Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara
| Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara South Australia | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
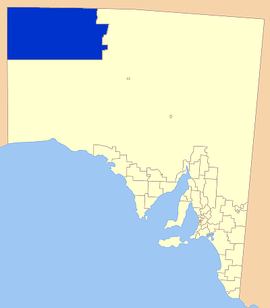 Location of the Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara | |||||||||||||||
| Population | 2,333 (LGA 2021)[1] | ||||||||||||||
| Established | 1981[2][3] | ||||||||||||||
| Area | 103,000 km2 (39,768.5 sq mi)[2][3] | ||||||||||||||
| Council seat | Umuwa | ||||||||||||||
| Region | Far North[4] | ||||||||||||||
| State electorate(s) | Giles[5] | ||||||||||||||
| Federal division(s) | Grey[6] | ||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| Website | Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||

Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara, also known as APY, APY Lands or the Lands, is a large, sparsely-populated local government area (LGA) for Aboriginal people, located in the remote north west of South Australia. Some of the Aṉangu (people) of the Western Desert cultural bloc, in particular Pitjantjatjara, Yankunytjatjara and Ngaanyatjarra peoples, inhabit the Lands.
Governance of the area is determined by the Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981 (or APYLRA), whereby an elected executive board reports to the Premier of South Australia. The APY's administration centre is located at Umuwa.
A large portion of the APY Lands was formerly the North-West Aboriginal Reserve.
Time zone
Due to its links with the Northern Territory and proximity to the border, the APY Lands do not observe daylight savings unlike the rest of South Australia. The time zone observed throughout the year is Australian Central Standard Time (UTC+9:30), in line with Darwin rather than Adelaide.
History
Early history
The Pitjantjatjara and Yankunytjatjara people (aṉangu) had lived in this area for many thousands of years. Even after the British began to colonise the Australian continent from 1788 onwards, and the colonisation of South Australia from 1836, the aṉangu remained more or less undisturbed for many more years, apart from very occasional encounters with a variety of European explorers.[citation needed]
20th century
In 1921, with white settlement now beginning to encroach on the aṉangu's traditional land, the South Australian Government proclaimed the North-West Aboriginal Reserve. This Reserve consisted of most of what is now known as the APY Lands, with the exception of the eastern part of the APY Lands, which was given over to pastoral leases to Europeans.[citation needed]
In 1937, the Presbyterian Church council, spearheaded by Charles Duguid, established the Ernabella Mission on the Lands at the place now known as Pukatja.[citation needed]
By the 1950s, many aṉangu were living at the Ernabella Mission, while many others lived at camps on pastoral leases on what are now the Lands, or nearby, where they would work. Those pastoral leases included Granite Downs, Everard Park, Victory Downs, De Rose Hill, Kenmore Park, and Mount Cavanagh.[citation needed]
In 1961, to prevent overcrowding at Ernabella Mission, the Church established what became the community of Amata, but which was originally known as Musgrave Park. At the same time the Church also established what is now the community of Kaltjiti, but which was then known as Fregon.[citation needed]
In 1968, what is now the community of Indulkana was established by the South Australian Government, as a base from which to provide welfare services to aṉangu living in camps on pastoral leases, where work was becoming increasingly difficult to find. At that time, the surrounding area was excised from pastoral leases and declared the Indulkana Aboriginal Reserve.[citation needed]
The body now known as Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara was formed in 1981 by the passing of the Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981[7] by the Parliament of South Australia under Premier Don Dunstan, and includes the Pitjantjatjara, Yankunytjatjara and Ngaanyatjarra groups.[8]
"Ara Irititja" is a project of the APY, commenced in 1994 to identify, copy and electronically record historical materials about the Anangu (Pitjantjatjara/Yankunytjatjara people). Its purpose is to prevent the loss of the history, and to allow the teaching of it to others in the community.[9]
21st century
By 2007 the peoples of the region had not had any major economic development, apart from tourism, but there had been proposals to mine in the area. The opal fields of Mintabie came under separate governance that time.[10]
The Musgrave Block in the Lands has been viewed as having billions of dollars in potential mineral deposits and petroleum. But anangu have been wary of opening up the area to mining, concerned about the impact on sacred sites and the environment. In 2003 mining companies were conducting discussions to try to allay these worries.[11]
A 2004 parliamentary report on an inquiry by a select committee led by Minister for Aboriginal Affairs Terry Roberts examined the shortcomings of the 1981 Act, which had not addressed entrenched social and economic problems in the Lands. The review noted shortcomings in the delivery of human services and infrastructure, and identified a "need to address the issue of the overall governance of the AP Lands and to formalise arrangements within an Act of Parliament and/or the Constitution of Anangu Pitjantjatjara". After wide consultation and consideration of many submissions, the committee made 15 recommendations. One of these was the establishment of a permanent police presence, as one of several strategies used to combat the problems of petrol sniffing and family violence.[12]
In July 2007 South Australia Police in co-operation with liquor outlets in Coober Pedy (250 km to the south-east entrance to the Lands) agreed to create a register of alcohol purchases, to enable police to identify persons who purchased large quantities of alcohol in Coober Pedy potentially for transportation into Aboriginal lands.[citation needed] Also in July, Commonwealth Indigenous Affairs Minister Mal Brough offered federal help for a "drug and alcohol crackdown" in South Australian Aboriginal lands – such as the APY Lands.[13]
In early August 2007, the Rann South Australian Labor Government announced a$ 34 million package to "improve well-being of Aboriginal people" in the APY Lands. $25m was to be spent on improving housing and most of the remaining $8m on law enforcement in Amata and Pukatja.[14] In November, SA Police Commissioner Mal Hyde announced the signing of a new enterprise agreement for South Australia Police that would include incentive packages to lure police to work in rural and remote areas such as the Lands.[15]
In May 2008, retired Supreme Court judge the Hon Ted Mullighan QC delivered his supplementary report to his Children in State Care Commission of Inquiry, entitled the "Children on Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Lands Commission of Inquiry – a Report into Sexual Abuse" (aka "the Mullighan report").[16]
In December 2009 the South Australian Parliament passed the Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights (Mintabie) Amendment Bill,[17] which was an amendment to the APY Land Rights Act 1981, the Opal Mining Act 1995, and by-laws under the APY Land Rights Act 1981, affecting the mainly non-Indigenous residents of the opal-mining town, Mintabie.[18] This amendment changed the licensing system for residential and commercial premises effective 1 July 2012, allowing the Minister responsible for the Opal Mining Act to grant licences.[19]
A 2017 report found many instances of non-compliance with the 2009 Amendment as well as other problems occurring in the settlement of Mintabie. It recommended closure of the township, with control reverting to APY.[19] After an appeal by residents failed, the final eviction date for the township was set at 31 December 2019.[20]
In March 2024, the Kulilaya Festival was held at Umuwa to celebrate the 40th anniversary of the 1981 APY Land Rights Act. It had been delayed for three years owing to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Artists, musicians, and dancers presented their history and stories to commemorate the occasion.[21] The word kulilaya approximates to the meaning of "listen", and was the name of a land rights protest song that was sung frequently in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and since then sung regularly by the Ernabella Choir, the APY Choir, and the Iwiri Choir.[22] Several inma ceremonies were performed,[23] politicians from across the spectrum attended the festival, and performers included Dem Mob, Docker River Band, the Iwiri Choir, Mala, the Pukatja Band, and Desert Rain.[22]
Geography and location
The Musgrave Ranges, straddling the border between South Australia and the Northern Territory and the Mann Ranges and Tomkinson Ranges, both in the north-west of South Australia, stretch from east to west on the southern side of the NT border. The APY area includes isolated ranges and hills and large sandhill plains, and APY people also have affiliations with land in the NT to the Petermann Ranges, and in Western Australia.[24]
Geology
There is a large palaeovalley, a geological term for an ancient, buried river, underneath the APY Lands. A map of the geological formation, complete with scientific and technical terminology, has been translated into Pitjantjatjara by a team of translators, based on the English-language map developed by government agencies.[25]
There is a long strip of limestone breaking through red soil near Fregon/Kaltjiti, where a new water source was found in 2019. The area is one of two places in the world which have landlocked tectonic plates, and drilling samples have been estimated to be between 5 and 10 million years old.[26]
Adjoining land
To the north of the APY Lands, the MacDonnell Shire Council was created by the Northern Territory in 2008, renamed MacDonnell Region in 2014, spanning the south of the Territory from west to east. Western Australia lies to the west. The South Australian LGA to the south of APY Lands is Maralinga Tjarutja (with the District Council of Coober Pedy to the east of that, but not adjoining APY).
The Outback Communities Authority is not an LGA, but is the statutory authority responsible for the development of areas adjoining the APY Lands (excluding the above-mentioned) as well as other large areas (63% of the state in total), to "manage the provision of public services and facilities to outback communities" which are widely dispersed across the region.[27]
Localities
The APY LGA encompasses a number of settlements of a range of sizes, many of them being located in the Musgrave Ranges. An interactive map shows the location of communities and further information about each on the Paper Tracker website.[28]
The main communities include Indulkana (Iwantja), Mimili, Kaltjiti (Fregon), Pukatja (Ernabella), Amata, Pipalyatjara, and Watarru; the larger homelands are Kalka, Kanpi, Nyapari and Yunyarinyi (homeland). The APY administration centre of the Lands is located at Umuwa.[2][29]
Mintabie was an opal-mining town, leased back to the Government of South Australia between 1981 and 2019, when the residents were evicted.[20][30][31][32]
The list of Aboriginal communities (c) and homelands (h):[2]
- Amata (c)
- Indulkana (c)
- Irintata (h)
- Iwantja (c)
- Kaljiti/Fregon
- Kalka (h)
- Kanpi (h)
- Mimili (c)
- Murputja (c)
- Nyapari (h)
- Pipalyatjara (c)
- Pukatja/Ernabella (c)
- Tjurma (h)
- Turkey Bore
- Umuwa – administrative centre
- Watarru (c)
- Watinuma
- Yunyarinyi (h)
Governance
Governance of the area is determined by the APY Land Rights Act 1981 (amended 2017), whereby an elected executive board reports to the Premier of South Australia.[33][34] The board appoints a general manager for a fixed term. Richard King was elected by the board in April 2015, and his term was extended for a year in March 2023, despite opposition by some councillors.[35]
The statutory functions of the APY body corporate, a land council, are:[36]
- to ascertain the wishes and opinions of traditional owners in relation to the management, use and control of the lands and to seek, where practicable, to give effect to those wishes and opinions;
- to protect the interests of traditional owners in relation to the management, use and control of the lands; and
- to negotiate with persons desiring to use, occupy or gain access to any part of the lands;
- to administer land vested in Aṉangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara.
The area is usually referred to as the APY Lands.[37][38][39][40] A permit is required for visitors to any community on the APY Lands, as they are freehold lands owned by the Aboriginal people.[41]
Electoral boundaries
The Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Lands Rights (Miscellaneous) Amendment Act 2016 determined the boundaries of seven APY electorates to elect the executive board of Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara. The electorates would be:[42][43]
- (i) the community groups of Pipalyatjara and Kalka;
- (ii) the community groups of Kanypi, Nyapari, Angatja and Watarru;
- (iii) the community groups of Amata and Tjurma;
- (iv) the community groups of Kaltjiti, Irintata and Watinuma;
- (v) the community groups of Pukatja, Yunyarinyi, Anilalya and Turkey Bore;
- (vi) the community group of Mimili; and
- (vii) the community groups of Iwantja, Amuruna, Railway Bore, Witjintitja and Wallatinna.
Demographics
2016 census
- General
The 2016 census identified the following statistics:[44]
- APY Lands had 2,276 residents, 52.4% of whom were female and 83.6% of whom were Indigenous Australians (2.8% nationally), Australian Aboriginal ancestry 71.9% (0.5% nationally).
- 91.5% of the people were born in Australia (66.7% nationally); 84.9% of people had both parents born in Australia (47.3% nationally).
- There were 511 families.
- Median age of people was 28 years; children 0–14 years, 24.2% of the population; people aged 65+ years old, 5.2% of the population.
- 19.2% considered themselves affiliated to the Uniting Church, another 20.2% Christian (3.7%, 2.6% nationally).
- Languages spoken at home were: English only 12.9%; other languages included Pitjantjatjara 65.6%, Yankunytjatjara 3.0%, Western Arrarnta 0.4%, Warlpiri 0.3% and Ngaanyatjarra 0.2%.[a]
- 42.9% worked full-time (57.7% nationally) and 25.1% part-time (30.4% nationally).
- 91.3% of the population rented their homes (30.9 nationally), paying median rent of $75 ($250 nationally).
- 45% of dwellings had no motor vehicle (7.5% nationally).
- 35.9% of households accessed the internet from the dwelling (83.2% nationally).
- Largest town populations
Historical
The 2006 ABS census figures were not vastly different. The total number of residents was slightly lower, at 2,230, but with a higher percentage born in Australia, at 98%. There were fewer speakers of Pitjantjatjara (58.6%), and more Yankuntjatjara (14.3%). More (46.1%) identified as being affiliated with the Uniting Church, and a similar percentage rented their homes.[51]
Access and facilities
Main Access Road upgrade
The upgrade to the Main Access Road is a major project, originally scheduled to begin in 2015 and be completed in 2019, at a cost of A$106.25m (split 80/20 between federal and state governments). It is an upgrade to 210 kilometres (130 mi) of the main access road between the Stuart Highway and Pukatja/Ernabella, and 21 kilometres (13 mi) of community and airstrip access roads in Pukatja, Umuwa, Kaltjiti/Fregon, Mimili and Iwantja/Indulkana. It is expected to deliver safer road travel, better access to employment opportunities, improved delivery of food supplies, improved living standards, etc.[52] In January 2019 it was reported that construction started in 2017, and should be completed by 2021.[53]
Services
Based in Umuwa, Anangu Pitjantjatjara Services (AP Services), an incorporated body established in 1993, provides essential services such as roads and housing.[54] Regional Anangu Services Aboriginal Corporation (RASAC) was established in early 2010 as an offshoot of AP Services,[55] and is now the biggest employer of APY people, with headquarters in Alice Springs and seven community depots. It delivers services such as rental accommodation, aerodromes, building repairs and maintenance, civil works, community patrols, fuel supplies, homeland services and municipal services.[56]
Housing
A few months after his election in early 2018, Premier Steven Marshall, also responsible for Aboriginal Affairs, visited the APY Lands as part of his "whole-of-government" plan which aims to measure SA's progress on improving services to Aboriginal communities. He reported afterwards that employment, especially for young people, was a major issue that needed addressing; and the other one was housing. His government was working on a new funding agreement for remote housing with the federal government, after the 10-year National Partnership Agreement on Remote Housing had ended on 30 June. Susan Tilley, Uniting Communities Aboriginal policy and advocacy manager, said that there were about 75 families still on the waiting list for housing, and that maintenance of existing stock and new housing had to be continued.[57]
Health facilities
The Nganampa Health Council (NHC), an Aboriginal Community-Controlled Health Organisation, runs all of the clinics in the APY Lands and runs a wide range of services, such as the Tjilpi Pampaku Ngura Aged Care facility and health-related programs "including aged care, sexual health, environmental health, health worker training, dental, women's health, male health, children's health, immunisation, eye health and mental health".[58]
In 2014, a Mobile Dialysis Unit, a specially designed truck fitted with three dialysis chairs started operation, visiting remote Aboriginal communities across South Australia, including Pukatja, Mimili, Kaltjiti and Amata in the APY Lands, as well as Marla, Yalata, Coober Pedy, and Leigh Creek.[59] It is run from Purple House, a renal health clinic in Alice Springs, over 400 kilometres (250 mi) away. In July 2018, Health Minister Greg Hunt and Ken Wyatt, then Minister for Indigenous Health, announced increased funding for a number of health initiatives, including expanding renal health units in remote parts, through the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC).[60]
In November 2019, a four-bed dialysis clinic was opened in Pukatja, named after Kinyin Mckenzie, who died in Alice Springs while receiving dialysis. The first such clinic in remote South Australia, it was funded mostly by the federal government, but boosted by the sale of paintings by Ernabella Arts, which raised A$170,000 towards the centre. At full capacity, the clinic can provide dialysis for up to 16 patients, but there is still a need for some short-stay housing to accommodate those who travel from elsewhere for treatment at Pukatja.[61][62]
Policing
As of 2018, the APY Lands were served by police stations situated at Amata, Ernabella, Mimili, Murputja, Umuwa and the town of Marla. Specialist policing support is located at Umuwa, including CIB and domestic violence investigators.[63][64]
The station at Umuwa has not been permanently staffed.[65] As of 2020 a new, permanent policing complex is being built at Umawa. It will accommodate officers with specialist response capabilities, as well provide a base for a mobile unit which will be deployed in Fregon/Kaljiti, Indulkana and Pipalytjara. The service will work closely with child protection service agencies address child abuse and family violence issues.[66][67][66][67] The 2019–2020 Government of South Australia agency budget estimates the completion date as June 2021, with a total spend of A$4.28 million.[68]
Water
SA Water operates desalination plants at Indulkana, Mimili, Kaltjiti (Fregon) and Yunyarinyi (Kenmore Park), which treat the water from local bores.[69]
In early 2019, at a site near Kaljiti/Fregon, a new water source was found in a "palaeo-valley", where groundwater is held about 90 metres (300 ft) below the surface (existing sources being about 30 metres [100 ft] down). Core drill samples have been dated at 5–10 million years old. Pipes were temporarily capped, but elder Witjiti George said that he hoped the water could be used to support a cattle herd, helping to create jobs and an ongoing industry for isolated communities. The new source could also provide much needed drinking water. APY Lands general manager Richard King said the origin of the water was yet to be established, but the water is pure, with low salinity. Government experts were working with Flinders University and the CSIRO to learn more about the source.[26]
Feral camels
In January 2020, the government of South Australia declared that due to the 2019–20 Australian bushfire season and drought, feral camels in large numbers were destroying infrastructure and putting families and communities in danger as they searched for water sources.[70] They were also destroying native vegetation, contaminating water supplies and destroying cultural sites. On 8 January 2020 the South Australian Department for Environment and Water began a five-day cull of the camels, the first mass cull of camels in the area. Professional shooters would kill between 4,000 and 5,000 (or up to 10,000[70]) camels from helicopters, "...in accordance with the highest standards of animal welfare".[71]
Art
The APY is renowned for its artists, who are always well-represented in any exhibitions and awards for Indigenous Australian artists. In 2017, APY artists earned 25 nominations in the prestigious Telstra National Aboriginal & Torres Strait Islander Art Awards; two were named as finalists in the Archibald Prize (which was won by one of them, Vincent Namatjira);[72] 14 APY artists' work made the shortlist for the 2019 A$50,000 Wynne Prize for landscape painting; Peter Mungkuri from Iwantja Arts won the inaugural Hadley's Art Prize; and in 2019, APY artists also won or were shortlisted for the Ramsay Art Prize, the Sir John Sulman Prize, the Hazelhurst Art on Paper Award the John Fries Award, and others. Nici Cumpston, artistic director of Tarnanthi Festival at Art Gallery of South Australia, regularly visits the APY art centres.[73]
APY Art Centre Collective
The APY Art Centre Collective is a group of ten Indigenous-owned and -governed enterprises which supports artists from across the Lands and helps to market their work.[74] The idea was born in 2013, when artists from seven remote art centres got together to look for ways to help the Anangu artists create a network around Australia. It was initially funded from the proceeds of art sales only,[72] but in July 2017 was registered as a public benevolent institution,[75] and as of 2019 was receiving support from the Australia Council, federal and state governments. However the artists themselves manage the collective. The individual art centres saw collaboration as a natural progression, because "We're telling the same story, and when we work together it makes us stronger"; in addition, exploitation by third parties is reduced.[72]
The collective aims to create and investigate new markets for their work, increase income for each art centre and support their business development, and in addition support collaborative regional projects, such as the renowned Kulata Tjuta project, and the APY Photography initiative. Seven art centres across the Lands support the work of more than 500 Anangu artists,[74] from the oldest one, Ernabella Arts, to Iwantja Arts at Indulkana, whose residents include award-winning Vincent Namatjira.[72] As well as the APY centres, Maruku Arts from Uluru, Tjanpi Desert Weavers based in Alice Springs, and Ara Iritja Aboriginal Corporation bring the number up to ten.[74]
Artist Sally Scales (who was formerly the youngest person to have been chair of the APY Executive Board) has been involved with the Collective since 2017 and is as of 2021 a regional project coordinator.[76]
The Collective has galleries in Darlinghurst, Sydney, and, since May 2019, a gallery and studio space on Light Square (Wauwi) in Adelaide,[77] known as APY Gallery Adelaide. The Adelaide studio will function as another working space, the first to be established off-Country. An important aspect is that the artists are able to continue working when visiting healthcare facilities or family in Adelaide, with shuttle buses running between the centre and dialysis centre.[72] Nearly 30% of 2019 gallery sales were made by overseas purchasers, and about 50% from the Eastern states of Australia.[78] About 84% of artwork sales (A$1.6 million as of July 2020) has been returned to the communities through the APY Art centres, which are the only source of income in most of these communities apart from the government.[79]
The art centres represented are:[80]
- Tjala Arts (at Amata)
- Ernabella Arts
- Kaltjiti Arts
- Iwantja Arts
- Mimili Maku Arts
- Tjungu Palya (Nyapari)
- Ara Irititja (APY project)
- Maruku Arts (Yulara)
- Tjanpi Desert Weavers[b]
- Umoona Art Centre (Coober Pedy)
In 2019, 17 APY artists were finalists in the Wynne Prize at the Art Gallery of New South Wales.[78]
In early April 2020, the Adelaide gallery had to close to the public, in line with restrictions imposed by the government owing to the COVID-19 pandemic in Australia, so the gallery went online. In May 2020 it was announced that two of the gallery's resident painters, Sammy Lyons and Leah Brady, were finalists in the Telstra National Aboriginal & Torres Strait Islander Art Awards.[78]
In April 2021, a joint exhibition of the work of Sally Scales and her mother, Josephine Mick, Irititja – Old, Kuwaritja – New, Ngali – Us (a generational story), was opened by prominent Sydney artist Ben Quilty.[76][81]
See also
- Ngangkari – traditional healers
Notes
- ^ Yankunytjatjara and Pitjantjatjara are closely related dialects and both are likely to be spoken in the household; it is also possible that the census collectors spoke different dialects in different census years; in addition, there are other factors affecting the quality of language data, as described on the explanatory page on the ABS website (ABoS 2007).
- ^ "Tjanpi's artist base is made up of women from the Ngaanyatjarra Pitjantjatjara Yakunytjatjara Lands, an area approximately 350,000 square kilometres (140,000 sq mi) in size spanning the tri-state border region of the Northern Territory, Western Australia, and South Australia." (Tjanpi Desert Weavers)
Citations
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (28 June 2022). "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yunkunytjatjara (Local Government Area)". Australian Census 2021 QuickStats. Retrieved 28 June 2022.
- ^ a b c d APY: About us.
- ^ a b ATNS 2013.
- ^ Department of Planning.
- ^ ECSA 2016.
- ^ AEC 2016.
- ^ ALII 1981, p. i.
- ^ waru.org – organisations.
- ^ Ara Irititja.
- ^ OACDT.
- ^ Haxton 2003.
- ^ Standing Committee on Aboriginal Lands (Parliament of South Australia) (1 June 2004). Report of the Select Committee on Pitjantjatjara Land Rights: Third Session, Fiftieth Parliament 2003-2004 (PDF) (Report). Parliament of South Australia – via Austlii.
- ^ Adelaide Advertiser 2007b, p. 14.
- ^ SA Govt 2007.
- ^ ABC News 2007.
- ^ Mullighan Inquiry Report 2008.
- ^ Paper Tracker 2007.
- ^ APY Land Rights Bill 2009.
- ^ a b Mintabie Review 2018.
- ^ a b ABC News, Eviction 2019.
- ^ "APY Land Rights Act 1981 celebrated at Kulilaya Festival" (audio + text). SA Native Title. Aboriginal Way Podcast. 3 May 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ a b Maher, Kyam (11 April 2024). "Thursday, April 11 2024". Hansard Daily: Legislative Council. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "SANTS News". SA Native Title. 29 March 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ O'Connor 1997.
- ^ Lysaght 2021.
- ^ a b Martin & Puddy 2019.
- ^ OCA.
- ^ Paper Tracker – Anangu.
- ^ ESCoSA 2014.
- ^ Mann 2018.
- ^ Martin & Culliver 2018.
- ^ Martin & Culliver 2019.
- ^ APYLR Act 1981.
- ^ APYLR Act – Notes.
- ^ Tlozek, Eric (17 March 2023). "APY Lands board reappoints Richard King as general manager in special meeting". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ Land Rights Act, p. 8.
- ^ Road Upgrade FAQ.
- ^ TAFE SA.
- ^ APY Lands Communities.
- ^ MacLennan 2016.
- ^ Permits.
- ^ APYLR Amendment Act 2016.
- ^ APYLR Amendment Act – map 2016.
- ^ ABS 2016 Census.
- ^ Census 2016: Pukatja.
- ^ Census 2016: Amata.
- ^ Census 2016: Indulkana.
- ^ Census 2016: Kaltjiti.
- ^ Census 2016: Mimili.
- ^ Census 2016: Pipalyatjara.
- ^ ABS 2006 Census.
- ^ DPTI Road Upgrade FAQ 2018.
- ^ Road Upgrade 2019.
- ^ PY Media.
- ^ RASAC: Corporate Info.
- ^ RASAC Snapshot.
- ^ Richards 2018.
- ^ NHC.
- ^ SA Health.
- ^ NITV 2019.
- ^ ABC News 2019.
- ^ SBS 2019.
- ^ ABC: SAPOL statement 2018.
- ^ Boisvert 2018.
- ^ Adelaide Advertiser 2007a.
- ^ a b Henson 2018.
- ^ a b DPMC media release 2018.
- ^ SA State budget 2019.
- ^ SA Water 2020.
- ^ a b Ollie 2020.
- ^ Bogle 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Marsh 2019.
- ^ Moodie 2017.
- ^ a b c Apy Art Centre Collective 2017.
- ^ ABN Lookup 2014.
- ^ a b Keen 2021.
- ^ APY Gallery Adelaide.
- ^ a b c Skujins 2020.
- ^ Neyton 2020.
- ^ Apy Art Centre Collective.
- ^ APY Gallery.
Sources
- "$34 million package for the APY Lands". Government of South Australia. 3 August 2007. Archived from the original on 30 August 2007. Retrieved 8 August 2007.
- "2006 Census QuickStats: Anangu Pitjantjatjara (AC)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "2011 Census QuickStats: Anangu Pitjantjatjara (IARE)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Amata". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Anangu Pitjantjatjara (AC)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Indulkana (L)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Kaltjiti (Fregon) (L)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Mimili (L)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Pipalyatjara". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "2016 Census QuickStats: Pukatja (Ernabella)". quickstats. Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- 2017 Review of the Mintabie Lease and Mintabie Township Lease Agreement (PDF) (Report). Mintabie Review Panel, for the Government of South Australia. 3 January 2018.
- "2901.0 – Census Dictionary, 2006 (Reissue): Language Spoken at Home (LANP)". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 13 July 2007. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- "About Us". Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- "About Us". Apy Art Centre Collective. 26 February 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Anangu Communities". Paper Tracker. Uniting Communities. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara (APY) Lands – Main Access Road Upgrade – Stuart Highway to Pukatja". Government of Australia. Dept of Infrastructure, Regional Development and Cities. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights (Mintabie) Amendment Bill 2009". Government of South Australia Attorney-General's Department. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights (Miscellaneous) Amendment Act 2016". Legislation (South Australia). Government of South Australia. Attorney-General's Dept. 29 September 2016. Retrieved 12 March 2020.(See p. 3,7 in the Act.)
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981" (PDF). 1.7.2017. Government of South Australia. p. 8. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981". Government of South Australia. Attorney-General's Dept. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981 – Notes". Australasian Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- "Anangu tjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act". Australasian Legal Information Institute. 1981. p. i.
- "APY Lands". TAFE SA. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- "APY Lands Communities". Regional Anangu Services Aboriginal Corporation (RASAC). Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- "APY Lands Main Access Road Upgrade: FAQ". Government of South Australia. Dept of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure. 2018. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "APY Lands Regional Partnership Agreement". Agreements, Treaties and Negotiated Settlements (ATNS) project. 31 March 2013. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- "APY Lands: renewal of the Mintabie lease". The Anangu Lands Paper Tracker. 25 October 2007.
- Blakkarly, Jarni (8 November 2019). "The remote South Australian dialysis unit keeping Aboriginal patients on country". SBS News. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- Bogle, Isadora (7 January 2020). "Camel cull in South Australia's remote APY Lands to begin, following sharp increase in population". ABC News. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- Boisvert, Eugene (26 July 2018). "SA Premier refuses to push for police station in Fregon where nurse was murdered". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Brough offer on Aboriginal lands". Adelaide Advertiser. 3 August 2007b. p. 14.
- "Cash Incentives to boost rural SA policing". ABC News. 15 November 2007. Archived from the original on 13 November 2012. Retrieved 27 November 2007.
- "Corporate Information". RASAC – Regional Anangu Services Aboriginal Corporation. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Current Exhibitions". APY Gallery. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Currently Showing in Adelaide". APY Gallery. Archived from the original on 30 April 2021. Retrieved 30 April 2021.
- "District of Giles Background Profile". Electoral Commission SA. 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- "Enhanced police service delivery on APY Lands" (Press release). Australian Government. Dept of Prime Minister and Cabinet. 18 October 2018. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Far North SA Government Region" (PDF). Government of South Australia. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- "Frequently Asked Questions". APY Lands Main Access Road Upgrade. Department for Infrastructure and Transport, South Australia. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- Haxton, Nance (27 October 2003). "Anangu Pitjantjatjara people agree to discussions with mining industry". The World Today. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 5 June 2007.
- Henson, Elizabeth (17 October 2018). "New police complex at Umuwa and mobile pop-up station in $4.28 million APY Lands project". The Advertiser. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- "Historical details for ABN 37 959 235 321". ABN Lookup. November 2014. Retrieved 30 April 2021.
- "In far-north SA, an entire town is being evicted by the government". Australia: ABC News. 28 December 2019. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- Jonscher, Samantha (9 November 2019). "South Australia's first remote dialysis clinic changing lives for people in isolated communities". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- Keen, Suzie (15 April 2021). "Sally Scales and Josephine Mick: A generation story at APY Gallery". InDaily. Retrieved 30 April 2021.
- Liddle, Ryan (1 August 2018). "Funding boost to tackle challenges of dialysis in Central Australia". NITV. Retrieved 10 November 2019.
- Lysaght, Gary-Jon (28 January 2021). "Map of APY Lands translated to 'empower' First Nations people, giving them greater voice". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- MacLennan, Leah (17 March 2016). "'Heartbroken' woman forced to leave APY Lands due to serious fears for children". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- Mann, Alex (15 February 2018). "Damning review into outback town forces residents to leave within a year". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- "Map". waru.org. Archived from the original on 8 August 2007.
- "Map of Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Lands (Apy) 7 Electorates Comprised by the Community Groups as Referred to in the Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Lands Rights (Miscellaneous) Amendment Act 2016" (PDF) (map). Government of South Australia. Department of State Development, Aboriginal Affairs and Reconciliation. Heritage Information Team. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 12 March 2020.
- Marsh, Walter (20 May 2019). "New gallery run for and by Anangu artists opens in Adelaide". The Adelaide Review. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- Martin, Patrick; Culliver, Paul (3 June 2018). "Defending the 'last frontier' – outback locals say condemned town deserves a fair go". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 8 September 2018.
- Martin, Patrick; Culliver, Paul (13 February 2019). "Mintabie locals to fight permanent eviction". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- Martin, Patrick; Puddy, Rebecca (25 May 2019). "Water discovery in ancient underground valley boosts hopes of development in APY Lands". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Mintabie profile". Outback Areas Community Development Trust. Archived from the original on 29 August 2007.
- "Mobile Dialysis Unit for Aboriginal people". SA Health. Government of South Australia. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- Moodie, Georgia (27 July 2017). "Why the APY Lands dominate the Australian art scene". Australia: ABC News. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Mullighan Inquiry Report". Government of South Australia. 7 May 2008. Archived from the original on 11 May 2008.
- Neyton, John (29 July 2020). "Watarkurinytja Wiya brings culture, Country and family to SALA Festival". The Adelaide Review. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- O'Connor, Alan (1997). "Special Article – Aboriginal Lands in South Australia". 1301.4 – South Australian Year Book, 1997. With assistance from the Aboriginal landholding authorities. Australian Bureau of Statistics.
- Ollie, Emily (7 January 2020). "Camel cull in SA's APY lands to result in 10,000 camels being destroyed". Seven News. Retrieved 14 January 2020.
- "Online overview". Ara Irititja. Archived from the original on 14 July 2007. Retrieved 5 June 2007.
- "Organisations". waru.org. Archived from the original on 19 July 2007. Retrieved 5 June 2007.
- "Our art centres". Apy Art Centre Collective. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Our Artists". Tjanpi Desert Weavers. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- Part B Attachment 1: Aboriginal Community Sites (Report) (version 2.2 ed.). Essential Services Commission of South Australia. March 2014. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "Permits". Anangu. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- "Police Stations like ill-equipped sheds". Adelaide Advertiser. 7 July 2007a. Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Profile of the electoral division of Grey (SA)". Australian Electoral Commission. 2016. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- "RASAC Snapshot". RASAC – Regional Anangu Services Aboriginal Corporation. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- Richards, Stephanie (24 July 2018). "Marshall's "whole of government" approach to Aboriginal affairs". InDaily. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "SAWater – Desalination across the state". SA Water. 28 January 2020. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- Skujins, Angela (14 May 2020). "Buy nationally recognised art online from APY Art Centre Collective". CityMag. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- State Budget 2019–20: Agency Statement: Budget Paper 4 (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4. Government of South Australia. Dept of Treasury and Finance. 18 June 2019. ISSN 1440-8589. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 February 2020. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Statement from South Australia Police". Australian Story. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 5 March 2018. Retrieved 16 January 2020.
- "Umuwa". PY Media. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "Welcome to the Outback Communities Authority". Outback Communities Authority. Archived from the original on 14 April 2019. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Who we are". Nganampa Health Council. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
Further reading
- "Communities". Outback Communities Authority. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 26 May 2019. (Map showing location and boundaries)
- Aboriginal Lands Joint Standing Committee of South Australian Parliament (2006)
- ""The Pitjantjatjara Land Rights Act 1981" – Presentation by the Hon Robert Lawson MLC". The Bennelong Society 2003 Conference "An Indigenous Future? Challenges and Opportunities". 2003. Archived from the original on 13 August 2007.
a brief overview of the Pitjantjatjara Land Rights Act 1981..., its history, operations, limitations and its future.
External links
- Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Council website
- APY Art Centre Collective official website
- APY Gallery Adelaide website
- "Anangu Pitjantjatjara Yankunytjatjara Land Rights Act 1981". Government of South Australia. Attorney-General's Dept.(for latest version)
