Callicera
| Callicera | |
|---|---|

| |
| Illustration in Johann Wilhelm Meigen Europäischen Zweiflügeligen Figure 10 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: | |
| Genus: | Callicera Panzer, 1809 |
| |
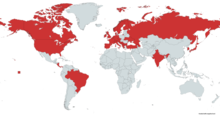
| range map 2023 | |
Callicera is a Holarctic genus of hoverflies[1]
They are beautiful metallic flies, with strikingly long antennae are medium-sized to rather large (wing length 9·75–15 mm.) bumblebee mimics. All the species are considered rare. Callicera larvae live in the moist rot-holes of overmature trees as saprophages.[2][3][4][5][6][7] [8] Callicera have been used as bioindicators.
Species
- C. aenea (Fabricius, 1781)[9]
- C. aurata (Rossi, 1790)
- C.christiani (Ghorpade, 1982)
- C.doleschalli (Verrall, 1913)
- C. duncani Curran, 1935
- C. erratica (Walker, 1849)
- C. exigua Smit, 2014
- C. fagesii Guérin-Menéville, 1844
- C. macquarti Rondani, 1844
- C. montensis Snow, 1892
- C. nitens (Coe, 1964)
- C.poultoni (Verrall, 1913)
- C.robusta (Coe, 1964)
- C. rohdendorfi Zimina, 1982
- C. rufa Schummel, 1842
- C.sackeni (Verrall, 1913)
- C. scintilla Smit, 2014
- C. spinolae Rondani, 1844
- C. sumatrensis (Meijere, 1919)
References
- ^ Stubbs, Alan E.; Falk, Steven J. (1983). British Hoverflies: An Illustrated Identification Guide. British Entomological & Natural History Society. pp. 253, xvpp.
- ^ Speight, M.C.D. (2011). "Species accounts of European Syrphidae (Diptera)" (PDF). Syrph the Net, the Database of European Syrphidae. 65: 285pp.
- ^ Van der Goot,V.S. (1981) De zweefvliegen van Noordwest – Europa en Europees Rusland, in het bijzonder van de Benelux. KNNV, Uitgave no.32: 275pp. Amsterdam.
- ^ Stubbs, Alan E. & Falk, Steven J. (1983). British Hoverflies: An Illustrated Identification Guide (2nd (revised) ed.). British Entomological & Natural History Society. p. 271, xvpp. ISBN 0-9502891-3-2.
- ^ Bei-Bienko, G.Y. & Steyskal, G.C. (1988a) Keys to the Insects of the European Part of the USSR, Volume V: Diptera and Siphonaptera, Part I. Amerind Publishing Co., New Delhi. ISBN 81-205-0080-6.
- ^ Van Veen, M. (2004) Hoverflies of Northwest Europe: identification keys to the Syrphidae. 256pp. KNNV Publishing, Utrecht.addendum
- ^ Coe, R.L. (1953) Diptera: Syrphidae. Handbks.ident.Br.insects, 10(1): 1–98. R.ent.Soc.London. pdf Archived 4 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Peck, L.V. (1988) Syrphidae. In: Soos, A. & Papp, L. (eds.) Catalogue of Palaearctic Diptera, 8: 11–230. Akad.Kiado, Budapest.
- ^ Barkalov, A.V. "Syrphidae collection of Siberian Zoological Museum". Novosibirsk, Russia: the Institute of Animal Systematics and Ecology, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original on 20 October 2008. Retrieved 29 July 2009.
External images
