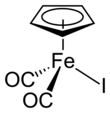
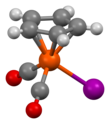
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide
| |||
 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.006 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5FeIO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 303.864 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Black crystalline solid (density = 2.374 g/cm3) | ||
| Melting point | 119 °C (246 °F; 392 K) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Cs | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H302, H312, H332 | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Here | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide is an organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I. It is a dark brown solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I, or FpI as it is often known, is an intermediate for the preparation of other organoiron compounds such as in ferraboranes.
Preparation
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl iodide is synthesized by the reaction of cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer with I2:[1]
- Cp2Fe2(CO)4 + I2 → 2 CpFe(CO)2I
It was first reported by Pauson and Hallam.[2]
Structure
The compound has Cs symmetry, with a mirror plane intersecting one carbon of the Cp ring as well as the iron and iodide centre. The compound adopts a piano stool structure: the cyclopentadienyl ligand is the "seat" and three other ligands are "legs". Such compounds are members of the half-sandwich family of compounds, which is a subgroup of the metallocenes. X-ray crystallography shows the following features: Fe-Cp centroid = 1.72, Fe-I = 2.61, and Fe-CO = 1.78 Å.[3]
Electron counting of this iron(II) complex indicates that (C5H5)Fe(CO)2I is an 18-electron complex: using the neutral method there are 8 electrons from the iron, 5 electrons from the cyclopentadienyl anion, 2 electrons from each of the carbonyls, and 1 electron from the iodide.
References
- ^ King, R. B.; Stone, F. G. A "Cyclopentadienyl Metal Carbonyls and some Derivatives" Inorg. Synth. 1963, volume 7, pp. 99-115. doi:10.1002/9780470132388.ch31
- ^ B. F. Hallam, P. L. Pauson "Ferrocene Derivatives. Part III. Cyclopentadienyliron Carbonyls" J. Chem. Soc. 1956, pp. 3031-3037.
- ^ Zeller, M.; Lazich, E.; Hunter, A. D. (2003). "Dicarbonyl(η5-cyclopentadienyl)iodoiron(II)". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 59 (10): m914 – m915. doi:10.1107/S1600536803019950.