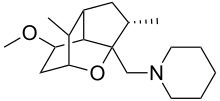
Valperinol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H27NO4 |
| Molar mass | 297.395 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Valperinol (INN; GA 30-905) is a drug which acts as a calcium channel blocker.[1][2] It was patented as a possible sedative, antiepileptic, and/or antiparkinsonian agent, but was never marketed.[3]
References
- ^ Thies PW, Asai A, Bán I, David S, Finner E (1984). "[The synthesis of valperinol and various 3-aminomethyl derivatives of 2,9-dioxatricyclo[4,3,1,0(3,7)]decane from didrovaltrate]". Arzneimittel-Forschung (in German). 34 (11): 1460–3. PMID 6543120.
- ^ Dose M (1984). "[Calcium antagonist properties of valperinol]". Arzneimittel-Forschung (in German). 34 (11): 1464–6. PMID 6098282.
- ^ Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents Volume 2. CRC Press. 1996-11-21. p. 2104. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
