Geography of Algeria
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | North Africa |
| Coordinates | 28°00′N 3°00′E / 28.000°N 3.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 10th |
| • Total | 2,381,741 km2 (919,595 sq mi) |
| • Land | 100% |
| • Water | 0% |
| Coastline | 2,148 km (1,335 mi) |
| Borders | Land boundaries: 6,343 km Morocco 1,559 km, Mali 1,376 km, Libya 982 km, Tunisia 965 km, Niger 956 km, Mauritania 463 km, Western Sahara 42 km |
| Maritime claims | 32–52 nm |
| Highest point | Mount Tahat, 3,003 m |
| Lowest point | Chott Melrhir, −40 m (131 ft) |
| Longest river | Chelif River, 230 km |
| Climate | arid to semiarid |
| Terrain | mostly high plateau and desert, mountains, narrow coastal plain[1] |
| Natural resources | petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zinc[1] |
| Natural hazards | earthquakes, mudslides, floods, droughts |
| Environmental issues | soil erosion, desertification, pollution |
| Exclusive economic zone | 126,353 km2 (48,785 sq mi) |


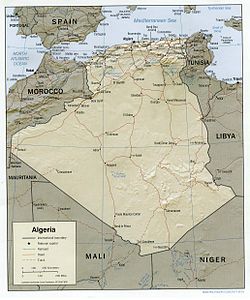
Algeria comprises 2,381,740 square kilometres (919,590 sq mi) of land, more than 80% of which is desert, in North Africa, between Morocco and Tunisia.[2][1] It is the largest country in Africa.[1] Its Arabic name, Al Jazair (the islands), is believed to derive from the rocky islands along the coastline of the Mediterranean Sea.[2] The northern portion, an area of mountains, valleys, and plateaus between the Mediterranean and the Sahara Desert, forms an integral part of the section of North Africa known as the Maghreb.[2] This area includes Morocco, Tunisia, and the northwestern portion of Libya known historically as Tripolitania.[2]
Size and boundaries
Land boundaries:
Total: 6,734 km (4,184 mi)[1]
Border countries: Libya 982 km (610 mi), Mali 1,376 km (855 mi), Mauritania 463 km (288 mi), Morocco 1,559 km (969 mi), Niger 956 km (594 mi), Tunisia 965 km (600 mi), Western Sahara 42 km (26 mi).[3][4]
Area – comparative: slightly larger than the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Saudi Arabia
Coastline: 2,148 km (1,335 mi)[5][6]
Maritime claims: Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi), contiguous zone: 24 nautical miles (44 km; 28 mi); exclusive fishing zone: 32 to 52 nmi (59 to 96 km; 37 to 60 mi)[1]
Geographic regions
The Tell
The fertile Tell is the country's heartland, containing most of its cities and population.[2] Made up of hills and plains of the narrow coastal region, the several Tell Atlas mountain ranges, and the intermediate valleys and basins, the Tell extends eastward from the Moroccan border to the mountains of the Grande Kabylie and the Bejaia Plain on the east.[2] Its eastern terminus is the Soummam River.[2]
The best agricultural areas are the gentle hills extending 100 kilometers westward from Algiers; the Mitidja Plain, which was a malarial swamp before being cleared by the French; and the Bejaia Plain.[2] The alluvial soils in these areas permitted the French to establish magnificent vineyards and citrus groves.[2] By contrast, in the great valley of the Chelif River and other interior valleys and basins, aridity and excessive summer heat have limited the development of agriculture.[2] The Grande Kabylie is a zone of impoverished small farm villages tucked into convoluted mountains.[2]
The High Plateaus and the Saharan Atlas

Stretching from the Moroccan border the Tell Atlas, including the Djebel Babor formation, is the dominant northwestern mountain range. Stretching more than 600 kilometers eastward from the Moroccan border, the high plateau area (often referred to by the French name Hautes Plaines or Hauts Plateaux) consist of undulating, steppe-like plains lying between the Tell and Saharan Atlas ranges.[2] The elevation averages between 1,100–1,300 metres (3,600–4,300 ft) in elevation in the west, dropping to 400 metres (1,300 ft) in the east.[2] The climate is so dry that these plains are sometimes thought of as part of the Sahara.[2] The plateau area is covered by alluvial debris formed when the mountains eroded.[2] An occasional ridge projects through the alluvial cover to interrupt the monotony of the landscape.[2]
Higher and more continuous than the Tell Atlas, the Sahara Atlas range is formed of three massifs: the Ksour Range near the Moroccan border, the Amour Range, and the Ouled-Naïl Range south of Algiers.[2] The mountains, which receive more rainfall than those of the High Plateaus, include some good grazing land.[2] Watercourses on the southern slopes of these massifs disappear into the desert but supply the wells of numerous oases along the northern edge of the desert, of which Biskra, Laghouat, and Béchar are the most prominent.[2]
Northeastern Algeria
Eastern Algeria consists of a massif area extensively dissected into mountains, plains, and basins.[2] It differs from the western portion of the country in that its prominent topographic features do not parallel the coast.[2] In its southern sector, the steep cliffs and long ridges of the Aurès Mountains create an almost impenetrable refuge that has played an important part in the history of the Maghrib since Roman times.[2] Near the northern coast, the Petite Kabylie Mountains are separated from the Grande Kabylie range at the eastward limits of the Tell by the Soummam River.[2] The coast is predominantly mountainous in the far eastern part of the country, but limited plains provide hinterlands for the port cities of Bejaïa, Skikda, and Annaba.[2] In the interior of the region, extensive high plains mark the region around Sétif and Constantine; these plains were developed during the French colonial period as the principal centers of grain cultivation.[2] Near Constantine, salt marshes offer seasonal grazing grounds to seminomadic sheep herders.[2]
The Sahara
The Algerian portion of the Sahara extends south of the Saharan Atlas for 1,500 kilometres (930 mi) to the Niger and Mali frontiers.[2] The desert is an otherworldly place, scarcely considered an integral part of the country.[2] Far from being covered wholly by sweeps of sand, however, it is a region of great diversity.[2] Immense areas of sand dunes called areg (sing., erg) occupy about one-quarter of the territory.[2] The largest such region is the Grand Erg Oriental (Great Eastern Erg), where enormous dunes two to five metres (6.6 to 16.4 ft) high are spaced about 40 metres (130 ft) apart.[2] Much of the remainder of the desert is covered by rocky platforms called humud (sing., hamada), and almost the entire southeastern quarter is taken up by the high, complex mass of the Ahaggar and Tassili n'Ajjer highlands, some parts of which reach more than 2,000 metres (6,600 ft).[2] Surrounding the Ahaggar are sandstone plateaus, cut into deep gorges by ancient rivers, and to the west a desert of pebbles stretches to the Mali frontier.[2]
The desert consists of readily distinguishable northern and southern sectors, the northern sector extending southward a little less than half the distance to the Niger and Mali frontiers.[2] The north, less arid than the south, supports most of the few persons who live in the region and contains most of the desert's oases.[2] Sand dunes are the most prominent features of this area's topography, but between the desert areas of the Grand Erg Oriental and the Grand Erg Occidental (Great Western Erg) and extending north to the Atlas Saharien are plateaus, including the Tademaït and a complex limestone structure called the M'zab where the Mozabite Berbers have settled.[2] The southern zone of the Sahara is almost totally arid and is inhabited only by the Tuareg nomads and, recently, by oil camp workers.[2] Barren rock predominates, but in some parts of Ahaggar and Tassili n'Ajjer alluvial deposits permit garden farming.[2]
Climate and hydrology


Northern Algeria is in the temperate zone and enjoys a mild, Mediterranean climate.[7] It lies within approximately the same latitudes as southern California and has somewhat similar climatic conditions.[7] Its broken topography, however, provides sharp local contrasts in both prevailing temperatures and incidence of rainfall.[7] Year-to-year variations in climatic conditions are also common.[7] This area, the most inhabited in Algeria, is commonly referred to as the Tell.
In the Tell, temperatures in summer average between 30 and 43 °C (86 and 109 °F) and in winter drop to 10 to 12 °C (50 to 54 °F).[7] Winters are not cold, but the humidity is high and houses are seldom adequately heated.[7] In eastern Algeria, the average temperatures are somewhat lower, and on the steppes of the High Plateaus winter temperatures hover only a few degrees above freezing.[7] A prominent feature of the climate in this region is the sirocco, a dusty, choking south wind blowing off the desert, sometimes at gale force.[7] This wind also occasionally reaches into the coastal Tell.[7]
In Algeria only a relatively small corner of the Sahara lies across the Tropic of Cancer in the torrid zone, but even in winter, midday desert temperatures can be very hot.[7] After sunset, however, the clear, dry air permits rapid loss of heat, and the nights are cool to chilly.[7] Enormous daily ranges in temperature are recorded.[7]
Rainfall is fairly abundant along the coastal part of the Tell, ranging from 400 to 670 mm (15.7 to 26.4 in) annually, the amount of precipitation increasing from west to east.[7] Precipitation is heaviest in the northern part of eastern Algeria, where it reaches as much as 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in some years.[7] Farther inland the rainfall is less plentiful.[7] Prevailing winds that are easterly and northeasterly in summer change to westerly and northerly in winter and carry with them a general increase in precipitation from September to December, a decrease in the late winter and spring months, and a near absence of rainfall during the summer months.[7]
| Climate data for Algiers (Houari Boumediene Airport ) 1976–2005 averages, extremes 1838–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.6 (81.7) |
31.4 (88.5) |
36.3 (97.3) |
36.5 (97.7) |
41.1 (106.0) |
44.6 (112.3) |
45.2 (113.4) |
47.5 (117.5) |
44.4 (111.9) |
39.5 (103.1) |
34.4 (93.9) |
30.4 (86.7) |
47.5 (117.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.9 (75.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
31.2 (88.2) |
32.2 (90.0) |
29.6 (85.3) |
25.9 (78.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
17.9 (64.2) |
23.7 (74.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 11.1 (52.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
13.2 (55.8) |
14.9 (58.8) |
18.1 (64.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
25.1 (77.2) |
26.0 (78.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
20.1 (68.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
12.6 (54.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
5.9 (42.6) |
7.1 (44.8) |
8.8 (47.8) |
12.3 (54.1) |
16.1 (61.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
2.6 (36.7) |
5.5 (41.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
9.5 (49.1) |
8.2 (46.8) |
4.1 (39.4) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 81.4 (3.20) |
72.7 (2.86) |
55.0 (2.17) |
58.4 (2.30) |
41.9 (1.65) |
8.5 (0.33) |
4.5 (0.18) |
8.2 (0.32) |
28.3 (1.11) |
58.8 (2.31) |
89.6 (3.53) |
91.0 (3.58) |
598.3 (23.56) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 11.4 | 10.6 | 9.7 | 9.1 | 7.3 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 8.6 | 11.1 | 12.1 | 91.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 71 | 66 | 65 | 62 | 66 | 66 | 67 | 65 | 68 | 66 | 68 | 68 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 139.5 | 158.2 | 207.7 | 228.0 | 300.7 | 300.0 | 353.4 | 325.5 | 267.0 | 198.4 | 153.0 | 145.7 | 2,777.1 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4.5 | 5.6 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 9.7 | 10.0 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 8.9 | 6.4 | 5.1 | 4.7 | 7.6 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization (average temperatures and precipitation, 1976–2005)[8] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Arab Meteorology Book (humidity and sun),[9] Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[10] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Adrar | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31.2 (88.2) |
36.0 (96.8) |
40.7 (105.3) |
43.8 (110.8) |
49.8 (121.6) |
48.9 (120.0) |
51.0 (123.8) |
49.8 (121.6) |
46.8 (116.2) |
43.5 (110.3) |
36.0 (96.8) |
31.8 (89.2) |
51.0 (123.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 20.6 (69.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
32.1 (89.8) |
36.7 (98.1) |
42.5 (108.5) |
45.0 (113.0) |
44.3 (111.7) |
40.0 (104.0) |
33.1 (91.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
32.8 (91.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.4 (54.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.6 (74.5) |
28.1 (82.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
36.0 (96.8) |
35.4 (95.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
25.0 (77.0) |
18.2 (64.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
10.7 (51.3) |
15.1 (59.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
10.2 (50.4) |
4.9 (40.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
0.5 (32.9) |
4.8 (40.6) |
8.9 (48.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
20.0 (68.0) |
15.2 (59.4) |
6.0 (42.8) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.3 (0.09) |
1.3 (0.05) |
2.6 (0.10) |
4.1 (0.16) |
0.3 (0.01) |
0.1 (0.00) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.01) |
0.2 (0.01) |
1.5 (0.06) |
0.6 (0.02) |
1.4 (0.06) |
14.6 (0.57) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 3.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 52 | 52 | 40 | 34 | 30 | 28 | 26 | 29 | 36 | 48 | 59 | 57 | 42 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 269.7 | 257.1 | 310.0 | 318.0 | 325.5 | 333.0 | 344.1 | 328.6 | 288.0 | 279.0 | 261.0 | 263.5 | 3,577.5 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 8.7 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 10.6 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 10.6 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 9.8 |
| Source 1: NOAA[11] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes, humidity and sun)[12] | |||||||||||||
Terrain
| Land use | (2014 est.) |
|---|---|
| • Arable land | 18.02% |
| • Permanent crops | 2.34% |
| • Permanent pastures | 79.63% |
| • Forest | 0.82% |
| • Other | 81.80% |
| Irrigated land | 13,600 km2 (5,300 sq mi) |

Clearing of land for agricultural use and cutting of timber over the centuries have severely reduced the once bountiful forest wealth.[13] Forest fires have also taken their toll.[13] In the higher and wetter portions of the Tell Atlas, cork oak and Aleppo pine grow in thick soils.[13] At lower levels on thinner soils, drought-resistant shrubs predominate.[13] The grapevine is indigenous to the coastal lowlands, and grasses and scrub cover the High Plateaus.[13] On the Saharan Atlas, little survives of the once extensive forests of Atlas cedar that have been exploited for fuel and timber since antiquity.[13]
The forest reserves in Algeria were severely reduced during the colonial period.[13] In 1967 it was calculated that the country's forested area extended over no more than 24,000 square kilometres (9,300 sq mi) of terrain, of which 18,000 km2 (6,900 sq mi) were overgrown with brushwood and scrub.[13] By contrast, woodlands in 1830 had covered 40,000 km2 (15,000 sq mi).[13] In the mid-1970s, however, the government embarked on a vast reforestation program to help control erosion, which was estimated to affect 100,000 cubic metres (3,500,000 cu ft) of arable land annually.[13] Among projects was one to create a barrage vert (green barrier) more or less following the ridge line of the Saharan Atlas and extending from Morocco to the Tunisian frontier in a zone 1,500 kilometres (930 mi) long and up to 20 kilometres (12 mi) wide.[13]
In Algeria forest cover is around 1% of the total land area, equivalent to 1,949,000 hectares (ha) of forest in 2020, up from 1,667,000 hectares (ha) in 1990. In 2020, naturally regenerating forest covered 1,439,000 hectares (ha) and planted forest covered 510,000 hectares (ha). Of the naturally regenerating forest 0% was reported to be primary forest (consisting of native tree species with no clearly visible indications of human activity) and around 6% of the forest area was found within protected areas. For the year 2015, 80% of the forest area was reported to be under public ownership, 18% private ownership and 2% with ownership listed as other or unknown.[14][15]
The barrage vert consists principally of Aleppo pine, a species that can thrive in areas of scanty rainfall.[13] It is designed to restore a damaged ecological balance and to halt the northern encroachment of the Sahara.[13] By the early 1980s, the desert had already penetrated the hilly gap between the Saharan Atlas and the Aurès Mountains as far as the town of Bou Saâda, a point well within the High Plateaus region.[13] The barrage vert project was ended in the late 1980s because of lack of funds.[13]
Algeria had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 5.22/10, ranking it 106th globally out of 172 countries.[16]
Statistics
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, phosphates, uranium, lead, zinc[1]
Natural hazards: mountainous areas subject to severe earthquakes; mudslides and floods in rainy season[1]
Environment – current issues: air pollution in major cities; soil erosion from overgrazing and other poor farming practices; desertification; dumping of raw sewage, petroleum refining wastes, and other industrial effluents is leading to the pollution of rivers and coastal waters; Mediterranean Sea, in particular, becoming polluted from oil wastes, soil erosion, and fertilizer runoff; inadequate supplies of potable water[1]
Environment – international agreements: party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Nuclear Test Ban[1]
Protected areas
Algeria has a number of protected areas including National Parks and nature reserves. An example of such a protected area is the Djebel Babor Nature Reserve within the Djebel Babor Mountains;[17] the Djebel Babor is also one of the few relict habitats for the endangered Barbary macaque, Macaca sylvanus.[18]
The national parks in Algeria are: Ahaggar, Belezma, Chréa, Djurdjura, El Kala, Gouraya, Tassili n'Ajjer, Taza, Théniet El Had, and Tlemcen.
Extreme points
Elevation extremes:
- Lowest point: Chott Melrhir: −40 metres (−130 ft)[1]
- Highest point: Mount Tahat: 2,908 metres (9,541 ft)[1]
Points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location:[citation needed]
- Northernmost point – Cap Takouch, Annaba Province or Cap Bougaroûn, Skikda province
- Easternmost point – the tripoint with Niger and Libya, Djanet Province
- Southernmost point – unnamed location on the border with Mali east of the Malian village of In-Abalen, In Guezzam Province
- Westernmost point – the western section of the border with Morocco/Western Sahara, Tindouf Province (Note: Algeria does not have a westernmost point, the border being formed by a line of longitude)
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Central Intelligence Agency (2 June 2020). The CIA World Factbook 2020-2021. Skyhorse. p. 158. ISBN 978-1-5107-5826-1.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al Deeb, Mary-Jane (1993). "Physical Setting". In Metz, Helen Chapin (ed.). Algeria: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 69–76. OCLC 44230753.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Ewan W. Anderson, Liam D. Anderson (2013). An Atlas of Middle Eastern Affairs. Routledge. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-136-64862-5.
- ^ Central Intelligence Agency (2011). The CIA World Factbook 2012. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-62873-181-1.
- ^ "Water Resources in Algeria". water.fanack.com. Fanack Water. July 30, 2019. Retrieved June 8, 2022.
With 1,622 km of coastline, Algeria has begun desalinating seawater to supply drinking water to cities and towns located up to 60 km away from the coast.
- ^ ElKhabar (2023-06-26). "دراسة جديدة ترفع طول الساحل الجزائري". elkhabar.com (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-11-23.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Deeb, Mary-Jane (1993). "Climate and Hydrology". In Metz, Helen Chapin (ed.). Algeria: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 74–75. OCLC 44230753.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "World Weather Information Service–Algiers". World Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 18 October 2016. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ "Appendix I: Meteorological Data" (PDF). Springer. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ "Station Alger" (in French). Meteo Climat. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ "Adrar Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ^ "Klimatafel von Adrar / Algerien" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Deeb, Mary-Jane (1993). "Terrain". In Metz, Helen Chapin (ed.). Algeria: a country study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 75–76. OCLC 44230753.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ Terms and Definitions FRA 2025 Forest Resources Assessment, Working Paper 194. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023.
- ^ "Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020, Algeria". Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ "Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan, (2008) Barbary Macaque: Macaca sylvanus, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. N. Strõmberg.
