Turkic languages
| Turkic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Eurasia |
| Ethnicity | Turkic peoples |
Native speakers | c. 200 million (2020)[1] |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Turkic |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-5 | trk |
| Glottolog | turk1311 |
 The distribution of the Turkic languages | |
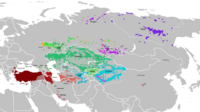
The Turkic languages are a language family of more than 35[2] documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and West Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken,[3] from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium.[4] They are characterized as a dialect continuum.[5]
Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people.[1] The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers, followed by Uzbek.[4]
Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family.[4] There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon moderate exposure, among the various Oghuz languages, which include Turkish, Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Qashqai, Chaharmahali Turkic, Gagauz, and Balkan Gagauz Turkish, as well as Oghuz-influenced Crimean Tatar.[6] Other Turkic languages demonstrate varying amounts of mutual intelligibility within their subgroups as well. Although methods of classification vary, the Turkic languages are usually considered to be divided into two branches: Oghur, of which the only surviving member is Chuvash, and Common Turkic, which includes all other Turkic languages.
Turkic languages show many similarities with the Mongolic, Tungusic, Koreanic, and Japonic languages. These similarities have led some linguists (including Talât Tekin) to propose an Altaic language family, though this proposal is widely rejected by historical linguists.[7][8] Similarities with the Uralic languages even caused these families to be regarded as one for a long time under the Ural-Altaic hypothesis.[9][10][11] However, there has not been sufficient evidence to conclude the existence of either of these macrofamilies. The shared characteristics between the languages are attributed presently to extensive prehistoric language contact.
Characteristics

Turkic languages are null-subject languages, have vowel harmony (with the notable exception of Uzbek due to strong Persian-Tajik influence), converbs, extensive agglutination by means of suffixes and postpositions, and lack of grammatical articles, noun classes, and grammatical gender. Subject–object–verb word order is universal within the family. In terms of the level of vowel harmony in the Turkic language family, Tuvan is characterized as almost fully harmonic whereas Uzbek is the least harmonic or not harmonic at all. Taking into account the documented historico-linguistic development of Turkic languages overall, both inscriptional and textual, the family provides over one millennium of documented stages as well as scenarios in the linguistic evolution of vowel harmony which, in turn, demonstrates harmony evolution along a confidently definable trajectory[12] Though vowel harmony is a common characteristic of major language families spoken in Inner Eurasia (Mongolic, Tungusic, Uralic and Turkic), the type of harmony found in them differs from each other, specifically, Uralic and Turkic have a shared type of vowel harmony (called palatal vowel harmony) whereas Mongolic and Tungusic represent a different type.
History
Pre-history
The homeland of the Turkic peoples and their language is suggested to be somewhere between the Transcaspian steppe and Northeastern Asia (Manchuria),[13] with genetic evidence pointing to the region near South Siberia and Mongolia as the "Inner Asian Homeland" of the Turkic ethnicity.[14] Similarly several linguists, including Juha Janhunen, Roger Blench and Matthew Spriggs, suggest that modern-day Mongolia is the homeland of the early Turkic language.[15] Relying on Proto-Turkic lexical items about the climate, topography, flora, fauna, people's modes of subsistence, Turkologist Peter Benjamin Golden locates the Proto-Turkic Urheimat in the southern, taiga-steppe zone of the Sayan-Altay region.[16]
Extensive contact took place between Proto-Turks and Proto-Mongols approximately during the first millennium BC; the shared cultural tradition between the two Eurasian nomadic groups is called the "Turco-Mongol" tradition. The two groups shared a similar religion system, Tengrism, and there exists a multitude of evident loanwords between Turkic languages and Mongolic languages. Although the loans were bidirectional, today Turkic loanwords constitute the largest foreign component in Mongolian vocabulary.[17]
Italian historian and philologist Igor de Rachewiltz noted a significant distinction of the Chuvash language from other Turkic languages. According to him, the Chuvash language does not share certain common characteristics with Turkic languages to such a degree that some scholars consider it an independent Chuvash family similar to Uralic and Turkic languages. Turkic classification of Chuvash was seen as a compromise solution for the classification purposes.[18]
Some lexical and extensive typological similarities between Turkic and the nearby Tungusic and Mongolic families, as well as the Korean and Japonic families has in more recent years been instead attributed to prehistoric contact amongst the group, sometimes referred to as the Northeast Asian sprachbund. A more recent (circa first millennium BC) contact between "core Altaic" (Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic) is distinguished from this, due to the existence of definitive common words that appear to have been mostly borrowed from Turkic into Mongolic, and later from Mongolic into Tungusic, as Turkic borrowings into Mongolic significantly outnumber Mongolic borrowings into Turkic, and Turkic and Tungusic do not share any words that do not also exist in Mongolic.

Turkic languages also show some Chinese loanwords that point to early contact during the time of Proto-Turkic.[19]
Early written records

The first established records of the Turkic languages are the eighth century AD Orkhon inscriptions by the Göktürks, recording the Old Turkic language, which were discovered in 1889 in the Orkhon Valley in Mongolia. The Compendium of the Turkic Dialects (Divânü Lügati't-Türk), written during the 11th century AD by Kaşgarlı Mahmud of the Kara-Khanid Khanate, constitutes an early linguistic treatment of the family. The Compendium is the first comprehensive dictionary of the Turkic languages and also includes the first known map of the Turkic speakers' geographical distribution. It mainly pertains to the Southwestern branch of the family.[20]
The Codex Cumanicus (12th–13th centuries AD) concerning the Northwestern branch is another early linguistic manual, between the Kipchak language and Latin, used by the Catholic missionaries sent to the Western Cumans inhabiting a region corresponding to present-day Hungary and Romania. The earliest records of the language spoken by Volga Bulgars, debatably the parent or a distant relative of Chuvash language, are dated to the 13th–14th centuries AD.[21][22]
Geographical expansion and development

With the Turkic expansion during the Early Middle Ages (c. 6th–11th centuries AD), Turkic languages, in the course of just a few centuries, spread across Central Asia, from Siberia to the Mediterranean. Various terminologies from the Turkic languages have passed into Persian, Urdu, Ukrainian, Russian,[23] Chinese, Mongolian, Hungarian and to a lesser extent, Arabic.[24][verification needed]
The geographical distribution of Turkic-speaking peoples across Eurasia since the Ottoman era ranges from the North-East of Siberia to Turkey in the West.[25] (See picture in the box on the right above.)
For centuries, the Turkic-speaking peoples have migrated extensively and intermingled continuously, and their languages have been influenced mutually and through contact with the surrounding languages, especially the Iranian, Slavic, and Mongolic languages.[26]
This has obscured the historical developments within each language and/or language group, and as a result, there exist several systems to classify the Turkic languages. The modern genetic classification schemes for Turkic are still largely indebted to Samoilovich (1922).[citation needed]
The Turkic languages may be divided into six branches:[27]
- Turkic
- Common Turkic
- Oghuz Turkic (Southwestern)
- Kipchak Turkic (Northwestern)
- Karluk Turkic (Southeastern)
- Siberian Turkic (Northeastern)
- Arghu Turkic
- Oghur Turkic
- Common Turkic
In this classification, Oghur Turkic is also referred to as Lir-Turkic, and the other branches are subsumed under the title of Shaz-Turkic or Common Turkic. It is not clear when these two major types of Turkic can be assumed to have diverged.[28]
With less certainty, the Southwestern, Northwestern, Southeastern and Oghur groups may further be summarized as West Turkic, the Northeastern, Kyrgyz-Kipchak, and Arghu (Khalaj) groups as East Turkic.[29]
Geographically and linguistically, the languages of the Northwestern and Southeastern subgroups belong to the central Turkic languages, while the Northeastern and Khalaj languages are the so-called peripheral languages.[citation needed]
Hruschka, et al. (2014)[30] use computational phylogenetic methods to calculate a tree of Turkic based on phonological sound changes.

Schema
The following isoglosses are traditionally used in the classification of the Turkic languages:[31][27]
- Rhotacism (or in some views, zetacism), e.g. in the last consonant of the word for "nine" *tokkuz. This separates the Oghur branch, which exhibits /r/, from the rest of Turkic, which exhibits /z/. In this case, rhotacism refers to the development of *-/r/, *-/z/, and *-/d/ to /r/,*-/k/,*-/kh/ in this branch.[32] See Antonov and Jacques (2012)[33] on the debate concerning rhotacism and lambdacism in Turkic.
- Intervocalic *d, e.g. the second consonant in the word for "foot" *hadaq
- Suffix-final -G, e.g. in the suffix *lIG, in e.g. *tāglïg
Additional isoglosses include:
- Preservation of word initial *h, e.g. in the word for "foot" *hadaq. This separates Khalaj as a peripheral language.
- Denasalisation of palatal *ń, e.g. in the word for "moon", *āń
*In the standard Istanbul dialect of Turkish, the ğ in dağ and dağlı is not realized as a consonant, but as a slight lengthening of the preceding vowel.
Members
The following table is based mainly upon the classification scheme presented by Lars Johanson.[34][35]
Vocabulary comparison
The following is a brief comparison of cognates among the basic vocabulary across the Turkic language family (about 60 words). Despite being cognates, some of the words may denote a different meaning.
Empty cells do not necessarily imply that a particular language is lacking a word to describe the concept, but rather that the word for the concept in that language may be formed from another stem and is not cognate with the other words in the row or that a loanword is used in its place.
Also, there may be shifts in the meaning from one language to another, and so the "Common meaning" given is only approximate. In some cases, the form given is found only in some dialects of the language, or a loanword is much more common (e.g. in Turkish, the preferred word for "fire" is the Persian-derived ateş, whereas the native od is dead). Forms are given in native Latin orthographies unless otherwise noted.
| Common meaning | Proto-Turkic | Old Turkic | Turkish | Azerbaijani | Karakhanid | Qashqai | Turkmen | Tatar | Karaim | Bashkir | Kazakh | Kyrgyz | Uzbek | Uyghur | Sakha/Yakut | Chuvash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Relationship |
father, ancestor | *ata, *kaŋ | ata, apa, qaŋ | baba, ata | baba, ata | apa, ata | bowa/ata | ata | ata, atay [g] | ata | ata, atay [h] | ata | ata | ota | ata [i] | ağa [j] | atte, aśu, aşşĕ [k] |
| mother | *ana, *ög | ana, ög | ana, anne | ana | ana, ene | ana/nänä | ene | ana, äni [l] | ana | ana, inä(y)/asay [m] | ana | ene, ana [n] | ona, acha | ana [o] | iỹe [p] | anne, annü, amăşĕ [q] | |
| son | *ogul | oɣul | oğul | oğul | oɣul, ohul | oğul | ogul | ul [r] | uvul | ul | ul [s] | uul [t] | oʻgʻil | oghul [u] | uol [v] | ıvăl, ul [w] | |
| man | *ēr, *érkek | er | erkek | ər/erkək | erkek | kiši | erkek | ir [x] | ėr | ir, irkäk [y] | er, erkek [z] | er, erkek [aa] | erkak | er [ab] | er [ac] | ar/arśın [ad] | |
| girl | *kï̄ŕ | qïz | kız | qız | qɨz | qïz/qez | gyz | qız [ae] | qɨz | qıð [af] | qyz [ag] | qız | qiz | qiz [ah] | kııs [ai] | hĕr [aj] | |
| person | *kiĺi, *yạlaŋuk | kiši, yalaŋuq | kişi | şəxs, adam | kiši | kişi | keşe [ak] | kiši | keşe | kisi [al] | kişi [am] | kishi | kishi [an] | kihi [ao] | śın [ap] | ||
| bride | *gélin | kelin | gelin | gəlin | qalɨŋ | gälin | gelin | kilen [aq] | kelin | kilen | kelin [ar] | kelin [as] | kelin | kelin [at] | kiyiit [au] | kin [av] | |
| mother-in-law | kaynana | qaynana | qäynänä | gaýyn ene | qayın ana [aw] | qäynä [ax] | qaıyn ene [ay] | qaynene [az] | qaynona | qeyinana [ba] | huńama [bb] | ||||||
Body parts |
heart | *yürek | yürek | yürek | ürək | jürek | iräg/üräg | ýürek | yöräk [bc] | üriak, jürek | yöräk | jürek [bd] | cürök [be] | yurak | yürek | sürex [bf] | çĕre [bg] |
| blood | *kiān | qan | kan | qan | qan | qan | gan | qan [bh] | qan | qan [bi] | qan [bj] | qan | qon | qan | xaan [bk] | yun | |
| head | *baĺč | baš | baş | baş | baš | baš | baş | baş | baš | baş | bas | baş | bosh | bash | bas | puś/poś | |
| hair | *s(i)ač, *kïl | sač, qïl | saç, kıl | saç, qıl | sač, qɨl | tik/qel | saç, gyl | çäç, qıl | čač, sač, qɨl | säs, qıl | shash, qyl | çaç, qıl | soch, qil | sach, qil | battax, kıl | śüś, hul | |
| eye | *göŕ | köz | göz | göz | köz | gez/göz | göz | küz | kioź, goz | küð | köz | köz | koʻz | köz | xarax, kös | kuś/koś | |
| eyelash | *kirpik | kirpik | kirpik | kirpik | kirpik | kirpig | kirpik | kerfek | kirpik | kerpek | kirpik | kirpik | kiprik | kirpik | kılaman, kirbii | hărpăk | |
| ear | *kulkak | qulqaq | kulak | qulaq | qulaq, qulqaq, qulxaq, qulɣaq | qulaq | gulak | qolaq | qulax | qolaq | qulaq | qulaq | quloq | qulaq | kulgaax | hălha | |
| nose | *burun | burun | burun | burun | burun | burn | burun | borın | burun | moron | muryn | murun | burun | burun | murun, munnu | murun | |
| arm | *kol | qol | kol | qol | qol | qol | gol | qul | kol | qul | qol | qol | qoʻl | qol | хol | hul | |
| hand | *el-ig | elig | el | əl | elig | äl | el | alaqan | alaqan | ilik | ilik | ilii | ală | ||||
| finger | *erŋek, *biarŋak | erŋek | parmak | barmaq | barmaq | burmaq | barmaq | barmaq | barmax | barmaq | barmaq | barmaq | barmoq | barmaq | tarbaq | pürne/porńa | |
| fingernail | *dïrŋak | tïrŋaq | tırnak | dırnaq | tɨrŋaq | dïrnaq | dyrnak | tırnaq | tɨrnax | tırnaq | tyrnaq | tırmaq | tirnoq | tirnaq | tıngıraq | çĕrne | |
| knee | *dīŕ, *dǖŕ | tiz | diz | diz | tizle-
(to press with one's knees) |
diz | dyz | tez | tɨz | teð | tize | tize | tizza | tiz | tobuk | çĕrśi, çĕrkuśśi | |
| calf | *baltïr | baltïr | baldır | baldır | baldɨr | ballïr | baldyr | baltır | baldɨr | baltır | baltyr | baltır | boldir | baldir | ballır | pıl | |
| foot | *(h)adak | adaq | ayak | ayaq | aδaq | ayaq | aýak | ayaq | ajax | ayaq | aıaq | but, ayaq | oyoq, adoq | ayaq | ataq | ura | |
| belly | *kạrïn | qarïn | karın | qarın | qarɨn | qarn | garyn | qarın | qarɨn | qarın | qaryn | qarın | qorin | qerin | xarın | hırăm | |
Animals |
horse | *(h)at | at | at | at | at | at | at | at | at | at | at | at | ot | at | at | ut/ot |
| cattle | *dabar | ingek, tabar | inek, davar, sığır | inək, sığır | ingek, ingen; tavar | seğer | sygyr | sıyır | sɨjɨr | hıyır | siyr | uy, sıyır, inek | sigir, inak | siyir | ınax | ĕne | |
| dog | *ït, *köpek | ït | it, köpek | it | ɨt | kepäg | it | et | it´ | et | ıt | it, köbök | it | it | ıt | yıtă | |
| fish | *bālïk | balïq | balık | balıq | balɨq | balïq | balyk | balıq | balɨx | balıq | balyq | balıq | baliq | beliq | balık | pulă | |
| louse | *bït | bit | bit | bit | bit | bit | bit | bet | bit | bet | bıt | bit | bit | bit | bıt | pıytă/puťă | |
Other nouns |
house | *eb, *bark | eb, barq | ev, bark | ev | ev | äv | öý | öy | üy, üv | öy | üı | üy | uy | öy | śurt | |
| tent | *otag, *gerekü | otaɣ, kerekü | çadır, otağ | çadır; otaq | otaɣ, kerekü | čador | çadyr; otag | çatır | oda | satır | shatyr; otau | çatır, otoo, otoq | chodir; oʻtoq | chadir; otaq | otuu | çatăr | |
| way | *yōl | yol | yol | yol | jol | yol | ýol | yul | jol | yul | jol | col | yoʻl | yol | suol | śul | |
| bridge | *köprüg | köprüg | köprü | körpü | köprüg | köpri | küper | kiopriu | küper | köpir | köpürö | koʻprik | kövrük | kürpe | kĕper | ||
| arrow | *ok | oq | ok | ox | oq | ox/tir | ok | uq | oq | uq | oq | oq | oʻq | oq | ox | uhă | |
| fire | *ōt | ōt | od, ateş (Pers.) | od | ot | ot | ot | ut | ot | ut | ot | ot | oʻt | ot | uot | vut/vot | |
| ash | *kül | kül | kül | kül | kül | kil/kül | kül | köl | kul | köl | kül | kül | kul | kül | kül | kĕl | |
| water | *sub, *sïb | sub | su | su | suv | su | suw | su | su | hıw | su | suu | suv | su | uu | şıv/şu | |
| ship, boat | *gḗmi | kemi | gemi | gəmi | kemi | gämi | köymä | gemi | kämä | keme | keme | kema | keme | kimĕ | |||
| lake | *kȫl | köl | göl | göl | köl | göl/gel | köl | kül | giol´ | kül | köl | köl | koʻl | köl | küöl | külĕ | |
| sun/day | *güneĺ, *gün | kün | güneş, gün | günəş, gün | kün, qujaš | gin/gün | gün | qoyaş, kön | kujaš | qoyaş, kön | kün | kün | quyosh, kun | quyash, kün | kün | hĕvel, kun | |
| cloud | *bulït | bulut | bulut | bulud | bulut | bulut | bulut | bolıt | bulut | bolot | bult | bulut | bulut | bulut | bılıt | pĕlĕt | |
| star | *yultuŕ | yultuz | yıldız | ulduz | julduz | ulluz | ýyldyz | yoldız | julduz | yondoð | juldyz | cıldız | yulduz | yultuz | sulus | śăltăr | |
| ground, earth | *toprak | topraq | toprak | torpaq | topraq | torpaq | toprak | tufraq | topraq, toprax | tupraq | topyraq | topuraq | tuproq | tupraq | toburax | tăpra | |
| hilltop | *tepö, *töpö | töpü | tepe | təpə | tepe | depe | tübä | tebe | tübä | töbe | döbö, töbö | tepa | töpe | töbö | tüpĕ | ||
| tree/wood | *ïgač | ïɣač | ağaç | ağac | jɨɣač | ağaĵ | agaç | ağaç | ahač | ağas | ağash | baq, daraq, cığaç | yogʻoch | yahach | mas | yıvăś | |
| god (Tengri) | *teŋri, *taŋrï | teŋri, burqan | tanrı | tanrı | teŋri | tarï/Allah/Xoda | taňry | täñre | Tieńri | täñre | täŋiri | teñir | tangri | tengri | tangara | tură/toră | |
| sky | *teŋri, *kȫk | kök, teŋri | gök | göy | kök | gey/göy | gök | kük | kök | kük | kök | kök | koʻk | kök | küöx | kăvak/koak | |
Adjectives |
long | *uŕïn | uzun | uzun | uzun | uzun | uzun | uzyn | ozın | uzun | oðon | uzyn | uzun | uzun | uzun | uhun | vărăm |
| new | *yaŋï, *yeŋi | yaŋï | yeni | yeni | jaŋɨ | yeŋi | ýaňy | yaña | jɨŋgɨ | yañı | jaña | cañı | yangi | yengi | saña | śĕnĕ | |
| fat | *semiŕ | semiz | semiz, şişman | səmiz | semiz | semiz | simez | semiz | himeð | semiz | semiz | semiz | semiz | emis | samăr | ||
| full | *dōlï | tolu | dolu | dolu | tolu | dolu | doly | tulı | tolɨ | tulı | toly | toluq, tolu, toluu, tolo | toʻla | toluq | toloru | tulli | |
| white | *āk, *ürüŋ | āq, ürüŋ | ak, beyaz (Ar.) | ağ | aq | aq | ak | aq | aq | aq | aq | aq | oq | aq | ürüñ (үрүҥ) | şură | |
| black | *kara | qara | kara, siyah (Pers.) | qara | qara | qärä | gara | qara | qara | qara | qara | qara | qora | qara | xara | hura, hora | |
| red | *kïŕïl | qïzïl | kızıl, kırmızı (Ar.) | qızıl | qɨzɨl | qïzïl | gyzyl | qızıl | qɨzɨl | qıðıl | qyzyl | qızıl | qizil | qizil | kıhıl | hĕrlĕ | |
Numbers |
1 | *bīr | bir | bir | bir | bir | bir | bir | ber | bir, bɨr | ber | bir | bir | bir | bir | biir | pĕrre, pĕr |
| 2 | *éki | eki | iki | iki | ẹki | ikki | iki | ike | eky | ike | eki | eki | ikki | ikki | ikki | ikkĕ, ikĕ, ik | |
| 3 | *üč | üč | üç | üç | üč | uǰ, u̇č | üç | öč | üć | ös | üş | üč | uch/u̇č | üch/üç | üs | viśśĕ, viśĕ, viś | |
| 4 | *dȫrt | tört | dört | dörd | tört | derd/dörd | dört | dürt | dört | dürt | tört | tört | toʻrt | tört | tüört | tăvattă, tăvată, tăvat | |
| 5 | *bēĺ(k) | béš | beş | beş | béš | bäş | beş | beš | biš | bes | beş | besh/beş | besh/beş | bies | pillĕk, pilĕk | ||
| 6 | *altï | altï | altı | altı | altï | altï | alty (altï) | altï | altï | altï | alty | altı | olti (ålti) | altä | alta | ulttă, ultă, ult | |
| 7 | *yéti | yeti | yedi | yeddi | jeti | yeddi | ýedi | cide | jedi | yete | jeti | ceti | yetti | yetti | sette | śiççĕ, śiçĕ, śiç | |
| 8 | *sekiŕ | säkiz | sekiz | səkkiz | sek(k)iz, sik(k)iz | sӓkkiz | sekiz | sigez | sekiz | higeð | segiz | segiz | säkkiz | säkkiz | aɣïs | sakkăr, sakăr | |
| 9 | *tokuŕ | toquz | dokuz | doqquz | toquz | doġġuz | dokuz | tugïz | toɣuz | tuɣïð | toğyz | toğuz | to’qqiz | toqquz | toɣus | tăxxăr, tăxăr | |
| 10 | *ōn | on | on | on | on | on | on | un | on | un | on | on | oʻn | on | uon | vunnă, vună, vun | |
| 20 | *yẹgirmi | yigirmi/yégirmi | yirmi | iyirmi | yigirmi, yigirme | igirmi, iyirmi | yigrimi | yegerme | yigirmi | yegerme | jiyirma | cıyırma | yigirmä | yigirmä | süürbe | śirĕm | |
| 30 | *otuŕ | otuz | otuz | otuz | otuz | ottiz | otuz (otuð) | otuz | otuz | utïð | otyz | otuz | o’ttiz | ottuz | otut | vătăr | |
| 40 | *kïrk | qïrq | kırk | qırx | qïrq | ġèrḫ (ɢərx) | kyrk (kïrk) | qırq (qïrq) | kïrx | qïrq | qyryq | qırq | qirq | qirq | tüört uon | xĕrĕx | |
| 50 | *ellig | älig | elli | ǝlli (älli) | el(l)ig | älli, ẹlli | elli | ille | elu | elüü | allă, ală, al | ||||||
| 60 | *altmïĺ | altmïš | altmış | altmış (altmïš) | altmïš | altmïš | altmyş (altmïš) | altmïš | altïmïš | altïmïš | alpys | altımış | oltmish (åltmiš) | altmiš | alta uon | ultmăl | |
| 70 | *yẹtmiĺ | yētmiš/s | yetmiş | yetmiş | yetmiš | yetmiš | ýetmiş (yetmiš) | ǰitmeš | yetmiš/s | yetmeš | jetpis | cetimiş | yetmiš | yätmiš | sette uon | śitmĕl | |
| 80 | *sekiŕ ōn | säkiz on | seksen | sǝksǝn (säksän) | seksün | sӓɣsen | segsen | seksen | seksen, seksan | hikhen | seksen | seksen | sakson (säksån) | säksän | aɣïs uon | sakăr vunnă, sakăr vun | |
| 90 | *dokuŕ ōn | toquz on | doksan | doxsan | toqsan | togsan | tuksan | toksan, toxsan | tukhan | toqsan | toqson | to'qson (tȯksån) | toqsan | toɣus uon | tăxăr vunnă, tăxăr vun | ||
| 100 | *yǖŕ | yüz | yüz | yüz | jüz | iz/yüz | ýüz | yöz | jiz, juz, jüz | yöð | jüz | cüz | yuz | yüz | süüs | śĕr | |
| 1000 | *bïŋ | bïŋ | bin | min | miŋ, men | min | müň (müŋ) | meŋ | min, bin | meŋ | myñ | miñ | ming (miŋ) | miŋ | tïhïïnča | pin | |
| Common meaning | Proto-Turkic | Old Turkic | Turkish | Azerbaijani | Karakhanid | Qashqai | Turkmen | Tatar | Karaim | Bashkir | Kazakh | Kyrgyz | Uzbek | Uyghur | Sakha/Yakut | Chuvash |
Azerbaijani "ǝ" and "ä": IPA /æ/
Azerbaijani "q": IPA /g/, word-final "q": IPA /x/
Turkish and Azerbaijani "ı", Karakhanid "ɨ", Turkmen "y", and Sakha "ï": IPA /ɯ/
Turkmen "ň", Karakhanid "ŋ": IPA /ŋ/
Turkish and Azerbaijani "y",Turkmen "ý" and "j" in other languages: IPA /j/
All "ş" and "š" letters: IPA /ʃ/
All "ç" and "č" letters: IPA /t͡ʃ/
Kyrgyz "c": IPA /d͡ʒ/
Kazakh "j": IPA /ʒ/
Other possible relations
The Turkic language family is currently regarded as one of the world's primary language families.[10] Turkic is one of the main members of the controversial Altaic language family, but Altaic currently lacks support from a majority of linguists. None of the theories linking Turkic languages to other families have a wide degree of acceptance at present. Shared features with languages grouped together as Altaic have been interpreted by most mainstream linguists to be the result of a sprachbund.[54]
Rejected or controversial theories
Korean
The possibility of a genetic relation between Turkic and Korean, independently from Altaic, is suggested by some linguists.[55][56][57] The linguist Kabak (2004) of the University of Würzburg states that Turkic and Korean share similar phonology as well as morphology. Li Yong-Sŏng (2014)[56] suggest that there are several cognates between Turkic and Old Korean. He states that these supposed cognates can be useful to reconstruct the early Turkic language. According to him, words related to nature, earth and ruling but especially to the sky and stars seem to be cognates.
The linguist Choi[57] suggested already in 1996 a close relationship between Turkic and Korean regardless of any Altaic connections:
In addition, the fact that the morphological elements are not easily borrowed between languages, added to the fact that the common morphological elements between Korean and Turkic are not less numerous than between Turkic and other Altaic languages, strengthens the possibility that there is a close genetic affinity between Korean and Turkic.
— Choi Han-Woo, A Comparative Study of Korean and Turkic (Hoseo University)
Many historians also point out a close non-linguistic relationship between Turkic peoples and Koreans.[58] Especially close were the relations between the Göktürks and Goguryeo.[59]
Uralic
Some linguists suggested a relation to Uralic languages, especially to the Ugric languages. This view is rejected and seen as obsolete by mainstream linguists. Similarities are because of language contact and borrowings mostly from Turkic into Ugric languages. Stachowski (2015) states that any relation between Turkic and Uralic must be a contact one.[60]
See also
- Altaic languages
- List of Turkic languages
- List of Turkic-languages poets
- List of Ukrainian words of Turkic origin
- Middle Turkic languages
- Old Turkic
- Old Turkic script
- Proto-Turkic language
Notes
- ^ Nikolai Baskakov and some others believe that the Kyrgyz–Kipchak subgroup originally belonged to the Siberian group, but was significantly influenced by the Kipchak languages and can now be included in the Kipchak group.[40][41][42]
- ^ Lars Johanson once considered Kyrgyz language to be a member of South Kipchak.(Johanson 1998)
- ^ Äynu contains a very large Persian vocabulary component, and is spoken exclusively by adult men, almost as a cryptolect.
- ^ Lars Johanson once classified South Siberian group into 4 subgroups (Sayan Turkic, Yenisei Turkic, Chulym Turkic and Altai Turkic). Sayan Turkic consisted of Tuvan (Soyot, Uriankhai) and Tofa (Karagas). Yenisei Turkic consisted of Khakas, Shor and related dialects (Saghay, Qaca, Qizil). Chulym Turkic consisted of dialects such as Küerik. Altai Turkic consisted of Altay (Oirot) and dialects such as Tuba, Qumanda, Qu, Teleut, Telengit. (Johanson 1998)
- ^ According to Lars Johanson, Fuyu Kyrgyz is considered to be closely related to Khakas.
- ^ Nikolai Baskakov and some others considered Southern Altai language to be a member of Kyrgyz-Kipchak subgroup.[40][41][42]
- ^ Cyrillic: ата, атай
- ^ Cyrillic: ата, атай
- ^ UEY: ئاتا
- ^ Cyrillic: аҕа
- ^ Cyrillic: атте, аҫу, ашшӗ
- ^ Cyrillic: ана, әни
- ^ Cyrillic: ана, инә(й)/асай
- ^ Cyrillic: эне, ана
- ^ UEY: ئانا
- ^ IPA /ij̃e/. Cyrillic: ийэ. The nasal glide /j̃/ is not distinguished from oral glide /j/ in orthography.
- ^ Cyrillic: анне, аннӳ, амӑшӗ
- ^ Cyrillic: ул
- ^ Cyrillic: ұл
- ^ Cyrillic: уул
- ^ UEY: ئوغۇل
- ^ Cyrillic: уол
- ^ Cyrillic: ывӑл, ул
- ^ Cyrillic: ир
- ^ Cyrillic: ир, иркәк
- ^ Cyrillic: ер, еркек
- ^ Cyrillic: эр, эркек
- ^ UEY: ئەر
- ^ Cyrillic: эр
- ^ Cyrillic: ар/арҫын
- ^ Cyrillic: кыз
- ^ Cyrillic: ҡыҙ
- ^ Cyrillic: қыз
- ^ UEY: قىز
- ^ Cyrillic: кыыс
- ^ Cyrillic: хӗр
- ^ Cyrillic: кеше
- ^ Cyrillic: кісі
- ^ Cyrillic: киши
- ^ UEY: كىشى
- ^ Cyrillic: киһи
- ^ Cyrillic: ҫын
- ^ Cyrillic: килен
- ^ Cyrillic: келін
- ^ Cyrillic: келин
- ^ UEY: كەلىن
- ^ Cyrillic: кийиит
- ^ Cyrillic: кин
- ^ Cyrillic: кайын ана
- ^ Cyrillic: ҡәйнә
- ^ Cyrillic: қайын ене
- ^ Cyrillic: кайнене
- ^ UEY: قەيىنانا
- ^ Cyrillic: хунама
- ^ Cyrillic: йөрәк
- ^ Cyrillic: жүрек
- ^ Cyrillic: жүрөк
- ^ Cyrillic: сүрэх
- ^ Cyrillic: чӗре
- ^ Cyrillic: кан
- ^ Cyrillic: ҡан
- ^ Cyrillic: қан
- ^ Cyrillic: хаан
References
- ^ a b Rybatzki, Volker (2020). "Altaic Languages: Tungusic, Mongolic, Turkic". In Martine Robbeets; Alexander Savelyev (eds.). The Oxford Guide to the Transeurasian Languages. Oxford University Press. pp. 22–28. doi:10.1093/oso/9780198804628.003.0003.
- ^ Dybo A.V. (2007). "ХРОНОЛОГИЯ ТЮРКСКИХ ЯЗЫКОВ И ЛИНГВИСТИЧЕСКИЕ КОНТАКТЫ РАННИХ ТЮРКОВ" [Chronology of Turkish Languages and Linguistic Contacts of Early Turks] (PDF) (in Russian). p. 766. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 March 2005. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Janhunen, Juha (2013). "Personal pronouns in Core Altaic". In Martine Irma Robbeets; Hubert Cuyckens (eds.). Shared Grammaticalization: With Special Focus on the Transeurasian Languages. John Benjamins. p. 223. ISBN 9789027205995. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2017.
- ^ a b c Katzner, Kenneth (March 2002). Languages of the World, Third Edition. Routledge, an imprint of Taylor & Francis Books Ltd. ISBN 978-0-415-25004-7.
- ^ Grenoble, L.A. (2003). Language Policy in the Soviet Union. Springer. p. 10. ISBN 9781402012983.
- ^ "Language Materials Project: Turkish". UCLA International Institute, Center for World Languages. February 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2007. Retrieved 26 April 2007.
- ^ Vovin, Alexander (2005). "The end of the Altaic controversy: In memory of Gerhard Doerfer". Central Asiatic Journal. 49 (1): 71–132. JSTOR 41928378.
- ^ Georg, Stefan; Michalove, Peter A.; Ramer, Alexis Manaster; Sidwell, Paul J. (1999). "Telling general linguists about Altaic". Journal of Linguistics. 35 (1): 65–98. doi:10.1017/S0022226798007312. JSTOR 4176504. S2CID 144613877.
- ^ Sinor, 1988, p.710
- ^ a b George van DRIEM: Handbuch der Orientalistik. Volume 1 Part 10. BRILL 2001. Page 336
- ^ M. A. Castrén, Nordische Reisen und Forschungen. V, St.-Petersburg, 1849
- ^ Standish, Russell K.; Bedau, Mark; Abbass, Hussein A. (25 August 2023). Artificial Life 8. MIT Press. p. 391. ISBN 9780262692816.
- ^ Yunusbayev, Bayazit; Metspalu, Mait; Metspalu, Ene; et al. (21 April 2015). "The Genetic Legacy of the Expansion of Turkic-Speaking Nomads across Eurasia". PLOS Genetics. 11 (4): e1005068. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005068. ISSN 1553-7390. PMC 4405460. PMID 25898006.
The origin and early dispersal history of the Turkic peoples is disputed, with candidates for their ancient homeland ranging from the Transcaspian steppe to Manchuria in Northeast Asia,
- ^ Yunusbayev, Bayazit; Metspalu, Mait; Metspalu, Ene; et al. (21 April 2015). "The Genetic Legacy of the Expansion of Turkic-Speaking Nomads across Eurasia". PLOS Genetics. 11 (4): e1005068. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005068. ISSN 1553-7390. PMC 4405460. PMID 25898006.
Thus, our study provides the first genetic evidence supporting one of the previously hypothesized IAHs to be near Mongolia and South Siberia.
- ^ Blench, Roger; Spriggs, Matthew (2003). Archaeology and Language II: Archaeological Data and Linguistic Hypotheses. Routledge. p. 203. ISBN 9781134828692. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 9 April 2020.
- ^ Golden, Peter Benjamin (2011). "Ethnogenesis in the tribal zone: The Shaping of the Turks". Studies on the peoples and cultures of the Eurasian steppes. Archived 26 October 2020 at the Wayback Machine. Bucureşti: Ed. Acad. Române. pp. 35–37.
- ^ Clark, Larry V. (1980). "Turkic Loanwords in Mongol, I: The Treatment of Non-initial S, Z, Š, Č". Central Asiatic Journal. 24 (1/2): 36–59. JSTOR 41927278.
- ^ Rachewiltz, Igor de. Introduction to Altaic philology: Turkic, Mongolian, Manchu / by Igor de Rachewiltz and Volker Rybatzki; with the collaboration of Hung Chin-fu. p. cm. — (Handbook of Oriental Studies = Handbuch der Orientalistik. Section 8, Central Asia; 20). — Leiden; Boston, 2010. — P. 7.
- ^ Johanson, Lars; Johanson, Éva Ágnes Csató (29 April 2015). The Turkic Languages. Routledge. ISBN 9781136825279. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 22 November 2020.
- ^ Soucek, Svat (March 2000). A History of Inner Asia. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-65169-1.
- ^ Johanson, Lars; Csató, Éva Á, eds. (2021). The Turkic Languages. Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781003243809. ISBN 9781003243809.
Another Turkic people in the Volga area are the Chuvash, who, like the Tatars, regard themselves as descendants of the Volga Bulghars in the historical and cultural sense. It is clear that Chuvash belongs to the Oghur branch of Turkic, as the language of the Volga Bulghars did, but no direct evidence for diachronic development between the two has been established. As there were several distinct Oghur languages in the Middle Ages, Volga Bulghar could represent one of these and Chuvash another.
- ^ Agyagási, K. (2020). "A Volga Bulgarian Classifier: A Historical and Areal Linguistic Study". University of Debrecen. 3: 9.
Modern Chuvash is the only descendant language of the Ogur branch. The ancestors of its speakers left the Khazar Empire in the 8th century and migrated to the region at the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers, where they founded the Volga Bulgarian Empire in the 10th century. In the central Volga region three Volga Bulgarian dialects developed, and Chuvash is the descendant of the 3rd dialect of Volga Bulgarian (Agyagási 2019: 160–183). Sources refer to it as a separate language beginning with 1508
- ^ Poppe, Nicolas J. (1966). "A Survey of Studies of Turkic Loan-Words in the Russian Language". Central Asiatic Journal. 11 (4): 287–310. ISSN 0008-9192. JSTOR 41926932. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2021.
- ^ Findley, Carter V. (October 2004). The Turks in World History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-517726-8.
- ^ Turkic Language tree Archived 14 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine entries provide the information on the Turkic-speaking regions.
- ^ Johanson, Lars (2001). Discoveries on the Turkic linguistic map. Stockholm: Swedish Research Institute in Istanbul. ISBN 91-86884-10-7. Retrieved 17 July 2024.
- ^ a b Lars Johanson, The History of Turkic. In Lars Johanson & Éva Ágnes Csató (eds), The Turkic Languages, London, New York: Routledge, 81–125, 1998.Classification of Turkic languages Archived 8 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ See the main article on Lir-Turkic.
- ^ Gordon, Raymond G. Jr., ed. (2005). "Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Language Family Trees – Turkic". Archived from the original on 14 September 2012. Retrieved 18 March 2007. The reliability of Ethnologue lies mainly in its statistics whereas its framework for the internal classification of Turkic is still based largely on Baskakov (1962) and the collective work in Deny et al. (1959–1964). A more up-to-date alternative to classifying these languages on internal comparative grounds is to be found in the work of Johanson and his co-workers.
- ^ Hruschka, Daniel J.; Branford, Simon; Smith, Eric D.; Wilkins, Jon; Meade, Andrew; Pagel, Mark; Bhattacharya, Tanmoy (2015). "Detecting Regular Sound Changes in Linguistics as Events of Concerted Evolution 10.1016/j.cub.2014.10.064". Current Biology. 25 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.10.064. PMC 4291143. PMID 25532895.
- ^ Самойлович, А. Н. (1922). Некоторые дополнения к классификации турецких языков (in Russian). Archived from the original on 19 July 2018. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- ^ Larry Clark, "Chuvash", in The Turkic Languages, eds. Lars Johanson & Éva Ágnes Csató (London–NY: Routledge, 2006), 434–452.
- ^ Anton Antonov & Guillaume Jacques, "Turkic kümüš 'silver' and the lambdaism vs sigmatism debate" Archived 15 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine, Turkic Languages 15, no. 2 (2012): 151–70.
- ^ Lars Johanson, "The classification of the Turkic languages" Archived 15 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine, in Martine Robbeets and Alexander Savelyev (eds.), The Oxford Guide to the Transeurasian Languages, 2020, Oxford University Press, pp. 105–114
- ^ a b c d "turcologica". Archived from the original on 8 April 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2021.
- ^ Deviating. Historically developed from Southwestern (Oghuz) (Johanson 1998) [1] Archived 8 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Johanson, Lars & Éva Agnes Csató (ed.). 1998. The Turkic languages. London: Routledge. 82-83p.
- ^ Urum Archived 4 December 2020 at the Wayback Machine – Glottolog
- ^ Krymchak Archived 7 July 2021 at the Wayback Machine – Glottolog
- ^ a b c Baskakov, N. A. (1958). "La Classification des Dialectes de la Langue Turque d'Altaï". Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae (in French). 8: 9–15. ISSN 0001-6446.
- ^ a b c Baskakov, N. A. (1969). Введение в изучение тюркских языков [Introduction to the study of the Turkic languages] (in Russian). Moscow: Nauka.
- ^ a b c Kormushin, I. V. (2018). "Алтайский язык" [Altai language]. Большая российская энциклопедия/Great Russian Encyclopedia Online (in Russian). Archived from the original on 27 July 2021. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ^ Ili Turki Archived 20 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine – Glottolog
- ^ Rassadin, V.I. "The Soyot Language". Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 3 May 2006. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ "Northern Altai". ELP Endangered Languages Project. Archived from the original on 25 November 2022. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ "Kumandin". ELP Endangered Languages Project. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2021.
- ^ Bitkeeva, A.N. "The Kumandin Language". Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Tazranova, A.R. "The Chelkan Language". Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Nevskaya, I.A. "The Teleut Language". Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia. UNESCO. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Coene 2009 Archived 15 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine, p. 75
- ^ Brown, Keith; Ogilvie, Sarah, eds. (2010). Concise Encyclopedia of Languages of the World (revised ed.). Elsevier. p. 1109. ISBN 978-0080877754. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- ^ Johanson, Lars, ed. (1998). The Mainz Meeting: Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Turkish Linguistics, August 3–6, 1994. Turcologica Series. Contributor Éva Ágnes Csató. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 28. ISBN 978-3447038645. Archived from the original on 15 January 2023. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
- ^ In Glottolog, Western Yugur is classified as Enisei-East Siberian Turkic.
- ^ Janhunen, Juha A. (17 January 2023). "The Unity and Diversity of Altaic". Annual Review of Linguistics. 9 (1): 135–154. doi:10.1146/annurev-linguistics-030521-042356. hdl:10138/355895. ISSN 2333-9683. S2CID 256126714.
- ^ Sibata, Takesi (1979). "Some syntactic similarities between Turkish, Korean, and Japanese". Central Asiatic Journal. 23 (3/4): 293–296. ISSN 0008-9192. JSTOR 41927271.
- ^ a b SOME STAR NAMES IN MODERN TURKIC LANGUAGES-I – Yong-Sŏng LI – Academy of Korean Studies Grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST) (AKS-2010-AGC-2101) – Seoul National University 2014
- ^ a b Choi, Han-Woo (1996). "A comparative study of Korean and Turkic: Is Korean Altaic?" (PDF). International Journal of Central Asian Studies. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
- ^ Babayar, Gaybullah (2004). "On the ancient relations between the Turkic and Korean peoples" (PDF). Journal of Turkic Civilization Studies (1): 151–155. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2019. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
- ^ Tae-Don, Noh (2016). "Relations between ancient Korea and Turkey: An examination of contacts between Koguryŏ and the Turkic Khaganate". Seoul Journal of Korean Studies. 29 (2): 361–369. doi:10.1353/seo.2016.0017. hdl:10371/164838. ISSN 2331-4826. S2CID 151445857. Archived from the original on 24 April 2019. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
- ^ Stachowski, Marek (2015). "Turkic pronouns against a Uralic background". Iran and the Caucasus. 19 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1163/1573384X-20150106. ISSN 1609-8498. Archived from the original on 24 November 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2019.
Further reading
- Akhatov G. Kh. 1960. "About the stress in the language of the Siberian Tatars in connection with the stress of modern Tatar literary language" .- Sat *"Problems of Turkic and the history of Russian Oriental Studies." Kazan. (in Russian)
- Akhatov G.Kh. 1963. "Dialect West Siberian Tatars" (monograph). Ufa. (in Russian)
- Baskakov, N. A. (1962, 1969). Introduction to the study of the Turkic languages. Moscow. (in Russian)
- Boeschoten, Hendrik & Lars Johanson. 2006. Turkic languages in contact. Turcologica, Bd. 61. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. ISBN 3-447-05212-0
- Clausen, Gerard. 1972. An etymological dictionary of pre-thirteenth-century Turkish. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Deny, Jean et al. 1959–1964. Philologiae Turcicae Fundamenta. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- Dolatkhah, Sohrab. 2016. Parlons qashqay. In: collection "parlons". Paris: L'Harmattan.
- Dolatkhah, Sohrab. 2016. Le qashqay: langue turcique d'Iran. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (online).
- Dolatkhah, Sohrab. 2015. Qashqay Folktales. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (online).
- Johanson, Lars & Éva Agnes Csató (ed.). 2022. The Turkic Languages. Second edition. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-73856-9.
- Johanson, Lars. 2022. "The history of Turkic." In: Johanson & Csató, pp. 83–120.[2] Archived 8 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Johanson, Lars. 1998. "Turkic languages." In: Encyclopædia Britannica. CD 98. Encyclopædia Britannica Online, 5 sept. 2007.[3] Archived 23 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Menges, K. H. 1968. The Turkic languages and peoples: An introduction to Turkic studies. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- Öztopçu, Kurtuluş. 1996. Dictionary of the Turkic languages: English, Azerbaijani, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Uighur, Uzbek. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-14198-2
- Samoilovich, A. N. 1922. Some additions to the classification of the Turkish languages. Petrograd.
- Savelyev, Alexander and Martine Robbeets. (2019). lexibank/savelyevturkic: Turkic Basic Vocabulary Database (Version v1.0) [Data set]. Zenodo. doi:10.5281/zenodo.3556518
- Schönig, Claus. 1997–1998. "A new attempt to classify the Turkic languages I-III." Turkic Languages 1:1.117–133, 1:2.262–277, 2:1.130–151.
- Schönig, Claus. "The Internal Division of Modern Turkic and Its Historical Implications". In: Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae, vol. 52, no. 1, 1999, pp. 63–95. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/43391369 Archived 3 January 2023 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed 3 Jan. 2023.
- Starostin, Sergei A., Anna V. Dybo, and Oleg A. Mudrak. 2003. Etymological Dictionary of the Altaic Languages. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 90-04-13153-1
- Voegelin, C.F. & F.M. Voegelin. 1977. Classification and index of the World's languages. New York: Elsevier.
External links
- Interactive map of Turkic languages
- Turkic Languages Verb Comparison
- Turkic Language Portal (English)
- Turkic Inscriptions of Orkhon Valley, Mongolia Archived 2 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Turkic Languages: Resources – University of Michigan
- Map of Turkic languages by Goethe University Frankfurt
- Classification of Turkic Languages by Lars Johanson
- Grouping chart of Turkic Languages
- Online Uyghur–English Dictionary
- Turkic language vocabulary comparison tool / dictionary
- Pauctle.com dictionaries of various Turkic Languages and games for learning words by Pamukkale University
- A Comparative Dictionary of Turkic Languages Open Project
- The Turkic Languages in a Nutshell Archived 12 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine with illustrations.
- Turkic basic vocabularies at Zenodo
- Monumenta Altaica Archived 26 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine (Grammar and other sources by Russian Academy of Sciences)
- Turkic Interlingua (NLP project for Turkic languages)
- Turkic Database at Elegant Lexicon (Comprehensive lexical database for Turkic languages)
- TurkLang Conference Archived 22 June 2022 at the Wayback Machine: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2013, Istanbul, Turkey, 2014 Archived 24 February 2021 at the Wayback Machine, Kazan, Tatarstan, 2015