Beijing–Hong Kong high-speed railway
| Beijing–Hong Kong high-speed railway | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overview | |||||||||||||||
| Other name(s) | Jinggang high-speed railway | ||||||||||||||
| Native name | 京港高速铁路 | ||||||||||||||
| Status | Operational | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | China Railway (Mainland section) MTR Corporation (Hong Kong section) | ||||||||||||||
| Locale | Beijing, Hebei, Shandong, Henan, Anhui, Jiangxi, Guangdong, Hong Kong | ||||||||||||||
| Termini | |||||||||||||||
| Service | |||||||||||||||
| Type | High-speed rail | ||||||||||||||
| System | Beijing–Hong Kong (Taipei) corridor | ||||||||||||||
| Operator(s) | China Railway High-speed (Mainland section) MTR (Hong Kong section) | ||||||||||||||
| Depot(s) | Beijing MU Depot Hefei MU Depot Nanchang MU Depot Guangzhou MU Depot Shenzhen MU Depot Shek Kong Depot | ||||||||||||||
| Rolling stock | China Railway CRH380A China Railway CRH380B China Railway CRH380D China Standardized EMU | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
| Opened | 1 December 2019 (Shangqiu-Hefei, Nanchang-Ganzhou) | ||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||
| Number of tracks | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Character | Elevated | ||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||||||||||||||
| Operating speed | 350 km/h (220 mph) | ||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 京港高速铁路 | ||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 京港高速鐵路 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
The Beijing–Hong Kong high-speed railway or Jinggang high-speed railway from its Chinese name is a high-speed railway corridor of the CRH passenger service, connecting Beijing Fengtai railway station in Beijing and Futian railway station in Shenzhen, Guangdong (from there onwards to cross the border to West Kowloon station in Kowloon, Hong Kong through the XRL). The existing, conventional Jingjiu railway runs largely parallel to the line.
The line forms part of the Beijing–Hong Kong (Taipei) corridor, based on the "Eight Verticals and Eight Horizontals" railway master plan announced in 2016. Note that it goes through Shandong, Anhui, Jiangxi where Beijing–Guangzhou high-speed railway does not. The relationship between the two is much like the conventional Beijing–Kowloon railway and Beijing–Guangzhou railway, parallel yet different.
History
Construction started in 2014.[1] The Shangqiu–Hefei and Nanchang–Ganzhou section opened in December 2019, the Ganzhou–Shenzhen section opened in December 2021.[2][3]
Sections
Operational lines in the table below are marked with green background.
| Section | Description | Designed speed (km/h) |
Length (km) |
Construction start date |
Open date |
Top trip speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing–Hong Kong high-speed railway | HSR Corridor connecting North with Central China, consisting of 6 segments between Beijing, Shangqiu, Hefei, Jiujiang, Nanchang, Ganzhou, Shenzhen and Hong Kong. | 350 | 2014-12-20 | See below | ||
| Beijing–Shangqiu section (Beijing–Shangqiu high-speed railway) |
HSR from Beijing Fengtai to Shangqiu | 350 | – | |||
| Shangqiu–Hefei section (Shangqiu–Hefei high-speed railway) |
HSR from Shangqiu to Hefei | 350 | 2015-11-30 | 2019-12-1 | – | |
| Hefei–Jiujiang Section[4] (Hefei–Jiujiang high-speed railway) |
HSR from Hefei to Jiujiang | 350 | 2015-12-25 | 2021-12-30 | – | |
| Jiujiang–Nanchang Section (Jiujiang–Nanchang high-speed railway) |
HSR from Jiujiang to Nanchang | 350 | ||||
| Nanchang-Ganzhou Section (Nanchang-Ganzhou high-speed railway) |
HSR from Nanchang to Ganzhou | 350 | 2014-12-20 | 2019-12-26 | ||
| Ganzhou-Shenzhen Section (Ganzhou-Shenzhen high-speed railway) |
HSR from Ganzhou to Shenzhen | 350 | 2016-12-22 | 2021-12-10 | ||
| Shenzhen–Hong Kong Section Mainland Portion (Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link) 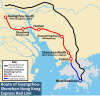
|
HSR from Shenzhen to Futian | 200 | 106 | 2005-12-18 | 2015-12-28 | 308 |
| Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Section Hong Kong Portion (Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link) 
|
HSR from Futian to West Kowloon | 200 | 36 (26 km in Hong Kong) | 2010-01-27[citation needed] | 2018-09-23[5] |
References
- ^ "昌吉赣客专正式开工 建设工期5年 昌赣2小时抵达". 凤凰网. 21 December 2014. Archived from the original on 1 December 2020. Retrieved 19 December 2019.
- ^ "How does the opening of the Ganzhou–Shenzhen section of the Beijing–Hong Kong high-speed rail from the old district to the special zone promote economic and social development along the line? _Xinhua Newspaper Net".
- ^ "New high-speed railway to bolster travel between Ganzhou, Shenzhen".
- ^ "Hefei-Anqing section of Beijing-Hong Kong high-speed railway starts operation".
- ^ "Hong Kong Launches First High Speed Rail Service". finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 26 September 2018.
