8×50mmR Lebel
| 8×50mmR (8 mm Lebel/Balle D) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||
| Type | Rifle | |||||||||||
| Place of origin | France, French Third Republic | |||||||||||
| Service history | ||||||||||||
| In service | 1887–1945[1][2] | |||||||||||
| Used by | See Users | |||||||||||
| Wars | French colonial campaigns, World War I, World War II, and other conflicts | |||||||||||
| Production history | ||||||||||||
| Designed | 1886 | |||||||||||
| Variants | Balle M, balle D, balle N, balle T, balle P | |||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||
| Parent case | 11×59mmR Gras | |||||||||||
| Case type | Rimmed, bottleneck | |||||||||||
| Bullet diameter | 8.30 mm (0.327 in) | |||||||||||
| Land diameter | 8.00 mm (0.315 in) | |||||||||||
| Neck diameter | 8.85 mm (0.348 in) | |||||||||||
| Shoulder diameter | 11.42 mm (0.450 in) | |||||||||||
| Base diameter | 13.77 mm (0.542 in) | |||||||||||
| Rim diameter | 16.00 mm (0.630 in) | |||||||||||
| Rim thickness | 1.40 mm (0.055 in) | |||||||||||
| Case length | 50.50 mm (1.988 in) | |||||||||||
| Overall length | 75.00 mm (2.953 in) | |||||||||||
| Rifling twist | 240 mm (1 in 9.45 inch) | |||||||||||
| Primer type | Large rifle | |||||||||||
| Maximum pressure | 320.00 MPa (46,412 psi) | |||||||||||
| Ballistic performance | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Source(s): C.I.P.[3][4] | ||||||||||||
The 8×50mmR Lebel (8mm Lebel) (designated as the 8 × 51 R Lebel by the C.I.P.[3]) rifle cartridge was the first smokeless powder cartridge to be made and adopted by any country. It was introduced by France in 1886. Formed by necking down the 11×59mmR Gras black powder cartridge, the smokeless 8mm Lebel cartridge started a revolution in military rifle ammunition. Standard 8mm Lebel military ammunition was also the first rifle ammunition to feature a spitzer boat tail bullet (balle D), which was adopted in 1898.[5] The long-range ballistic performance of the 8mm Lebel bullet itself was exceptional for its time. For use in the magazine tube-fed early Lebel rifle, the 8 mm case was designed to protect against accidental percussion inside the tube magazine by a circular groove around the primer cup which caught the tip of the following pointed bullet. However, the shape of its rimmed bottle-necked case, having been designed for the Lebel rifle's tube magazine, also precluded truly efficient vertical stacking inside a vertical magazine. The bolt thrust of the 8mm Lebel is relatively high compared to many other service rounds used in the early 20th century. Although it was once revolutionary, the 8mm Lebel was declared obsolete after World War I and was soon after replaced with the 7.5×54mm French round.
Note
There are two commercially available 8mm Lebel cartridges: one for the Lebel Model 1886 rifle, and one for the Modèle 1892 revolver. They are two entirely different cartridges and are not interchangeable. The term "8mm Lebel" for the French Mle 1892 revolver ammunition, is only applied outside France for commercial reasons and has nothing to do with the Lebel rifle. However, the term "8mm Lebel", used to identify a rifle cartridge, is widely recognized to distinguish the French rifle cartridge from other 8 mm rifle cartridges, such as the 8×50mmR Mannlicher cartridge used by Austria-Hungary and its successor states.
8×50mmR Lebel rifle ammunition

The cartridge for the tube-fed long arm was originally loaded with a 15.0 g (232 grains) cupro-nickel-jacketed, lead-cored, flat-nosed, wadcutter-style bullet, called "balle M", which had been designed by Lieutenant Colonel Nicolas Lebel. The flat point (flat nose or tip) of this bullet had been designed to be safe inside the newly commissioned rifle's tube magazine. It was propelled by the first practical smokeless, nitrocellulose-based powder (Poudre B), as developed by Paul Vieille in 1884. The ballistic performance and range of balle M with the new propellant eclipsed all the previous military ammunitions in existence at the time (1886).
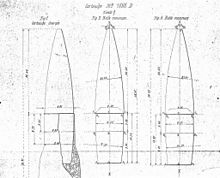
This balle M was replaced in 1898 by a new design, a 12.8 g (198 grains) 90/10 bronze mono-metal, pointed (spitzer) boat-tail bullet called "balle D", which provided a flatter trajectory and improved long-range performance. Designed at the Atelier de Puteaux (APX) by Captain Georges Desaleux, the balle D was the first pointed and boat-tailed bullet to be placed into service by any military. Later on in 1912, the round was improved into the balle D am ("am" stands for "amorçage modifié" or "modified primer"), done by crimping the primer in more deeply to prevent primer expulsions when fired in machine guns. This ammunition was in near-universal service during World War I (1914–1918) in all Lebel-caliber weapons. The balle D am ammunition was followed in 1932 by balle N ammunition, which featured a lead-cored, cupro-nickel-over-steel-jacketed, pointed boat-tail bullet weighing 15.0 g (232 grains). It was thicker (8.3 mm instead of 8.17) and was held into a case that had a slightly larger neck diameter than that for the older balle D am ammunition. The new balle N was again heavier than the balle D am, and had been designed to improve the long-range performance of the issued Hotchkiss machine guns. Rechambering practically all French Lebel-caliber rifles and carbines to use the "N"-type ammunition was carried out during the 1930s. A balle T (tracer ammunition) and balle P armor-piercing rounds were also produced, along with blank and reduced charge cartridges.


In order to safely accommodate pointed (spitzer) bullets inside the Lebel rifle magazine, a circular groove was machined around each primer cup at the case base on both balle D am and balle N ammunitions. The role of that circular groove is to receive the pointed bullet tip of the following round loaded inside the tube magazine, and keep it at the side of the case base of the previous cartridge, so the tip does not easily slide to the base center where the primer is located. The tapered form of the case itself did help too to keep pointed tips away from the primer cup of a round in front of another in the tube. Furthermore, all balle D and balle M French military ammunitions featured convex primer covers which are crimped in over the primer itself. Those small covers are not noticeable, but do provide a second effective protection against accidental primer percussion inside the Lebel's tube magazine. Wartime experiences (1914–1918) involving hundreds of millions of Lebel rounds fired in combat have entirely confirmed the effectiveness of these protections.

While revolutionary for its time in terms of ballistic performance, the 8×50mmR Lebel cartridge had its drawbacks. Formed by necking down the 11mm Gras rifle cartridge case, it was an odd design, with a thick rim and a rapid double taper. This made it more difficult to feed from standard magazine firearms such as the Berthier rifles and the Chauchat machine guns, and is the reason for the distinct curvature in the magazines of those firearms. The Lebel rifle from which it was fired was also rather outdated by the time balle D, let alone the balle N, came along.
A balle N round can only be fired from Lebel or Berthier rifles, if the chamber has been reamed to accept the larger neck of the N-type cartridge. Such weapons are stamped N on top of the barrel, just in front of the receiver and behind the rear sight. The balle N ammunition is identifiable by the fact that the bullet, while pointed like the solid-brass balle D, is lead-cored and jacketed with soft steel.

While newly manufactured 8×50mmR Lebel ammunition has become available in the U.S., reloadable cartridge cases can also be produced by reforming .348 Winchester brass. The 8mm Lebel round produced by Prvi Partizan is of excellent quality and replicates the performance of the original round. However, Privi Partizan's older style brass cases lack the circular groove around the primer cup, so reloaders use round-nosed or flat-nosed bullets when producing handloads for the tube-magazine Lebel rifles with these cases. The older Privi Partizan cases loaded with spire point bullets should only be fired single shot. More recently, Privi Partizan manufactured Lebel ammunition with spitzer bullets do incorporate the circular groove at the base, and are safe when stacked in the box-magazine of Berthier rifles and the tubular magazine of Lebel rifles. Newer cases with circular groove follow the balle D specifications, and shooters may use the magazine for loading.
In 1929, the 7.5×54mm MAS mod. 1929 (7.5 French) cartridge was introduced. This made the 8×50mmR Lebel cartridge obsolete, but due to post-World War I financial constraints and political neglect, it was not introduced as a rifle cartridge until the adoption, just before World War II, of the MAS-36 rifle.
Downrange performance comparison
1886 pattern 8×51mmR Lebel balle M load
| Distance (m) | 0 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1,000 | 1,500 | 2,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trajectory (m) | 0 | 0.14 | 0.81 | 2.39 | 5.27 | 9.83 | 31.71 | 75.61 |
| Velocity (m/s) | 628 | 488 | 397 | 335 | 290 | 255 | 197 | 160 |
1898 pattern 8×51mmR Lebel balle D load
| Distance (m) | 0 | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1,000 | 1,500 | 2,000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trajectory (m) | 0 | 0.12 | 0.54 | 1.43 | 3.01 | 5.60 | 18.30 | 44.0 |
| Velocity (m/s) | 700 | 607 | 521 | 448 | 388 | 342 | 278 | 240 |
Weapons using the 8mm Lebel round
Rifles
- Lebel Model 1886 rifle
- Berthier rifles and carbines
- Model 1917 semi-automatic rifle
- Fusil Gras mle 1874
- Remington Rolling Block rifle - a limited production for France before & during WWI
Machine guns
- Hotchkiss M1909 Benét–Mercié machine gun
- Hotchkiss M1914 machine gun
- Chauchat light machine gun
- Madsen machine gun
- Chauchat-Ribeyrolles 1918 submachine gun
- St. Étienne Mle 1907
- Vickers machine gun
Users
 France
France French Empire
French Empire Kingdom of Greece Saint Etienne machine gun in 1917–1940
Kingdom of Greece Saint Etienne machine gun in 1917–1940 Kingdom of Italy: Saint Etienne machine gun in 1917–18
Kingdom of Italy: Saint Etienne machine gun in 1917–18 Russian Empire: Hotchkiss Portative Mle 1909, Hotchkiss Mle 1914, C.S.R.G. and St. Etienne machine guns and many rifles in 1916-1921
Russian Empire: Hotchkiss Portative Mle 1909, Hotchkiss Mle 1914, C.S.R.G. and St. Etienne machine guns and many rifles in 1916-1921 Finland: Chauchat Mle 1915 C.S.R.G. machine gun - few from Russia in 1918, 5000 from France during Winter War 1939-1940
Finland: Chauchat Mle 1915 C.S.R.G. machine gun - few from Russia in 1918, 5000 from France during Winter War 1939-1940 Nazi Germany: Captured Lebel M1886 rifles (Designated Gewehr 301 (f)) were issued to the Volkssturm, Hotchkiss Mle 1914 machine gun adopted as s.MG 257(f)
Nazi Germany: Captured Lebel M1886 rifles (Designated Gewehr 301 (f)) were issued to the Volkssturm, Hotchkiss Mle 1914 machine gun adopted as s.MG 257(f) Second Polish Republic: Lebel and Berthier rifles were brought into Poland by the Blue Army and used in the Polish-Soviet War. Surplus rifles and Chauchats were obtained in large numbers as part of French military aid.
Second Polish Republic: Lebel and Berthier rifles were brought into Poland by the Blue Army and used in the Polish-Soviet War. Surplus rifles and Chauchats were obtained in large numbers as part of French military aid. Second Spanish Republic: Lebel rifles obtained from France along with Berthier rifles and carbines received from Poland were used by Republican forces during the Spanish Civil War.[6]
Second Spanish Republic: Lebel rifles obtained from France along with Berthier rifles and carbines received from Poland were used by Republican forces during the Spanish Civil War.[6] United States: Hotchkiss machine gun and Chauchat machine-rifle in 1917–18
United States: Hotchkiss machine gun and Chauchat machine-rifle in 1917–18
See also
References
- ^ Historicfirearm. (n.d.). Historicalfirearms. Historical Firearms. Retrieved April 20, 2022, from https://www.historicalfirearms.info/page/163
- ^ Jardim, F. (2022, March 24). Austria-Hungary's M95 rifle. GUNS Magazine. Retrieved April 20, 2022, from https://gunsmagazine.com/our-experts/surplus-classic/austria-hungarys-m95-rifle/
- ^ a b "C.I.P. TDCC datasheet 8 × 51 R Lebel" (PDF).
- ^ Johnson, Melvin M. Jr. (1944). Rifles and Machine Guns. New York: William Morrow & Company. p. 384.
- ^ Chuck Hawks. "The 8x50R Lebel (8mm Lebel)".
- ^ "Foreign Rifles of the Spanish Republic, 1936-1939 – Surplused". 15 June 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
Sources
- Hamilton, Douglas Thomas (1916). Cartridge manufacture; a treatise covering the manufacture of rifle cartridge cases, bullets, powders, primers and cartridge clips, and the designing and making of the tools used in connection with the production of cartridge cases and bullets. New York: The Industrial press. p. 142.
- "Balle M, D, N, T, and P". Conjay. Archived from the original on 2007-07-31. Retrieved 2007-03-11.
- "8x51R LEBEL". PPU USA.
- Huon, Jean (1988). Military Rifle and Machine Gun Cartridges. Alexandria, Va.: Ironside International Publishers. ISBN 0-935554-05-X.

