Heathrow Terminal 5 station
| Heathrow Terminal 5 | |
|---|---|
 Heathrow Terminal 5 station platform as seen in June 2022 | |
| Location | Heathrow Terminal 5 |
| Local authority | London Borough of Hillingdon |
| Managed by | Heathrow Express |
| Owner | Heathrow Airport Holdings |
| Station code(s) | HWV |
| Number of platforms | 4 (6 total) |
| Accessible | Yes[1] |
| Fare zone | 6 (excluding Heathrow Express services) |
| National Rail annual entry and exit | |
| 2019–20 | |
| 2020–21 | |
| 2021–22 | |
| 2022–23 | |
| 2023–24 | |
| Railway companies | |
| Original company | Heathrow Airport Holdings |
| Key dates | |
| 27 March 2008 | Station opened |
| Other information | |
| External links | |
| Coordinates | 51°28′20″N 0°29′17″W / 51.4723°N 0.488°W |
Heathrow Terminal 5 is a shared railway and London Underground station serving Heathrow Terminal 5. It serves as a terminus for Heathrow Express services to Paddington, and for Elizabeth line and London Underground Piccadilly line services to central London. It is managed and staffed by Heathrow Express.[3]
The London Underground section of the station is situated in Travelcard Zone 6; it is the westernmost below-ground station on the network. It is also the westernmost National Rail station in London.
History
Following the longest public inquiry ever undertaken in the UK,[4] construction of the station was granted in November 2001 by transport minister Stephen Byers as part of the approval of the Heathrow Terminal 5 project.[5][6] The proposed terminal site was not welcomed by London Underground, as it would be impossible for all three stations to be served from the same route. Instead, twin tunnels would be built from Terminals 1, 2, 3 to the new terminal.[7]
Construction of the extension as part of the T5 construction took 6 years, funded by British Airport Authority (BAA). As part of the construction, the Terminal 5 project team shut down two aircraft stands from Terminal 3 so that an access shaft could be constructed. The new junction was then built into a concrete box which connected all the underground tunnels.[8] Heathrow Terminal 4 tube station was closed for 20 months between January 2005 and September 2006 to allow these connecting junctions to be constructed.[9] Train testing started when the extension was handed over to London Underground on 18 July 2007.[10]
The station opened on 27 March 2008 coinciding with that of Heathrow Terminal 5.[11][12] It was designed by architects HOK in conjunction with Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners.[13] Although situated underground, parts of the station's roofing are made of translucent ETFE laminate panels, allowing natural daylight to flood down both ends of all six platforms.[14]
Since May 2022, Heathrow Terminal 5 has been served by the Elizabeth line.[15]
Services
Heathrow area rail services | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Terminal 5 station is the only one at Heathrow Airport where Heathrow Express, Elizabeth line and Piccadilly line services share the same station. The following rail services are provided:[16]
- Piccadilly line from platforms 5 and 6: half the trains on the Heathrow branch terminate here, via Hatton Cross and Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3. The other half do not serve Heathrow Terminal 5, running instead via the loop to service Heathrow Terminal 4 and Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3, before returning eastbound.
- Heathrow Express terminus to and from Paddington station from platforms 3 and 4.
- Elizabeth line terminus to and from Shenfield station from platforms 3 and 4.
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terminus | Piccadilly line | Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 towards Cockfosters or Arnos Grove | ||
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
| Terminus | Heathrow Express | Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 towards London Paddington | ||
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
| Terminus | Elizabeth line | Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 towards Shenfield | ||
Free intra-terminal transfers
Until 2012, free transfer was not possible between terminals via the Underground, unlike on the Heathrow Express. In January 2012, free travel was introduced for Oyster card and contactless payment card holders between the Heathrow stations on the Piccadilly line. Journeys from Heathrow Terminal 5 to Terminal 4 via the Piccadilly line require a change at Hatton Cross; this journey is free.
Future links
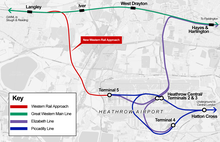
Network Rail has put forward a proposal for a Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a short spur of track in tunnel which would run from a junction east of Langley to Terminal 5 station. This would permit Great Western Main Line trains to run directly from Slough and Reading into Heathrow, without the need to change at Paddington. The proposal is currently at consultation stage and remains unconfirmed.[17]
In addition to the above rail links, Terminal 5 station also has two safeguarded "heavy rail" platforms for use by a west-facing connection to the National Rail network. The south-leaning proposal would spur off the Waterloo to Reading Line west of Staines railway station (originally dubbed Heathrow Airtrack, with a newer proposal named Heathrow Southern Railway). It proposes direct rail services to London Waterloo, Reading, Woking, Guildford and Gatwick Airport.[18] Due to the cost of replacing three level crossings, one in a very urban part of Egham, the proposals are currently unfunded.
Connections
London Buses routes 350, 423, 482, 490 and night route N9 serve the station.[19] First Berkshire & The Thames Valley, National Express and Oxford Bus Company also operate connecting bus and coach services.
References
- ^ "Step free Tube Guide" (PDF). Transport for London. April 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 May 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "Estimates of station usage". Rail statistics. Office of Rail Regulation. Please note: Some methodology may vary year on year.
- ^ "Station facilities for Heathrow Terminal 5 (Rail Station Only)". National Rail Enquiries. Retrieved 1 September 2020.
- ^ "Heathrow Terminal 5 Inquiry". Department for Transport. January 2005. Archived from the original on 24 December 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ Harper, Keith (20 November 2001). "Long-awaited go-ahead for Heathrow terminal 5". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "Green light for Piccadilly line extension to new Terminal 5". thetube.com (Press release). 20 November 2001. Archived from the original on 3 February 2003. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ^ Horne, Mike (2007). The Piccadilly Tube – A History of the First Hundred Years. Capital Transport. pp. 137–138. ISBN 978-1-85414-305-1.
- ^ "Tube One Step Closer for Heathrow Terminal 5" (Press release). Transport for London. 14 September 2006. Archived from the original on 17 August 2020. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- ^ "Tube one step closer for Heathrow Terminal 5". Transport for London (Press release). 14 September 2006. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ^ "First Piccadilly line trains travel to Heathrow Terminal 5". Transport for London. 18 July 2007. Retrieved 9 September 2020.
- ^ "First Piccadilly line passengers travel to Heathrow Terminal 5". Transport for London (Press release). 27 March 2008. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ^ "Heathrow Terminal 5 opens" (PDF). London Underground Railway Society. May 2008. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "Terminal 5, Heathrow - London - Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners". Rogers Stirk Harbour + Partners. Archived from the original on 27 May 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ^ "Heathrow Airport T5: London Architecture", e-architect, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ^ "Heathrow - New agreement to boost Heathrow rail services". Heathrow Media Centre. 4 July 2017. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ Transport for London (March 2008). "Central London to Heathrow" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 September 2008. Retrieved 22 March 2008. - transport map for Heathrow showing Underground, Heathrow Express and Heathrow Connect rail, and the N9 night bus
- ^ "Heathrow rail link -". Network Rail. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ "Heathrow Airtrack". BAA. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- ^ Heathrow Airport Terminal 5 Transport for London
External links
- Train times and station information for Heathrow Terminal 5 station from National Rail
- Proposed AirTrack Rail Link

