Habar Yoonis
| Habar yunis هبر يونس | |
|---|---|
| Isaaq Somali Clan | |
| Ethnicity | |
| Location | |
| Descended from | Sheikh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad |
| Parent tribe | Isaaq |
| Branches |
|
| Language | |
| Religion | Sunni, Islam |
 |
| Part of a series on |
| Somali clans |
|---|
The Habar Yoonis (Arabic: هبر يونس, full Nasab: Said ibn Al-Qādhī Ismā'īl ibn ash-Shaykh Isḥāq ibn Aḥmad[1]) alternatively spelled as Habr Yunis is a major clan part of the wider Isaaq clan. As descendants of Ismail bin Sheikh Isaaq, its members form a part of the wider Habar Magaadle confederation which constitutes the largest sub-clan of the Isaaq.[2][3][4][5]
Distribution
The Habar Yoonis inhabit the western Togdheer, Eastern Maroodi Jeex, southern Sahil, northern and western Sool and north,central and western and Eastern Sanaag regions of Somaliland. They also inhabit the Degehbur,and Wardheer zones in the Haud region of Ethiopia. They also have a large settlement in Kenya where they are known as a constituent segment of the Ishaqid (Isahakia) community.[6][7] The Ishaq Arreh and musa abdallah subclans of the Habr Yunis inhabit the Maroodi Jeex region of Somaliland.[8]
History
Medieval period
Historically the Habr Yunis took part in the conquest of Abyssinia and were part of the Adal Sultanate and are mentioned in the book Futuh Al-Habash (Conquest of Abyssinia) as the Habar Magaadle. The Habar Magaadle are known for producing a historical figure known as Ahmad Gurey bin Husain who was the right-hand man of Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi.[9]
I. M. Lewis discusses the existence of another leader named Ahmad Gurey, and suggests that the two leaders have been conflated into one historical figure:
The text refers to two Ahmad's with the nickname 'Left-handed'. One is regularly presented as 'Ahmad Guray, the Somali' (...) identified as Ahmad Gurey Xuseyn, chief of the Habar Magadle . Another reference, however, appears to link the Habar Magadle with the Eidagal. The other Ahmad is simply referred to as 'Imam Ahmad' or simply the 'Imam'.This Ahmad is not qualified by the adjective Somali (...) The two Ahmad's have been conflated into one figure, the heroic Ahmed Guray[10]
Some descendants of the Habr Yunis knights who participated in the conquest still inhabit regions west of Harar near Hirna. Ulrich Braukämper in A History of the Hadiyya in Southern Ethiopia states :
Amongst the troops recruited from the eastern pans of the Horn of Africa for the Jihad, warriors of Somali descent occasionally stayed in the conquered territories of the west and settled in the principalities of Hadiyya, Sarha and Bale. In present-day Arsi land there are still sporadic recollections of these Ogaadeen peoples. Occasionally they are still identifiable by their ethnic origin, like the Habr Yuunis and Garjeeda. Preserving bonds of interethnic clan relations with the Somali inhabited region...the Habr Yuunis from the vicinity of Hirna in Carcar joined the exodus to the west at the time of Amir Nur and occupied an area suitable for livestock-breeding east of Lake Zay.
Habr Yunis Sultanate

The sultanate was founded by the Rer Ainanshe sub branch of the Habr Yunis. The clan takes its name from their 18th century Patriarch Ainanshe Hersi who was a Chieftain of the Habar Yoonis clan. As was the norm of Somali chieftains, Ainanshe had multiple wives. His first wife belonged to the Jibrahil clan and was the mother of his eldest son Sugulle who would go on to found the Ba Jibrhil Rer Sugulle which is the section of the clan that all the Habr Yunis Sultan's descend.[11][12] Ainanshe's other wives Mun, Basla and Egalo bore him 16 sons who are collectively known as the Baha Ainanshe.[13] The etymology of the name Ainanshe originates from the word Ainan which in Somali means the horse's reins, when suffixed with she it takes on the meaning of one who is holding the reins, leading and guiding from disaster.[14] Ainanshe's tomb is located to the south of Burao in the town of Jameecada Caynaanshe near the Oodweyne district border.
Enrico Baudi i Vesme who visited Burao in 1889 met the sons of Burao Chieftains Guled Ahmed Sugulle and Awad Gal, they relayed to him the following:
..They told me the story of their tribe. The chieftain of the Habr Yunis lineage, named Ainanshe, had 17 sons, one of whose name was Sugulle. First they stayed together, then they separated, forming one Rer Sugulle, who are the most numerous, the other 16 sons together, the Baha Ainanshe. When, a few years ago, there was war between Awad and Nur, the latter ended up settling in Toyo with part of the Habr Yunis.[15]
Volume 7 of Etiopia rassegna illustrata dell'Impero describing the Rer Ainanshe states :
Rer Ainanshe (Baha) and Rer Sugulle belonging to the Ismail Arreh are the center of the Habr Yunis group and also their backbone. Their prestige is probably the highest among the Somalis, and both in number, compactness, fighting ability and raids may perhaps be considered to occupy the first place together being equal to each other. The Rer Sugulle, in fact, belongs to the main branch of the Ainanshe but can be considered a separate group. The two are not at all interwined but in case of a Habr Yunis movement the tribe may gather around these two sub-tribes.[16]

The Habr Yunis Sultanate finds its roots in the Isaaq Sultanate which was established by the Rer Guled branch of the Eidagale after the Isaaq successfully defeated the Absame clan at Lafaruug in the 17th century. With time the Habr Yunis and later the Habr Awal and Habr Je'lo would break from the Isaaq Sultanate with the Habr Yunis forming their own Sultanate led by Sugulle the son of the previous Habr Yunis Chieftain, Ainanshe Hersi.[17][18] The Sultan Deria Sugulleh would establish his capital at Wadhan (Waram) near the Sheikh pass and tax and administer the affairs of the Habr Yunis from the town. Large caravans bound for Berbera would pass through Habr Yunis territory through Burao and then Wadhan and proved a lucrative source of income for Sultan Deria.[19] Deria was succeeded by Hersi the son of Aman Deria who had died before his Sultan father, he was an important Habr Yunis chieftain. Vesme Baudi travelling through Habr Je'lo country east of Burao in 1889 gives an account of Aman's tomb.
At nine o'clock we arrived at Baiadowal, on the Thug Dehr, a charming site, where the trees form a small forest, in which the most delightful coolness is enjoyed. A few hundred meters away there is a tomb surrounded by a palisade of tree trunks made with care. There rests a chieftain of the Habr Junis, by name Ohman-Dhirrin [Aman Deria]..his tribe had intermingled with the Habr Gialeh, and when that chief had died, they had made him that tomb with a palisade in memory of his great merits.[20]
Hersi Aman is remembered for his successful conquests and expansion of Garhajis territory in the Haud.[21] His reign was abruptly ended when he was killed in a battle against the kindred Baha Sugulleh. Ismail Mire in his famous poem Ragow Kibirka Waa Lagu Kufaa (Pride Comes Before a Fall) comments on Hersi's conquests, pride and desire to rule.
Kaysaha adduun Ina Ammaan koos dhan buu helaye |
With worldly pride Ina Ammaan gained a whole land |
| —Ismail Mire Ragaw Kibirka Waa Lagu Kufaa[22] |
Dual Sultans Era

After the death of Sultan Hersi Aman, the Baha Deria and Baha Makahil sections of the Sugulle dynasty vied for the Sultanship, which divided the Habr Yunis clan into two factions, the Baha Deria faction led by Guled Haji crowned Awad Deria a surviving son of the Sultan Deria Sugulleh. The Bah Makahil crowned Nur Ahmed Aman a young Mullah and nephew of Hersi Aman. Nur was initially uneasy and preferred his life as a Mullah rather than being the Sultan designate. The Habr Yunis were not interrupted by the British Somaliland protectorate which had been established in 1884 and was still largely relegated to the coast and its capital of Berbera.[23][24] The two Sultans engaged in a lengthy war and divided the Sultanate's territory, where Awad ruled the Sultanate from his chosen capital of Burao and Nur from the Tuuyo plains and Oodweyne.[25]
Frank Linsly James visited Sultan Awad at Burao in 1884 and witnessed the dissenting situation between the two Sultans. Describing the political situation in the region and frequent raids between the two rival Rer Sugulleh factions and their allied Habr Yunis subclans
It appeared the great Habr Gerhajis tribe was divided into two rival factions, the one owning allegiance to Sultan Owd, the other to his cousin, Sultan Noor. Between these two the country was about evenly divided, and the border-line was an everlasting scene of wars and rumours of wars, cattle raids, and attempted murders.[26]
The Haber-Gerhajis tribe had formerly been under one Sultan and were very powerful, making frequent raids into Ogadayn, but on his death, two cousins, Awad and Nur, divided the country between them.[27]
Awad was killed fighting in Ogaden by the Reer Ali.[28][29] This allowed Nur to establish himself at Burao and rule over the entirety of the Habr Yunis. The Baha Deria still did not concede defeat and would eventually choose Awad's nephew, Madar Hersi, as their successor following Nur's death.[30] Sultan Nur convened a shir of the Habr Yunis and decided to draw lots to settle the dispute with his challenger Madar Hersi rather than continue the senseless infighting that had lasted since Hersi Aman's death. Sultan Nur won the draw and gave Madar Hersi 100 camels as compensation and was proclaimed the uncontested Sultan of the Habr Yunis.[31] The reunified rule under one Sultan Nur would last until the formation of the Dervish Movement several years later in 1899.
Early Dervish period
Sultan Nur had been the architect of disturbances at Berbera and was the man who narrated the famous story of French Catholic missionaries in Berbera converting Somali children.[32][33] According to the consul-general James Hayes Sadler this news was either spread or concocted by Sultan Nur of the Habr Yunis. Madar Hersi his former rival for the Sultan title had aided the Mullahs of Kob Fardod in recovering livestock that was previously looted by some of the Habr Yunis and this reignited after receiving aid from the Mullahs there notably Mohammed Abdullah Hassan.[34][35] Upon his visit to Oodweyne in July 1899 Sultan Nur convened a great shir of the western Habr Yunis clans and called on them to join the new Dervish movement and upon their refusal he would leave to Burao and successfully rallied the eastern sections of the clan. The Dervish would declare war from Burao on 1 September of 1899.[36] Madar was soon propagated as the legitimate Sultan by British authorities and managed the western sections of the clan throughout the period of the Dervish wars.
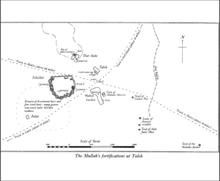
The last intelligence report mention of Sultan Nur in the Italian archives was in 1907.[37] After the death of Sultan Nur 1907/1908 in the Dervish camp at Taleh his son Dolal Nur ascended the sultanate in the dervish camp.[38]
Sultan Nur was buried by his dervish in a large domed tomb in Taleh, his tomb predated the later dervish forts. His white tomb in the dervish capital is a testimony to his contribution to the movement. Few dervish founders are commemorated in Taleh, numbering only four.[39]
William Archibald Macfadyen, a British geologist and the only scholar to study the structures of Taleh fort, mentioned the handful of tombs constructed by the dervish for their leaders and gave a detailed description of the tombs in 1931. In his article Macfayden only identified Sultan Nur's tomb by name out of the four dervish entombed in Taleh:
"South of the main cave-well is the considerable tomb of Abdullah Hasan senior, well plastered inside and out; it is now said to be empty. Adjoining this on the west is a walled garden with massive gateway and guard-house; the rest of the wall is not more than 5 feet high and plastered. There are still odd bushes and signs of cultivation to be seen, but the comparatively deep well in the middle is dry. To the east lies a row of four tombs. The most northerly is that of oneSoldan Nur of the Habr Yunis tribe; the next two, neither being plastered.and the first with the top left unfinished, are those of Hawiya notables whosenames my Somalis did not know. The most southerly tomb is that of aman of the Habr Jaalo tribe. The isolated tomb still farther east is that of'AbdullahHasan's mother. All the tombs are provided with narrow but very massive wooden doors, swinging about vertical extensions from top and baseof one side."[39]
After the Bombing campaign of the Taleh fort and the Dervish retreat into Ethiopia, Tribal Chief Haji Mohammad Bullaleh (Haji the Hyena), a cousin of Sultan Nur, commanded a 3000 strong army that consisted of Habr Yunis, Habr Je'lo and Dhulbahante warriors and pursued the fleeing Dervishes. They attacked Muhammad Abdallah Hassan and his army in the Ogaden region and swiftly defeated them, causing Muhammad to flee to the town of Imi. Haji and his army looted 60,000 livestock and 700 rifles from the dervishes, which dealt a severe blow to them economically, a blow from which they did not recover.[40][41][42][43]
Rulers
The Habr Yunis Sultanate had eight rulers throughout its duration and the institution of Sultan still lasts today with the Baha Deria leading I conflict still not being completely resolved. The Bah Makahil maintain a well respected pretender although the current Sultan Osman Ali Madar of the Baha Deria is considered as the Sultan of the Habr Yunis.[44]
| House of Ainanshe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Haji Sharmarke Ali Saleh, governor of Berbera, Zeila and Tadjoura

The Habr Yunis exercised real power over Zeila and its adjacent regions and had established themselves as a coastal power, with Sharmarke Ali Saleh (Musa Arreh) solidifying and consolidating his power in governing Zeila, Berbera and Tadjoura. In 1841 Sharmarke with fifty Matchlock men, two cannons and an army of mounted spearmen managed to invade Zeila and depose its Arab Governor, Mohammed Al Barr. Sharmarke used the canons to fire at the city walls which frightened Al Barr's followers and caused them to flee. Sharmarke succeeded Al Barr as the ruler of Zeila and its dependencies.[45][46] Sharmarke's governorship had an instant effect on the city, as he maneuvered to monopolize as much of the regional trade as possible, with his sights set as far as Harar and the Ogaden.[47] Having secured Zeila, in 1845 Sharmarke moved on to Berbera which at the time was experiencing instability as a result of a war between the Habr Awal Reer Yunis Nur and Reer Ahmed Nur sub-clans over the control of Berbera's trade. Sharmarke took advantage of this rivalry and supported the Reer Ahmed Nuh who had since been expelled from Berbera. Sharmarke took over Berbera and built four Martello towers in the vicinity of the town and garrisoned them with 30 Matchlock men. A war ensued with in the city as Reer Yunis Nuh tried gain a foothold within Berbera, the Reer Yunis Nuh were no match for Sharmarke and his modern weapons and thus failed. The Reer Yunis Nuh were expelled and moved to Bulhar[48] Sharmarke's influence was not limited to the coast as he had many allies in the interior of the Somali country and even further in Abyssinia. Among his allies were the Kings of Shewa. When there was tension between the Amir of Harar Abu Bakr II ibn `Abd al-Munan and Sharmarke, as a result of the Amir arresting one of his agents in Harar, Sharmarke persuaded the son of Sahle Selassie, the King of Shewa, to imprison on his behalf about 300 citizens of Harar then resident in Shewa, for a length of two years.[49] In 1855, in an act seen as defiant of foreign powers, Sharmarke refused to sell to M. Richet, the French agent at Jeddah, a house in Zeila, citing "how easily an Agency becomes a fort", and preferring "a considerable loss to the presence of dangerous friends".[50]
Burao Tax Revolt and RAF bombing

Sections of the Habr Yunis once again clashed with the British in 1922 after a heavy tax was imposed upon them at Burao, the Hersi Osman clan revolted in opposition to the tax and this caused them to clash with other sections of the Habr Yunis and the British colonial government. In the ensuing riot and shootout between the British and Hersi Osman, Captain Allan Gibb, a Dervish war veteran and district commissioner, was shot and killed. The British fearing they could not contain the revolt requested from Sir Winston Churchill, then Secretary of State for the Colonies, to send troops from Aden and Airplane bombers in order to bomb Burao and livestock of the revolting clans to quell any further rebellion.[51] The RAF planes arrived at Burao within two days and proceeded to Bomb the town with incendiaries, effectively burning the entire settlement to the ground.[52][53][54][55]
Telegram from Sir Geoffrey Archer, Governor of British Somaliland to Sir Winston Churchill the Secretary of State for the Colonies:
I deeply regret to inform that during an affray at Burao yesterday between Rer Sugulleh and Akils of other tribes Captain Gibb was shot dead. Having called out Camel corps company to quell the disturbance, he went forward himself with his interperter, whereupon fire opened on him by some Rer segulleh riflemen and he was instantly killed..Miscreants then disappeared under the cover of darkness. In order to meet the situation created by the Murder of Gibb, we require two aeroplanes for about fourteen days. I have arranged with resident, Aden, for these. And made formal application, which please confirm. It is proposed they fly via Perim, confining sea crossing to 12 miles. We propose to inflict fine of 2,500 camels on implicated sections, who are practically isolated and demand surrender of man who killed Gibbs. He is known. Fine to be doubled in failure to comply with latter conditions and aeroplanes to be used to bomb stock on grazing grounds.[56]
Sir Winston Churchill reporting on the Burao incident at the House of Commons:
On 25th February the Governor of Somaliland telegraphed that an affray between tribesmen had taken place at Burao on the previous day, in the course of which Captain Allan Gibb, D.S.O., D.C.M., the District Commissioner at Burao, had been shot dead. Captain Gibb had advanced with his interpreter to quell the disturbance, when 1954 fire was opened upon him by some riflemen, and he was instantly killed. The murderers escaped under cover of falling darkness. Captain Gibb was an officer of long and valued service in Somaliland, whose loss I deeply regret. From the information available, his murder does not appear to have been premeditated, but it inevitably had a disturbing effect upon the surrounding tribes, and immediate dispositions of troops became necessary in order to ensure the apprehension and punishment of those responsible for the murder. On 27th February the Governor telegraphed that, in order to meet the situation which had arisen, he required two aeroplanes for purposes of demonstration, and suggested that two aeroplanes from the Royal Air Force Detachment at Aden should fly over to Berber a from Aden. He also telegraphed that in certain circumstances it might become necessary to ask for reinforcements of troops to be sent to the Protectorate.[57]
James Lawrence author of Imperial Rearguard: Wars of Empire writes
[Gibb]..was murdered by rioters during a protest against taxation at Burao. Governor Archer immediately called for aircraft which were at Burao within two days. The inhabitants of the native township were turned out of their houses, and the entire area was razed by a combination of bombing, machine-gun fire and burning.[58]
After the RAF aircraft bombed Burao to the ground, the Hersi Osman eventually acquiesced, agreeing to pay a fine for Gibbs death, but they refused to identify and apprehend the accused individuals. Most of the men responsible for Gibb's shooting evaded capture. In light of the failure to implement the taxation without provoking a violent response, the British abandoned the policy altogether.[59][60][55]
Somali civil war and the Somali National Movement (SNM)

The Somali National Movement (SNM) was a 1980s–1990s rebel group. The SNM was organized in London, England, on 6 April 1981, by Hassan Adan Wadadid a former Somali diplomat and several other Isaaq intellectuals, he stated that the group's purpose was to overthrow the Siad Barre regime.[61] The SNM gathered its main base of support from members of the Isaaq clan, who formed and supported the movement in response to years of systematic discrimination by the Siad Barre government.[citation needed]
Habar Yoonis members served twice as chairman of the movement, with Colonel Abdiqadir Kosar Abdi and Abdirahman Tuur and once as Vice chairman with Hassan Adan Wadadid. Habar Yoonis Commanders carried out many successful operations that led to the decisive victory of the group and to the downfall of the Siad Barre regime. Such operations included the Birjeex raid led by Colonel Ibrahim Koodbuur and Operation Mandheera led by Mohamed Hashi Lihle Lixle where they successfully freed hundreds of Isaaq political prisoners whose executions were imminent.[62]

Under the leadership of Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur the SNM carried out a successful invasion of Northern Somalia overthrowing the Communist regime and establishing the democratic state of Somaliland. Abdirahman was sworn in as Somaliland's first president.
List of Habar Yoonis SNM leaders:[63][64]
- Abdirahman Tuur
- Abdiqadir Kosar
- Mohamed Hashi Lihle
- Mohamed Ali
- Haragwaafi
- Madah-diin
- Ahmed Mire
- General Hassan Kayd
Clan Tree

A summarized clan family tree of the major Garhajis subclan of Habar Yunis is presented below.[65][66]
- Ishaaq bin Ahmed
- Habar Habuusheed
- Ahmed (Tol-Ja'lo)
- Muuse (Habr Je'lo)
- Ibrahiim (Sanbuur)
- Muhammad ('Ibraan)
- Habar Magaadle
- Abdirahman (Habr Awal)
- Ayub
- Muhammad (Arap)
- Ismail (Garhajis)
- Sa'id (Habar Yunis)
- Ali Sa'id
- Logeh Ali
- Baleh Ali
- Haji Salah Ali
- Farah Haji
- Hasan Haji
- Samatar Hasan
- 'Uthman Hasan
- Samakab Hasan
- Abdi Hasan
- Abdullah Hasan
- Ziyad Hasan
- Arreh Sa'id
- Ishaq Arreh
- Abdalle Ishaq
- Qaasim Ishaq
- Kalil Ishaq
- Musa Arreh
- Hassan Musa
- Ibrahim Musa
- Damal Musa (Dir Roble)
- Ismail Arreh
- Sa'ad Yunis
- Mahamoud Sa'ad
- Hasan (Barkad) Sa'ad
- Mohammed (Idrays) Sa'ad
- Musa Ismail
- Salah Musa (Turwa)
- Mohammed Musa (Urursuge)
- Yunis Musa
- Abdallah Ismail
- Idris (Idrays)
- Musa Idris
- Mahamad Idris
- Sa'eed Idris
- Musa Abdallah
- Mohammed Musa
- Farah Mohammed
- Hasan Farah
- Hussein Farah (Ba Gumaron)
- Allamagan Farah
- Jibril Farah
- 'Ali Farah
- Hasan 'Ali
- Omar 'Ali
- 'Amar 'Ali
- 'Abdallah 'Ali
- Farah Mohammed
- Logeh Musa
- Abokor Logeh
- Musa Abokor
- 'Ali Abokor
- Hasan 'Ali
- Hagar 'Ali
- Egal Abokor
- Mohammed Egal
- Hassan Egal (Rer Diriyeh)
- Bayle Egal
- Maax Egal (Rer Maah)
- Abokor Logeh
- Mohammed Musa
- Omar Abdallah
- Kalil Omar
- Ugadh Omar
- Adan Omar
- Elmi Adan
- Egal Adan
- Mohamed Adan
- Roble Mohamed (Arabala)
- Hildid Mohamed
- Hussein Hildid(Rer Hussein)
- Hassan Hildid (Gumbur)
- Abokor Hildid
- Osman Hildid
- Abdi Osman (Ba Dhulbahante)
- Ali Osman (Ba Dhulbahante)
- Mumin Osman (Rer Mumin)
- Hersi Osman
- Fahiya Hersi
- Warsama Hersi
- Ali Hersi
- Yusuf Hersi
- Hildid Hersi
- Said Hersi
- Warsama Said (Rer Waraba)
- Weid said (Rer Waid)
- Egal Said
- Abdi Hersi
- Reer Diriye
- Jamal Osman
- Reer Diriye
- Ainanshe Hersi (Current holders of the Habr Yunis Sultanate
- Sugulleh Ainashe
- Eise Ainanshe
- Wa’ays Ainanshe
- Suban Ainanshe
- Abdi Ainanshe
- Egal Ainanshe
- Omar Ainanshe
- Koshin Ainanshe
- Maygag Ainanshe
- Butiye Ainanshe
- Ahmed Ainanshe
- Farah Ainanshe
- Samaale Ainanshe
- Hersi Ainanshe
- Guled Ainanshe
- Gutale Ainanshe
- Liibaan Ainanshe
- Idris (Idrays)
- Sa'ad Yunis
- Ishaq Arreh
- Ali Sa'id
- Sa'id (Habar Yunis)
- Habar Habuusheed
Notable people

- Abdillahi Diiriye Guled - Literary scholar and discoverer of the Somali prosodic system
- Abdiqadir Kosar Abdi – Former chairman of the SNM and army colonel
- Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur – the first president of Somaliland and the last Somali National Movement(SNM) Chairman
- Sheekh Dalmar – ex governor erigavo 1960 to 1968
- Abdirahman Mohamed Abdullahi – former Speaker of the House of Representatives of Somaliland and the newly elected president of Somaliland.
- Abdirisaq Ibrahim Abdi – current mayor of Burao
- Abdisalam Yasin Mohamed – Prominent Somali intellectual and one of the founding fathers of the SNM
- Abdullahi Qarshe – Somali musician, poet and playwright; known as the "father of Somali music"
- Ahmed Hassan Diria – Somali Tanzanian diplomat and politician, served as Minister of Foreign Affairs
- Ahmed Said Ahmed - international footballer who plays for VJS, as a defender[67][68]
- Ali Ibrahim Jama - Governor of the Bank of Somaliland
- Ali Ismail Yacqub - First Minister of Defence for the Somali Republic
- Ali Mohamed Warancadde - Somali politician, former minister Minister of Interior of Somaliland and Minister of Civil Aviation of Somaliland
- Ali Sugule Egal – one of the greatest composers, poets and playwrights of the Somali language.
- Amina Moghe Hersi – prominent businesswoman and wealthiest Somali woman
- Awad Deria – 5th Sultan of the Habr Yunis clan
- Deria Sugulleh Ainashe – 2nd Sultan of the Habr Yunis clan
- Dolal Nur – 6th Sultan of the Habr Yunis clan
- Fowsiyo Yusuf Haji Adan – former Foreign Minister of Somalia and MP in Federal Parliament
- Haji Yusuf Iman Guled - Minister of Defence of Somalia 1967-1969
- Hassan Adan Wadadid – Somali Republic ambassador to Saudi Arabia and Pakistan and one of the original founders and Vice Chairman of the Somali National Movement
- Hassan Ismail Yusuf – Somali politician and served as the Minister of Health of Somaliland
- Hersi Aman – 3rd Sultan of the Habr Yunis clan
- Hussein Ali Duale – diplomat and politician who served as the Finance Minister of Somaliland
- Ismail Haji Nour – current mayor of Erigavo since 2002
- Madar Hersi - 7th Sultan of the Habr Yunis
- Mohamed Ainanshe Guled - Brigadier General of SNA and the vice president of the Somali Democratic Republic from 1969 to 1971
- Mohamed Bullaleh - Prominent 20th Century tribal chief and commander of the Hagoogane raid that destroyed Dervish movement
- Mohamed Ali - Somali military commander and revolutionary. He is known for his leadership within Western Somali Liberation Front, Afraad and later the Somali National Movement.
- Mohamed Hashi Lihle - Colonel of the SNA and later the commander of the military wing of the Somali National Movement
- Mona Kosar Abdi – news anchor for ABC's Good Morning America
- Nur Ahmed Aman – 4th sultan of the Habr Yunis and one of the founders of the Somali Dervish movement
- Osman Jama Ali - Prime Minister of Somalia under the Transitional National Government
- Ridwan Hirsi Mohamed – Former Deputy Prime Minister of Somalia and Former Minister of Religious Affairs of Somalia.
- Said Sulub Mohamed – Somali politician, who is currently serving as the Minister of Livestock and Fisheries of Somaliland.
- Salah Ahmed Jama - Current Deputy Prime Minister of the Federal Government of Somalia
- Sharmarke Ali Saleh - 1775-1861 – governor of Berbera, Zeila and Tadjoura
- Shukri Haji Ismail - Somali politician, who currently serving as the Minister of Environment and Rural Development of Somaliland
References
- ^ Gori, Alessandro (2003). Studi sulla letteratura agiografica islamica somala in lingua araba. Quaderni di semitistica. Firenze: Università di Firenze, Dipartimento di linguistica. ISBN 978-88-901340-0-5.
- ^ Lewis, I. M. (1999). I.M Lewis, A pastoral democracy, p. 10. James Currey Publishers. ISBN 9780852552803.
- ^ A General survey of the Somaliland protectorate 1944-1950, p.122, table 18
- ^ "Africa, Volumes 29-30, Oxford University Press, 1959, p.276". 1959.
- ^ "Welcome Home to Nothing: Refugees Repatriate to a Forgotten Somaliland, p.17" (PDF).
- ^ Waal, Alexander De (1993). "Violent deeds live on: landmines in Somalia and Somaliland, p. 63". |
- ^ Lewis, I. M. (3 February 2017). I.M Lewis : peoples of the Horn of Africa. Routledge. ISBN 9781315308173. |
- ^ Mataan, Asad Cabdullahi (28 November 2012). "Qabaa'ilka Soomaalidu ma isbahaysi baa, mise waa dhalasho?". Caasimada Online. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ "مخطوطات > بهجة الزمان > الصفحة رقم 16". makhtota.ksu.edu.sa. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- ^ Morin, Didier (2004). Dictionnaire historique afar: 1288-1982 (in French). KARTHALA Editions. ISBN 9782845864924.
- ^ The Journal of The anthropological institute of Great Britain and Ireland| Vol.21 p. 161
- ^ Bollettino della Società geografica italiana Volume 6, 1893. pp.203
- ^ Genealogies of the Somal. Eyre and Spottiswoode (London). 1896.
- ^ Qaamuuska AF‒Soomaaliga, by Annarita Puglielli iyo Cabdalla Cumar Mansuur, pp. 140.
- ^ Cosmos: communicazioni sui progressi recenti e notevoli della geografia e delle scienze affini di Guido Cora, p. 201.
- ^ Etiopia rassegna illustrata dell'Impero, 1947, vol. 7, p. 15.
- ^ YouTube, a Google company. YouTube. Archived from the original on 10 October 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ NEW ISSUES IN REFUGEE RESEARCH Working Paper No. 65 Pastoral society and transnational refugees: population movements in Somaliland and eastern Ethiopia 1988 - 2000 Guido Ambroso, Table 1, pg.5
- ^ The Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society 1850, Volume 9, p.133
- ^ Cosmos: communicazioni sui progressi recenti e notevoli della geografia e delle scienze affini di Guido Cora. Vol 10 pt 2 pp.29
- ^ Andrzejewski, B.W. and I.M. Lewis, 1964, Somali Poetry: An Introduction, Oxford University Press, Oxford, p.106
- ^ War and Peace: An Anthology of Somali literature, p.178
- ^ British Somaliland by Drake Brockman, pp.79 - 82
- ^ 1912 Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society and Monthly Record of Geography 1885, Volume 7, p.627
- ^ The Academy: a weekly review of literature, science, and art. Volume 35, 1889, p.126
- ^ The Unknown Horn of Africa: An Exploration From Berbera to the Leopard River, 1888
- ^ Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society and Monthly Record of Geography, 1885, Volume 7, p.627
- ^ British Somaliland. Drake Bromen. 1912.
- ^ Notes on Somali history. Leicestershire Regment: By Captain G.D Carelton.
- ^ Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland, Vol. 21, p.161
- ^ British Somaliland by Drake Brockman, pages 79–82, 1912.
- ^ Under the flag: and Somali coast stories by Walsh, Langton Prendergast. p. 243
- ^ Somali Coast administration Report of the protectorate 1892–1893, Bombay Castle, NAY, New Delhi
- ^ Churchill and the Mad Mullah of Somaliland: Betrayal and Redemption 1899-1921. p. 24 by Roy Irons
- ^ Correspondence respecting the Rising of Mullah Muhammed Abdullah in Somaliland, and consequent military operations, 1899-1901. P. 4.
- ^ Correspondence respecting the Rising of Mullah Muhammed Abdullah in Somaliland, and consequent military operations, 1899-1901. P. 8.
- ^ Ferro e fuoco in Somalia, con lettera introduttiva di Emilio de Bono. Francesco Saverio Caroselli. pp.105-106
- ^ British SomaliLand by Ralph E Drake Brockman .1012. p. 82
- ^ a b Taleh by W. A. MacFadyen, The Geographical Journal Vol. 78, No. 2 (Aug., 1931), pp. 125–128.
- ^ Irons, Roy (4 November 2013). Churchill and the Mad Mullah of Somaliland, p. 209. Pen and Sword. ISBN 9781783463800.
- ^ Nicolosi, Gerardo (2002). Imperialismo e resistenza in corno d'Africa: Mohammed Abdullah Hassan, P.305. Rubbettino Editore. ISBN 9788849803846.
- ^ "King's College London, King's collection: Ismay's summary as Intelligence Officer (1916-1918) of Mohammed Abdullah Hassan".
- ^ Beachey, R. W. (1990). The warrior mullah: the Horn aflame, 1892-1920, by R.W Beachey, p.153. Bellew. ISBN 9780947792435.
- ^ "Suldaan Cismaan Suldaan Cali Madar Oo Farriimo Culus U Diray Maamulka Muuse Biixi Iyo Maamulka Farmaajo". Sayruuq News. 9 January 2018. Archived from the original on 3 March 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ First Footsteps in East Africa, by Richard Burton, p.16-p.30
- ^ Sun, sand and Somals; leaves from the note-book of a district commissioner in British Somaliland, by Rayne Henry. p.15-16
- ^ Ethiopia: the Era of the Princes: The Challenge of Islam and Re-unification of the Christian Empire, 1769-1855. p.18
- ^ Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society, Vol. 8, p. 185 By Bombay Geographical Society
- ^ Burton, First Footsteps, pp. 176 and note
- ^ First footsteps in East Africa : or, An exploration of Harar by Burton, Richard Francis, Sir, 1821–1890; Burton, Isabel, Lady, Published 1894
- ^ Colonial Office, 11 April 1922
- ^ The British Empire as a Superpower By Anthony Clayton pp.223
- ^ Public Record Office file CO 1069/13 Part 1, by the first officer commanding "B" (Nyasaland) Company SCC.
- ^ The King's African Rifles by H. Moyse-Bartlett
- ^ a b Correspondence between Governor of British Somaliland and Secretary of State for the Colonies. Colonial Office, 26 March 1922.
- ^ Correspondence between Governor of British Somaliland and Secretary of State for the Colonies. Colonial Office, 28th February, 1922
- ^ 1922 Commons sitting. HC Deb 14 March 1922 vol 151 cc1953-4
- ^ Imperial Rearguard: Wars of Empire, 1919-1985 pp.168
- ^ British Somaliland: An Administrative History, 1920-1960 pp.110
- ^ Jaques, Tony (2007). Dictionary of battles and sieges P-Z, p.991. Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 9780313335396.
- ^ Helen Chapin Metz, Somalia: a country study, Volume 550, Issues 86-993, (The Division: 1993), p.xxviii.
- ^ MGoth (13 January 2018). "The Rebirth of Somaliland;Operation Birjeex (SNM Rescue Unit)-Part 7".
- ^ Forberg, Ekkehard; Terlinden, Ulf (13 April 1999). Small Arms in Somaliland: Their Role and Diffusion. BITS. ISBN 9783933111012 – via Google Books.
- ^ Horn of Africa, Volume 13, Issue 2
- ^ Kirk, J. W. C. (31 October 2010). A grammar of the Somali Language, p.140. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781108013260.
- ^ A general survey of the Somaliland Protectorate 1944-1950, p147
- ^ "Ahmed Said Ahmed" (in Finnish). Football Association of Finland. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
Kansallisuus: Suomi
- ^ "#80 Said Ahmed, Ahmed" (in Finnish). Veikkausliiga. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
Kansalaisuus FI