Wayang kulit
| Wayang kulit | |
|---|---|
 Wayang kulit performance with dalang | |
| Types | Indonesian wayang form |
| Ancestor arts | Javanese |
| Originating culture | Indonesia |
| Originating era | Hindu—Buddhist civilisations |
| Wayang puppet theatre | |
|---|---|
| Country | Indonesia |
| Reference | 00063 |
| Region | Asia and the Pacific |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2008 (3rd session) |
| List | Representative |
| Wayang kulit, wayang golek, wayang klitik | |

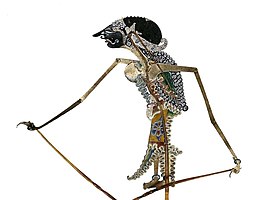
Wayang kulit (Javanese: ꦮꦪꦁꦏꦸꦭꦶꦠ꧀ (in the ngoko register))[1] is a traditional form of shadow puppetry originally found in the cultures of Java and Bali in Indonesia.[2] In a wayang kulit performance, the puppet figures are rear-projected on a taut linen screen with a coconut oil (or electric) light. The dalang (shadow artist) manipulates carved leather figures between the lamp and the screen to bring the shadows to life. The narratives of wayang kulit often have to do with the major theme of good vs. evil.
Wayang kulit is one of the many different forms of wayang theatre found in Indonesia; the others include wayang beber, wayang klitik, wayang golek, wayang topeng, and wayang wong. Wayang kulit is among the best known, offering a unique combination of ritual, lesson and entertainment.
On November 7, 2003, UNESCO designated Wayang the flat leather shadow puppet (wayang kulit), the flat wooden puppet (wayang klitik), and the three-dimensional wooden puppet (wayang golek) theatre, as a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity. In return for the acknowledgment, UNESCO required Indonesians to preserve the tradition.[3]
Etymology
The term wayang (ꦮꦪꦁ)[1] is the Javanese word in the ngoko register for "shadow"[4] or "imagination". Its equivalent in Indonesian is bayang. In modern daily Javanese and Indonesian vocabulary, wayang can refer to the puppet itself or the whole puppet theatre performance.[1] Kulit (Javanese: ꦏꦸꦭꦶꦠ꧀) means "skin" or "leather",[5] the material from which the figures are carved.
History

Wayang is the traditional puppet theatre of Indonesia.[6][7][8] It is an ancient form of storytelling known for its elaborate puppets and complex musical styles.[9] The earliest evidence of wayang comes from medieval-era texts and archeological sites dating from the late 1st millennium CE. There are four theories concerning where wayang originated (indigenous to Java; Java–India; India; and China), but of these, two are more favored: Java and India.
Regardless of its origins, states Brandon, wayang developed and matured into a Javanese phenomenon. There is no true contemporary puppet shadow artwork in either China or India with the sophistication, depth, and creativity expressed in wayang in Java, Indonesia.[10]
Indigenous origin in Java
According to academic James R. Brandon, the puppets of wayang are native to Java. He states wayang is closely related to Javanese social culture and religious life, and presents parallel developments from ancient Indonesian culture, such as gamelan, the monetary system, metric forms, batik, astronomy, wet rice field agriculture, and government administration. He asserts that wayang was not derived from any other type of shadow puppetry of mainland Asia, but was an indigenous creation of the Javanese. Indian puppets differ from wayang, and all wayang technical terms are Javanese, not Sanskrit. Similarly, some of the other technical terms used in the wayang kulit found in Java and Bali are based on local languages, even when the play overlaps with Buddhist or Hindu mythologies.[10]
G. A. J. Hazeu[who?] also says that wayang came from Java. The puppet structure, puppeteering techniques, storytelling voices, language, and expressions are all composed according to old traditions. The technical design, the style, and the composition of the Javanese play grew from the worship of ancestors.[citation needed]
Kats[who?] argues that the technical terms come from Java and that wayang was born without the help of India. Before the 9th century, it belonged to the Javanese. It was closely related to religious practices, such as incense and night / wandering spirits. Panakawan uses a Javanese name, different from the Indian heroes.[citation needed]
Kruyt[who?] argues that wayang originated from shamanism, and makes comparisons with ancient archipelago ceremonial forms which aim to contact the spirit world by presenting religious poetry praising the greatness of the soul.[citation needed]
The movement of the Javanese across Maritime Southeast Asia right up to the 20th century has also spread art form beyond its insular origin; this may come directly performed in areas where many Javanese settled such as western Selangor in Peninsular Malaysia,[11] or indirectly integrating local elements, such as the Wayang Kulit Kelantan performed in Kelantan north of the Peninsular where Kelantanese dalang was said to have learned from original masters themselves in Java.[12]

Origin in India
Hinduism and Buddhism arrived on the Indonesian islands in the early centuries of the 1st millennium, and along with theology, the peoples of Indonesia and the Indian subcontinent exchanged culture, architecture, and traded goods.[10][13][14] Puppet arts and dramatic plays have been documented in ancient Indian texts, dating to the last centuries of the 1st millennium BCE and the early centuries of the Common Era.[15] Further, the eastern coastal region of India (Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu), which most interacted with Indonesian islands, has had traditions of intricate, leather-based puppet arts called tholu bommalata, tholpavakoothu, and rabana chhaya, which share many elements with wayang.[7][16]
Some characters such as the Vidusaka in Sanskrit drama and Semar in wayang are very similar. Indian mythologies and characters from the Hindu epics feature in many major wayang plays, which suggests possible Indian origins, or at least an influence in the pre-Islamic period of Indonesian history.[10] Jivan Pani states that wayang developed from two art forms from Odisha in eastern India: the Ravana Chhaya puppet theatre and the Chhau dance.[17]
Records
The oldest known record concerning wayang is from the 9th century. Old Javanese (Kawi) inscriptions called Jaha Inscriptions, dating from around 840 CE and issued by Maharaja Sri Lokapala from the Mataram Kingdom in Central Java, mention three sorts of performers: atapukan (lit. 'mask dance show'), aringgit (lit. 'wayang puppet show'), and abanwal / abanol (lit. 'joke art'). Ringgit is described in an 11th-century Javanese poem as a leather shadow figure.
In 903 CE, the Mantyasih inscription (Balitung charter) was created by King Balitung of the Sanjaya dynasty of the Ancient Mataram Kingdom. They state, "Si Galigi Mawayang Buat Hyang Macarita Bimma Ya Kumara", which means 'Galigi held a puppet show for gods by taking the story of Bima Kumara'.[18] It seems certain features of traditional puppet theatre have survived from that time. Galigi was an itinerant performer who was requested to perform for a special royal occasion. At that event, he performed a story about the hero Bhima from the Mahabharata.

Mpu Kanwa, the poet of Airlangga's court of the Kahuripan kingdom, writes in 1035 CE in his kakawin (narrative poem) Arjunawiwaha, "santoṣâhĕlĕtan kĕlir sira sakêng sang hyang Jagatkāraṇa", which means, "He is steadfast and just a wayang screen away from the 'Mover of the World'." As kĕlir is the Javanese word for the wayang screen, the verse eloquently compares actual life to a wayang performance where the almighty Jagatkāraṇa (the mover of the world) as the ultimate dalang (puppet master) is just a thin screen away from mortals. This reference to wayang as shadow plays suggested that wayang performance was already familiar in Airlangga's court and wayang tradition had been established in Java, perhaps even earlier. An inscription from this period also mentions some occupations such as awayang and aringgit.[19]
Wayang kulit is a unique form of theatre employing light and shadow. The puppets are crafted from buffalo hide and mounted on bamboo sticks. When held up behind a piece of white cloth, with an electric bulb or an oil lamp as the light source, shadows are cast on the screen. The plays are typically based on romantic tales and religious legends, especially adaptations of the classic Indian epics, the Mahabharata, and the Ramayana. Some of the plays are also based on local stories like Panji tales.[20]
Wayang puppet figures

The wayang comes in sizes from 25 cm to 75 cm. The important characters are usually represented by several puppets each. The wayang is usually made out of water buffalo and goat hide and mounted onto bamboo sticks. However, the best wayang is typically made from young female buffalo parchment, cured for up to ten years. The carving and punching of the rawhide, which is most responsible for the character's image and the shadows that are cast, are guided by this sketch. A mallet is used to tap special tools, called tatah, to punch the holes through the rawhide. Making the wayang sticks from the horn is a complicated process of sawing, heating, hand-molding, and sanding until the desired effect is achieved. When the materials are ready, the artist attaches the handle by precisely molding the ends of the horn around the individual wayang figure and securing it with thread. A large character may take months to produce.
There are important differences between the three islands where wayang kulit is played (due to local religious canon). [21] [22]
In Java (where Islam is predominant), the puppets (named ringgit) are elongated, the play lasts all night and the lamp ({{jv}} (talk)) is, nowadays, almost always electric. A full gamelan with (pe)sinden is typically used.[23]
- Some Javanese wayang kulit Figures
In Bali (where Hinduism is predominant), the puppets look more realistic, the play lasts a few hours, and, at night, the lamp uses coconut oil. Music is mainly by the four-gender wayang, with drums only if the story is from the Ramayana. There are no sinden. The dalang does the singing. Balinese dalangs are often also priests (amangku dalang). As such, they may also perform during daylight, for religious purposes (exorcism), without a lamp and screen (wayang sakral, or "lemah")[24]
- Some Balinese wayang Kulit Figures
In Lombok (where Islam is predominant and Bali's influence is strong), vernacular wayang kulit is known as wayang sasak, with puppets similar to Javanese ringgits, a small orchestra with no sinden, but flutes, metallophones and drums. The repertoire is unique to the island and is based on the Muslim Menak Cycle (the adventures of Amir Hamzah).
- Some Sasak wayang Kulit Figures
In the Cocos (Keeling) Islands, members of Javanese diaspora communities continued the art form from the nineteenth century, until the death of Nek Ichang, the island's dalang (puppeteer) in 1949.[25][26] Examples of the wayang kulit are in the collection of Pulu Cocos Museum and were featured on a set of Australian $1 and $2 stamps in 2018.[26]
Performance

The stage of a wayang performance includes several components. A stretched linen canvas (Javanese: ꦏꦼꦭꦶꦂ, romanized: kelir)[27] acts as a canvas, dividing the dalang (puppeteer) and the spectator. A coconut oil lamp (Javanese: ꦧ꧀ꦭꦺꦚ꧀ꦕꦺꦴꦁ, romanized: bléncong;[28] Balinese: damar) – which in modern times is usually replaced with electric light – casts shadows onto the screen. A banana trunk (Javanese: ꦒꦼꦢꦼꦧꦺꦴꦒ꧀, romanized: gedebog;[29] Balinese: gedebong) lies on the ground between the screen and the dalang, where the figures are stuck to hold them in place. To the right of the dalang sits the puppet chest, which the dalang uses as a drum during the performance, hitting it with a wooden mallet. In a Javanese wayang kulit performance, the dalang may use a cymbal-like percussion instrument at his feet to cue the musicians. The musicians sit behind the dalang in a gamelan orchestra setting. The gamelan orchestra is an integral part of the Javanese wayang kulit performance. The performance is accompanied by female singers (pasindhèn) and male singers (wirasuara).

The setting of the banana trunk on the ground and the canvas in the air symbolizes the earth and the sky; the whole composition symbolizes the entire cosmos. When the dalang animates the puppet figures and moves them across the screen, divine forces are understood to be acting in the hands with which he directs the happening. The lamp is a symbol of the sun as well as the eye of the dalang.[30]
A traditional wayang kulit performance begins after dark. The first of the three phases, in which the characters are introduced and the conflict is launched, lasts until midnight. The battles and intrigues of the second phase last about three hours. The third phase of reconciliation and friendship is finished at dawn.[31]
Wayang shadow plays are usually tales from the two major Hindu epics, the Ramayana and Mahabharata. The puppet master contextualizes stories from the plays, making them relevant to current community, national, or global issues. Gamelan players respond to the direction of the dalang.
- Gallery of wayang kulit
- The puppet figures of a Javanese wayang kulit
- Painting the wayang kulit in a Yogyakarta factory
- Carving the leather in a Yogyakarta factory
- In the specialized village of Sukawati, Bali
- All stages of the making of a wayang kulit
- Central Javanese wayang kulit
- Balinese wayang kulit
- Wayang kulit performance
See also
References
- ^ a b c Robson & Wibisono (2002:803–804)
- ^ Ness, Edward C. Van; Prawirohardjo, Shita (1980). Javanese Wayang Kulit: An Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195804140.
- ^ ""Wayang puppet theatre", Inscribed in 2008 (3.COM) on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (originally proclaimed in 2003)". UNESCO. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- ^ Mair, Victor H. Painting and Performance: Picture Recitation and Its Indian Genesis. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press, 1988. p. 58.
- ^ Robson & Wibisono (2002:409)
- ^ James R. Brandon (2009). Theatre in Southeast Asia. Harvard University Press. pp. 143–145, 352–353. ISBN 978-0-674-02874-6.
- ^ a b "Wayang: Indonesian Theatre". Encyclopaedia Britannica. 2012.
- ^ Don Rubin; Chua Soo Pong; Ravi Chaturvedi; et al. (2001). The World Encyclopedia of Contemporary Theatre: Asia/Pacific. Taylor & Francis. pp. 184–186. ISBN 978-0-415-26087-9.
- ^ ""Wayang puppet theatre", Inscribed in 2008 (3.COM) on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity (originally proclaimed in 2003)". UNESCO. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- ^ a b c d James R. Brandon (2009). Theatre in Southeast Asia. Harvard University Press. pp. 42–44, 65, 92–94, 278. ISBN 978-0-674-02874-6.
- ^ Linda Sunarti; Teuku Reza Fadeli (2018). "Tracing Javanese Identity And Culture In Malaysia Asimilation And Adaptation Of Javanese In Malaysia". Paramita: Historical Studies Journal. 28 (1): 52, 54–5. doi:10.15294/paramita.v28i1.10923. ISSN 0854-0039.
- ^ Maho A. Ishiguro (Spring 2018). "Malay Theatre: Intangible Cultural Heritage and Islam: Wayang Kulit Kelantan and Mak Yong by Kathy Foley and Patricia Hardwick, and: Tradition in Transition: Intangible Heritage in South and Southeast Asia (review)". Asian Theatre Journal. 35 (1): 216–21.
- ^ Miyao, J. (1977). "P. L. Amin Sweeney and Akira Goto (ed.) An International Seminar on the Shadow Plays of Asia". Southeast Asia: History and Culture. 1977 (7). Japan Society for Southeast Asian Studies: 142–146. doi:10.5512/sea.1977.142.
- ^ Yves Bonnefoy (1993). Asian Mythologies. University of Chicago Press. p. 162. ISBN 978-0-226-06456-7.
- ^ Kathy Foley (2016). Siyuan Liu (ed.). Routledge Handbook of Asian Theatre. Routledge. pp. 181–182. ISBN 978-1-317-27886-3.
- ^ Kathy Foley (2016). Siyuan Liu (ed.). Routledge Handbook of Asian Theatre. Routledge. pp. 182–184. ISBN 978-1-317-27886-3.
- ^ Varadpande, Manohar Laxman (1987). History of Indian Theatre, Volume 1. New Delhi: Abhinav Publications. p. 75. ISBN 9788170172215.
- ^ "Keragaman Wayang Indonesia". indonesia.go.id. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ Drs. R. Soekmono (1973). Pengantar Sejarah Kebudayaan Indonesia 2, 2nd ed. 5th reprint edition in 1988. Yogyakarta: Penerbit Kanisius. p. 56.
- ^ "Cerita Panji, Pusaka Budaya Nusantara yang tidak Habis Digali". www.mediaindonesia.com. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Claire Holt. Art in Indonesia, Continuities and Changes. Cornell University Press.
- ^ Guenter Spitzing. Das Indonesische Schattenspiel. Dumont Taschenbuecher.
- ^ James R. Brandon. On Thrones of Gold, Javanese Shadow Plays. Harvard University Press.
- ^ Religion in Bali, by C. Hooykaas, University of Leiden
- ^ Ricasa, Lourdes Odette Aquitania (2020-12-21). Love Echoes...Share and Inspire. AuthorHouse. ISBN 978-1-6655-0940-4.
- ^ a b "Cocos (Keeling) Islands Shadow Puppets". Australia Post Collectables. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- ^ Robson & Wibisono (2002:350)
- ^ Robson & Wibisono (2002:102)
- ^ Robson & Wibisono (2002:236)
- ^ Foley, Kathy (1990). "My Bodies: The Performer in West Java". TDR. 34 (2): 62–80. doi:10.2307/1146027. JSTOR 1146027. here p. 75f.
- ^ Korsovitis, Constantine (2001). "Ways of the Wayang". India International Centre Quarterly. 28 (2): 59–68. JSTOR 23005511. here p. 60.
Sources
- Robson, Stuart; Wibisono, Singgih (2002). Javanese English Dictionary. Periplus Editions. ISBN 0-7946-0000-X.
External links
- "Bali & Beyond Educational Resources". www.balibeyond.com. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- "Wayang Kulit - a shadow play". minyos.its.rmit.edu.au. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- Shadow Music of Java, CD with thirteen-page booklet. Rounder CD 5060.
- Ghani, Dahlan Abdul; Ishak, Sidin Bin Ahmad (2012). "Relationship Between The Art of Wayang Kulit and Disney's Twelve Principles of Animation" (PDF). Revista de Cercetare şi Intervenţie Socială (37): 162–179.
- Yousof, Ghulam-Sarwar; Khor, Kheng-Kia (2017). "Wayang Kulit Kelantan: A Study of Characterization and Puppets". Asian Theatre Journal. 34 (1): 1–25. doi:10.1353/atj.2017.0002. S2CID 164974717.
- https://www.storiesbysoumya.com/wayang-kulit-indonesian-shadow-puppets/