Health impacts of sawdust

Any type of woodworking that involves cutting, either by hand or machine, releases sawdust (or wood dust). Because fine sawdust can float through the air, it can be easily inhaled without proper protection, leading to damaging injuries to a woodworker's skin and lungs. Sawdust is also an IARC group 1 Carcinogen.
Exposure

Sawdust is most commonly generated when working with wood, whether it be sanding, sawing, or routing. Uncommonly, sawdust exposure can come from sweeping dust off of old furniture, which may haw sawdust particles inside. Occupations at higher risk include carpenters, construction workers, shipbuilding workers, cleaning or maintenance staff (sawdust generation or reintroduction), and workers in logging, sawmills, furniture, and cabinet making.[1]
When the dust is inhaled, it is deposited in the nose, throat, and other airways. The amount of dust deposited within the airways depends on the size, shape, and density of the dust particles and the strength (turbulence and velocity) of the air-flow. Particles with a diameter larger than 5 μm (inspirable particles) are deposited almost completely in the nose, whereas particles 0.5 to 5 μm in diameter (respirable particles) are deposited in the lower airways (IARC 1981, 1995).[2]
Wood dust usually is measured as the concentration of airborne dust, by particle size distribution, by type of wood, and by other characteristics of wood. Total airborne dust concentration is reported as mass per unit volume (usually milligrams of dust per cubic meter of air). Wood dust generally is collected by a standard gravimetric method, whereby a sampling pump is used to collect a known volume of air through a special membrane filter contained in a plastic cassette.[2] Some sampling studies reported that the particle size distribution varied according to the woodworking operation, with sanding producing smaller particles than sawing, but others found no consistent differences (IARC 1995). The majority of the wood-dust mass was reported to be contributed by particles larger than 10 μm in aerodynamic diameter; however, between 61% and 65% of the particles by count measured between 1 and 5 μm in diameter (IARC 1995).[2]
Handling of compost
Exposure to wood dust also occurs through handling of compost containing wood dust. One study measured dust concentrations resulting from handling of compost material consisting of successive layers of chopped leaves, bark, and wood; visible clouds of fine particles were easily generated when the compost material was agitated.[2] The reported background concentration of respirable dust sampled upwind of the compost pile was 0.32 mg/m3. During loading and unloading of compost, samplers in the breathing zone detected inspirable dust at 0.74 mg/m3 and respirable dust at 0.42 mg/m3. Samples collected directly from the visible clouds of particles generated by compost agitation contained inspirable dust at 149 mg/m3 and respirable dust at 83 mg/m3 (Weber et al. 1993).[2]
Workers
The National Occupational Exposure Survey (conducted from 1981 to 1983) estimated that nearly 600,000 workers were exposed to woods (NIOSH 1990). Teschke et al. (1999) analyzed 1,632 measurements of personal time-weighted-average airborne wood-dust concentrations in 609 establishments on 634 inspection visits that were reported to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration Integrated Management Information System between 1979 and 1997.[2] Exposures ranged from less than 0.03 to 604 mg/m3, with an arithmetic mean of 7.93mg/m and a geometric mean of 1.86mg/m. Exposure levels decreased significantly over time; the unadjusted geometric mean was 4.59 mg/m3 in 1979 and 0.14 mg/m3 in 1997.[2] Occupations with high exposure to wood dust included sander in the transportation equipment industry (unadjusted geometric mean = 17.5 mg/m3), press operator in the wood products industry (12.3 mg/m3), lathe operator in the furniture industry (7.46 mg/m3), and sander in the wood cabinet industry (5.83 mg/m3).[2] High exposures occurred in the chemical, petroleum, rubber, and plastics products industries, in sanding, pattern making, and mill and saw operations. The lowest exposures occurred in industrial pattern-making facilities, paper and paperboard mills, schools and institutional training facilities, and veneer and plywood mills.[2]
Dusty process
Use of hand-held electric sanders has been identified as a particularly dusty process that leads to dust exposure. Wood-dust concentrations vary with type of dust extraction, amount of wood removed, and type of sander (Thorpe and Brown 1994).[2] For electric belt sanders used to sand dowels, total dust concentrations ranged from 0.22 mg/m with external dust extraction to 3.74 mg/m without extraction, and concentrations of respirable dust ranged from 0.003 mg/m3 with extraction to 0.936 mg/m3 without extraction.[2] Rotary sanders tested with flat wood samples produced total dust concentrations ranging from 0.002 mg/m3 with extraction to 0.699 mg/ m3 without extraction; concentrations of respirable dust ranged from 0.001 mg/m3 with extraction to 0.088 mg/m3 without extraction. Comparable decreases in dust concentration were observed when dust extraction was used with electrical orbital sanders.[2]
Potential hazards
Both the skin and respiratory system can become sensitized to wood dust. When a person becomes sensitized to wood dust, he or she can suffer severe allergic reactions (such as asthma or dermatitis) after repeated exposure or exposure to lower concentrations of the dust.[3]
Other common symptoms associated with wood dust exposure include skin and eye irritation; nasal dryness and obstruction; and prolonged colds.[3] Different species of wood can cause different toxic effects. Human body absorbs the chemicals in the wood through the lungs, skin and digestive system, resulting in breathlessness, headaches, dizziness, cramps, irregular heartbeat and weight loss. Other substances used on or in wood (e.g., pesticides, paint, paint strippers, glues, adhesives, resins, waterproofing compounds, dyes, lacquers, varnishes and sealants, etc.) may also cause health problems.[1]
Sawdust is an IARC group 1 Carcinogen.[4] The OSHA permissible exposure limit for nuisance dust is 15 mg/m3 , total dust (5 mg/m3 , respirable fraction) 8 hour time weighted average. NIOSH has set a recommended exposure level of 1 mg/m3 total dust. The ACGIH has recommended a 0.5 mg/m3 Threshold Limit Value for western red cedar based on its asthma effects. Certain species of hardwood—such as oak, mahogany, beech, walnut, birch, elm, and ash— have been reported to cause nasal cancer in woodworkers. This is particularly true when exposures are high.[3]
Respiratory
Human lungs have the capability to filter out big chunks of sawdust. However, the main risk are the fine particles that can easily float in the air and bypass a lung's natural filter. These small particles clog up air passageways within the lungs. Symptoms such as sneezing, watery eyes and breathing problems are the first signs of damaging sawdust exposure.[5] Shortness of breath, decreased lung capacity and allergic reactions in the lungs (e.g., hypersensitivity pneumonitis) can also occur.[1] Breathing in wood dust can lead to asthma and lung cancer.[5]
Skin

Contact dermatitis can be caused from long exposure of sawdust with direct contact with skin. Itchiness is the leading symptom, followed with rashes, blisters, and scaling.[6]
Wood Types
Woods such as plywood or fiberwood produce above average amounts of sawdust due to being primarily made of wood chips or particles, and are especially dangerous. When cut, these chips and particles are released into the air, only smaller.
Some woodworkers may have allergic reactions to certain woods, which can amplify the symptoms above if not treated.
Prevention
Engineering controls


- Wood dust is emitted at high velocity by moving or spinning machine components. The primary method of controlling wood dust is with local exhaust ventilation (LEV), which removes dust at or near its source. LEV systems can often be integrated with machine guards. Exhaust hoods should be located as close as possible to the emission source, either on the woodworking machinery itself or near to the machine. The local exhaust systems should have an efficient air cleaning device.[3]
- For LEV systems to provide maximum protection, they should be properly maintained. Check and clean ducts and dust collectors at regular intervals. Inspect ducts to ensure that they are not loose, broken, or damaged. Check the V-belts on the drive units of belt-driven exhaust fans for slippage or breakage. Make sure the duct velocity is maintained at a minimum of 2,500 to 4,000 feet per minute to effectively remove light, dry saw dust, heavy wood chips, and green shavings, and to prevent these from plugging the system.[3]

- Sanders, shapers, and routers generally produce the greatest amount of dust. Conventional means for exhausting these machines are not very effective. NIOSH has developed means for controlling dust exposure from these machines. These methods either increase the exhaust volume or velocity, or supply pressurized air to help blow dust particles from the machine into an exhaust hood.[3]
LEV recommendations for individual machines
- Exhaust the saw through the bottom of the table. Provide LEV under the blade slot. To decrease the open area between the table and the lower hood, attach a strip of flexible material to the machinery that will cover this area when the hood operates.[3]
- For increased dust control, add a local exhaust hood above the top of the saw blade. The hood should be integrated with the guard on the upper part of the blade.[3]
- For further information on control of wood dust from circular and other kinds of table saws, please consult the NIOSH Hazard Controls 10.[3]
- Provide LEV under the blade slot. To increase the collection area of the hood, add holes (1/8 inch in diameter) in the table around the ot area.[3]
- To collect wood dust from the saw teeth, place a suction nozzle above the table, at the rear of the w blade.[3]
- Place a hood underneath the machine head.[3]
- Control each head with an open-faced hood, located on the table behind the head. For additional protection, use a combination of fixed and adjustable hoods. A fixed open-faced hood can be attached to the rear of the table between the shaper heads. Movable open-faced hoods also can be used on the table. For further information please consult the NIOSH Hazard Controls 5: Wood Dust from Shapers.[3]
- Place open-faced hoods above the spinning heads of planers. Each head can be ventilated separately, or one hood can be used to control several heads.[3]
- Place open-faced hoods around the spinning components of moulders. Each head should be separately controlled.[3]
- For increased dust control, add a small open-faced hood along the side of the moulder between the main head and the worker.[3]
- Place an open-faced hood attached to a movable mechanical arm at the point of operation.[3]
- Sanders produce a considerable amount of dust and are difficult to control. Conventional methods do not effectively remove dust. New innovative systems have been developed for controlling dust emissions from horizontal belt sanders, large-diameter disc sanders, random orbital hand sanders, and orbital hand sanders. Although these systems are not yet commercially available, more information can be obtained from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The following NIOSH Hazard Controls deal with horizontal belt sanders, large diameter disc sanders, random orbital hand sanders and orbital hand sanders respectively: HC4, HC 7, HC 8 and HC 9. Some of these systems are discussed below.[3]
- Enclose disc sanders with an exhaust hood, installed below the table; cover the back of the sanding disc at points above the worktable. A system has been developed that supplies pressurized air to the disc inside the hood. The jet of high speed air blows dust particles out of the disc air layer so that they can be captured by the exhaust hood.[3]
- On random orbital sanders, use an aspirator in combination with a perforated sanding pad. The aspirator creates a vacuum that draws wood dust up through the holes of the sanding pad. An innovative dust control system has been developed that uses additional exhaust and a slottedanding pad.[3]

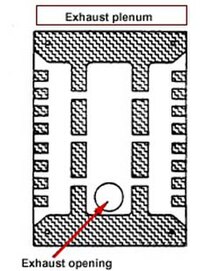
- A new dust control plenum has been designed for orbital sanders. The plenum fits between the sanding pad and the sander body and has a series of exhaust slots along its edges.[3]
- Enclose horizontal belt sanders with exhaust hoods covering each end of the belt. These hoods control the dust carried by the belt. To further control dust emissions, install an additional hood above the area where the wood is processed. To increase the effectiveness of this system, add a narrow hood and a stripper.[3]
- Place two open-faced hoods behind the heads of the router table. Connect the hoods to the exhaust ductwork via a flexible hose.[3]
- Locate an open-faced or slot hood at the rear end of the router table.[3]
Woodworking Equipment

- A vacuum is a simple way to prevent sawdust exposure. Any sawdust remaining on the ground is prone to being kicked up and inhaled. Vacumming regularly after each cut will minimize any exposure.
- A dust bag or collector can be attached to most woodworking machinery, collecting any sawdust automatically.
Clothing and Gear
One way to prevent sawdust exposure is by wearing the gear for woodworking.
- A dust mask will prevent sawdust from being inhaled.
- Gloves and long but fitting clothes will prevent sawdust from irritating the skin.
History of health concerns and regulation
See also
- Air pollution
- Angle grinder
- Construction waste
- Do it yourself
- Dust explosion
- Formaldehyde
- Environment and health
- Health impact of asbestos
- Health effects of coal ash
- Health effects of wood smoke
- Hierarchy of hazard controls
- Renovation
- Ultrafine particles
- Wood ash
- Wood glue
- Wood preservative (e.g., pesticides)
References
- ^ a b c Government of Canada, Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety (2023-06-13). "CCOHS: Wood Dust - Health Effects". www.ccohs.ca. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Report on Carcinogens, Fifteenth Edition, Wood Dust" (PDF). NTP (National Toxicology Program), Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service. Retrieved 29 Oct 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac "eTool : Woodworking". Occupational Safety and Health Administration. OSHA. Retrieved 29 Oct 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "List of Classifications, Agents classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–124". IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Risk to Humans. IARC. 7 July 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
- ^ a b Zealand, WorkSafe New (2022-12-19). "Wood dust: controlling the risks". WorkSafe. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
- ^ Smith, Chris (2017-04-12). "The Hidden Health Dangers of Sawdust". Monarch Metal. Retrieved 2023-10-20.
Attribution:
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
