Leeds and Bradford Railway
The Leeds and Bradford Railway Company (L&BR)[note 1] opened a railway line between the towns[note 2] on 1 July 1846. It extended its line from Shipley through Keighley to Skipton and Colne, in 1847 and 1848.
While the extension was being constructed, the L&BR negotiated with the Manchester and Leeds Railway, with a view to leasing its line to the M&LR. George Hudson, the so-called Railway King, was chairman of the rival Midland Railway at the time and by controversial means, secured the lease of the L&BR for his own company in 1846. Five years later the Midland Railway took over the L&BR company.
The former L&BR network was used by the Midland Railway for its own extension to Carlisle, and with allied companies, into Scotland, and as the original core line became busier and more congested, widening schemes were implemented. The first Leeds terminal station has long been superseded, and the line between Skipton and Colne was closed in 1970, but most of the original network continues in use at the present day.
Origin and construction
Before the Leeds and Bradford

In the early nineteenth century Bradford was the seat of the British woollen industry, and the greatest wool centre in the world.[1] The difficulty for Bradford was the poor state of transport links, although there had been a Bradford Canal from 1774.[2] Conveyance of raw materials in and finished goods out by animal power was slow and expensive. In 1840 the best passenger connection between Bradford and the railway network was at Brighouse, over 6 miles away: the demand was such that 40,000 passengers annually used the horse-drawn coach link in 1844.[3]
In the early part of the 1830s, the North Midland Railway was being planned; it was to run from Derby to Leeds; the merchants of Bradford asked the NMR company to extend to their town. However the directors of the NMR stated that building a 72-mile railway was already quite enough for them, and they declined. George Stephenson was the engineer of the NMR and advised the Bradford people that forming their own company for a line would be a practical way forward, but this advice was not acted upon.[1] The North Midland Railway opened throughout to Leeds on 1 July 1840.[4]
Formation of the Leeds and Bradford Railway
| Leeds and Bradford Railway Act 1844 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for making a Railway from Leeds to Bradford, with a Branch to the North Midland Railway. |
| Citation | 7 & 8 Vict. c. lix |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 4 July 1844 |
In reaction to the lack of progress, business interests in Bradford decided to form their own company, and they considered themselves fortunate to secure the services of George Stephenson as engineer, and of George Hudson as chairman. Their company's act of Parliament, the Leeds and Bradford Railway Act 1844 (7 & 8 Vict. c. lix), obtained royal assent on 4 July 1844.[1] Authorised share capital was £400,000.[5] This was achieved in the face of opposition from rival groups, one of which intended to use atmospheric traction to overcome the difficulty of the steep gradients their line would involve. As part of the Parliamentary process of gaining authorisation, the Leeds and Bradford promoters undertook to build extensions from Shipley to Keighley and from Bradford to Halifax.[3][6][7]
The authorising act also provided for a new Wellington Station in Leeds together with a connection to the North Midland Railway at Hunslet.[6]
Construction and opening
The line was 13 miles in length. The terrain was distinctly unfavourable to railway alignment, and Stephenson routed the line north out of Bradford to Shipley, turning east there. There was a 1,300 yard tunnel at Thackley.[1]
The Leeds and Bradford company built "a splendid new station"[1] at Wellington, in Leeds, the first in the centre of Leeds. Up until that time the Midland Railway had been using a terminus station at Hunslet Lane, some distance from the centre of Leeds and "in an unsuitable district",[1] but now was given the facility of using the Leeds and Bradford station, to the advantage of both companies.[8][9]
On 30 May 1846 the contractor had substantially completed the construction of the line, and arranged a day excursion from Hunslet Junction, Leeds to Bradford for the directors and their friends. The formal opening took place on 30 June 1846, and the general opening to the public followed on 1 July 1846. There were no intermediate stations at first. The Bradford station was referred to as "Market Street" until its name was changed to Forster Square in 1924.[1][5][10][11]
Public services began between Leeds and Bradford on 1 July 1846 with a regular hourly service, 18 trains per day in each direction on a weekday with five each way on Sundays.[6]
Formation of the Midland Railway
While the bill for the Leeds and Bradford Railway was in Parliament, the Midland Railway was formed in 1844, by an act of Parliament, the Midland Railway (Consolidation) Act 1844 (7 & 8 Vict. c. xviii), of 10 May 1844. It was created by the amalgamation of the North Midland Railway, the Birmingham and Derby Junction Railway, and the Midland Counties Railway.[12] Now the people of Bradford saw that they had another chance, and they petitioned the new Midland Railway to build a branch line to their town. Once again they were rebuffed, as the Midland board said that they "had enough irons in the fire" with the Nottingham to Lincoln line and the Syston to Peterborough line.[1]
Leasing the line
In 1845 the Manchester and Leeds Railway was expressing interest in amalgamation with the Leeds and Bradford Railway. A new line across Bradford would be built, linking the present-day Interchange and Forster Square stations. The M&LR was associated with the London and York Railway, which was to become the Great Northern Railway. Suddenly in July 1846 the Leeds and Bradford company withdrew from negotiations, accusing the M&LR of bad faith in drafting the agreements. The Leeds and Bradford immediately courted the Midland Railway. The M&LR had offered to lease the Leeds and Bradford line guaranteeing 10% on its share capital, and it was hardly tenable for the Midland to propose less than that.
George Hudson was the chairman of the Midland Railway at the time, and when the matter came on the shareholders' meeting agenda, he declared that the Midland would offer 10% to the Leeds and Bradford, of which he was also chairman. This was an obvious conflict of interest, which he should have avoided by standing down for the discussion and vote. But in a continuation of the sharp practices for which he became notorious, he faced down the calls for him to do so, and recommended acceptance of the proposal. There was uproar, but a director, John Ellis appealed for calm reflection on the interests of the Midland, and the motion was passed. The Midland would lease the Leeds and Bradford at 10% of its £900,000 share capital, and moreover it would furnish any additional capital required to complete the line. Hudson made a considerable sum of money personally from this, but his reputation was sullied forever.[1][13]
Stretton comments that as far as Hudson's conduct was concerned, it "shook his reputation to the very foundation and proved to be the turning point, the beginning of the end of Mr Hudson's great and remarkable railway career".[1]
The process had more public repercussions: the Leeds and Bradford and the M&LR had planned to arrange a through connection between the two Bradford termini; this idea fell away, and the two terminus stations, 300 yards apart, remained forever unconnected.[10]
Extension to Skipton and Colne
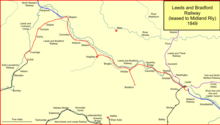
The Leeds and Bradford Railway had been authorised in 1844, and in the following parliamentary session it obtained authorisation to extend from Shipley to Skipton, there turning south-westward to Colne, where it would make a junction with the East Lancashire Railway. The ELR would give a through connection to Manchester and Liverpool.[14]
Another independent company was being projected at this time, the North Western Railway, which was planned to form a junction with the Leeds and Bradford extension line at Skipton, and continue west to Morecambe Bay, making a junction en route with the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway. The Midland Railway's alliance with the Leeds and Bradford Railway was proving fruitful, by giving access to these proposed connecting lines.[1]
| Leeds and Bradford Railway Act 1845 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for enabling the Leeds and Bradford Railway Company to make a Railway from Shipley to Colne, with a Branch to Haworth. |
| Citation | 8 & 9 Vict. c. xxxviii |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 30 June 1845 |
During the parliamentary hearings for the Leeds and Bradford Railway Bill, the company had given an undertaking to extend the line as far as Keighley. In fact the company considered the matter and decided to extend still further, to Skipton and Colne. An end-on junction at Colne with the East Lancashire Railway would give through access to Liverpool and Manchester.[14] This was authorised by the Leeds and Bradford Railway Act 1845 (8 & 9 Vict. c. xxxviii), of 30 June 1845. This was an authorising act of Parliament, but there was never separate company for the extension: the L&BR was leased to the Midland Railway.[15][16]

The extension was opened in stages. The 6-mile line from Shipley to Keighley was ready for the Board of Trade inspection by Captain Simmons, which took place on 13 March 1847. Simmons approved the line for opening, and it did so on 16 March 1847.[17] The line from Keighley to Skipton, 9 miles, was inspected on 28 August 1847, and opened on 8 September 1847.,[5][18][17] from a double junction at Shipley to Keighley on 16 March 1847.[16] On 7 September 1847 a single line from Keighley to Skipton was in use; the line was doubled by the end of 1847. The continuation to Colne was opened on 2 October 1848. In April 1849 the connecting Lancashire lines were ready, and express passenger trains started running between Leeds and Liverpool via Colne. At 81 miles in length, the journey took about 3+1⁄2 hours. For a period the LNWR trans-Pennine line was not yet open, so this was a competitive journey time.[19][20][21][22]
In August 1848 both the East Lancashire Railway and the L&BR had agreed that each would work its own line to Colne, and in the following month details were agreed as to the joint station there, which was to be built by the Leeds and Bradford Company. The line between Skipton and Colne opened on 2 October 1848. Although the line was useful in connecting intermediate communities to the railway network, it was seen as primarily a through route between Yorkshire and Lancashire.[16]
Absorbed by the Midland Railway
The Leeds and Bradford Railway met for the last time on 4 June 1851, to approve the transfer of their company to the Midland Railway; the motion was passed unanimously.[1] The L&BR was absorbed by the Midland Railway by an act of Parliament[which?] of 24 July 1851.[23][24]
Connecting and branch railways
As the Leeds and Bradford Railway was the first line in the area through which it ran, many later railways connected into it or branched from it.
North Western Railway
At the height of the railway mania, promoters saw that a railway connection might be fruitful between Skipton, shortly to be connected to the Leeds and Bradford Railway, and the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway, under construction and promising a connection to Scotland. The North Western Railway was incorporated on 26 July 1846 to build such a line to Low Gill in what was then Westmorland, now Cumbria. The company was unconnected with the London and North Western Railway, and is often referred to informally as the "Little" North Western Railway. The company found it impossible to fund the ambitious construction, and it opened only from Skipton to Ingleton on 30 July 1849.[25]
Keighley and Worth Valley Railway
Earlier schemes having failed, local interests proposed a railway in the Worth Valley and the Midland Railway agreed to operate it. After much delay in construction, the line opened as the Keighley and Worth Valley Railway on 13 April 1867. The Keighley station was on the Skipton side of Bradford Road level crossing; that was converted to a bridge in 1879 and the Keighley station was moved to the Leeds side of the bridge with separate platforms for Worth Valley trains on 6 May 1883.[26]
Developments at Bradford and Manningham

In 1868 a station was opened at Manningham, on the northern margin of Bradford. At first simply a suburb, it quickly developed into a conurbation in its own right, housing Manningham Mills, built in the 1870s and forming Europe's largest silk spinning mill. In 1890 the Market Street terminus at Bradford was redeveloped as a six platform station.[10]
Barnoldswick branch
The Barnoldswick Railway was authorised by an act of Parliament, the Barnoldswick Railway Act 1867 (30 & 31 Vict. clxxxi), of 12 August 1865 to build a two-mile branch from Earby to the cotton town of Barnoldswick. The branch was opened on 8 February 1871, and it was worked by the Midland from the outset. The little company was absorbed by the Midland Railway by the Midland Railway Act 1899 (62 & 63 Vict. c. cvii) of 13 July 1899. The line was not well-used, and it closed to passengers on 27 September 1965, and to goods on 1 August 1966.[27][28][29][30][31][32]
GNR at Shipley
The Great Northern Railway opened a line from Bradford to its own terminus at Shipley, in 1874. The GNR ran alongside the Midland line at Shipley, but although a connection was made (on 1 November 1875), through running was discouraged for many years.[33]
Settle and Carlisle Railway

The North Western Railway remained an insignificant minor railway, only reaching from Skipton to Ingleton on the Lancaster and Carlisle main line. The Midland Railway had pinned its hopes on reaching Carlisle over the NWR and the Ingleton connection; the LNWR as successor to the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway did all it could to frustrate this use of the line, and at length the Midland Railway decided to construct its own line to Carlisle: the Settle and Carlisle Line. The Midland had leased the North Western Railway from 1 January 1859, and absorbed it on 1 July 1871.[34] The Carlisle line started at Settle, bringing the Leeds and Bradford line and its extension to Skipton onto a new main line. It opened on 2 August 1875 for goods and on 1 May 1876 for passengers.[35][36][37]
Connections to Ilkley
The Midland Railway and the North Eastern Railway agreed to construct a joint railway between Otley and Ilkley, the Otley and Ilkley Joint Railway. The NER built its own connection to Otley from Arthington, and the Midland Railway opened a connection from the former Leeds and Bradford at Apperley Junction to form a triangular junction at Milner Wood and Burley in Wharfedale, giving connection to Otley and Ilkley respectively. The lines opened on 1 August 1865 to passengers, 1 October 1866 to goods.[38][39]
The Midland Railway opened a direct line from Shipley (Guiseley Junction) to Guiseley forming a triangular junction off the original Leeds and Bradford main line, opening it on 4 December 1876.[40][39]
On 16 July 1883 a scheme for a line 11+1⁄2 miles long from Skipton to Ilkley was authorised. It opened on 1 October 1887 and was served by two platforms at Skipton quite distinct from the rest of the station; the line climbed to cross over the main line and curved away towards Embsay.[27][40][39]
Train services
On 1 June 1874 the first regular passenger service to include Pullman cars went into operation between Bradford and London, the southbound train departing at 8.30am and reaching St Pancras at 2.05pm. The down train departed from St Pancras at midnight with arrival at Bradford at 5.30am. Lucky passengers were allowed to sleep on until a more civilised hour before detraining. In true Midland style this train made history by being the first British one which was both heated and which allowed passengers to move from one end to another, even though they had to negotiate the American-style open ends.[41] However the service was withdrawn after 30 April 1876 so that the Pullman cars could be used on the new Settle and Carlisle line.[42]
Skipton to Colne in the twentieth century
Local passenger services on the Skipton to Colne section were handled by diesel multiple units from 4 January 1960, and most trains on the route were dieselised from 6 March 1961. The final ordinary passenger service on the Skipton to Colne route was on 1 February 1970, but an enthusiasts' special ran the following day. The former Midland Railway station at Colne was later demolished. As a terminus from the Burnley direction, it was provided with a minimal one-platform facility, having no descent from the Leeds and Bradford Railway.[43]
Location list
Leeds to Bradford
- Leeds (Wellington); opened 1 July 1846; temporary station replaced by permanent building by autumn of 1849; combined with Leeds New station as Leeds City 2 May 1938;
- Hunslet Junction;
- Armley; opened late September or 1 October 1847; Canal Road added 25 September 1950; station moved from east of Canal Road to west between 1908 and 1921
- Kirkstall; opened 16 July 1846; closed 22 March 1965;
- Kirkstall Forge; opened 2 July 1860; closed 1 August 1905; reopened 19 June 2016; still open;
- Newlay; opened 1 September 1846; closed 22 March 1965;
- Calverley Bridge; opened between 16 and 30 July 1846; renamed Calverley & Rodley 1847 or 1848; closed 22 March 1965;
- Apperley Junction; divergence of Guiseley branch 1865 to date;
- Apperley Bridge; opened 16/30 July 1846; closed 22 March 1965; new station opened 440 yards nearer Leeds opened 13 December 2015; still open;
- Thackley Tunnel;
- Idle; opened by 1 September 1847; closed September 1848;
- Shipley, Guiseley Junction; convergence from Guiseley; 1876 to date;
- Shipley; opened by 16 July 1846; re-sited about 1/8 mile north summer 1849; made triangular 14 May 1979 for down trains, 9 March 1980 for up; still open;
- Frizinghall; opened 1 February 1875; closed 22 March 1965; reopened 7 September 1987; still open.
- Manningham; opened 17 February 1868; closed 22 March 1965;
- Valley goods;1877 - 1984;
- Bradford; opened 1 July 1846; probably not known as Bradford Market Street until 1875 just B M S; replaced by Bradford Forster Square opened 2 March 1890; Forster Square added in Bradshaw 2 June 1924; station resited 11 June 1990.[44]
Shipley to Colne
- Shipley; above;
- Saltaire; opened 1 April 1856; closed 22 March 1965; reopened 9 April 1984; still open;
- Crossflatts; opened 17 May 1982; still open;
- Thwaites; opened 1 June 1892; closed 1 July 1909;
- Keighley; opened 16 March 1847; relocated 6 May 1883; still open;
- Keighley and Worth Valley Railway 1861 - 1962;
- Steeton; opened 7 September 1847; renamed Steeton & Silsden 1 September 1868; re-sited north of level crossing 28 February 1892; closed 22 March 1965; reopened 14 May 1990; still open;
- Kildwick; opened 7 September 1847; re-sited 16 chains west 7 April 1889; closed 22 March 1965;
- Cononley; opened 7 September 1847; closed 22 March 1965; reopened 20 April 1988; still open;
- Skipton; convergence from Bolton Abbey 1888 – 1965 (to Embsay only 1968); and Grassington 1902 - 1969;
- Skipton North Junction; divergence to North Western Railway 1849 and Settle & Carlisle 1875;
- Elslack; opened December 1848; closed 3 March 1952;
- Thornton; opened 14 October 1878; closed 23 May 1955;
- Barnoldswick Junction; divergence to Barnoldswick 1871 - 1966;
- Foulridge; opened 2 October 1848; closed 5 January 1959;
- Colne; opened 2 October 1848; end on junction to Manchester and Leeds Railway; still open.[44]
Notes
- ^ The abbreviation L&BR is more commonly seen referring to the London and Birmingham Railway.
- ^ Leeds obtained city status in 1893; Bradford became a city in 1897.
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Clement E Stretton, The History of the Midland Railway, Methuen & Co, London, 1901, pages 116 to 120
- ^ Charles Hadfield and Gordon Biddle, The Canals Of North West England, volume 1, David and Charles, Newton Abbot, 1970, ISBN 0-7153-4956-2, pages 80 and 81
- ^ a b David Joy, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: Volume 8: South and West Yorkshire, David St John Thomas, Newton Abbot, second edition 1984, ISBN 0 946537 11 9, pages 76 to 78
- ^ Donald J Grant, Directory of the Railway Companies of Great Britain, Matador, Kibworth Beauchamp, 2017, ISBN 9781788037686, page 414
- ^ a b c E F Carter, An Historical Geography of the Railways of the British Isles, Cassell, London, 1959, page 86
- ^ a b c A Haigh, Railways in West Yorkshire, Dalesman Books, Clapham, second edition 1978, ISBN 0 85206459 4, page 8
- ^ Martin Bairstow, Railways Through Airedale and Wharfedale, self published by Bairstow, Pudsey, 1985, ISBN 0 9510302 2 1, page 19
- ^ Joy, Yorkshire, page 39
- ^ Roy Williams, The Midland Railway: a New History, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 1988, ISBN 0 7153 8750 2, page 52
- ^ a b c Joy, Yorkshire, page 78
- ^ Donald Binns, The Skipton – Colne Railway and the Barnoldswick Branch, Trackside Publications, Skipton, 1995, ISBN 1 900095 00 9, page 3
- ^ Grant, page378
- ^ Joy, Yorkshire, pages 62 and 77
- ^ a b Joy, Yorkshire, page 61
- ^ Carter, pages 107 and 108
- ^ a b c Binns, page 7
- ^ a b Bairstow, page 20
- ^ Haigh, page 9
- ^ Gough, John (1989). The Midland Railway : a Chronology (Revised and expanded ed.). Mold, Clwyd: Railway & Canal Historical Society. ISBN 0-901461-12-1. pages 162-8, 171-5
- ^ M D Greville, Chronology of Lancashire Railways, Reprinted from the Transactions of the Historic Society of Lancashire and Cheshire, volume 105, 1953, page 197
- ^ Joy, Yorkshire, page 62
- ^ G O Holt, revised by Gordon Biddle, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume X: the North West, David St John Thomas, Newton Abbot, 1986, ISBN 0 946537 34 8, page 172
- ^ Grant, page 307
- ^ Binns, page 5
- ^ Holt, revised Biddle, pages 175 – 177
- ^ Bairstow, page 21
- ^ a b Holt, revised Biddle, page 175
- ^ Gordon Suggitt, Lost Railways of Lancashire, Countryside Books, Newbury, 2003, ISBN 1 85306 801 2, pages 77 and 79
- ^ Christopher Awdry, Encyclopaedia of British Railway Companies, Patrick Stephens Limited, Wellingborough, 1990, ISBN 1 85260 049 7, page 60
- ^ Carter, page 389
- ^ Grant, page 30
- ^ Binns, page 12
- ^ Joy, Yorkshire, page 95
- ^ David Joy, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain, volume XIV, the Lake Counties, David & Charles, Newton Abbot, 1983, ISBN 0 946537 02 X, page 42
- ^ Holt revised Biddle, page 180
- ^ Williams, page 93
- ^ Joy, Lake Counties, page 50
- ^ H C Casserley, Britain's Joint Lines, Ian Allan, Shepperton, 1968, ISBN 0 7110 0024 7, pages 159 and 160
- ^ a b c Joy, Yorkshire, pages 246 and 247
- ^ a b Bairstow, page 22
- ^ Williams, page 139
- ^ Joy, Yorkshire, page 99
- ^ Binns, page 21
- ^ a b M E Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England, Wales and Scotland: A Chronology, version 5.03, September 2021, Railway and Canal Historical Society, electronic download
