6th century
| Millennium |
|---|
| 1st millennium |
| Centuries |
| Timelines |
| State leaders |
| Decades |
| Categories: |
|
Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |

The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar.
In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire.
Owing in part to the collapse of the Roman Empire along with its literature and civilization, the sixth century is generally considered to be the least known about in the Dark Ages.[a]
In its second golden age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.[3] The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in the mid-6th century. In Japan, the Kofun period gave way to the Asuka period. After being divided for more than 150 years among the Northern and Southern dynasties, China was reunited under the Sui dynasty toward the end of the 6th century. The Three Kingdoms of Korea persisted throughout the century. The Göktürks became a major power in Central Asia after defeating the Rouran.
In the Americas, Teotihuacan began to decline in the 6th century after having reached its zenith between AD 150 and 450. Classic period of the Maya civilization in Central America.
Events
- Early 6th century – Ah Suytok Tutul Xiu founds Uxmal.

Eastern Hemisphere at the beginning of the 6th century - Early 6th century – Archangel ivory, panel of a diptych probably from the court workshop at Constantinople, is made. It is now kept at The British Museum, London.
- Early 6th century – Vienna Genesis, from "Book of Genesis", probably made in Syria or Palestine, is made. It is now kept at Österreichische Nationalbibliothek, Vienna.
- By 6th century – Shilpa Shastras is written.
- Early 6th century – first academy of the east the Academy of Gundeshapur founded in Iran by Khosrau I of Persia.
- Early 6th century – Irish colonists and invaders, the Scots, began migrating to Caledonia (later known as Scotland). Migration from south-west Britain to Brittany.
- Early 6th century – Glendalough monastery, Wicklow Ireland founded on St. Kevin. Many similar foundations in Ireland and Wales.
- Early 6th century – Zen Buddhism enters Vietnam from China.
- Early 6th century – Haniwa, from Kyoto, is made during the Kofun period.

Uxmal is founded in the early 6th century. - Early 6th century – Basilica of Sant'Apollinare in Classe's apse's mosaic is completed.
- 502: Chinese annals mentioned the existence of the Buddhist Kingdom, Kanto Lim in South Sumatra, presumably in the neighborhood of present-day Palembang.
- 507: The Franks commanded by Clovis I wrest Aquitania from Alaric II's Visigoths at the Battle of Vouillé.
- 518: Eastern Roman Emperor Anastasius I dies and is succeeded by Justin I.
- 522: Romans obtain silkworm eggs and begin silkworm cultivation
- c. 524: Boethius writes his On the Consolation of Philosophy.
- 525: Having settled in Rome c. 500, Scythian monk Dionysius Exiguus invents the Anno Domini era calendar based on the estimated birth year of Jesus Christ.
- 527: Justinian I succeeds Justin I as Emperor of the Eastern Roman Empire.
- 529: Saint Benedict of Nursia founds the monastery of Monte Cassino in Italy.
- 532: Nika riots in Constantinople; the cathedral is destroyed. They are put down a week later by Belisarius and Mundus; up to 30,000 people are killed in the Hippodrome.
- 535: Postulated volcanic eruption in the tropics which causes several years of abnormally cold weather, resulting in mass famine in the Northern Hemisphere. (See Extreme weather events of 535–536.)

This Buddhist stela from China, Northern Wei period, was built in the early 6th century. - 537: Battle of Camlann, final battle of legendary King Arthur.
- 541–542: First pandemic of bubonic plague (Plague of Justinian) hits Constantinople and the rest of Byzantine Empire.
- 543/544: One of Justinian's edict leads to the Three-Chapter Controversy
- 545: Nubian Kingdom of Nobatia converts to Christianity.
- Mid-6th century – Cassiodorus founds a cenobitic monastery and scriptorium at Vivarium in Italy
- Mid-6th century – Buddhist Jataka stories are translated into Persian by order of the Zoroastrian king Khosrau.
- Mid-6th century – Cave-Temple of Shiva at Elephanta Caves, Maharashtra, India, is built. Post-Gupta period.
- Mid-6th century – Eternal Shiva, rock-cut relief in the Cave-Temple of Shiva at Elephanta Caves, is made
- Mid-6th century – Jogeshwari Caves excavated during 6th century A.D. is one of the finest specimen of Brahmanical Rock-Cut Architecture and bears similarity with Elephanta Caves (Cave No. 1) and Dhumar Lena (Cave No. 29) at Ellora Caves.
- Second half of 6th century – Virgin and Child with Saints and Angels, icon, is made. It is now kept at Saint Catherine's Monastery, Egypt.
- 550: Kingdom of Funan dies out.
- 551: Bumin Khagan founded the Turkic Khaganate in Central Asia
- 552: Buddhism introduced to Japan from Baekje during the Asuka period.
- 553: Second Council of Constantinople
- 554: Eviction of the Ostrogoths from Rome, and the re-unification of all Italy under Roman rule.
- 561 to 592: Buddhist monk Jnanagupta translates 39 sutras from Sanskrit to Chinese.
- 563: The monastery on Iona is founded by St. Columba.
- 566: Birth of Lǐ Yuān, founder of the Tang dynasty and Emperor of China under the name of Gaozu (618-626)
- 568: Lombards invade Italy and establish a federation of dukedoms under a king.
- 569: Nubian kingdom of Alodia converts to Christianity.
- 569: Nubian kingdom of Makuria converts to Christianity.
- 570: Birth of the last Islamic Prophet Muhammad.
- 574: The Roman Empire is invaded by various Slavs, who plunder the Balkans.
- 577: China's last of the Southern dynasties, the Chen dynasty invents matches.
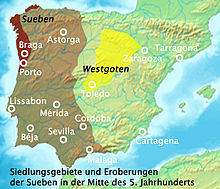
The Suebi Kingdom would eventually be conquered by the Visigoths in the 6th century - 578: The world's oldest ongoing company, Kongō Gumi, is founded in Osaka, Japan.
- 579–590: Reign of Persian Shah Hormizd IV.
- 582–602: Reign of Roman Emperor Maurice.
- 585: Suebian Kingdom conquered by Visigoths in Spain.
- 587: Reccared, king of the Visigoths in Spain, converts to Catholicism.
- 588: Shivadeva ascends the throne of the Lichchhavi dynasty in Nepal.
- 589: Third Council of Toledo adds the "filioque" clause to the Nicene Creed in Spain.
- 589: China reunified under the Sui dynasty (589 – 618).
- 590: Gregory the Great succeeds Pope Pelagius II (who dies of plague) as the 64th pope.
- 594: Beginning of the Bengali Calendar or (বঙ্গাব্দ Bônggabdô or Banggabda).
- 595: Pope Gregory sends Roman monks led by Augustine to England.
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- Dionysius Exiguus creates the Anno Domini system, inspired by the birth of Jesus, in 525. This is the system upon which the Gregorian calendar and Common Era systems are based.
- The technology of cutting and polishing diamonds was invented in India, Ratna Pariksha, a text dated to 6th century talks about diamond cutting.
- Backgammon (nard) invented in Persia by Burzoe.
- Chess, as chaturanga, entered Persia from India and was modified to shatranj.
- Breast-strap horse harness in use in Frankish kingdom.
- Byzantine Empire acquires silk technology from China.
- Chen dynasty from China invents matches in 577.
- Silk is a protected palace industry in the Byzantine Empire.
- Vaghbata, Indian medical books.
- In 589 AD, the Chinese scholar-official Yan Zhitui makes the first reference to the use of toilet paper in history.[4]
- Significant to the history of agriculture, the Chinese author Jia Sixia wrote the treatise Qi Min Yao Shu in 535, and although it quotes 160 previous Chinese agronomy books, it is the oldest existent Chinese agriculture treatise. In over one hundred thousand written Chinese characters, the book covered land preparation, seeding, cultivation, orchard management, forestry, animal husbandry, trade, and culinary uses for crops.
Notes
- ^ This view is shown in several reputable sources about the Dark Ages. In his book "The Inheritance of Rome: Illuminating the Dark Ages, 400-1000", the historian Chris Wickham writes that "the sixth century is the least documented of any century of the 'Dark Ages'".[1] Similarly, the historian Charles Oman writes in "The Dark Ages: 476-918" that "the 6th century was a period of such confusion and turmoil that it has been compared to the deluge of Noah".[2] These sources reflect the widely accepted view among historians that the 6th century in the Dark Ages is the least known about.
References
- ^ Wickham, Chris (2009). "Introduction". The Inheritance of Rome: Illuminating the Dark Ages, 400-1000. New York: Viking. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-670-02098-0.
- ^ Oman, Charles (1914). "The Sixth Century". The Dark Ages: 476-918. London: Rivingtons. p. 23.
- ^ Roberts, J: "History of the World". Penguin, 1994.
- ^ Green, Hilary (2022). International Trade in the Middle Ages. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-9841-0.
