainder of the YF-22 test program would be concentrated on "the manoeuvrability of the aeroplane, both supersonic and subsonic".[34]
During the flight test program, unlike the YF-23, weapon firings and high (60°) angle of attack (AoA, or high-alpha) flights were carried out on the YF-22.[54] Although not a program requirement, the aircraft fired AIM-9 Sidewinder and AIM-120 AMRAAM missiles from internal weapon bays.[54][55] Flight testing also demonstrated that the YF-22 with its thrust vectoring nozzles achieved pitch rates more than double that of the F-16 at low-speed maneuvering as well as having excellent high angle-of-attack characteristics, with trimmed alpha of over 60° flown. The first prototype, PAV-1 with the General Electric engines, achieved Mach 1.58 in supercruise, while PAV-2 with the Pratt & Whitney engines reached a maximum supercruise speed of Mach 1.43; maximum speed was in excess of Mach 2.0.[56][57] Flight testing continued until 28 December 1990, by which time 74 flights were completed and 91.6 airborne hours were accumulated.[18][58] Following flight testing, the contractor teams submitted proposals for ATF full-scale development, with the Lockheed team's PSC F-22 design being significantly refined and evolving to Configuration 638 for its submission.[59]
On 23 April 1991, the Lockheed team was announced by Secretary of the Air Force Donald Rice as the winner of the ATF competition. The Lockheed team was rated higher on technical aspects, was considered lower risk (the YF-22 flew considerably more hours and sorties than its counterpart), and was considered to have more effective program management.[60][61] Both designs met or exceeded all performance requirements; the YF-23 was stealthier and faster, but the YF-22 was more agile.[62] It was speculated in the aviation press that the Lockheed design was also seen as more adaptable to the Navy's NATF, but the U.S. Navy abandoned NATF by 1992.[54][63] Instead of being retired, as with the case of PAV-1, PAV-2 subsequently flew sorties following the competition – it amassed another 61.6 flying hours during 39 flights.[54] On 25 April 1992, the aircraft sustained serious damage during a go-around attempt as a result of pilot-induced oscillations. It was repaired but never flew again, and instead served as a static test vehicle thereafter.[64][65] In 1991, it was anticipated that 650 production F-22s would be procured.[66]
F-22 production

As the Lockheed team won the ATF competition, it was awarded the full-scale development, or engineering, manufacturing and development (EMD) contract in August 1991 initially worth about $11 billion (~$21.9 billion in 2023), which would ultimately allow it to proceed with production of operational aircraft. The EMD/production design would be refined and evolve into Configuration 645.[23] The EMD initially called for seven single-seat F-22A and two twin-seat F-22Bs, although the latter was eventually canceled to save on development costs and the orders were converted to single-seaters. On 9 April 1997, the first of these, Spirit of America, was rolled out. During the ceremony, the F-22 was officially named "Raptor". Due to limited funding, the first flight, which had previously been scheduled for mid-1996, occurred on 7 September 1997.[64] Flight testing for the F-22 continued until 2005, and on 15 December 2005 the USAF announced that the Raptor had reached its initial operational capability (IOC); with the collapse of the Soviet Union and the Department of Defense focused on counterinsurgency at that time, F-22 production only reached 195 aircraft and ended in 2011.[67][68]
In many respects, the YF-22s were different from EMD/production F-22s as the design progressed from relatively immature Configuration 632/1132 to the final Configuration 645. Contrary to the F-117 Nighthawk, which was initially difficult to control because of small vertical stabilizers, the YF-22 had its fin area over-specified by Lockheed. Therefore, the company reduced the size of those on F-22s by 20–30 percent. Lockheed and its partners recontoured the shape of the wing and stabilator trailing edges to improve aerodynamics, strength, and stealth characteristics; the wing and stabilitor sweep was reduced by 6° from 48°. The shapes of the radome and fuselage were changed to improve radar performance and aerodynamics. The dedicated airbrake was eliminated in favor of feathering control surfaces using the control laws. The systems arrangement and structural design were refined. Finally, to improve pilot visibility, the canopy was moved forward 7 inches (178 mm), and the engine intakes were moved rearward 14 inches (356 mm).[69][70][23]
Accidents
In April 1992, the second YF-22 crashed while executing a go-around at Edwards AFB. The test pilot, Tom Morgenfeld, escaped without injury. The cause of the crash was found to be a flight control software error that failed to prevent a pilot-induced oscillation while performing a low altitude demonstration flight. The aircraft was superficially repaired but never flew again and was later used as an antenna test model. In light of this mishap, the F-22 flight control laws, the algorithms governing how control inputs translate into aircraft motions and reactions, were altered to better account for non-linear effects of control surface rate/position saturation and PIO triggering mechanisms.[71]
Surviving aircraft

- YF-22A PAV-1, S/N 87-0700, registration number N22YF – on display at the Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards Air Force Base, California (was previously loaned to the National Museum of the United States Air Force near Dayton, Ohio)[72]
- YF-22A PAV-2, S/N 87-0701, registration number N22YX – stored at Rome Laboratory, Rome, New York.[73]
Specifications (YF-22A)

Data from Miller,[74] Pace,[75] Baker,[76] Sweetman,[77] and Aronstein & Hirschberg[78] (note, some specifications are estimated)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 (pilot)
- Length: 64 ft 2 in (19.55 m)
- Wingspan: 43 ft 0 in (13.1 m)
- Height: 17 ft 9 in (5.39 m)
- Wing area: 830 sq ft (77.1 m2)
- Empty weight: 31,000 lb (14,061 kg) contractor weight (without engines)
- Gross weight: 62,000 lb (28,123 kg) takeoff
- Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney YF119-PW-100L or General Electric YF120-GE-100L afterburning turbofans, 23,500 lbf (105 kN) thrust each (YF120) dry, 30,000 or 35,000 lbf (130 or 160 kN) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.2, 1,452 mph (1,262 kn; 2,337 km/h) at altitude
- Supercruise: Mach 1.58, 1,043 mph (906 kn; 1,679 km/h) at altitude (military power only)
- Range: 2,000 nmi (2,300 mi, 3,700 km)
- Combat range: 700–800 nmi (810–920 mi, 1,300–1,500 km)
- Service ceiling: 65,000 ft (19,800 m)
- g limits: +7.9 g (highest tested)
- Wing loading: 74.7 lb/sq ft (365 kg/m2)
- Thrust/weight: 1.13
Armament
Provisions made for:
- 1 × 20 mm (0.79 in) M61 Vulcan cannon
- 4 × AIM-120 AMRAAM medium-range air-to-air missiles
- 2 × AIM-9 Sidewinder short-range air-to-air missiles
See also
Related development
- Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor – American stealth air superiority fighter
- Lockheed Martin FB-22 – Proposed bomber aircraft for the U.S. Air Force derived from the F-22 Raptor
- Lockheed Martin X-44 MANTA – Conceptual aircraft design by Lockheed Martin
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
- Northrop YF-23 – Prototype demonstrator aircraft for the U.S. Air Force Advanced Tactical Fighter program
Related lists
References
Notes
- ^ Lockheed merged with Martin Marietta in 1995 to form Lockheed Martin.
- ^ A stealthy curved radome was the last challenge Lockheed overcame in early 1985.[3]
- ^ The seven bidding companies were Lockheed, Boeing, General Dynamics, McDonnell Douglas, Northrop, Grumman, and North American Rockwell.[14]
- ^ The contractor teams were to give the SPO "sealed envelope" flight performance predictions against which their prototypes would be evaluated, rather than against each other.[19]
- ^ A clipped-fin variant of the AMRAAM, the AIM-120C, was eventually developed to increase the F-22's internal missile load back to eight.[25]
- ^ Richard Heppe, president of Lockheed California Company, would also play a major role.[26]
Citations
- ^ a b "Fact sheet: Lockheed-Boeing-General Dynamics YF-22". U.S. Air Force. 11 February 2009. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 30.
- ^ a b c d e Hehs 1998, Part 1.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 39–42.
- ^ Sweetman 1991, pp. 10–13.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 45–58.
- ^ a b Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 70–78.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Williams 2002, p. 5.
- ^ Mullin 2012, p. 13.
- ^ Mullin 2012, pp. 18–19.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 82–85.
- ^ Mullin 2012, pp. 19–21.
- ^ Miller 2005, pp. 14, 19.
- ^ Goodall 1992, p. 94.
- ^ Miller 2005, pp. 19–20.
- ^ Jenkins and Landis 2008, pp. 233–234.
- ^ a b Williams 2002, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 137.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 87–88.
- ^ a b c d Jenkins and Landis 2008, p. 235.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 164.
- ^ a b c d e f g Hehs 1998, Part 2.
- ^ Mullin 2012, pp. 31–32.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 184–185.
- ^ Mullin 2019.
- ^ Mullin 2012, p. 29.
- ^ a b Miller 2005, pp. 19–24.
- ^ Mullin 2012, p. 30.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 119.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 104–121.
- ^ Kohn, Lt. Col. Allen E.; Rainey, Lt. Col. Steven M. (9 April 1999). "F-22 Flight Test Program Update". SETP 41st Symposium. Society of Experimental Test Pilots. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014.
- ^ Williams 2002, p. 5.
- ^ a b c "YF-22 flies as ATFs head for deadline". Flight International. 138 (4237). London: Reed Business Information: 6. 10–16 October 1990. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 21 May 2011. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ Bailey 1990, p. 34.
- ^ Goodall 1992, p. 99.
- ^ "Military Aircraft Names". Aerospaceweb.org. Archived from the original on 12 October 2009. Retrieved 26 September 2010.
- ^ ""Lockheed Martin Joint Strike Fighter Officially Named 'Lightning II'" (Press release). Official Joint Strike Fighter program office. 7 July 2006. Archived from the original on 15 July 2006. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ a b c Mullin 2012, pp. 38–39.
- ^ a b Miller 2005, p. 74.
- ^ "ATF procurement launches new era". Flight International. 130 (4037). London: Reed Business Information: 10–11. 9–15 November 1986. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 24 July 2012. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
- ^ Miller 2005, pp. 90–93.
- ^ "Pentagon relaxes ATF design secrecy". Flight International. 137 (4217). London: Reed Business Information: 4. 23–29 May 1990. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
- ^ "Lockheed's ATF Stresses Agility". Flight International. 138 (4233). London: Reed Business Information: 46–47. 12–18 September 1990. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- ^ "YF-23 fact sheet". National Museum of the U.S. Air Force. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 284.
- ^ Katz, Dan (7 July 2017). "The Physics And Techniques of Infrared Stealth". Aviation Week. Penton Media. Archived from the original on 14 August 2018. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, pp. 131–132, 144.
- ^ Miller 2005, p. 83.
- ^ "Naval YF-22 Would Have Swing Wings, But No Prototype Needed". Aerospace Daily. McGraw-Hill, Inc. 31 August 1990. p. 359.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg 1998, p. 237.
- ^ Aronstein and Hirschberg, p. 239.
- ^ "A/F-X Unveiled". Flight International. Reed Business Information: 12–13. 26 January – 1 February 1994.
- ^ a b c d Williams 2002, p. 6.
- ^ "YF-23 would undergo subtle changes if it wins competition". Defense Daily, pp. 62–63, 14 January 1991.
- ^ Jenkins and Landis 2008, p. 236.
- ^ Goodall 1992, pp. 102–103.
- ^ Morgenfeld, Thomas A. (17 April 2022). YF-22 – Road to the Raptor with Tom Morgenfeld, Test Pilot. Torrance, California: Western Museum of Flight. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ Miller 2005, pp. 38–39.
- ^ Jenkins and Landis 2008, p. 234.
- ^ Miller 2005, p. 38.
- ^ Goodall 1992, p. 110.
- ^ Miller 2005, p. 76.
- ^ a b Williams 2002, pp. 6–7.
- ^ Warwick, Graham (6–12 May 1992). "Software suspected in YF-22 ATF accident". Flight International. 141 (4317). London: Reed Business Information: 12. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 25 September 2011. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
- ^ Pearlstein, Steven; Gellman, Barton (24 April 1991). "Lockheed Wins Huge Jet Contract; Air Force Plans to Buy 650 Stealth Planes At $100 million Each". The Washington Post.
- ^ "F-22A Raptor goes operational". U.S. Air Force. 15 December 2005. Archived from the original on 23 July 2012. Retrieved 24 June 2011.
- ^ Parsons, Gary. "Final F-22 Delivered". Archived 13 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Combat Aircraft Monthly, 3 May 2012. Retrieved 10 April 2014.
- ^ Williams 2002, p. 5.
- ^ Pace 1999, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Harris, Jeffrey; Black, G. T. "F-22 control law development and flying qualities, AIAA Paper 96-3379 (A96-35101)". 21st Atmospheric Flight Mechanics Conference. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: 156. doi:10.2514/6.1996-3379.
- ^ "YF-22 Raptor/87-700". aerialvisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 18 June 2021.
- ^ "YF-22 Raptor/87-701". aerialvisuals.ca. Archived from the original on 28 March 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ Miller 2005, p. 102.
- ^ Pace 1999, pp. 14–15.
- ^ Baker 1995, pp. 28–29, 32.
- ^ Sweetman 1991, p. 93.
- ^ Aronstein 1998, pp. 131, 154.
Bibliography
- Aronstein, David C.; Hirschberg, Michael J. (1998). Advanced Tactical Fighter to F-22 Raptor: Origins of the 21st Century Air Dominance Fighter. Arlington, Virginia: American Institute of Aeronautics & Astronomy. ISBN 978-1-56347-282-4.
- Bailey, John (5–11 September 1990). "YF-22 ATF prototype set for maiden flight". Flight International. 138 (4232). London: Reed Business Information: 34. ISSN 0015-3710. Archived from the original on 5 November 2012. Retrieved 23 June 2011.
- Baker, David (January 1995). "From ATF to Lightning II: A Bolt in Anger: Part Two: Lockheed's YF-22A". Air International. 48 (1): 27–38. ISSN 0306-5634.
- Goodall, James C. (1992). "The Lockheed YF-22 and Northrop YF-23 Advanced Tactical Fighters". America's Stealth Fighters and Bombers, B-2, F-117, YF-22, and YF-23. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing Company. ISBN 0-87938-609-6.
- Hehs, Eric (16 October 1998). "Design Evolution of the F-22, Part 1 and 2". Code One. Lockheed Martin. Archived from the original on 18 May 2024.
- Jenkins, Dennis R.; Landis, Tony R. (2008). Experimental & Prototype U.S. Air Force Jet Fighters. Minnesota, US: Specialty Press. ISBN 978-1-58007-111-6.
- Miller, Jay (2005). Lockheed Martin F/A-22 Raptor, Stealth Fighter. Hinckley, UK: Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-158-X.
- Mullin, Sherman N. (June 2012). "Winning the ATF" (PDF). Mitchell Institute for Airpower Studies. Arlington, VA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2024.
- ------- (24 January 2019). "Oral history interview with Sherman Mullin. Second Interview". Aerospace Oral History Project (Interview). Interviewed by Westwick, Peter; Deverell, William. San Marino, California: The Huntington Library, Art Museum, and Botanical Gardens.
- Pace, Steve (1999). F-22 Raptor, America's Next Lethal War Machine. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-134271-0.
- Sweetman, Bill (1991). YF-22 and YF-23 Advanced Tactical Fighters. St. Paul, Minnesota: Motorbooks International Publishing. ISBN 0-87938-505-7.
- Williams, Mel, ed. (2002). Superfighters: The Next Generation of Combat Aircraft. London: AIRtime Publishing. ISBN 1-880588-53-6.
Additional sources
- Abrams, Richard; Miller, Jay (1992). Lockheed F-22. Leicester, England: Midland County Publications. ISBN 0-942548-53-1.
- Crosby, Francis (2002). Fighter Aircraft. London: Lorenz Books. ISBN 0-7548-0990-0.
- Miller, Jay (1995). Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works: The Official History... Leicester, UK: Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-037-0.
- Mullin, Sherman N. (August 1992). "The Evolution of the F-22 Advanced Tactical Fighter". American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Arlington, VA. doi:10.2514/6.1992-4188.
- Pace, Steve (1991). X-Fighters: USAF Experimental and Prototype Fighters, XP-59 to YF-23. Osceola, Wisconsin: Motorbooks International. ISBN 0-87938-540-5.
- Sweetman, Bill (July 2000). "Fighter EW: The Next Generation". Journal of Electronic Defense. 23 (7). ISSN 0192-429X.
- ------- (1998). F-22 Raptor. St. Paul, Minnesota, USA: Motorbooks International Publishing. ISBN 0-7603-0484-X.
- Winchester, Jim, ed. (2005). "Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23". Concept Aircraft: Prototypes, X-Planes, And Experimental Aircraft. The Aviation Factfile. Rochester, Kent, UK: Grange Books. ISBN 1-84013-809-2.
