Castra of Triphulum
| Triphulum | |
|---|---|
| Alternative name(s) | Castra of Orheiu Bistriței |
| Founded | 2nd century AD[1][2] |
| Abandoned | 3rd century AD[1][2] |
| Place in the Roman world | |
| Province | Dacia |
| Administrative unit | Dacia Apulensis |
| Administrative unit | Dacia Superior |
| Limes | Porolissensis |
| Directly connected to | (Livezile) |
| Structure | |
| — Stone structure — | |
| Size and area | 203 m × 144 m (2.9[3] ha) |
| Wall thickness | 1.30 m |
| Construction technique | Opus quadratum[3] |
| Stationed military units | |
| — Cohorts — | |
| — Alae — | |
| I Illyricorum[4] | |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 47°05′46″N 24°35′32″E / 47.096014°N 24.592319°E |
| Town | Orheiu Bistriței |
| County | Bistrița-Năsăud |
| Country | |
| Reference | |
| RO-LMI | BN-I-s-A-01377[2] |
| RO-RAN | 32928.01[1] |
| Site notes | |
| Recognition | |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Excavation dates |
|
| Archaeologists | |
Triphulum[7] was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia.[1][2] It was built in the 2nd century AD.[1][2] Archaeological research also identified the nearby vicus.[1][2] The castra and the nearby settlement were both abandoned in the 3rd century AD.[1][2] The ruins of the fort are located in Orheiu Bistriței (commune Cetate, Romania).[1][2]

Location
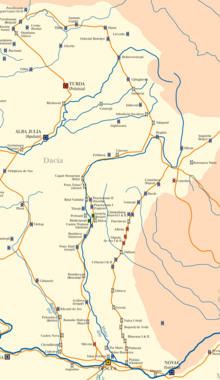
The remains of the fort lie on flat ground on the western side of the Budac river, on the western periphery of today's town. Part of the rear part of the camp lies under the disused Protestant cemetery. The fort could have played a strategically important role as the Castra of Livezile fort 7 km away was only used temporarily, and it was located on the approximately 85 km route between the Ilișua fort and the Castra of Brâncovenești fort.[8]
See also
External links
- Roman castra from Romania - Google Maps / Earth Archived 2012-12-05 at archive.today
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g h "32928.01". National Archaeological Record of Romania (RAN). ran.cimec.ro. 2009-04-13. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Lista Monumentelor Istorice 2010 ("2010 List of Historic Monuments")" (PDF). Monitorul Oficial al României, Partea I, Nr. 670 ("Romania's Official Journal, Part I, Nr. 670"), page 475. Ministerul Culturii și Patrimoniului Naţional. 1 October 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 June 2012. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ a b "Orheiu Bistriței". STRATEG MAPS: Defensive strategies and trans-border policies at the Lower Danube in Roman Antiquity (An interdisciplinary project). Archived from the original on 14 May 2012. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ a b c d Protase, Dumitru (2008). Castrul roman de la Orheiu Bistriței / Das römische Kastell von Orheiu Bistriței ("Roman Fort at Orheiu Bistriței") (PDF) (in Romanian and German). Cluj-Napoca: Accent. ISBN 978-973-8915-64-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-04-27. Retrieved 2013-01-10.
- ^ Ureche, Petru. "Tactică, strategie și specific de luptă la cohortele equitate din Dacia Romană" (PDF). www.irregular.ro. Retrieved 10 January 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Turcuș, Veronica; et al. (2008). "Protase, Dumitru (n. 1926), Membru de onoare al Academiei Române (2003)". Bibliografia lucrărilor științifice ale membrilor Institutului de Istorie din Cluj 1920-2005. www.history-cluj.ro. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ Deac, Dan (2013-01-01). "Dan Deac, The Toponymy of Dacia Porolissensis. Recent Research and New Approaches". Ephemeris Napocensis XXIII.
- ^ Dumitru Protase: Das romische Kastell von Orheiu Bistriţei. In: Revista Bistriţei, XXI/1 (2007), S. 113f
47°05′48″N 24°35′37″E / 47.09667°N 24.59361°E