Cross-border language
A cross-border language[1] or trans-border language[2] is a language spoken by a population (an ethnic group or nation) that lives in a geographical area in two or several internationally recognized countries that have common land or maritime borders.
Types
There are four types of cross-border languages. They are measured according to the criteria of the size of the geographical area in which they are spoken as well as their number of speakers. According to the geographical criteria, cross-border languages can be limited international languages or simply international languages.[3]
Cross-border languages are limited international languages when they are spread over a geographical area which is small compared to the size of the country; they may or may not have official status. They are international when they are situated over one or several geographical areas (ranging from regional to continental) with official status in at least one country. According to the population criteria, cross-border languages are either symmetrical or asymmetrical.[3] Symmetrical border languages are those spoken by small or large linguistic groups on both sides of a border. Many are languages which may seem insignificant, but which play an important role in interactions, integration and economic activity.
Asymmetrical border languages are spoken by large groups on one side of a border and small groups on the other. As they are dominant in at least one country, they have the potential to be used in larger domains, depending on the speakers' resources.[3]

1 - Symmetrical and limited: Gagauz in yellow
2 - Symmetrical and international: German in green
3 - Asymmetrical and limited: Basque in purple
4 - Asymmetrical and international: Hungarian in blue
- Symmetrical and limited; Gagauz, spoken by 250,000 people, of which 170,000 in Moldova, has no international recognition. It is spoken by various communities in Ukraine and Romania, as well as Bulgaria. Ojibwe is spoken around the Great Lakes, on or close to the US-Canadian border, with no official status. These languages are the most common, the most diverse and at the highest threat of extinction. They have little or no recognition on both sides of the border and represent the majority of the cross-border languages in the world.
- Symmetrical and international; German has official status and is the majority language in Austria and Germany. The language is spoken in eight countries. Many languages disappear in favour of such languages. These languages, which are few in number globally, represent "projects of linguicide"[4] for the majority of minor languages, and the UNESCO report on endangered languages shows that, as an example, French, which is in this category, seriously threatens 26 languages and dialects in France and 13 languages in Quebec.[5]
- Asymmetrical and limited; Basque is recognised as an official language alongside Spanish in 4 of the 7 provinces of the Basque Country (it has partial regional recognition in Navarre). In the 3 provinces of the French Basque Country, it has no recognition. Wolof, the de facto lingua franca and majority language in Senegal, is also a minority language in Mauritania, where it has no official status.
- Asymmetrical and international; Hungarian is a minority language in Romania (Transylvania), in Slovakia, in Serbia (Vojvodina) with or without minority rights in all the countries bordering Hungary, where it is the only official language. Russian in Kazakhstan has become strongly marginalised compared to its previous predominance following the establishment of a linguistic policy which aims to reduce the Russian-speaking presence, which still represents 30% of the total population. However, Russian remains an international language despite the fall of the USSR, although it is losing ground in all the ex-republics except Russia.
Changes in status

Languages can change status due to all sorts of political circumstances. Kurdish, a minority language in Turkey, Syria, Iran and Iraq, was considered a symmetrical and limited language, but thanks to the recognition of Kurdish as an official language in Iraqi Kurdistan in the new constitution of Iraq,[6] it became an asymmetrical and limited cross-border language with the 15 October 2005 referendum. This strengthened the possibilities for survival and vigorous use of the language, as well as giving hope to neighbouring communities.
Difference in population
When considering both asymmetrical and symmetrical cross-border languages, the population of the country in question remains key. A minority language among small language groups in a small country may be more important than a language with a large number of speakers in a large country.
The population which speaks Hausa numbers 25 million people in total, of which 18 million are part of the population of 140 million in Nigeria. They are a large linguistic population, but they are a minority in the country, representing only 13% of Nigerians. On the other hand, there are only 5 million Hausas in Niger, out of a population of 11 million, but they are proportionally greater than in Nigeria, as 45% of the population, that is, 3.5 times the proportion of the population of the country as a whole. Hausa is thus more important sociolinguistically in Niger than in Nigeria.
Cross-border languages and international languages

A cross-border language is always an international language (spoken in two or more nations) but not all international languages are cross-border languages. For example, Portuguese, which is an international language spoken in Angola, Brazil, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal, Timor-Leste, São Tomé and Principe and Cape Verde, has no territorial continuity between these countries (except arguably if Galician, spoken in Spain, generally considered a separate language, is considered a dialect of Portuguese). The Lusophone countries over four continents have no common borders.
In defining cross-border languages, the fundamental criterion is the presence of a language on both sides of a border. If a language is spoken in two countries without common borders such as French in Canada and France, it may be preferable to refer to a world language or a shared language. French is however also a cross-border language, spoken on both sides of the borders of France, Belgium, Luxembourg, Monaco, Switzerland and Italy (Aosta Valley).
In the current global economy, English is an international language for the exchange of goods and services. It became a cross-border language following the conquests of the British Empire, notably with the establishment of the Canada–United States border and the partition of Ireland. Languages such as Vietnamese or Japanese, which are not cross-border languages, have little chance of being used in cross-border exchanges, and their use remains limited to the confines of one country. Another exception is Chinese, an official language in three sovereign states, which is an international language but not trans-border. Singapore (76% ethnic Chinese), Taiwan and China have no territorial continuity.
Cross-border languages rarely have no native speakers in the border regions, excepting international lingua francas. Swahili is one exception; although it is the native language of a mere 5 million people on the coasts of Kenya and Tanzania, it is used as a lingua franca and a cross-border language over 11 borders and with 55 million speakers. Swahili is used as a trade language between Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Despite its small territory and low number of monolingual native speakers, Swahili, particularly in contact with Arabic, became the language of choice for communication between various groups of people.
Status of speakers
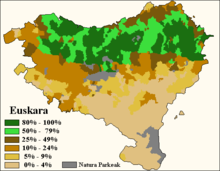
An individual living in an area where a cross-border language is spoken can exhibit various levels of comprehension. The four categories of speakers in terms of comprehension[citation needed] can be illustrated by the example of Basque, which is spoken in the western Pyrenees, on both sides of the border between the states of Spain and France.
- Cross-border language monolinguals. A Basque monolingual is a person who only speaks Basque in France or Spain. They represent a very small number, 0.7% of the population (20000 people).
- Active bilinguals. These are people who speak two languages, be it French and Basque or Spanish and Basque. They represent 26.9% of the population, split into three categories.
- 40% French- or Spanish- (erdara-, that is, non-Basque-) dominant bilinguals.
- 29% balanced bilinguals.
- 32% Basque-dominant bilinguals.
- Passive bilinguals. These are people who understand written and/or spoken Basque but who have little speaking ability. They represent 15.3% of the population.
- Official language or lingua franca monolinguals. Non-Basque-speaking monolinguals are those who speak only Spanish or French in the Basque Country. They are the majority, representing 57.8% of the population.
Relationship with the border
Border control regimes (police, customs, military posts, etc.), as a symbol of sovereignty and the means of regulating circulation of people and goods, are perceived as lines of separation and alienation by the people living on either side.[7]
Ethnolinguistic identities which cross arbitrary borders are often ignored by states and their officials. The feelings of the peoples divided by the separation border may be manifested in a strengthening of networks between different groups on both sides and a desire to ignore or supersede the national borders.
The presence of the border can contribute to two types of nationalism: either an ethnolinguistic nationalism based on a common (trans-border) language, or political nationalist movements identifying with the nations on each side of the border.
Cross-border languages are often codified in different ways on each side of a border, with different orthographic norms, etc. This complicates the standardisation of resources for education and literature and increases the cost of language planning for a given language, which is often necessary to prevent language endangerment.
Functions
Cross-border languages commonly have an economic role. The existence of trade between one country and another requires the use of an international and/or a cross-border language to facilitate exchange. English plays a major role in the relations between the United States and Canada, two of the most intertwined economies in the world.
The political milieu in many countries uses international languages most of the time, but trans-border languages are often used, in an informal or an official manner. Following the resolution of the border conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea, Eritrea uses Tigrinya and Arabic as working languages. Tigrinya and Arabic are spoken on both sides of the border with Ethiopia[8] and Sudan, respectively.
Culture is closely bound to language. A Flemish author or director from Belgium can easily release a book or film in the Netherlands. Dutch is a cross-border language which facilitates cultural and social exchanges.

Trans-border languages can play an intermediary role in the spread of religions. Institutions make use of cross-border languages as a propaganda tool to convert new populations. As an example, certain Christian churches evangelise populations in Africa with translations of the Bible and the help of associations such as the Summer Institute of Linguistics7. For instance, the Kimbanguist church, founded by a Congolese man converted by a Protestant missionary society, operates in the territory of the Kikongo language[9] (18 million speakers across Angola, Gabon and the western regions of Congo-Kinshasa and Congo-Brazzaville). Already over a century ago, oblate missionaries in the Congo studied Kikongo in Ipamu as part of their training.
Cross-border languages can represent a refuge. Many Basques became refugees in France during the Franco regime. Many Pashto speakers cross the Durand line to Pakistan to escape economic hardships as well as Taliban and American repression in Afghanistan. These speakers of a cross-border language are often not included in the census.
Smuggling is very widespread among cross-border linguistic minorities who can find a livelihood in it. Mohawk is used by indigenous people in Quebec or Ontario who can cross the American border with no problems, as their reservation straddles the Canada–United States border.[10]
Linguistic assimilation by trans-border languages, most often those which are asymmetrical and considered important by the rest of the population of the country, continues at the detriment of less prestigious languages. At the beginning of the 20th century, Brussels underwent a rather significant reduction in use of Dutch in favour of French, given the international status of the latter.
Future
Cross-border languages are normally defined in accordance with the laws of internationally-recognised states. However, so-called cross-border languages predate the establishment of state borders. For example, the Lunda language is primarily that of a language community and territory in southern-central Africa, before it is a minority language of the states of Angola, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The borders were created and enforced after the existence of the group, as is the case in many regions of the world.
Estimates based on current language policies assert that 90% of the 6000-7000 languages[11][12] in the world will become extinct in a century.[11] Language policies will determine the survival of cross-border languages in most countries. Certain tools exist such as the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, which protect minority languages and are supported by the language policy of the European Union, which can leave space to confront the linguistic imperialism of international languages.
List of cross-border languages
North America
- Canada / United States: English, French, Ojibwe/Chippewa, Seneca, Mohawk, Malecite-Passamaquoddy, Blackfoot, Salish and Okanagan. Alaska / British Columbia, & Yukon: Upper Tanana, Hän, Inupiaq, Tlingit, Tsimshian and English.
- United States / Russia: Aleut and Central Yupik.
- United States / Mexico: Spanglish, Spanish, Kumeyaay, O'odham, Afro-Seminole Creole and Kickapoo.
Central America
- Mexico / Guatemala: Spanish, Q'eqchi', Lacandon, Chuj, Jakaltek, Mam and Tektitek.
- Mexico / Belize: Spanish and Yucatec Maya.
- Belize / Guatemala: Spanish, Garifuna and Q'eqchi'.
- Haiti / Dominican Republic: Haitian Creole.
- Saint Martin: English (to some extent, French, Dutch and Papiamento).
- Guatemala / Honduras: Spanish, Garifuna, Pipil and Ch'orti'.
- Honduras / El Salvador: Spanish, Lenca and Pipil.
- Guatemala / El Salvador and Costa Rica / Nicaragua: Spanish.
- Nicaragua / Honduras: Spanish and Miskito.
- Costa Rica / Panama : Spanish, Bribri and Ngäbere.
- Panama / Colombia: Spanish, Embera and Kuna.
South America
- Argentina / Bolivia: Spanish, Wichí, Jujuy Quechua and Iyo'wujwa Chorote.
- Argentina / Brazil: Kaiwá, Spanish and Mbyá Guarani.
- Argentina / Chile: Spanish, Central Aymara, Huilliche, Mapudungun and Jujuy Quechua.
- Argentina / Paraguay : Spanish, Paraguayan Guarani, Wichí, Iyo'wujwa Chorote, Toba Qom, Kaiwá and Mbyá Guarani.
- Argentina / Uruguay: Spanish.
- Bolivia / Chile: Spanish, Central Aymara and South Bolivian Quechua.
- Brazil / French Guiana: Palikur, Portuguese, Emérillon, Karipúna and Wayampi.
- Brazil / Suriname: Portuguese and Sikiana.
- Brazil / Guyana: Portuguese, Akawaio, Patamona, Wapishana and Macushi.
- Brazil / Venezuela: Pemon, Ninam, Arutani, Yanomami and Nheengatu.
- Brazil / Colombia: Curripaco, Cubeo, Guanano, Tariana, Tucano, Macuna, Waimajã, Hup, Ticuna and Huitoto.
- Brazil / Peru: Matsés, Pisabo, Yaminawa, (Ucayali-Yurúa) Ashéninka, Amahuaca, Kulina, Arara Shawãdawa and Kashinawa.
- Brazil / Bolivia: Portuguese, Yaminawa, Wariʼ, Purubora, Chamacoco, Mekéns and Chiquitano. *
- Brazil / Uruguay: Mbyá Guarani.
- Brazil / Paraguay: Portuguese, Ava Guarani, Kaiwá, Paraguayan Guarani, Chamacoco, Toba Qom, Guaná and Pai Tavytera.
- Colombia / Ecuador : Spanish, Awa Pit, Cofán, Kichwa, Siona and Huitoto.
- Colombia / Peru: Spanish, Murui Huitoto, Nüpode Huitoto, Minica Huitoto, Inga, Resígaro, Yagua, Ticuna and Bora.
- Colombia / Venezuela: Spanish, Wayuu, Japreria, Yukpa, Barí, Tunebo, Guahibo, Cuiba, Puinave, Curripaco and Piapoco.
- Guyana / Suriname: Arawak.
- Guyana / Venezuela / Warao, Akawaio, Pemon and Arawak.
- Suriname / French Guiana: Wayana, Ndyuka and Carib (Kaliña).
- Peru / Ecuador: Spanish, Shuar, Achuar Shiwiar, Pastaza Quichua, Napo Quichua, Záparo and Secoya.
- Peru / Chile: Spanish and Aymara.
- Peru / Bolivia: Spanish, Central Aymara, North Bolivian Quechua, Ese Ejja and Yaminawá.
South Asia
- Afghanistan / Pakistan: Pashto, Balochi
- Pakistan / India: Urdu, Punjabi, Sindhi, Urdu
- India / Myanmar: Meitei (Manipuri)
- India / Nepal: Nepali, Bhojpuri
- India / Bhutan: Nepali, Lepcha
- India / Bangladesh: Bengali, Meitei (Manipuri), Chakma, Kokborok
- India / China: Tibetan
- India / Sri Lanka: Tamil
- India / Maldives: Divehi
References
- ^ Ndhlovu, Finex (2013-04-01). "Cross-border Languages in Southern African Economic and Political Integration". African Studies. 72 (1): 19–40. doi:10.1080/00020184.2013.776196. ISSN 0002-0184.
- ^ Chumbow, Beban Sammy (1999-01-01). "Transborder languages of Africa". Social Dynamics. 25 (1): 51–69. doi:10.1080/02533959908458661. ISSN 0253-3952.
- ^ a b c Bamgbose, Ayo (1993). "Deprived, Endangered, and Dying Languages". Diogenes. 41 (161): 19–25. doi:10.1177/039219219304116102. ISSN 0392-1921.
- ^ "Entreprises de linguicide", term used by Claude Hagège, Halte à la morte des langues, Paris, Éditions Odile Jacob, coll. « Poches Odile Jacob, 98. », 2002, 381 p.
- ^ "UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in danger". www.unesco.org. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- ^ "Iraq's Constitution of 2005 - Constitute Project" (PDF).
The Arabic language and the Kurdish language are the two official languages of Iraq. The right of Iraqis to educate their children in their mother tongue, such as Turkmen, Assyrian, and Armenian shall be guaranteed in government educational institutions in accordance with educational guidelines, or in any other language in private educational institutions.
- ^ "Transborder Languages of Africa and trans-national co-operation", Prof. Sammy Chumbow, University of Yaoundé.
- ^ Dias, Alexandra Magnólia (2011-12-20). "The Conduct of an Inter-state War and Multiple Dimensions of Territory: 1998-2000 Eritrea-Ethiopia war". Cadernos de Estudos Africanos (22): 21–41. doi:10.4000/cea.384. hdl:10071/3189. ISSN 1645-3794.
- ^ Hermann Hochegger, Grammaire du kiKongo ya leta, CEEBA, sér. III : travaux linguistiques, vol. 6).
- ^ Keating, Joshua. "The Nation That Sits Astride the U.S.-Canada Border". POLITICO Magazine. Retrieved 2019-06-26.
- ^ a b McWhorter, John H. (2015-01-02). "What the World Will Speak in 2115". Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved 2019-06-26.
- ^ "How many languages are there in the world?". Ethnologue. 2016-05-03. Retrieved 2019-06-26.
