Major second

| Inverse | minor seventh |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Other names | whole tone, whole step |
| Abbreviation | M2 |
| Size | |
| Semitones | 2 |
| Interval class | 2 |
| Just interval | 9:8[1] or 10:9[1] |
| Cents | |
| 12-Tone equal temperament | 200[1] |
| Just intonation | 204[1] or 182[1] |

In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (ⓘ). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more details). For example, the interval from C to D is a major second, as the note D lies two semitones above C, and the two notes are notated on adjacent staff positions. Diminished, minor and augmented seconds are notated on adjacent staff positions as well, but consist of a different number of semitones (zero, one, and three).
The intervals from the tonic (keynote) in an upward direction to the second, to the third, to the sixth, and to the seventh scale degrees of a major scale are called major.[2]
The major second is the interval that occurs between the first and second degrees of a major scale, the tonic and the supertonic. On a musical keyboard, a major second is the interval between two keys separated by one key, counting white and black keys alike. On a guitar string, it is the interval separated by two frets. In moveable-do solfège, it is the interval between do and re. It is considered a melodic step, as opposed to larger intervals called skips.
Intervals composed of two semitones, such as the major second and the diminished third, are also called tones, whole tones, or whole steps.[3][4][5][6][7][8] In just intonation, major seconds can occur in at least two different frequency ratios:[9] 9:8 (about 203.9 cents) and 10:9 (about 182.4 cents). The largest (9:8) ones are called major tones or greater tones, the smallest (10:9) are called minor tones or lesser tones. Their size differs by exactly one syntonic comma (81:80, or about 21.5 cents). Some equal temperaments, such as 15-ET and 22-ET, also distinguish between a greater and a lesser tone.
The major second was historically considered one of the most dissonant intervals of the diatonic scale, although much 20th-century music saw it reimagined as a consonance.[citation needed] It is common in many different musical systems, including Arabic music, Turkish music and music of the Balkans, among others. It occurs in both diatonic and pentatonic scales.
ⓘ. Here, middle C is followed by D, which is a tone 200 cents sharper than C, and then by both tones together.
Major and minor tones
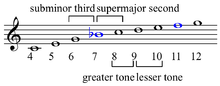

In tuning systems using just intonation, such as 5-limit tuning, in which major seconds occur in two different sizes, the wider of them is called a major tone or greater tone, and the narrower minor tone or, lesser tone. The difference in size between a major tone and a minor tone is equal to one syntonic comma (about 21.51 cents).
The major tone is the 9:8 interval[11] ⓘ, and it is an approximation thereof in other tuning systems, while the minor tone is the 10:9 ratio[11] ⓘ. The major tone may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the eighth and ninth harmonics. The minor tone may be derived from the harmonic series as the interval between the ninth and tenth harmonics. The 10:9 minor tone arises in the C major scale between D & E and G & A, and is "a sharper dissonance" than 9:8.[12][13] The 9:8 major tone arises in the C major scale between C & D, F & G, and A & B.[12] This 9:8 interval was named epogdoon (meaning 'one eighth in addition') by the Pythagoreans.
Notice that in these tuning systems, a third kind of whole tone, even wider than the major tone, exists. This interval of two semitones, with ratio 256:225, is simply called the diminished third (for further details, see Five-limit tuning § Size of intervals).
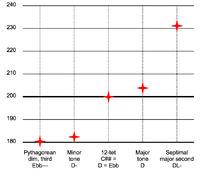
Some equal temperaments also produce major seconds of two different sizes, called greater and lesser tones (or major and minor tones). For instance, this is true for 15-ET, 22-ET, 34-ET, 41-ET, 53-ET, and 72-ET. Conversely, in twelve-tone equal temperament, Pythagorean tuning, and meantone temperament (including 19-ET and 31-ET) all major seconds have the same size, so there cannot be a distinction between a greater and a lesser tone.
In any system where there is only one size of major second, the terms greater and lesser tone (or major and minor tone) are rarely used with a different meaning. Namely, they are used to indicate the two distinct kinds of whole tone, more commonly and more appropriately called major second (M2) and diminished third (d3). Similarly, major semitones and minor semitones are more often and more appropriately referred to as minor seconds (m2) and augmented unisons (A1), or diatonic and chromatic semitones.
Unlike almost all uses of the terms major and minor, these intervals span the same number of semitones. They both span 2 semitones, while, for example, a major third (4 semitones) and minor third (3 semitones) differ by one semitone. Thus, to avoid ambiguity, it is preferable to call them greater tone and lesser tone (see also greater and lesser diesis).
Two major tones equal a ditone.
Epogdoon

In Pythagorean music theory, the epogdoon (Ancient Greek: ἐπόγδοον) is the interval with the ratio 9 to 8. The word is composed of the prefix epi- meaning "on top of" and ogdoon meaning "one eighth"; so it means "one eighth in addition". For example, the natural numbers are 8 and 9 in this relation (8+(×8)=9).
According to Plutarch, the Pythagoreans hated the number 17 because it separates the 16 from its Epogdoon 18.[14]
"[Epogdoos] is the 9:8 ratio that corresponds to the tone, [hêmiolios] is the 3:2 ratio that is associated with the musical fifth, and [epitritos] is the 4:3 ratio associated with the musical fourth. It is common to translate epogdoos as 'tone' [major second]."[15]
Further reading
- Barker, Andrew (2007). The Science of Harmonics in Classical Greece. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521879514.
- Plutarch (2005). Moralia. Translated by Frank Cole Babbitt. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 9781417905003.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e Duffin, Ross W. (2008). How equal temperament ruined harmony : (and why you should care) (First published as a Norton paperback. ed.). New York: W. W. Norton. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-393-33420-3. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ Benward, Bruce & Saker, Marilyn (2003). Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I, p.52. Seventh Edition. ISBN 978-0-07-294262-0.
- ^ "Whole step – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary". Merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ "Oxford Dictionaries – Dictionary, Thesaurus, & Grammar". Askoxford.com. 2015-02-11. Archived from the original on October 31, 2007. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ "Whole step | Define Whole step at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.reference.com. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ "Whole tone | Define Whole tone at Dictionary.com". Dictionary.reference.com. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ Miller, Michael (2005). The Complete Idiot's Guide to Music Theory – Michael Miller – Google Books. ISBN 9781592574377. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ Pilhofer, Michael; Day, Holly (2011-02-25). Music Theory For Dummies – Michael Pilhofer, Holly Day – Google Books. ISBN 9781118054444. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ Leta E. Miller, Fredric Lieberman (2006). Lou Harrison, p.72. ISBN 0-252-03120-2.
- ^ Leta E. Miller, ed. (1988). Lou Harrison: Selected keyboard and chamber music, 1937–1994, p.xliii. ISBN 978-0-89579-414-7.
- ^ a b Royal Society (Great Britain) (1880, digitized Feb 26, 2008). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Volume 30, p.531. Harvard University.
- ^ a b Paul, Oscar (1885) [page needed]
- ^ Paul, Oscar (2010-05-25). "A Manual of Harmony for Use in Music-schools and Seminaries and for Self ... – Oscar Paul – Google Books". Retrieved 2015-02-25.[page needed]
- ^ "Plutarch • Isis and Osiris (Part 3 of 5)". Penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2015-02-25.
- ^ "Proclus : Commentary on Plato's Timaeus". Philpapers.org. Retrieved 25 February 2015.



