United States Department of Justice
 Seal of the U.S. Department of Justice | |
 Flag of the U.S. Department of Justice | |
 The Robert F. Kennedy Building is the headquarters of the U.S. Department of Justice. (2024) | |
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | July 1, 1870 |
| Type | Executive department |
| Jurisdiction | U.S. federal government |
| Headquarters | Robert F. Kennedy Department of Justice Building 950 Pennsylvania Avenue NW Washington, D.C., United States 38°53′36″N 77°1′30″W / 38.89333°N 77.02500°W |
| Motto | "Qui Pro Domina Justitia Sequitur" (Latin: "Who prosecutes on behalf of justice (or the Lady Justice)")[1][2] |
| Employees | 113,114 (2019)[3] |
| Annual budget | $37.52 billion (FY 2024) |
| Agency executives |
|
| Website | justice.gov |
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of federal laws and the administration of justice. It is equivalent to the justice or interior ministries of other countries. The department is headed by the U.S. attorney general, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. Merrick Garland has served as attorney general since March 2021.[5]
The Justice Department contains most of the United States' federal law enforcement agencies, including the Federal Bureau of Investigation, the U.S. Marshals Service, the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, the Drug Enforcement Administration, and the Federal Bureau of Prisons. The department also has eight divisions of lawyers who represent the federal government in litigation: the Criminal, Civil, Antitrust, Tax, Civil Rights, Environment and Natural Resources, National Security, and Justice Management Divisions. The DOJ includes the U.S. Attorneys' Offices for each of the 94 U.S. federal judicial districts.
The U.S. Congress created the Justice Department in 1870, during the presidency of Ulysses S. Grant. Its functions originally date to 1789, when Congress created the office of the Attorney General.
History
The office of the attorney general was established by the Judiciary Act of 1789 as a part-time job for one person, but grew with the bureaucracy. At one time, the attorney general gave legal advice to the U.S. Congress, as well as the president; however, in 1819, the attorney general began advising Congress alone to ensure a manageable workload.[6] Until 1853, the salary of the attorney general was set by statute at less than the amount paid to other Cabinet members. Early attorneys general supplemented their salaries by running private law practices, often arguing cases before the courts as attorneys for paying litigants.[2] The lightness of the office is exemplified by Edward Bates (1793–1869), attorney general under President Abraham Lincoln (1861–1864). Bates had only a small operation, with a staff of just six. Their main function was to generate legal opinions at the request of Lincoln and cabinet members, and handle occasional cases before the Supreme Court. Lincoln's cabinet was full of experienced lawyers who seldom felt the need to ask for his opinions. In addition, Bates had no authority over the US Attorneys around the country. The federal court system was handled by the Department of the Interior, and the Department of the Treasury handled claims. Most of the opinions turned out by Bates's office were of minor importance. Lincoln gave him no special assignments and did not seek his advice on Supreme Court appointments. Bates did have an opportunity to comment on general policy as a cabinet member with a strong political base, but he seldom spoke up.[7]
Following unsuccessful efforts in 1830 and 1846 to make attorney general a full-time job,[2] in 1867, the U.S. House Committee on the Judiciary, led by Congressman William Lawrence, conducted an inquiry into the creation of a "law department" headed by the attorney general and also composed of the various department solicitors and United States attorneys. On February 19, 1868, Lawrence introduced a bill in Congress to create the Department of Justice. President Ulysses S. Grant signed the bill into law on June 22, 1870.[8]
Grant appointed Amos T. Akerman as attorney general and Benjamin H. Bristow as America's first solicitor general the same week that Congress created the Department of Justice. The Department's immediate function was to preserve civil rights. It set about fighting against domestic terrorist groups who had been using both violence and litigation to oppose the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution.[9]

Both Akerman and Bristow used the Department of Justice to vigorously prosecute Ku Klux Klan members in the early 1870s. In the first few years of Grant's first term in office, there were 1000 indictments against Klan members, with over 550 convictions from the Department of Justice. By 1871, there were 3000 indictments and 600 convictions, with most only serving brief sentences, while the ringleaders were imprisoned for up to five years in the federal penitentiary in Albany, New York. The result was a dramatic decrease in violence in the South. Akerman gave credit to Grant and told a friend that no one was "better" or "stronger" than Grant when it came to prosecuting terrorists.[10] George H. Williams, who succeeded Akerman in December 1871, continued to prosecute the Klan throughout 1872 until the spring of 1873, during Grant's second term in office. Williams then placed a moratorium on Klan prosecutions partially because the Justice Department, inundated by cases involving the Klan, did not have the manpower to continue prosecutions.[11]
The "Act to Establish the Department of Justice" drastically increased the attorney general's responsibilities to include the supervision of all United States attorneys, formerly under the Department of the Interior, the prosecution of all federal crimes, and the representation of the United States in all court actions, barring the use of private attorneys by the federal government.[12] The law also created the office of Solicitor General to supervise and conduct government litigation in the Supreme Court of the United States.[13]
With the passage of the Interstate Commerce Act in 1887, the federal government took on some law enforcement responsibilities, and the Department of Justice was tasked with performing these.[14]
In 1884, control of federal prisons was transferred to the new department, from the Department of the Interior. New facilities were built, including the penitentiary at Leavenworth in 1895, and a facility for women located in West Virginia, at Alderson was established in 1924.[15]
In 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt issued an executive order which gave the Department of Justice responsibility for the "functions of prosecuting in the courts of the United States claims and demands by, and offsenses [sic] against, the Government of the United States, and of defending claims and demands against the Government, and of supervising the work of United States attorneys, marshals, and clerks in connection therewith, now exercised by any agency or officer..."[16]
Headquarters
The U.S. Department of Justice building was completed in 1935 from a design by Milton Bennett Medary. Upon Medary's death in 1929, the other partners of his Philadelphia firm Zantzinger, Borie and Medary took over the project. On a lot bordered by Constitution and Pennsylvania Avenues and Ninth and Tenth Streets, Northwest, it holds over 1,000,000 square feet (93,000 m2) of space.
Various efforts, none entirely successful, have been made to determine the original intended meaning of the Latin motto appearing on the Department of Justice seal, Qui Pro Domina Justitia Sequitur (literally "Who For Lady Justice Strives"). It is not even known exactly when the original version of the DOJ seal itself was adopted, or when the motto first appeared on the seal. The most authoritative opinion of the DOJ suggests that the motto refers to the Attorney General (and thus, by extension, to the Department of Justice) "who prosecutes on behalf of justice (or the Lady Justice)".[2]
The motto's conception of the prosecutor (or government attorney) as being the servant of justice itself finds concrete expression in a similarly-ordered English-language inscription ("THE UNITED STATES WINS ITS POINT WHENEVER JUSTICE IS DONE ITS CITIZENS IN THE COURTS") in the above-door paneling in the ceremonial rotunda anteroom just outside the Attorney General's office in the Department of Justice Main Building in Washington, D.C.[2] The building was renamed in honor of former Attorney General Robert F. Kennedy in 2001. It is sometimes referred to as "Main Justice".[17]
Organization
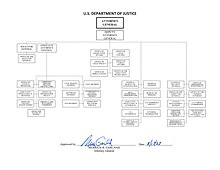
Leadership offices
- Office of the Attorney General
- Office of the Deputy Attorney General
- Office of the Associate Attorney General
- Office of the United States Principal Deputy Associate Attorney General
- Office of the Solicitor General of the United States
Divisions
| Division | Year established (as formal division) |
|---|---|
| Antitrust Division | 1919[18] |
| Civil Division[a] | 1933[19] |
| Civil Rights Division | 1957[21] |
| Criminal Division | 1919[22] |
| Environment and Natural Resources Division (ENRD)[b] | 1909[23] |
| Justice Management Division (JMD)[c] | 1945[24] |
| National Security Division (NSD) | 2006[25] |
| Tax Division | 1933[26] |
The Justice Department also had a War Division during World War II. It was created in 1942 and disestablished in 1945.[27]
Law enforcement agencies
Several federal law enforcement agencies are administered by the Department of Justice:
- United States Marshals Service (USMS) – The office of U.S. Marshal was established by the Judiciary Act of 1789. The U.S. Marshals Service was established as an agency in 1969, and it was elevated to full bureau status under the Justice Department in 1974.[28][29]
- Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) – On July 26, 1908, a small investigative force was created within the Justice Department under Attorney General Charles Bonaparte. The following year, this force was officially named the Bureau of Investigation by Attorney General George W. Wickersham. In 1935, the bureau adopted its current name.[30]
- Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) – the Three Prisons Act of 1891 created the federal prison system. Congress created the Federal Bureau of Prisons in 1930 by Pub. L. No. 71–218, 46 Stat. 325, signed into law by President Hoover on May 14, 1930.[31][32][33]
- National Institute of Corrections (NIC) – Founded in 1974, the National Institute of Corrections is organized under the Federal Bureau of Prisons and has a legislatively mandated mission to assist state and local correctional institutions, and to manage the American Federal Prison System by keeping records of inmates.
- Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) – Except for a brief period during Prohibition, ATF's predecessor bureaus were part of the Department of the Treasury for more than two hundred years.[34] ATF was first established by Department of Treasury Order No. 221, effective July 1, 1972; this order "transferred the functions, powers, and duties arising under laws relating to alcohol, tobacco, firearms, and explosives from the Internal Revenue Service to ATF.[35] In 2003, under the terms of the Homeland Security Act, ATF was split into two agencies – the new Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) was transferred to the Department of Justice, while the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) was retained by the Department of the Treasury.[34]
- Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) – Created in 1973 as part of the war on drugs, the DEA was formed from various previously existing law enforcement agencies that were parts of either the Department of Justice, Department of the Treasury or the Food and Drug Administration. The DEA enforces the Controlled Substances Act and also interdicts foreign drug trafficking.
- Office of the Inspector General (OIG) – The Office of Inspector General performs basic internal auditing functions, and has the power to make arrests and prosecute members of the Department of Justice who are found to be in violation of laws regulating conduct of government officials.
Offices
- Executive Office for Immigration Review (EOIR)
- Executive Office for U.S. Attorneys (EOUSA)
- Executive Office of the United States Trustee (EOUST)
- Office of Attorney Recruitment and Management (OARM)
- Office of the Chief Information Officer
- In May 2014, the department appointed Joseph Klimavicz as CIO.[36] Klimavicz succeeds Kevin Deeley, who served as acting CIO since November 2013 when the previous office holder, Luke McCormack, left to take the CIO post at the Department of Homeland Security.[36]
- Office of Dispute Resolution
- Office of the Federal Detention Trustee (OFDT)
- Office of the Executive Secretariat
- Office of Immigration Litigation
- Office of Information Policy
- Office of Intelligence Policy and Review (OIPR)
- Office of Justice Programs (OJP)
- Bureau of Justice Assistance (BJA)
- Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS)
- National Institute of Justice (NIJ)
- Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP)
- Office for Victims of Crime (OVC)
- Sex Offender Sentencing, Monitoring, Apprehending, Registering, and Tracking Office (SMART)
- Office of the Police Corps and Law Enforcement Education
- Office of Legal Counsel (OLC)
- Office of Legal Policy (OLP)
- Office of Legislative Affairs
- Office of the Pardon Attorney
- Office of Privacy and Civil Liberties (OPCL)
- Office of Professional Responsibility (OPR)
- Office of Public Affairs
- Office on Sexual Violence and Crimes against Children
- Office of Tribal Justice
- Office on Violence Against Women (OVW)
- Professional Responsibility Advisory Office (PRAO)
- United States Attorneys Offices
- United States Trustees Offices
- Office of Community Oriented Policing Services (COPS)
- Community Relations Service (CRS)
Other offices and programs
- Foreign Claims Settlement Commission of the United States
- INTERPOL, U.S. National Central Bureau
- National Drug Intelligence Center
- Obscenity Prosecution Task Force
- United States Parole Commission
In March 2003, the United States Immigration and Naturalization Service was abolished and its functions transferred to the United States Department of Homeland Security. The Executive Office for Immigration Review and the Board of Immigration Appeals, which review decisions made by government officials under Immigration and Nationality law, remain under jurisdiction of the Department of Justice. Similarly the Office of Domestic Preparedness left the Justice Department for the Department of Homeland Security, but only for executive purposes. The Office of Domestic Preparedness is still centralized within the Department of Justice, since its personnel are still officially employed within the Department of Justice.
In 2003, the Department of Justice created LifeAndLiberty.gov, a website that supported the USA PATRIOT Act. It was criticized by government watchdog groups for its alleged violation of U.S. Code Title 18 Section 1913, which forbids money appropriated by Congress to be used to lobby in favor of any law, actual or proposed.[37] The website has since been taken offline.
On October 5, 2021, U.S. Deputy Attorney General Lisa Monaco has announced the formation of a "Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team" during the Aspen Cyber Summit.[38]
Finances and budget
| Program | FY 2022 (millions) | FY 2023 (millions) | FY 2024 proposed (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Law Enforcement | $19,286 | $20,543 | $21,292 |
| Litigation | 1,552 | 1,752 | 2,091 |
| Admin/Technology/Other | 880 | 652 | 2,009 |
| Prisons and Detention | 10,223 | 10,802 | 9,988 |
| State and Local Grants | $3,630 | $4,195 | $4,912 |
| ATR and USTP Fees | (551) | (459) | (556) |
| Total, Discretionary BA with Fees | $35,020 | $37,485 | $39,736 |
See also
- Capital punishment in the United States
- Incarceration in the United States
- Justice
- Litigation
- OneDOJ
- Punishment
Footnotes
- ^ The Civil Division was originally called the Claims Division; it adopted its current name on February 13, 1953.[19][20]
- ^ The ENRD was originally called the Land and Natural Resources Division; it adopted its current name in 1990.[23]
- ^ The JMD was originally called the Administrative Division; it adopted its current name in 1985.[24]
References
- ^ Revision of Original Letter Dated 14 February 1992 Archived September 19, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, United States Department of Justice.
- ^ a b c d e Madan, Rafael (Fall 2008). "The Sign and Seal of Justice" (PDF). Ave Maria Law Review. 7: 123, 191–192. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2014.
- ^ "2020 Budget Summary". The United States Department of Justice. Archived from the original on April 13, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2019.
- ^ "Meet the Acting Solicitor General". justice.gov. January 20, 2021. Archived from the original on January 21, 2021. Retrieved January 21, 2021.
- ^ @TheJusticeDept (March 11, 2021). "Judge Merrick Garland takes his oath of office as the 86th Attorney General of the United States as he is sworn in by Assistant Attorney General for Administration Lee Lofthus" (Tweet). Retrieved March 11, 2021– via Twitter.
- ^ "United States Department of Justice: About DOJ". September 16, 2014. Archived from the original on July 12, 2014. Retrieved November 22, 2020.
- ^ John P. Frank, "Edward Bates, Lincoln's Attorney General", American Journal of Legal History 10#1 (1966) pp 34-50.
- ^ "Public Acts of the Forty First Congress". Archived from the original on December 25, 2016. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- ^ Chernow, Ron (2017). Grant. Penguin Press. p. 700.
- ^ Smith 2001, pp. 542–547.
- ^ Williams (1996), The Great South Carolina Ku Klux Klan Trials, 1871–1872, p. 123
- ^ "Act to Establish the Department of Justice". Memory.loc.gov. Archived from the original on December 25, 2016. Retrieved January 27, 2012.
- ^ "About DOJ – DOJ – Department of Justice". September 16, 2014. Archived from the original on November 22, 2020. Retrieved November 22, 2020.
- ^ Langeluttig, Albert (1927). The Department of Justice of the United States. Johns Hopkins Press. pp. 9–14.
- ^ Langeluttig, Albert (1927). The Department of Justice of the United States. Johns Hopkins Press. pp. 14–15.
- ^ Executive Order 6166, Sec. 5 (June 12, 1933), at [1] Archived October 18, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "PRESIDENTIAL MEMORANDUM DIRECTS DESIGNATION OF MAIN JUSTICE BUILDING AS THE "ROBERT F. KENNEDY JUSTICE BUILDING"". U.S. Department of Justice. Archived from the original on July 13, 2015. Retrieved December 8, 2014.
- ^ History of the Antitrust Division Archived July 13, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, United States Department of Justice.
- ^ a b Gregory Sisk & Michael F. Noone, Litigation with the Federal Government (4th ed.) (American Law Institute, 2006), pp. 10–11.
- ^ Former Assistant Attorneys General: Civil Division Archived January 31, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Department of Justice.
- ^ Kevin Alonso & R. Bruce Anderson, "Civil Rights Legislation and Policy" in Postwar America: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural, and Economic History (2006, ed. James Ciment), p. 233.
- ^ Organization, Mission and Functions Manual: Criminal Division Archived December 3, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, United States Department of Justice.
- ^ a b Arnold W. Reitze, Air Pollution Control Law: Compliance and Enforcement (Environmental Law Institute, 2001), p. 571.
- ^ a b Cornell W. Clayton, The Politics of Justice: The Attorney General and the Making of Legal Policy (M.E. Sharpe, Inc., 1992), p. 34.
- ^ National Security Cultures: Patterns of Global Governance (Routledge, 2010; eds. Emil J. Kirchner & James Sperling), p. 195.
- ^ Nancy Staudt, The Judicial Power of the Purse: How Courts Fund National Defense in Times of Crisis (University of Chicago Press, 2011), p. 34.
- ^ Civilian Agency Records: Department of Justice Records Archived October 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, National Archived and Records Administration.
- ^ Larry K. Gaines & Victor E. Kappeler, Policing in America (8th ed. 2015), pp. 38–39.
- ^ United States Marshals Service Then ... and Now (Office of the Director, United States Marshals Service, U.S. Department of Justice, 1978).
- ^ The FBI: A Comprehensive Reference Guide (Oryz Press, 1999, ed. Athan G. Theoharis), p. 102.
- ^ Mitchel P. Roth, Prisons and Prison Systems: A Global Encyclopedia (Greenwood, 2006), pp. 278–79.
- ^ Dean J. Champion, Sentencing: A Reference Handbook (ABC-CLIO, Inc.: 2008), pp. 22–23.
- ^ James O. Windell, Looking Back in Crime: What Happened on This Date in Criminal Justice History? (CRC Press, 2015), p. 91.
- ^ a b Transfer of ATF to U.S. Department of Justice[permanent dead link], Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives.
- ^ Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives Bureau Archived April 7, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Federal Register.
- ^ a b Malykhina, Elena (April 25, 2014). "Justice Department Names New CIO". Government. InformationWeek. Archived from the original on April 26, 2014. Retrieved April 26, 2014.
- ^ Dotgovwatch.com Archived November 9, 2020, at the Wayback Machine, October 18, 2007
- ^ "DOJ Forms Cryptocurrency Enforcement Team - October 6, 2021". Daily News Brief. October 6, 2021. Archived from the original on August 9, 2022. Retrieved October 6, 2021.
- ^ "U.S. DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE FY 2024 BUDGET SUMMARY" (PDF). justice.gov. 2023.
External links
- Official website

- United States Department of Justice at the Wayback Machine (archive index)
- Department of Justice on USAspending.gov
- USDOJ in the Federal Register

