Dobruja
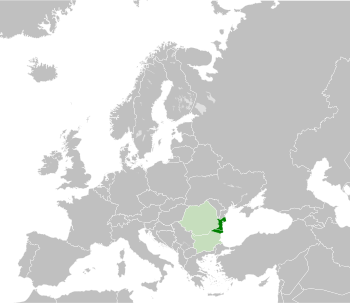

Dobruja or Dobrudja (US: /ˈdoʊbrʊdʒə/;[1] Bulgarian: Добруджа, romanized: Dobrudzha or Dobrudža; Romanian: Dobrogea, pronounced [ˈdobrodʒe̯a] or [doˈbrodʒe̯a]; Ukrainian: Задунав'я, romanized: Zadunav"ya; Turkish: Dobruca; Dobrujan Tatar: Tomrîğa) is a geographical and historical region in Southeastern Europe that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. It is situated between the lower Danube River and the Black Sea, and includes the Danube Delta, the Romanian coast, and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast. The territory of Dobruja is made up of Northern Dobruja, which is a part of Romania, and Southern Dobruja, which is a part of Bulgaria.
The territory of the Romanian region Dobrogea is organised as the counties of Constanța and Tulcea, with a combined area of 15,588 km2 (6,019 sq mi) and, as of 2021, a population of slightly less than 850,000. Its main cities are Constanța, Tulcea, Medgidia, and Mangalia. Dobrogea is represented by dolphins in the coat of arms of Romania.
The Bulgarian region Dobrudzha is divided among the provinces of Dobrich and Silistra; the following villages of Razgrad Province: Konevo, Rainino, Terter and Madrevo; and the village General Kantardzhievo (Varna). The region has a total area of 7,566 km2 (2,921 sq mi), with a combined population as of 2021 of some 250,000 people. The main towns are Dobrich and Silistra, the administrative centers of the two provinces.
Geography
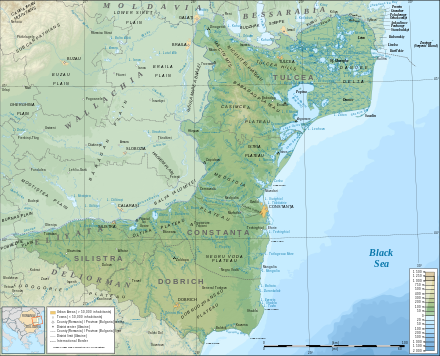



Except for the Danube Delta, a marshy region located in its northeastern corner, Dobruja is hilly, with an average altitude of about 200–300 metres. The highest point is the Țuțuiatu (Greci) Peak in the Măcin Mountains, having a height of 467 m. The Dobruja Plateau covers most of the Romanian part of Dobruja. The Ludogorie Plateau is found in Bulgaria. Lake Razelm is one of the most important lakes in Northern Dobruja.
Dobruja lies in the temperate continental climatic area; the local climate is determined by the influx of oceanic air from the northwest and northeast and continental air from the East European Plain. Dobruja's relatively level terrain and its bare location facilitate the influx of humid, warm air in the spring, summer, and autumn from the northwest, as well as that of northern and northeastern polar air in the winter. The Black Sea also exerts an influence over the region's climate, particularly within 40–60 kilometres from the coast. The average annual temperatures range from 11 °C inland and along the Danube, to 11.8 °C on the coast and less than 10 °C in the higher parts of the plateau. The coastal region of Southern Dobruja is the most arid part of Bulgaria, with an annual precipitation of 450 millimetres.
Dobruja is a windy region once known for its windmills. There is wind during about 85–90% of all days; it usually comes from the north or northeast. The average wind speed is about twice higher than the average in Bulgaria. Due to the limited precipitation and the proximity to the sea, rivers in Dobruja are usually short and with low discharge. The region has several shallow seaside lakes with brackish water.[2]
Etymology
The most widespread opinion among scholars is that the origin of the term Dobruja is to be found in the Turkish rendition of the name of a 14th‑century Bulgarian ruler, despot Dobrotitsa.[3][4][5] It was common for the Turks to name countries after one of their early rulers (for example, nearby Moldavia was known as Bogdan Iflak by the Turks, named after Bogdan I). Other etymologies have been considered, but never gained widespread acceptance.
Abdolonyme Ubicini believed the name meant "good lands", derived from Slavic dobro ("good"), an opinion that was adopted by several 19th‑century scholars. This derivation appears to contrast with the usual 19th‑century description of Dobruja as a dry barren land; it has been explained as expressing the point of view of Ruthenes, who considered the Danube delta in the northern Dobruja as a significant improvement over the steppes to the North.[6] I. A. Nazarettean combines the Slavic word with the Tatar budjak ("corner"), thus proposing the etymology "good corner".
A version matching contemporaneous descriptions was suggested by Kanitz, who associated the name with the Bulgarian dobrice ("rocky and unproductive terrain").[7] According to Gheorghe I. Brătianu, the name is a Slavic derivation from the Turkic word Bordjan or Brudjars, which referred to the Turkic Proto-Bulgarians; this term was also used by Arabic writers.
One of the earliest documented uses of the name can be found in the Turkish Oghuz-name narrative, dated to the 15th century, where it appears as Dobruja-éli. The possessive suffix el-i indicated that the land was considered as belonging to Dobrotitsa ("دوبرجه" in the original Ottoman Turkish).[8] The loss of the final particle is not unusual in the Turkish world, a similar evolution being observed in the name of Aydın, originally Aydın-éli.[9] Another early use is in the 16th‑century Latin translation of Laonicus Chalcondyles' Histories, where the term Dobroditia is used for the original Greek "Dobrotitsa's country" (Δοβροτίκεω χώρα).[10] In the 17th century, the region was referred to in more accounts, with renditions such as Dobrucia, Dobrutcha, Dobrus, Dobruccia, Dobroudja, Dobrudscha, and others being used by foreign authors.[11]
Initially, the name meant just the steppe of the southern region, between the forests around Babadag in the north and the Silistra–Dobrich–Balchik line in the south.[12] Eventually, the term was extended to include the northern part and the Danube Delta.[13] In the 19th century, some authors used the name to refer just to the territory between the southernmost branch of the Danube (St. George) in the north and the Karasu Valley (nowadays the Danube-Black Sea Canal) in the south.[14]
History
Prehistory
The territory of Dobruja has been inhabited by humans since Middle and Upper Palaeolithic,[15] as the remains at Babadag, Slava Rusă and Enisala demonstrate. Paleolithic people made tools of silex and ate fruits, fish, and other hunted animals. In this period fire was discovered, and at its end, the bow with arrows and the boat sculpted from a trunk tree was invented. There were found tools in caves, inclusive Gura Dobrogei. In the Neolithic, the territory was occupied by members of the Hamangia culture (named after a village on the Dobrujan coast), Boian culture, and Karanovo V culture. At the end of the fifth millennium BC, the Gumelniţa culture appeared in the region under the influence of Aegeo-Mediterranean tribes and cultures. In the Eneolithic, populations migrating from the north of the Black Sea, of the Kurgan culture, mixed with the previous population, creating the Cernavodă I culture. Under the influence of Kurgan II , the Cernavodă II culture emerged. Through the combination of the Cernavodă I and Ezero culture, the Cernavodă III culture developed. The region had commercial contact with the Mediterranean world by the 14th century BC, as proven by a Mycenaean sword discovered at Medgidia,[16] but under the reserve demanded by lack of hard evidence in what concerns the provenience/manufacturer of such armours. [clarification needed]
Ancient history
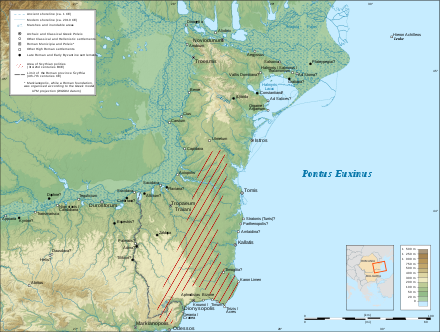

During the early Iron Age (8th–6th centuries BC), there was increased differentiation of the local Getic tribes from the Thracian mass. In the second part of the 8th century BC, the first signs of commercial relations between the indigenous population and the Greeks appeared on the shore of the Halmyris Gulf (now the Sinoe Lake).
In 657/656 BC ancient Greek colonists from Miletus founded a colony in the region: Histria.[17] In the 7th and 6th centuries BC, more Greek colonies were founded on the Dobrujan coast (Callatis, Tomis, Dionysopolis, Parthenopolis, Aphrodisias, Eumenia etc.). In the 5th century BC these colonies were under the influence of the Delian League, passing in this period from oligarchy to democracy.[18] In the 6th century BC, the first Scythian groups began to enter the region. Two Getic tribes, the Crobyzi and Terizi, and the town of Orgame (Argamum) were mentioned on the territory of present Dobruja by Hekataios of Miletus (540–470 BC).[19]
In 514/512 BC King Darius I of Persia subdued the Getae living in the region during his expedition against Scythians living north of the Danube.[20] At about 430 BC, the Odrysian kingdom under Sitalkes extended its rule to the mouths of the Danube.[21] In 429 BC, Getae from the region participated in an Odrysian campaign in Macedonia.[22] In the 4th century BC, the Scythians brought Dobruja under their sway. In 341–339 BC, one of their kings, Atheas, fought against Histria, which was supported by a Histrianorum rex (probably a local Getic ruler). In 339 BC, King Atheas was defeated by the Macedonians under King Philip II, who afterwards extended his rule over Dobruja.[23]
In 313 BC and again in 310–309 BC, the Greek colonies led by Callatis, supported by Antigonus I Monophthalmus, revolted against Macedonian rule.[citation needed] The revolts were suppressed by Lysimachus, the diadochus of Thrace, who also began a military expedition against Dromichaetes, the ruler of the Getae north of the Danube, in 300 BC. In the 3rd century BC, colonies on the Dobrujan coast paid tribute to the basilei Zalmodegikos and Moskon, who probably also ruled northern Dobruja.[citation needed] In the same century, Celts settled in the north of the region. In 260 BC, Byzantion lost the war with Callatis and Histria for the control of Tomis. At the end of the 3rd century BC and the beginning of the 2nd century BC, the Bastarnae settled in the area of the Danube Delta. Around 200 BC, the Thracian king Zoltes invaded the province several times, but was defeated by Rhemaxos, who became the protector of the Greek colonies.[citation needed]
Early Greek scholars such as Herodotus appear to have regarded the region as the south-western extension of Scythia – a practice also followed in a 2nd-century BC inscription, recording a decree made in Histria, which refers to the region surrounding the Greek city as Scythia. However, the toponym Μικρά Σκυθία (Mikra Skythia), usually translated as Scythia Minor appears to have become the name for the region later known as Dobruja.[citation needed] The earliest known usage of Mikra Skythia is found in Strabo's early Geography (1st century AD). The Greeks thus apparently distinguished it from Scythia Major, which lay north of the Danube delta.
Around 100 BC King Mithridates VI of Pontus extended his authority over the Greek cities in Dobruja.[24] However, in 72–71 BC, during the Third Mithridatic War, these cities were occupied by the forces of Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus, the Roman proconsul of Macedonia. A foedus was signed between the Greek colonies and the Roman Republic, but in 62–61 BC the colonies revolted.[25] Gaius Antonius Hybrida intervened, but was defeated by Getae and Bastarnae at the Battle of Histria. After 55 BC the Dacian Kingdom under King Burebista conquered Dobruja and all the Greek colonies on the coast.[26]
Roman rule
In 28/29 BC Rholes, a Getic ruler from Southern Dobruja, supported the proconsul of Macedonia, Marcus Licinius Crassus, in his action against the Bastarnae. Declared friend and ally of the Roman people by Octavian,[27] Rholes helped Crassus in conquering the states of Dapyx (in central Dobruja) and Zyraxes (in the north of the region).[28] Dobruja became part of the client kingdom of the Odrysians,[citation needed] while the Greek cities on the coast came under direct rule of the governor of Macedonia.[citation needed]
In 6 AD the Roman province of Moesia was created when mention is made of its governor, Caecina Severus.,[29] but Dobruja, under the name Ripa Thraciae, remained part of the Odrysian kingdom.[citation needed] The Greek cities on the coast formed a praefectura orae maritimae.
In 12 AD and 15 AD, Getic armies succeeded in conquering the cities of Aegyssus and Troesmis for a short time, but Odrysian king Rhoemetalces I defeated them with the help of the Roman army.[citation needed]
In 46 AD Thracia became a Roman province and the territories of present Dobruja were absorbed into the province of Moesia.[citation needed] The Geto–Dacians invaded the region several times in the 1st century AD, especially between 62 and 70.[citation needed] In the same period, the base of the Roman Danube fleet (classis Flavia Moesica) was moved to Noviodunum. The praefectura was annexed to Moesia in 86 AD. In the same year Domitian divided Moesia, Dobruja being included in the eastern part, Moesia Inferior.[citation needed]

In the winter of 101–102 the Dacian king Decebalus led a coalition of Dacians, Carpians, Sarmatians and Burs in an attack against Moesia Inferior. The invading army was defeated by the Roman legions under Emperor Trajan on the Yantra river. (Later Nicopolis ad Istrum was founded there to commemorate the victory.) The invaders were also defeated near the modern village of Adamclisi, in the southern part of Dobruja. The latter victory was commemorated by the Tropaeum Traiani monument built in 109 at the site and the founding of the city of the same name. After 105, Legio XI Claudia and Legio V Macedonica were moved to Durostorum and Troesmis, respectively.
In 118 Hadrian intervened in the region to calm a Sarmatian rebellion.[citation needed] In 170 Costoboci invaded Dobruja, attacking Libida, Ulmetum and Tropaeum.[citation needed] The province was generally stable and prosperous until the crisis of the Third Century, which led to the weakening of defences and numerous barbarian invasions. In the Gothic War (248-253) a coalition of Goths under King Cniva devastated Dobruja.[30] Barbarian attacks followed in 258, 263 and 267. In 269 a fleet of allied Goths, Heruli, Bastarnae and Sarmatians attacked the cities on the coast, including Tomis.[31] In 272 Aurelian defeated the Carpians north of the Danube and settled a part of them near Carsium.[citation needed] The same emperor put an end to the crisis in the Roman Empire, thus helping the reconstruction of the province.
During the reign of Diocletian, Dobruja was organized administratively as a separate province, called Scythia, part of the Diocese of Thracia. Its capital city was Tomis. Diocletian created Legio II Herculia and Legio I Iovia and installed them at Troesmis and Noviodunum respectively. In 331–332 Constantine the Great defeated the Goths who attacked the province.[citation needed] But Dobruja was devastated again by Ostrogoths in 384–386. Under the Roman emperors Licinius, Julian the Apostate, and Valens, the cities of the region were repaired or rebuilt.
Byzantine rule
After the division of the Roman Empire, Dobruja was absorbed into the Eastern Roman Empire. Between 513 and 520, the region participated in a revolt against Anastasius I. Its leader, Vitalian, native of Zaldapa in Southern Dobruja, defeated the Byzantine general Hypatius near Kaliakra. During Justin I's rule, Antes and Slavs invaded the region, but Germanus Justinus defeated them. In 529, the Gepid commander Mundus repelled a new invasion by Bulgars and Antes. Kutrigurs and Avars invaded the region several times, until 561–562, when the Avars under Bayan I were settled south of the Danube as foederati. During the rule of Mauricius Tiberius, the Slavs devastated Dobruja, destroying the cities of Dorostolon, Zaldapa, and Tropaeum. In 591/593, Byzantine general Priscus tried to stop invasions, attacking and defeating the Slavs under Ardagast in the north of the province. In 602 during the mutiny of the Byzantine army in the Balkans under Phocas, a large mass of Slavs crossed the Danube, settling south of the Danube. Dobruja remained under loose Byzantine control, and was reorganised during the reign of Constantine IV as Thema Scythia.[32]
First Bulgarian Empire rule

The results of archaeological research indicate that the Byzantine presence on Dobruja's mainland and the banks of the Danube were reduced at the end of the 6th century, under the pressure of the Migration Period. In the coastal fortifications on the southern bank of the Danube, the latest Byzantine coin found dates from the time of the emperors Tiberius II Constantine (574–582) and Heraclius (610–641). After that period, all inland Byzantine cities were demolished by the invaders and abandoned.[33]
Some of the earliest Slavic settlements to the south of Danube have been discovered in Dobruja, near the villages of Popina, Garvăn and Nova Cherna. They have been dated to the end of the 6th and the beginning of the 7th centuries.[34] These lands became the main zone of compact Bulgar settlement in the end of the 7th century.[35]
According to the peace treaty of 681, signed after the Bulgarian victory over Byzantines in the Battle of Ongala, Dobruja became part of the First Bulgarian Empire.[36] Shortly after, the Bulgar founded the city of Pliska, which became the first Bulgarian capital, near the southern border of Dobruja.[37] They rebuilt Madara as a major Bulgar pagan religious centre.[38] According to the Bulgarian Apocryphal Chronicle, from the 11th century, Bulgarian Tsar Ispor "accepted the Bulgarian tsardom", created "great cities, Drastar on the Danube", a "great wall from Danube to the sea", "the city of Pliska" and "populated the lands of Karvuna" (nowadays Balchik).[39]
According to Bulgarian historians, during the 7th–10th centuries, the region was fortified by construction of a large network of earthen and wooden strongholds and ramparts.[40] Around the end of the 8th century, widespread building of new stone fortresses and defensive walls began.[41] The Bulgarians also reconstructed some of the ruined Byzantine fortresses (Kaliakra and Silistra in the 8th century, Madara and Varna in the 9th).[42] According to Barnea, among other historians, during the following three centuries of Bulgarian domination, Byzantines still controlled the Black Sea coast and the mouths of Danube, and for short periods, even some cities.[43] But Bulgarian archaeologists note that the last Byzantine coins found, which are considered a proof of Byzantine presence, date in Kaliakra from the time of Emperor Justin II (565–578),[44] in Varna from the time of Emperor Heraclius (610–641),[45] and in Tomis from Constantine IV's rule (668–685).[46]
At the beginning of the 8th century, Justinian II visited Dobruja to ask Bulgarian Khan Tervel for military help. Khan Omurtag (815–831) built a "glorious home on the Danube" and erected a mound in the middle of the distance between Pliska and his new building, according to his inscription kept in SS. Forty Martyrs Church in Veliko Tarnovo. The location of this edifice is unclear; the main theories place it at Silistra or at Păcuiul lui Soare.[47] Many early medieval Bulgar stone inscriptions were found in Dobruja, including historical narratives, inventories of armament or buildings, and commemorative texts.[48] During this period Silistra became an important Bulgarian ecclesiastical centre—an episcopate after 865 and seat of the Bulgarian Patriarch at the end of the 10th century.[49] In 895, Magyar tribes from Budjak invaded Dobruja and northeastern Bulgaria. An old Slavic inscription, found at Mircea Vodă, mentions Zhupan Dimitri (Дѣимитрѣ жѹпанѣ), a local feudal landlord prominent in the south of the region in 943.[50]
Return of Byzantine rule and late migrations
With financial encouragement from the Byzantine emperor, Nikephoros II Phocas, Sviatoslav I of Kiev agreed to assist the Byzantines in their war with the Bulgarians. Sviatoslav defeated the Bulgarians (led by Boris II) and proceeded to occupy the whole of northern Bulgaria. He occupied Dobruja in 968 and moved the capital of Kievan Rus' to Pereyaslavets, in the north of the region. Sviatoslav refused to turn his Balkan conquests over to the Byzantines, and the parties fell out as a result. So the Byzantines under John I Tzimisces reconquered Dobruja in 971 and included it in the theme 'Mesopotamia of the West' (Μεσοποταμια της Δυσεον).[51]
According to some historians, soon after 976[52] or in 986, the southern part of Dobruja was included in the Bulgarian state then ruled by Samuel. The northern part remained under Byzantine rule, being reorganised in an autonomous klimata.[53][54] Other historians are of the view that Northern Dobruja was reconquered by Bulgarians as well.[55] In 1000, a Byzantine army commanded by Theodorokanos reconquered the whole of Dobruja,[56] organizing the region as the Strategia of Dorostolon and, after 1020, as Paristrion (Paradounavon).
To prevent mounted attacks from the north, the Byzantines constructed three ramparts from the Black Sea down to the Danube, in the 10th–11th centuries.[57][58] According to Bulgarian archaeologists and historians, these fortifications may have been built much earlier and were erected by the First Bulgarian Empire in response to the threat of Khazars' raids.[59][60]
From the 10th century, Byzantines accepted small groups of Pechenegs settling in Dobruja.[61] In the spring of 1036, an invasion of the Pecheneg devastated large parts of the region,[62] destroying the forts at Capidava and Dervent, and burning the settlement of Dinogeţia. In 1046 the Byzantines accepted the Pecheneg under Kegen settling in Paristrion as foederati.[63] The Pecheneg dominated the region until 1059, when Isaac I Komnenos reconquered Dobruja.
In 1064, an invasion by the Oghuz Turks affected the region. During 1072 to 1074, when Nestor (the new strategos of Paristrion) was in Dristra, he found that the Pecheneg ruler, Tatrys, was leading a rebellion. In 1091, three autonomous, probably Pecheneg,[64] rulers were mentioned in the Alexiad: Tatos (Τατοῦ) or Chalis (χαλῆ), in the area of Dristra (probably the same person as Tatrys),[65] and Sesthlav (Σεσθλάβου) and Satza (Σατζά) in the area of Vicina.[66] The Cumans moved into Dobruja in 1094 and were influential in the region until the advent of the Ottoman Empire.[67]
Second Bulgarian Empire and Mongol domination

In 1187 the Byzantines lost control of Dobruja to the restored Bulgarian Empire. In 1241, the first Tatar groups, under Kadan, invaded Dobruja starting a century long history of turmoil in the region.[68] Around 1263–64, Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaeologus gave permission to Sultan Kaykaus II to settle in the area with a group of Seljuk Turks from Anatolia.[69] A missionary Turkish mystic, Sarı Saltuk, was the spiritual leader of this group.[70] His tomb in Babadag (which was named after him)[71] is still a place of pilgrimage for Muslims.[72] Arab chronicles of the 13th century mentioned Dobrogea under the name "Şakji" and the Vlachs inhabitants under the names "al-Awalak" and "ulaqut".[73] In 1265, the Bulgarian Emperor Constantine Tikh Asen hired 20,000 Tatars to cross the Danube and attack Byzantine Thrace.[74][75] On their way back, the Tatars forced most of the Seljuk Turks, including their chief Sarı Saltuk, to resettle in Kipchak (Cumania).[76][77]
In the second part of the 13th century, the Turco–Mongolian Golden Horde Empire continuously raided and plundered Dobruja.[78] The inability of the Bulgarian authorities to cope with the numerous raids became the main reason for the uprising, led by Ivailo (1277–1280), that broke out in eastern Bulgaria.[79] Ivailo's army defeated the Tatars, who were forced to leave the Bulgarian territory; he next outed Constantine Tikh's army, and Ivailo has crowned Emperor of Bulgaria.
The war with the Tatars continued. In 1278, after a new Tatar invasion in Dobruja, Ivailo was forced to retreat to the strong fortress of Silistra, where he withstood a three-month siege.[80] In 1280 the Bulgarian nobility, which feared the growing influence of the peasant emperor, organised a coup. Ivailo had to flee to his enemy the Tatar Nogai Khan, who later killed him.[81] In 1300 Toqta, the new Khan of the Golden Horde, ceded Bessarabia to Emperor Theodore Svetoslav.[82]

Autonomous Dobruja
In 1325, the Ecumenical Patriarch nominated Methodius as Metropolitan of Varna and Carvona.[83] After this date, Balik/Balica[84] is mentioned as a local ruler in Southern Dobruja. In 1346, he supported John V Palaeologus in his dispute for the Byzantine throne with John VI Cantacuzenus. He sent an army corps under his son Dobrotitsa/Dobrotici and his brother, Theodore, to help the mother of John Palaeologus, Anna of Savoy. For his bravery, Dobrotitsa received the title of strategos and married the daughter of megadux Apokaukos.[85] After the reconciliation of the two pretenders, a territorial dispute broke out between the Dobrujan polity and the Byzantine Empire for the port of Midia.[86] In 1347, at John V Palaeologus' request, Emir Bahud-din Umur, Bey of Aydın, led a naval expedition against Balik, destroying Dobruja's seaports. Balik and Theodore died during the confrontation, and Dobrotitsa became the new ruler.[87]

Between 1352 and 1359, with the collapse of Golden Horde rule in Northern Dobruja, a new state appeared. It was controlled by Tatar prince Demetrius, who claimed to be the protector of the river mouths of the Danube.[88]
In 1357 Dobrotitsa was mentioned as a despot ruling over a large territory, including the fortresses of Varna, Kozeakos (near Obzor), and Emona.[89] In 1366, John V Palaeologus visited Rome and Buda, trying to gather military support for his campaigns. On his return, he was captured at Vidin by Ivan Alexander, Tsar of Tarnovo, who believed that the new alliances were directed against his realm. An anti-Ottoman crusade under Amadeus VI of Savoy, supported by the republics of Venice and Genoa, was diverted to free the Byzantine emperor. Dobrotitsa collaborated with the crusaders, and after the allies conquered several Bulgarian forts on the Black Sea, Ivan Alexander freed John and negotiated a peace agreement. Dobrotitsa's role in this conflict brought him numerous political advantages: his daughter married one of John V's sons, Michael, and his principality extended its control over some of the forts lost by the Bulgarians (Anchialos and Mesembria).
In 1368, after the death of prince Demetrius, Dobrotitsa was recognised as ruler by Pangalia and other cities on the right bank of the Danube. In 1369, together with Vladislav I of Wallachia, Dobrotitsa helped Prince Stratsimir to win back the throne of Vidin.
Between 1370 and 1375, allied with Venice, Dobritsia challenged Genoese power in the Black Sea. In 1376, he tried to impose his son-in-law, Michael, as Emperor of Trebizond, but was unsuccessful. Dobrotitsa supported John V Palaeologus against his son Andronicus IV Palaeologus. In 1379, the Dobrujan fleet participated in the blockade of Constantinople, fighting with the Genoese fleet.
In 1386, Dobrotitsa died and was succeeded by Ivanko. That same year he accepted a peace agreement with Murad I and in 1387 signed a commercial treaty with Genoa. Ivanko was killed in 1388 during the expedition of Ottoman Grand Vizier Çandarli Ali Pasha against Tarnovo and Dristra. The expedition brought most of the Dobrujan forts under Turkish rule.
Wallachian rule
In 1388/1389 Dobruja (Terrae Dobrodicii—as mentioned in a document from 1390) and Dristra (Dârstor) came under the control of Mircea the Elder, ruler of Wallachia, who defeated the Ottoman Grand Vizier.

Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I conquered the southern part of the territory in 1393, attacking Mircea one year later, but without success. In the spring of 1395 Mircea regained the lost Dobrujan territories, with the help of his Hungarian allies.
The Ottomans recaptured Dobruja in 1397 and ruled it to 1404, although in 1401 Mircea strongly defeated an Ottoman army.
The defeat of Sultan Beyezid I by Tamerlane at Ankara in 1402 opened a period of anarchy in the Ottoman Empire. Mircea took advantage of it to organise a new anti-Ottoman campaign: in 1403, he occupied the Genoese fort of Kilia at the mouths of the Danube. Thus in 1404, he could impose his authority on Dobruja. In 1416, Mircea supported the revolt against Sultan Mehmed I, led by Sheikh Bedreddin in the area of Deliorman, in Southern Dobruja.[90]
After Mircea died in 1418, his son Mihail I fought against the amplified Ottoman attacks, eventually being killed in a battle in 1420. That year, Sultan Mehmed I conducted the definitive conquest of Dobruja by the Turks. Wallachia kept only the mouths of the Danube, but not for a long duration.
In the late 14th century, German traveller Johann Schiltberger described these lands as follows:[91]
I was in three regions, and all three were called Bulgaria. ... The third Bulgaria is there, where the Danube flows into the sea. Its capital is called Kaliakra.
Ottoman rule

Annexed by the Ottoman Empire in 1420, the region remained under Ottoman control until the late 19th century. Initially, it was organised as an udj (border province), included in the sanjak of Silistra, part of the Eyalet of Rumelia. Later, under Murad II or Suleiman I, the sanjak of Silistra and surrounding territories were organised as a separate eyalet.[92] In 1555, a revolt led by the "false" (düzme) Mustafa, a pretender to the Turkish throne, broke out against Ottoman administration in Rumelia and rapidly spread to Dobruja, but was repressed by the beylerbey of Nigbolu.[93][94] In 1603 and 1612, the region suffered from the forays of Cossacks, who burnt down Isaķči and plundered Küstendje.
The Russian Empire occupied Dobruja several times during the Russo-Turkish wars — in 1771–1774, 1790–1791, 1809–1810, 1829, and 1853. The most violent invasion was that of 1829, which resulted in the depopulation of numerous villages and towns. The Treaty of Adrianople of 1829 ceded the Danube Delta to the Russian Empire. However, Russia was forced to return it to the Ottomans in 1856, after the Crimean War. In 1864 Dobruja was included in the Vilayet of Danube.
Russo-Turkish War of 1878 and aftermath


After the 1878 war, the Treaty of San Stefano awarded Dobruja to Russia and the newly established Principality of Bulgaria. The northern portion, held by Russia, was ceded to Romania in exchange for Russia obtaining territories in Southern Bessarabia, thereby securing direct access to the mouths of the Danube. The population included a Bulgarian ethnic enclave in the northeast (around Babadag), as well as an important Muslim majority (mostly Turks and Tatars) scattered around the region.
The southern portion, held by Bulgaria, was reduced the same year by the Treaty of Berlin. At the advice of the French envoy, a strip of land extended inland from the port of Mangalia (shown orange on the map) was ceded to Romania, since its southwestern corner contained a compact area of ethnic Romanians. The town of Silistra, located at the area's most southwestern point, remained Bulgarian due to its large Bulgarian population. Romania subsequently tried to occupy the town as well, but in 1879 a new international commission allowed Romania to occupy only the fort Arab Tabia, which overlooked Silistra, but not the town itself.

At the beginning of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, most of Dobruja's population was composed of ethnic Tatars, and Turks, with minorities of Romanians, and Bulgarians. During the war, a large part of the Muslim population was evacuated to Bulgaria and Turkey.[95] After 1878, the Romanian government encouraged Romanians from other regions to settle in Northern Dobruja and accepted the return of some Muslim population displaced by the war.[96]
According to Bulgarian historians, after 1878 the Romanian church authorities took control over all local churches, with the exception of two in the towns of Tulcea and Constanţa, which managed to retain use of their Bulgarian Slavonic liturgy.[97] Between 1879 and 1900, Bulgarians built 15 new churches in Northern Dobruja.[98] After 1880, Italians from Friuli and Veneto settled in Greci, Cataloi and Măcin in Northern Dobruja. Most of them worked in the granite quarries in the Măcin Mountains, while some became farmers.[99] The Bulgarian authorities encouraged the settling of ethnic Bulgarians in the territory of Southern Dobruja.[100]
Balkan Wars and World War I
In May 1913, the Great Powers awarded Silistra and the area in a 3 km radius around it to Romania, at the Saint Petersburg Conference. In August 1913, after the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria lost Southern Dobruja (Cadrilater) to Romania (See Treaty of Bucharest, 1913). With Romania's entry in World War I on the side of France and Russia, the Central Powers occupied all of Dobruja and gave the Cadrilater, as well as the southern portion of Northern Dobruja, to Bulgaria in the Treaty of Bucharest of 1918. This situation lasted for a short period. As the Allied Powers emerged victorious at the end of the war, Romania regained the lost territories in the Treaty of Neuilly of 1919. Between 1926 and 1938, about 30,000 Aromanians from Bulgaria, Macedonia, and Greece, were resettled in Southern Dobruja. Some Megleno-Romanians also emigrated to the region.
In 1923 the Internal Dobrujan Revolutionary Organisation (IDRO), a Bulgarian nationalist organisation, was established. Active in Southern Dobruja under different forms until 1940, the IDRO detachments fought against the widespread brigandage in the region,[101] as well as the Romanian administration. Thus, while considered "a terrorist organisation" by the Romanian authorities, the IDRO was regarded by ethnic Bulgarians as a liberation movement. In 1925, part of the Bulgarian revolutionary committees formed the Dobrujan Revolutionary Organisation (DRO), which later became subordinated to the Communist Party of Romania. In contrast with the IDRO, which fought for the inclusion of the region in the Bulgarian state, the DRO requested the independence of Dobruja and its inclusion in a projected Federative Republic of the Balkans.[102] The means used by DRO to attain its goals were also more peaceful.
World War II and aftermath
During World War II, Bulgaria regained Southern Dobruja in the September 1940 Axis-sponsored Treaty of Craiova, despite Romanian negotiators' insistence that Balchik and other towns should remain in Romania. As part of the treaty, the Romanian inhabitants (Aromanian and Megleno-Romanian refugee-settlers, settlers from other regions of Romania, and the Romanians indigenous to the region) were forced to leave the regained territory, while the Bulgarian minority in the north was expelled to go to Bulgaria in a population exchange. The post-war Paris Peace Treaties of 1947 reaffirmed the 1940 border.
In 1948 and again in 1961–1962, Bulgaria proposed a border rectification in the area of Silistra, consisting mainly of the transfer of a Romanian territory containing the water source of that city. Romania made an alternative proposal that did not involve a territorial change and, ultimately, no rectification took place.[103]
In Romania, 14 November is a holiday observed as Dobruja Day.[104]
Demographic history
Ottoman era

During Ottoman rule, groups of Turk, Arab, Muslim Romani people and Crimean Tatars settled in the region, the latter, especially between 1512 and 1514. During the reign of Peter I of Russia and Catherine the Great, Lipovans immigrated to the region of the Danube Delta. On account of the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774), one of the greatest migration events of the region occurred where an estimated 200,000 Tatars emigrated to the Dobruja region between 1770 and 1784. Whereas, a large group of Christians (likely Greeks and Slavs) moved the other direction into the Tatar's recently-loss region of Azov in 1778.[105] After the destruction of Zaporozhian Sich in 1775, Cossacks were settled in the area north of Lake Razim by the Turkish authorities (where they founded the Danubian Sich). They were forced to leave Dobruja in 1828.
In the second part of the nineteenth century, Ruthenians from the Austrian Empire also settled in the Danube Delta. After the Crimean War, a large number of Tatars were forcibly driven away from Crimea, immigrating to then-Ottoman Dobruja and settling mainly in the Karasu Valley in the centre of the region and around Bābā Dāgh. In 1864, Circassians fleeing from the Russian invasion and genocide of the Caucasus were settled in the wooded region near Babadag, forming a community there. Germans from Bessarabia also founded colonies in Dobruja between 1840 and 1892.

According to Bulgarian historian Lyubomir Miletich, most Bulgarians living in Dobruja in 1900 were nineteenth-century settlers or their descendants.[106][107] In 1850, the scholar Ion Ionescu de la Brad, wrote in a study on Dobruja, ordered by the Ottoman government, that Bulgarians came to the region "in the last twenty years or so".[108] According to his study, there were 2,285 Bulgarian families (out of 8,194 Christian families) in the region,[109] 1,194 of them in Northern Dobruja.[110] Lyubomir Miletich puts the number of Bulgarian families in Northern Dobruja in the same year at 2,097.[111] According to the statistics of the Bulgarian Exarchate, before 1877 there were 9,324 Bulgarian families out of a total 12,364 Christian families in the Northern Dobruja.[112] According to Russian knyaz Vladimir Cherkassky, chief of the Provisional Russian government in Bulgaria in 1877–1878, the Bulgarian population in Dobruja was larger than the Romanian one.[112] However, count Shuvalov, the Russian representative to the Congress of Berlin, stated that Romania deserved Dobruja "more than anybody else, because of its population".[113] In 1878, the statistics of the Russian governor of Dobruja, Bieloserkovitsch, showed a number of 4,750 Bulgarian "family chiefs" (out of 14,612 Christian family chiefs) in the northern half of the region.[110]
The Christian religious organisation of the region was put under the authority of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church by a firman of the Sultan, promulgated on February 28, 1870.[114] However, the ethnic Greeks and most Romanians in Northern Dobruja remained under the authority of the Greek Archdiocese of Tulça (founded in 1829).[115][116]
20th century
In 1913, Dobruja was all made part of Romania in the aftermath of the 1913 Treaty of Bucharest which ended the Second Balkan War. Romania acquired Southern Dobruja from Bulgaria, a territory with a population of 300,000 from which only 6,000 (2%) were Romanians.[117] In 1913, Romanian-held Northern Dobruja had a population of 380,430, from which 216,425 (56.8%) were Romanians.[118] Thus, when Dobruja was unified within Romania in 1913, there were over 222,000 Romanians in the region out of a total population of 680,000, or nearly 33% of the population. By 1930, the Romanian population within Dobruja had increased to 44.2%.[119]
Northern Dobruja
| Ethnicity | 1878[120] | 1880[121] | 1899[121] | 1913[118] | 19301[122] | 1956[123] | 1966[123] | 1977[123] | 1992[123] | 2002[123] | 2011[124] | 2021[125] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 225,692 | 139,671 | 258,242 | 380,430 | 437,131 | 593,659 | 702,461 | 863,348 | 1,019,766 | 971,643 | 897,165 | 849,352 |
| Romanian | 46,504 (21%) | 43,671 (31%) | 118,919 (46%) | 216,425 (56.8%) | 282,844 (64.7%) | 514,331 (86.6%) | 622,996 (88.7%) | 784,934 (90.9%) | 926,608 (90.8%) | 883,620 (90.9%) | 751,250 (83.7%) | 657,438 (77.4%) |
| Turkish | 48,783 (21.6%) | 18,624 (13%) | 12,146 (4%) | 20,092 (5.3%) | 21,748 (5%) | 11,994 (2%) | 16,209 (2.3%) | 21,666 (2.5%) | 27,685 (2.7%) | 27,580 (2.8%) | 22,500 (2.5%) | 17,114 (2%) |
| Tatar | 71,146 (31.5%) | 29,476 (21%) | 28,670 (11%) | 21,350 (5.6%) | 15,546 (3.6%) | 20,239 (3.4%) | 21,939 (3.1%) | 22,875 (2.65%) | 24,185 (2.4%) | 23,409 (2.4%) | 19,720 (2.2%) | 17,024 (2%) |
| Russian-Lipovan | 12,748 (5.6%) | 8,250 (6%) | 12,801 (5%) | 35,859 (9.4%) | 26,210 (6%)2 | 29,944 (5%) | 30,509 (4.35%) | 24,098 (2.8%) | 26,154 (2.6%) | 21,623 (2.2%) | 13,910 (1.6%) | 12,094 (1.4%) |
| Ruthenian (Ukrainian from 1956) |
455 (0.3%) | 13,680 (5%) | 33 (0.01%) | 7,025 (1.18%) | 5,154 (0.73%) | 2,639 (0.3%) | 4,101 (0.4%) | 1,465 (0.1%) | 1,177 (0.1%) | 1,033 (0.1%) | ||
| Dobrujan Germans | 1,134 (0,5%) | 2,461 (1.7%) | 8,566 (3%) | 7,697 (2%) | 12,023 (2.75%) | 735 (0.12%) | 599 (0.09%) | 648 (0.08%) | 677 (0.07%) | 398 (0.04%) | 166 (0.02%) | 187 (0.02%) |
| Greek | 3,480 (1.6%) | 4,015 (2.8%) | 8,445 (3%) | 9,999 (2.6%) | 7,743 (1.8%) | 1,399 (0.24%) | 908 (0.13%) | 635 (0.07%) | 1,230 (0.12%) | 2,270 (0.23%) | 1,447 (0.16%) | 498 (0.06%) |
| Bulgarian | 30,177 (13.3%) | 24,915 (17%) | 38,439 (14%) | 51,149 (13.4%) | 42,070 (9.6%) | 749 (0.13%) | 524 (0.07%) | 415 (0.05%) | 311 (0.03%) | 135 (0.01%) | 58 (0.01%) | 106 (0.01%) |
| Roma | 702 (0.5%) | 2,252 (0.87%) | 3,263 (0.9%) | 3,831 (0.88%) | 1,176 (0.2%) | 378 (0.05%) | 2,565 (0.3%) | 5,983 (0.59%) | 8,295 (0.85%) | 11,977 (1.3%) | 10,556 (1.2%) | |
| N/A | - | - | - | - | 134 | 327 | 95 | - | 7 | 67 | 72,488 (8%) | 130,231 (15.3%) |
- 1According to the 1926–1938 Romanian administrative division (counties of Constanța and Tulcea), which excluded a part of today's Romania (chiefly the communes of Ostrov and Lipnița, now part of Constanța County) and included a part of today's Bulgaria (parts of General Toshevo and Krushari municipalities)
- 2Only Russians. (Russians and Lipovans counted separately)
Southern Dobruja
| Ethnicity | 1910 | 19301[122] | 2001[126] | 2011[127] | 2021[128] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 282,007 | 378,344 | 357,217 | 283,3953 | 231,9384 |
| Bulgarian | 134,355 (47.6%) | 143,209 (37.9%) | 248,382 (69.5%) | 192,698 (68%) | 160,620 (69.25%) |
| Turkish | 106,568 (37.8%) | 129,025 (34.1%) | 76,992 (21.6%) | 72,963 (25.75%) | 53,227 (22.9%) |
| Roma | 12,192 (4.3%) | 7,615 (2%) | 25,127 (7%) | 12,163 (4.29%) | 15,362 (6.62%) |
| Tatar | 11,718 (4.2%) | 6,546 (1.7%) | 4,515 (1.3%) | 808 (0.29%) | n/a |
| Romanian | 6,348 (2.3%)2 | 77,728 (20.5%) | 591 (0.2%)2 | 947 (0.33%) | n/a |
- 1According to the 1926–1938 Romanian administrative division (counties of Durostor and Caliacra), which included a part of today's Romania (chiefly the communes of Ostrov and Lipnița, now part of Constanța County) and excluded a part of today's Bulgaria (parts of General Toshevo and Krushari municipalities)
- 2Including persons counted as Vlachs in Bulgarian Census
- 3Only includes persons who answered the optional question on ethnic identity. The total population was 309,151.
- 4Only includes persons who answered the optional question on ethnic identity. The total population was 247,916.
Area, population and cities
The entire region of Dobruja has an area of around 23,100 km2 (8,919 sq mi) and a population of around 1.2 million, of which just over two-thirds of the former and nearly three-quarters of the latter lie in the Romanian part.
| Ethnicity | Dobruja | Romanian Dobruja[124] | Bulgarian Dobruja[127] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage | |
| All | 1,180,560 | 100.00% | 897,165 | 100.00% | 283,395 | 100.00% |
| Romanian | 752,197 | 63.72% | 751,250 | 83.74% | 947 | 0.33% |
| Bulgarian | 192,756 | 16.33% | 58 | 0.01% | 192,698 | 68% |
| Turkish | 95,463 | 8.09% | 22,500 | 2.51% | 72,963 | 25.75% |
| Tatar | 20,528 | 1.74% | 19,720 | 2.20% | 808 | 0.29% |
| Roma | 24,140 | 2.04% | 11,977 | 1.33% | 12,163 | 4.29% |
| Russian | 14,608 | 1.24% | 13,910 | 1.55% | 698 | 0.25% |
| Ukrainian | 1,250 | 0.11% | 1,177 | 0.13% | 73 | 0.03% |
| Greek | 1,467 | 0.12% | 1,447 | 0.16% | 20 | 0.01% |
Major cities are Constanța, Tulcea, Medgidia and Mangalia in Romania, and Dobrich and Silistra in Bulgaria.
See also
Notes
- ^ "Dobruja". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- ^ Фол, Александър (1984). История на Добруджа (History of Dobruja). Sofia: Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. OCLC 165781151.
- ^ A. Ischirkoff, Les Bulgares en Dobroudja, p. 4, attributes this opinion, among others, to Johann Christian von Engel, Felix Philipp Kanitz, Marin Drinov, Josef Jireček, Grigore Tocilescu
- ^ Paul Wittek, Yazijioghlu 'Ali on the Christian Turks of the Dobruja, p. 639
- ^ Davidova, R. (1984). "Приподно-географски условия в Добруджа". In Fol, Aleksander; Dimitrov, Strashimir (eds.). История на Добруджа (in Bulgarian). Vol. 1. Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. p. 9. OCLC 11916334.
- ^ A. Ischirkoff, Les Bulgares en Dobroudja, p. 4, attributes this opinion to Camille Allard, Ami Boué, Heinrich Brunn
- ^ G. Dănescu, Dobrogea (La Dobroudja). Étude de Géographie physique et ethnographique, pp. 35–36
- ^ Paul Wittek, Yazijioghlu 'Ali on the Christian Turks of the Dobruja, p. 653
- ^ İnalcık, Halil (1998). "Dobrudja". Encyclopaedia of Islam. Vol. II. Leiden: E. J. Brill. p. 610 a. ISBN 978-90-04-07026-4.
- ^ A. Ischirkoff, Les Bulgares en Dobroudja, p. 4
- ^ A. Ischirkoff, Les Bulgares en Dobroudja, pp. 5–7
- ^ Allard, Camille (1857). Mission médicale dans la Tatarie-Dobroutscha (in French). Paris. pp. 7–8. OCLC 36764237.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Stănciugel, Robert; Bălaşa, Liliana Monica (2005). Dobrogea în Secolele VII–XIX. Evoluţie istorică (in Romanian). București. pp. 68–70.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Forester, Thomas (1857). The Danube and the Black Sea: Memoir on Their Junction by a Railway between Tchernavoda and a Free Port at Kustendje. London: Edward Stanford. p. 96. OCLC 26010612.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 13
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 30
- ^ Eusebios–Hieronymos (2005). Ibarez, Josh Miguel Blasco (ed.). Hieronymi Chronicon (in Latin). p. 167. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
- ^ Aristotle (2000). ""Politics", Book V, 6". In Jowett, Benjamin (ed.). Aristotle's Politics. Adelaide: University of Adelaide. Archived from the original on February 22, 2008. Retrieved 2007-04-30.
- ^ C. Müller, Fragmenta historicorum Graecorum, Paris, 1841, I, pp. 170–173
- ^ Herodotus (1920). "The Histories, Book IV, 93". In Godley, A. D. (ed.). Herodotus. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. OCLC 1610641. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
- ^ Thucydides (1910). "The Peloponnesian War, Book II, Ch. 97". In Crawley, Richard (ed.). History of the Peloponnesian war. London: J.M. Dent. OCLC 7727833. Retrieved 2007-04-30.
- ^ Thucydides, The Peloponnesian War, Book VII, Ch. 98
- ^ Marcus Junianus Justinus (1853). "Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus, Book IX, 2". In Watson, John Selby (ed.). Justin, Cornelius Nepos, and Eutropius. London: H.G. Bohn. pp. 81–82. OCLC 11259464. Retrieved 2007-04-30.
- ^ Kalogeropoulos, Xenofon (2023-04-28). "Enemy of my Enemy: King Mithradates VI of Pontos and his alternative model of Hellenistic kingship". Kleio His Journal. Retrieved 2024-05-26.
- ^ Roller, Duane W. (2020). "Lucullus and Mithridates VI". Empire of the Black Sea: The Rise and Fall of the Mithridatic World. Oxford University Press. pp. 174–191. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190887841.003.0012. ISBN 9780197500552.
- ^ Paroń, Aleksander (2021-05-24), "Black Sea-Caspian Steppe: Outline of Ethnic and Political Relations to the End of the Ninth Century", The Pechenegs: Nomads in the Political and Cultural Landscape of Medieval Europe, Brill, pp. 47–84, ISBN 978-90-04-44109-5, retrieved 2024-05-26
- ^ Cassius Dio (1917). "Book LI, Ch. 24". In Cary, Earnest; Foster, Herbert Baldwin (eds.). Dio's Roman History, Vol VI. The Loeb classical library. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press. pp. 71–72. OCLC 688941.
- ^ Cassius Dio, Roman History, Book LI, Ch. 26, Vol VI, pp. 75–77
- ^ Cassius Dio, lv.29
- ^ Iordanes, The Origin and Deeds of the Goths, Ch. XVIII Archived 2006-04-24 at the Wayback Machine, sect. 101–102
- ^ Zosimos (1814). "Book I". The History of Count Zosimus, Sometime Advocate and Chancellor of the Roman Empire. London: Printed for J. Davis by W. Green and T. Chaplin. p. 22. OCLC 56628978.
- ^ Constantine Porphyrogennetos (1864). "Περί των Θεμάτων (De thematibus)" (PDF). In Migne, J. P. (ed.). Του σοφωτάτου δεσπότου και αυτοκράτορος Κωνσταντίνου, του Πορφυρογεννήτου, τα ευρισκόμενα πάντα. Τομ. β (PDF). Patrologiae cursus completus v.113 (in Greek). Paris: Apud Garnier Fratres, editores et J.-P. Migne, successores. OCLC 54878095. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 10, 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-01.
- ^ S. Vaklinov, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI–XI век", p. 65
- ^ S. Vaklinov, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI–XI век", pp. 48-50
- ^ S. Vaklinov, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI–XI век", p. 64
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, p. 28
- ^ Petar Mutafchiev, Добруджа. Сборник от Студии, Sofia,
- ^ Веселин Бешевлиев, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI-XI век", София, 1977, стр. 97–103.
- ^ Petkanova, Donka (1981). "Българско творчество в традициите на апокрифите. Български апокрифен летопис". Стара българска литература. Апокрифи (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Български писател. OCLC 177289940.
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.) Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, pp. 16–44.
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.), Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, pp. 45-91.
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.), Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, pp. 179, 257, 294.
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, p. 11
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.), Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, p. 257.
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.), Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, p. 293.
- ^ S. Vaklinov, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI-XI век", p. 65.
- ^ Beshevliev, Veselin (1979). Първобългарски надписи. Sofia: Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. pp. 192–200. OCLC 5310246.
- ^ V Beshevliev, "Първобългарски надписи"
- ^ A. Kuzev, V. Gyuzelev (eds.), Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море, p. 186.
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani şi bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, p. 71
- ^ Leo Diaconus (1988). "Книга Девястая". Лев Диакон. История. Памятники исторической мысли (in Russian). Moscow: Наука. ISBN 978-5-02-008918-1. Archived from the original on 2006-09-07.
- ^ Mutafchiev, Petar (1947). "Добруджа в миналото". Добруджа, Сборник от студии (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Хемус. p. 3. OCLC 15533292.
- ^ V. Mărculeţ, Asupra organizării teritoriilor bizantine de la Dunărea de Jos în secolele X-XII
- ^ Madgearu, Alexandru (2001). "The Church Organization at the Lower Danube, between 971 and 1020" (PDF). In Popescu, Emilian; Tudor, Teotei (eds.). Études byzantines et post-byzantines. Vol. IV. Iași: Trinitas. p. 75. ISBN 978-973-8179-38-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-10-27. Retrieved 2007-05-13.
- ^ Levchenko, M.V. (1951). "Ценный источник по вопросу русско-византийских отношений в X веке". Византийский Временник (in Russian). 4: 66–68. ISSN 0132-3776.
- ^ Cedrenus, Georgius (1889). Migne, J. P. (ed.). "Σύνοψις Ιστοριών (Compendium Historiarum), II, s. 452" Γεωργίου του Κεδρηνού Σύνοψις ιστοριών. Τομ. Β (PDF). Patrologiae cursus completus v.122 (in Greek). Paris: Garnier. OCLC 64824669. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 9, 2008. Retrieved 2011-02-04.
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, pp. 112–115
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, pp. 184–185
- ^ Rashev, Rasho (1977). "Землените укрепителни строежи на Долния Дунав (VII–X в.)". Candidate Dissertation. Typewritten (in Bulgarian). Sofia: 79–81.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ S. Vaklinov, "Формиране на старобългарската култура VI-XI век", pp. 79–81.
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, pp. 122–123
- ^ Cedrenus, Historiarum compendium, II, s. 514–515 Archived April 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cedrenus, Historiarum compendium, II, s. 582–584 Archived April 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tatos is mentioned as a Patzinak by a contemporaneous Byzantine source (Joannes Zonaras (1887). "Epitome historiarum, lib. 13–18, s. 713" (PDF). In Migne, J.P. (ed.). Ιωάννου του Ζωναρά τα ευρισκόμενα πάντα: ιστορικά, κανονικά, δογματικά (μέροςβ΄). Patrologiae cursus completus v.135 (in Greek). Paris. OCLC 38636706. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-10. Retrieved 2007-05-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)). This opinion is supported by modern historians (Madgearu, Alexandru (1999). "Dunărea în epoca bizantină (secolele X-XII): o frontieră permeabilă" (PDF). Revista istorică (in Romanian). 10 (1–2): 48–49. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-09. Retrieved 2007-04-16.). They were considered to be Vlach or Russian by some authors. For a survey of these opinions see I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani şi bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, pp. 139–147 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original on July 10, 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-16.{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani şi bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, pp. 136, 141
- ^ Comnena, Anna (1928). "Book VI, 14". In Elizabeth A. Dawes (ed.). The Alexiad. London: Routledge, Kegan, Paul. p. 164. OCLC 67891792. Archived from the original on 2020-04-13. Retrieved 2007-04-28.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, pp. 192–193
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 194
- ^ P. Wittek, Yazijioghlu 'Ali on the Christian Turks of the Dobruja, pp. 640, 648
- ^ P. Wittek, Yazijioghlu 'Ali on the Christian Turks of the Dobruja, pp. 648, 658
- ^ Rezachevici, Constantin (May 1997). "Găgăuzii". Magazin Istoric (6). OCLC 50096285. Archived from the original on January 26, 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ Ив. К. Димитровъ, Прѣселение на селджукски турци въ Добруджа около срѣдата на XIII вѣкъ, стр. 32—33
- ^ Dimitri Korobeinikov, "A broken mirror: the Kipçak world in the thirteenth century", In: The Other Europe from the Middle Ages, Edited by Florin Curta, Brill 2008, p. 396
- ^ Andreev, Yordan; Lalkov, Milcho (1996). Българските ханове и царе от хан Кубрат до цар Борис III (in Bulgarian). Veliko Tarnovo: Абагар. p. 214. ISBN 978-954-427-216-6.
- ^ Pachymeres, ib., pp. 230-231
- ^ Ив. К. Димитровъ, каз. стат., стр. 33–34
- ^ Васил Н. Златарски, История на българската държава през срeднитe вeкове. Том III. Второ българско царство. България при Асeневци (1187–1280), стр. 517
- ^ П. Ников, каз. съч., стр. 143
- ^ Васил Н. Златарски, История на българската държава през срeднитe вeкове. Том III. Второ българско царство. България при Асeневци (1187–1280), стр. 545-549
- ^ Y. Andreev, M. Lalkov, Българските ханове и царе, p. 226
- ^ Васил Н. Златарски, История на българската държава през срeднитe вeкове. Том III. Второ българско царство. България при Асeневци (1187—1280), стр. 554
- ^ Y. Andreev, M. Lalkov, Българските ханове и царе, p. 247
- ^ Miklosich, Franz; Müller, eds. (1860). "LXIII. 6883—1325 maio-iunio ind. VIII. Synodus dirimit sex controversias". Acta et diplomata Graeca medii aevi sacra et profana, vol. I. Vien: Carolus Gerold. p. 135.
- ^ Names of the rulers of the Principality of Karvuna are given here as spelled in modern Bulgarian and Romanian, respectively.
- ^ Ioannes Cantacuzenus (1866). "Historiae, II, s. 584–585" (PDF). In Migne, J.P. (ed.). Ιωάννου του Καντακουζηνού τα ευρισκόμενα πάντα: ιστορικά, θεολογικά, απολογητικά, μέρος 1ο (PDF). Patrologiae cursus completus v.153 (in Greek). Paris: Apud J.-P. Migne. OCLC 17356688. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 10, 2007. Retrieved 2007-05-01.
- ^ Miller, Timothy S. (1975). "The War of Galata, according to the History of John Cantacuzenus (1348)". The History of John Cantacuzenus (Book IV): Text, Translation and Commentary. Catholic University of America. Archived from the original on 2007-09-26. Retrieved 2007-04-28 – via De Re Militari.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 197
- ^ I. Barnea, Şt.Ştefănescu, Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos, p. 351
- ^ Miklosich, Franz; Müller, eds. (1860). "CLXVI. (6865—1357) iunio ind. X. Synodus metropolitae Mesembriae restituit duo castella". Acta et diplomata Graeca medii aevi sacra et profana, vol. I. Vien: Carolus Gerold. p. 367.
- ^ İnalcık, Halil (1998). "Dobrudja". Encyclopaedia of Islam. Vol. II. Leiden: E. J. Brill. p. 611 b. ISBN 978-90-04-07026-4.
- ^ Delev, Petǎr; Valeri Kacunov; Plamen Mitev; Evgenija Kalinova; Iskra Baeva; Bojan Dobrev (2006). "19. Bǎlgarija pri Car Ivan Aleksandǎr". Istorija i civilizacija za 11. klas (in Bulgarian). Trud, Sirma.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 205
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 249
- ^ Shaw, Stanford Jay; Ezel Kural Shaw (1977). History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-521-29163-7.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 333
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, pp. 358–360
- ^ Kosev et al., Възстановяване и утвърждаване на българската държава p. 416
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 365
- ^ Mihalcea, Alexandru (2005-01-21). "150 de ani de istorie comuna. Italienii din Dobrogea -mica Italie a unor mesteri mari". România Liberă (in Romanian). Archived from the original on June 7, 2006. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, pp. 363-364, 381
- ^ Borders, Boundaries and Belonging in Post-Ottoman Space in the Interwar Period, Brill, 2022-11-21, ISBN 978-90-04-52990-8, retrieved 2024-05-26
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 430
- ^ Cojoc, Mariana; Tiță, Magdalena (2006-09-06). "Proiecții teritoriale bulgare". Ziua de Constanţa (in Romanian). Retrieved 2007-02-15.
- ^ "Ziua Dobrogei". Agerpres (in Romanian). 14 November 2019. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2020.
- ^ Quataert, Donald; İnalcık, Halil (1997). An Economic and Social History of the Ottoman Empire. Cambridge University Press. p. 650. ISBN 978-0-521-57456-3.
- ^ Miletich, Liubomir (1902). Старото българско население в северо-източна България (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Книжовно Дружество. p. 6. OCLC 67304814.
- ^ Miletich, Liubomir (1903). Südslavische Dialektstudien: das Ostbulgarische (in German). Vienna: 1903. p. 19. OCLC 65828513.
- ^ "Les Bulgares sont venus dans la Dobrodja depuis une vingtaine d'années, abandonnant des terres ingrates pour celles bien plus fertiles qu'ils ont trouvée dans ce pays" in Jonesco, J. (1850). Excursion agricole dans la plaine de la Dobrodja (in French). Constantinopole: Imprimerie du Journal de Constantinopole. p. 82. OCLC 251025693.
- ^ Lampato, Francesco, ed. (1851). Annali universali di statistica, economia, pubblica, geografia, storia, viaggi e commercio (in Italian). Milano: Presso la Societa' degli Editori degli Annali Universali delle Scienze e dell'Industria. p. 211.
- ^ a b Seişanu, Romulus (1928). Dobrogea. Gurile Dunării şi Insula Şerpilor. Schiţă monografică (in Romanian). București: Tipografia ziarului "Universul". p. 177.
- ^ L. Miletich, Старото българско население в северо-източна България, pp. 169–170
- ^ a b Kosev, D.; Hristov, Hr.; Todorov, N.; Angelov, D. (1991). Възстановяване и утвърждаване на българската държава. Националноосвободителни борби 1878–1903. История на България (in Bulgarian). Vol. 7. Sofia: Издателство на Българската академия на науките. p. 412. OCLC 63809870.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, p. 337
- ^ Kosev et al., Възстановяване и утвърждаване на българската държава, pp. 460–461
- ^ Baron d'Hogguer (February 1879). Informaţiuni asupra Dobrogei. Starea eĭ de astăḍi. Resursele şi viitorul ei (in Romanian). Bucureşci: Editura Librăriei SOCEC.
- ^ A. Rădulescu, I. Bitoleanu, Istoria Dobrogei, pp. 322–323
- ^ U.S. Government Printing Office, 1957, Documents on German foreign policy, 1918–1945, from the archives of the German Foreign Ministry, p. 336
- ^ a b Roman, I. N. (1919). "La population de la Dobrogea. D'apres le recensement du 1er janvier 1913". In Demetrescu, A (ed.). La Dobrogea Roumaine. Études et documents (in French). Bucarest. OCLC 80634772.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Lucian Boia, Central European University Press, 2001, History and Myth in Romanian Consciousness, p. 182
- ^ K. Karpat, : Correspondance Politique des Consuls. Turguie (Tulqa). 1 (1878) 280-82
- ^ a b G. Dănescu, Dobrogea (La Dobroudja). Étude de Géographie physique et ethnographique
- ^ a b Calculated from results of the 1930 census per county, taken from Mănuilă, Sabin (1939). La Population de la Dobroudja (in French). Bucarest: Institut Central de Statistique. OCLC 1983592.
- ^ a b c d e Calculated from statistics for the counties of Tulcea and Constanța from "Populația după etnie la recensămintele din perioada 1930–2002, pe judete" (PDF) (in Romanian). Guvernul României — Agenţia Națională pentru Romi. pp. 5–6, 13–14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ a b 2011 census results per county, cities and towns "Populaţia stabilă pe sexe, după etnie – categorii de localităţi, macroregiuni, regiuni de dezvoltare şi judeţe" (in Romanian). Institutul Național de Statistică. Archived from the original (XLS) on 2019-08-15. Retrieved 2015-11-20.
- ^ "Ethnic population at the censuses in the period 1930–2021" (in Romanian). INSSE. Retrieved 24 April 2024.
- ^ Calculated from the results of the 2001 Bulgarian census for the administrative regions of Dobrich and Silistra, from "Население към 01.03.2001 г. по области и етническа група" (in Bulgarian). Националния статистически институт. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ a b Calculated from the results of the 2011 Bulgarian census for the administrative regions of Dobrich and Silistra, from "Население по етническа група и майчин език" (in Bulgarian). Националния статистически институт. Archived from the original on 2015-12-19. Retrieved 2015-11-20.
- ^ Calculated from the results of the 2011 Bulgarian census for the administrative regions of Dobrich and Silistra, from"POPULATION BY ETHNIC GROUP, STATISTICAL REGIONS, DISTRICTS AND MUNICIPALITIES AS OF 07.09.2021". infostat.nsi.bg. National Statistical Institute, Bulgaria.
References
- Dănescu, Grigore (1903). Dobrogea (La Dobroudja). Étude de Géographie physique et ethnographique (in French). Bucarest: Imprimerie de l'Indépendance Roumaine. OCLC 10596414.
- Ischirkoff, A. (1919). Les Bulgares en Dobroudja; aperçu historique et ethnographique (in French). Berne: Imprimerie Pochon-Jent & Bühler. OCLC 4061330.
- Wittek, Paul (1952). "Yazijioghlu 'Ali on the Christian Turks of the Dobruja". Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies. 14 (3). Cambridge University Press on behalf of School of Oriental and African Studies: 639–668. doi:10.1017/S0041977X00088595. ISSN 0041-977X. JSTOR 609124. S2CID 140172969.. Subscription needed for online access.
- Barnea, Ion; Ștefănescu, Ștefan (1971). Bizantini, romani și bulgari la Dunărea de Jos. Din Istoria Dobrogei (in Romanian). Vol. 3. București: Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste România. OCLC 1113905.
- Vaklinov, Stancho (1977). Формиране на старобългарската култура VI-XI век (in Bulgarian). Sofia: Издателство Наука и Изкуство. OCLC 71440284.
- Kuzev, Aleksandar; Gyuzelev, Vasil, eds. (1981). Градове и крепости но Дунава и Черно море. Български средновековни градове и крепости (in Bulgarian). Vol. 1. Varna: Книгоиздателство "Георги Бакалов". OCLC 10020724.
- Rădulescu, Adrian; Bitoleanu, Ion (1998). Istoria Dobrogei (in Romanian). Constanţa: Editura Ex Ponto. ISBN 978-973-9385-32-9.
- Mărculeţ, Vasile (2003). "Asupra organizării teritoriilor bizantine de la Dunărea de Jos în secolele X-XII: thema Mesopotamia Apusului, strategatul Dristrei, thema Paristrion – Paradunavon". In Dobre, Manuela (ed.). Istorie şi ideologie (in Romanian). București: Editura Universității din București. ISBN 978-973-575-658-1. Archived from the original on 2018-04-18. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- Hitchins, Keith (2004). Romania 1866–1947 (in Romanian) (II ed.). București: Humanitas. ISBN 978-973-50-0551-1.
Further reading
- Strabo (1903). "Book VII". In Hans Claude Hamilton; W. Falconer (eds.). The Geography of Strabo. London: George Bell & Sons. OCLC 250411. Retrieved 2007-04-29.
- Rădulescu, Adrian; Bitoleanu, Ion (1979). Istoria românilor dintre Dunăre şi Mare: Dobrogea (in Romanian). București: Editura Științifică și Enciclopedică. OCLC 5832576.
- Iordachi, Constantin (2001), "The California of the Romanians": The Integration of Northern Dobrogea into Romania, 1878-1913, in Nation-Building and Contested Identities Romanian & Hungarian Case Studies
- Sallanz, Josef, ed. (2005). Die Dobrudscha. Ethnische Minderheiten, Kulturlandschaft, Transformation; Ergebnisse eines Geländekurses des Instituts für Geographie der Universität Potsdam im Südosten Rumäniens. (= Praxis Kultur- und Sozialgeographie; 35) (in German) (II ed.). Potsdam: Universitätsverlag Potsdam. ISBN 978-3-937786-76-6.
- Sallanz, Josef (2007). Bedeutungswandel von Ethnizität unter dem Einfluss von Globalisierung. Die rumänische Dobrudscha als Beispiel. (= Potsdamer Geographische Forschungen; 26) (in German). Potsdam: Universitätsverlag Potsdam. ISBN 978-3-939469-81-0.






