Unitary state
| Part of the Politics series |
| Basic forms of government |
|---|
| List of forms · List of countries |
|
|
A unitary state is a (sovereign) state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or sub state units). Such units exercise only the powers that the central government chooses to delegate. Although political power may be delegated through devolution to regional or local governments by statute, the central government may alter the statute, to override the decisions of devolved governments or expand their powers.
The modern unitary state concept originated in France; in the aftermath of the Hundred Years' War, national feelings that emerged from the war unified France. The war accelerated the process of transforming France from a feudal monarchy to a unitary state. The French then later spread unitary states by conquests, throughout Europe during and after the Napoleonic Wars, and to the world through the vast French colonial empire.[1] Presently, prefects remain an illustration of the French unitary state system, as the representatives of the State in each department, tasked with upholding central government policies.
Unitary states stand in contrast to federations, also known as federal states. A large majority of the UN member countries, 166 out of 193, have a unitary system of government, while significant population and land mass is under some kind of federation.[2]
Devolution compared with federalism
A unitary system of government can be considered to be the opposite of federalism. In federations, the provincial/regional governments share powers with the central government as equal actors through a written constitution, to which the consent of both is required to make amendments. This means that the sub-national units have a right to existence and powers that cannot be unilaterally changed by the central government.[3]
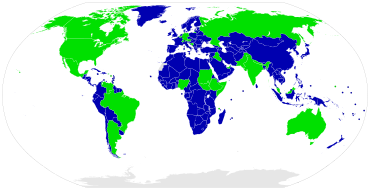
List of current unitary sovereign states
Italics: States with limited recognition from other sovereign states or intergovernmental organizations.
Unitary republics
 Abkhazia
Abkhazia Afghanistan (internationally recognized)
Afghanistan (internationally recognized) Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria Angola
Angola Armenia
Armenia Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bangladesh[4]
Bangladesh[4] Barbados[5]
Barbados[5] Belarus
Belarus Benin
Benin Bolivia
Bolivia Botswana
Botswana Bulgaria
Bulgaria Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Burundi
Burundi Cameroon
Cameroon Cape Verde
Cape Verde Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Chile
Chile People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Democratic Republic of the Congo[4]
Democratic Republic of the Congo[4] Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Costa Rica
Costa Rica Croatia
Croatia Cuba
Cuba Cyprus
Cyprus North Cyprus
North Cyprus Czech Republic
Czech Republic Djibouti
Djibouti Dominica
Dominica Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic East Timor
East Timor Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt El Salvador
El Salvador Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Eritrea
Eritrea Estonia
Estonia Fiji
Fiji Finland
Finland France
France Gabon
Gabon Gambia
Gambia Georgia
Georgia Ghana
Ghana Greece
Greece Guatemala[4]
Guatemala[4] Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Guyana
Guyana Haiti[4]
Haiti[4] Honduras
Honduras Hungary
Hungary Iceland[4]
Iceland[4] Indonesia[4]
Indonesia[4] Iran
Iran Ireland
Ireland Israel
Israel Italy[4]
Italy[4] Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast Kazakhstan[4]
Kazakhstan[4] Kenya[4]
Kenya[4] Kiribati
Kiribati North Korea
North Korea South Korea
South Korea Kosovo
Kosovo Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Laos
Laos Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Liberia
Liberia Libya
Libya Lithuania
Lithuania Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Malta
Malta Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands Mauritania
Mauritania Mauritius
Mauritius Moldova
Moldova Mongolia
Mongolia Montenegro
Montenegro Mozambique
Mozambique Myanmar
Myanmar Namibia
Namibia Nauru
Nauru Nicaragua
Nicaragua Niger
Niger North Macedonia
North Macedonia Palau
Palau Palestine
Palestine Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Philippines[4]
Philippines[4] Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Romania
Romania Rwanda
Rwanda Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic Samoa
Samoa San Marino
San Marino São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe Senegal
Senegal Serbia
Serbia Seychelles
Seychelles Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Singapore
Singapore Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia South Africa
South Africa South Ossetia
South Ossetia Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Suriname
Suriname Syria
Syria Republic of China (Taiwan)[6]
Republic of China (Taiwan)[6] Tajikistan
Tajikistan Tanzania
Tanzania Togo
Togo Transnistria
Transnistria Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Uganda[4]
Uganda[4] Ukraine
Ukraine Uruguay
Uruguay Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan Vanuatu
Vanuatu Vietnam
Vietnam Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Unitary monarchies
The United Kingdom is an example of a unitary state. Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have a degree of autonomous devolved power, but such power is delegated by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which may enact laws unilaterally altering or abolishing devolution. Similarly in Spain, the devolved powers are delegated through the central government.
 Andorra
Andorra Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Bahamas
Bahamas Bahrain
Bahrain Belize
Belize Bhutan
Bhutan Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam Cambodia
Cambodia Kingdom of Denmark[4]
Kingdom of Denmark[4] Eswatini
Eswatini Grenada
Grenada Jamaica
Jamaica Japan[4]
Japan[4] Jordan
Jordan Kuwait
Kuwait Lesotho
Lesotho Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Luxembourg
Luxembourg Monaco
Monaco Morocco[4]
Morocco[4] Kingdom of the Netherlands
Kingdom of the Netherlands New Zealand[7]
New Zealand[7] Kingdom of Norway
Kingdom of Norway Oman
Oman Papua New Guinea[3]
Papua New Guinea[3] Qatar
Qatar Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Spain
Spain Kingdom of Sweden
Kingdom of Sweden Thailand
Thailand Tonga
Tonga Tuvalu
Tuvalu United Kingdom[8][4]
United Kingdom[8][4] Vatican City
Vatican City
Unitary states with a unique form of government
List of former unitary states
 /
/ Belgium (1830–1993)
Belgium (1830–1993) /
/ Brazil (1822–1889)
Brazil (1822–1889) Bosnia and Herzegovina (1992–1995)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (1992–1995) /
/ Comoros (1975-1978)
Comoros (1975-1978) /
/ /
/ /
/ Ethiopia (1270–1995)
Ethiopia (1270–1995) /
/ /
/ /
/ /
/ Iraq (1932–2005)
Iraq (1932–2005) /
/ /
/ Nepal (1768–2008)
Nepal (1768–2008) Somalia (1960–2004)
Somalia (1960–2004) Yemen (1990–2022)
Yemen (1990–2022)
See also
- Centralized government
- Constitutional economics
- Political economy
- Regional state
- Rule according to higher law
- Unicameralism
- Unitary authority
References
- ^ Holmes, Urban T. Jr. & Schutz, Alexander Herman [in German] (1948). A History of the French Language (revised ed.). Columbus, OH: Harold L. Hedrick. p. 61.[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Democracy". United Nations. 2015-11-20. Archived from the original on 2021-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-22.
- ^ a b Ghai, Yash; Regan, Anthony J. (September 2006). "Unitary state, devolution, autonomy, secession: State building and nation building in Bougainville, Papua New Guinea". The Round Table. 95 (386): 589–608. doi:10.1080/00358530600931178. ISSN 0035-8533. S2CID 153980559.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "What is a Unitary State?". WorldAtlas. August 2017. Retrieved 2019-02-22.
- ^ Faulconbridge, Guy; Ellsworth, Brian (2021-11-30). "Barbados ditches Britain's Queen Elizabeth to become a republic". Reuters. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- ^ See also Political status of Taiwan, two Chinas and Cross-Strait relations.
- ^ "Story: Nation and government – From colony to nation". The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Manatū Taonga Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 29 August 2013. Retrieved 19 April 2014.
- ^ Spicker, Paul (June 30, 2014). "Social policy in the UK". An introduction to Social Policy. Robert Gordon University – Aberdeen Business School. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 19 April 2014.
- ^ Gul, Ayaz (28 September 2021). "Taliban Say They Will Use Parts of Monarchy Constitution to Run Afghanistan for Now". Voice of America. Islamabad, Pakistan. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
The Taliban said Tuesday they plan to temporarily enact articles from Afghanistan's 1964 constitution that are 'not in conflict with Islamic Sharia (law)' to govern the country.
- ^ "Constitution of Afghanistan = Assasi Qanun (1964)". University of Nebraska-Omaha. Retrieved 21 October 2022.
Afghanistan is a Constitutional Monarchy; an independent, unitary and indivisible state.
- ^ George, Susannah (18 February 2023). "Inside the Taliban campaign to forge a religious emirate". The Washington Post. Retrieved 19 February 2023.
