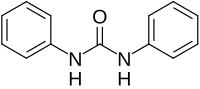
1,3-Diphenylurea
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N,N′-Diphenylurea | |
| Other names 1,3-Diphenylurea; Diphenylurea; carbanilide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 782650 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.731 |
| EC Number |
|
| 143821 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 212.252 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 239–241 °C (462–466 °F; 512–514 K) |
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K) |
| -127.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
1,3-Diphenylurea is a phenylurea-type compound with the formula (PhNH)2CO (Ph = C6H5). It is a colorless solid that is prepared by transamidation of urea with aniline.
DPU is a cytokinin, a type of plant hormone that induces flower development. The cytokinin effect of DPU is relatively low, but other more potent phenylurea-type cytokinins have been reported.[1]
It was detected in coconut milk.[2]
References
- ^ Effect of cytokinin-active phenylurea derivatives on shoot multiplication. T. Genkov and I. Ivanova, Bulg. J. Plant Physiol., 1995, 21(1), pages 73–83 (link to article at researchgate)
- ^ Shantz, E. M.; Steward, F. C. (1955). "The Identification of Compound A from Coconut Milk as 1,3-Diphenylurea". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 77 (23): 6351. doi:10.1021/ja01628a079.
External links
 The dictionary definition of Diphenylurea at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Diphenylurea at Wiktionary
