Kozyrev mirror

A Kozyrev mirror (Russian: Зеркало Козырева, romanized: Zerkalo Kozyreva), in Russian esoteric literature from the 1990s, is a pseudoscientific device made from long sheets of aluminum (sometimes from glass, or a reflecting, mirror-like material) curled into a cylindrical spiral. It is alleged to focus different types of radiation, including that coming from biological objects, when those objects are placed inside it.[1][2] Kozyrev mirrors were used in experiments related to extrasensory perception (ESP), conducted in the Institute of Experimental Medicine of Siberia, division of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Name
This device is named after the astronomer Nikolai Aleksandrovich Kozyrev.
Reported uses
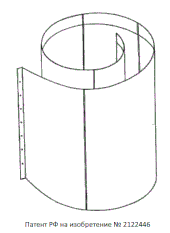
Humans, placed into the spirals, allegedly experienced anomalous psycho-physical sensations.[4]
Kozyrev mirrors were shown in a documentary on the Russian state TV channel[5] and articles about them were published in tabloid newspapers in Russia and Ukraine[6] but not in scientific journals.
There is a claim that during one of early experiments in the Arctic village of Dikson, scientists placed an ancient symbol of Trinity into a mirror installation and perceived a field of force around the setup. The experiment was led by Vlail Kaznacheev, of the Russian Academy of Medical Science.[citation needed]
Materials
Highly conductive pure alloy of aluminium built into a spiral shape with a magnetic alloy on the inside layer of the structure.[citation needed]
References
- ^ RU96113190A, Казначеев, В. П. & Трофимов, А. В., "DEVICE FOR CORRECTION OF PSYCHOSOMATIC HUMAN DISEASES", issued 1998-10-27
- ^ Kaznacheev, Vlail (1992). Cosmic consciousness of humanity : problems of new cosmogony. Russia. pp. 33–36.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "RU212244: Device for correction of man's psychosomatic diseases". Scribd. Retrieved 13 August 2014.
- ^ Энциклопедия чудес, загадок и тайн (Encyclopaedia of miracles, riddles and mysteries). Moskva. 2006.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: Mirrors - Breaking the Future. YouTube.
- ^ "NovaYA - Онлайн журнал для женщин".
External links
 Media related to Kozyrev mirror at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kozyrev mirror at Wikimedia Commons
