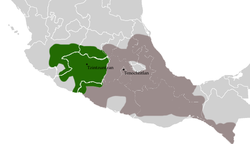
Purépecha Empire
Purépecha Empire Iréchikwa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1300–1530 | |||||||
 | |||||||
| Capital | Tzintzuntzan | ||||||
| Common languages | Purépecha Tecuexe | ||||||
| Religion | Polytheism | ||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||
| Cazonci | |||||||
• 1300–1350 | Tariácuri (founder) | ||||||
• 1520–1530 | Tangáxuan II (last) | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | c. 1300 | ||||||
| 1530 | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
| 1450[1] | 75,000 km2 (29,000 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1519[2] | 1,500,000 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Mexico | ||||||
The Purépecha Empire, also known by the term Iréchikwa, was a polity in pre-Columbian Mexico. Its territory roughly covered the geographic area of the present-day Mexican state of Michoacán, as well as parts of Guanajuato, Guerrero, and Jalisco. At the time of the Spanish conquest, it was the second-largest state in Mesoamerica.[3] The state is also known as the Tarascan Empire.[4][5][6]
The empire was founded in the early 14th century and lost its independence to the Spanish in 1530. In 1543 it officially became the governorship of Michoacán, from the Nahuatl exonym for the Purépecha Empire, Michuacān from mich- ("fish"), -ua ("possessor of"), and -cān ("place of") and means "place of fishers."
The Purépecha Empire was constituted of a network of tributary systems and gradually became increasingly centralized, under the control of the ruler of the empire called the Irecha or Cazonci. The Purépecha capital was located at Tzintzuntzan, from Ts'inzúnzani meaning "place of hummingbirds", on the banks of Lake Pátzcuaro and, according to Purépecha oral tradition, was founded by the first Cazonci Tariácuri and dominated by his lineage, the Uacusecha, from Wakúsïecha meaning "eagles". The largest city before the inception of the empire may have been Angamuco, extensive ruins of which were discovered in 2012 using LiDAR technology.
The Purépecha Empire was a contemporary and enemy of the Aztec Empire, against which it fought many wars. The Purépecha Empire blocked Aztec expansion to the northwest, fortifying and patrolling their frontiers with the Aztecs, possibly developing the first truly territorial state of Mesoamerica.
Due to its relative isolation within Mesoamerica, the Purépecha Empire had many cultural traits completely distinct from those of the Mesoamerican cultural group. It is particularly noteworthy for being among the few Mesoamerican civilizations to use metal for tools, and even weapons.[7]

Etymology and definitions
The word "Purépecha" in modern usage is the hispanicized form of the then and still used term P'orhépicha, meaning "commoner/s" in the Purépecha language. The word's root p'orhe- means "to go someplace", alluding to the people strolling to and from their daily errands.
In the Relación de Cuiseo de la Laguna it states, "And this name was given to them because their king ordinarily took them cargoed to wars, and found them to be stronger, both for this and for their crops."
Another word by which the Purépecha people have been called is Tarascan, from Spanish "Tarasco" from the Purépecha word "Tarhaskwa", meaning "parent-in-law/child-in-law". This term is pejorative to most Purépecha communities but still occasionally used in others.
Ethnic groups
The empire included different groups, primarily Purépecha people and additionally Matlazincas and Mazahuas in the east, Chichimecs such as Otomíes and Tecuexes in the Bajio, Cocas around Lake Chapala, Chontales de Guerrero/Tuxtecos around the Balsas River valley, Chumbios around Zacatula, and Nahuas both on the Pacific coast and in the heartland.[8]
Geography and lithic occupation

The territory that would eventually form the setting of the Purepecha Empire is the high volcanic region constituting the western extension of the Mexican Mesa Central, in between two large rivers: the Lerma and Balsas Rivers. Including temperate, subtropical and tropical climate zones, it is dominated by Cenozoic volcanic mountains and lake basins above 2000 meters (6500 feet) altitude, but also includes lower land in the southwestern coastal regions. Most common soil types in the central plateau are young volcanic andosols, luvisols and less fertile acrisols. The vegetation is mainly pine, pine-oak and fir. Human occupation has focused on the lake basins, which are abundant in resources. In the north, near the Lerma river, there are obsidian resources and thermal springs. The Iréchikwa was centered around the Lake Pátzcuaro basin.
History of the Iréchikwa

Early archaeological evidence
The Purepecha area has been inhabited at least since the early Pre-classic period. Early lithic evidence from before 2500 BC, like fluted points and stone utensils are found at some megafauna kill sites. The earliest radio-carbon dates of archeological sites fall around 1200 BC. The best known early Pre-classic culture of Michoacán was the Chupícuaro culture. Most Chupícuaro sites are found on lake islands which can be seen as a sign of it having traits relating it to the later Purepecha cultural patterns. In the early Classic period, ballcourts and other artifacts demonstrate a Teotihuacan influence in the Michoacán region.
Ethnohistorical sources
The most useful ethnohistorical source has been the Relación de Michoacán,[9] written around 1540 by the Franciscan priest Fray Jeronimo de Acalá, containing translated and transcribed narratives from Purepecha noblemen. This Relación contains parts of the "official Tarascan history" as carried down through oral tradition: one part focuses on Purepecha state religion, the second on Purepecha society, and the last on Purepecha history and the Spanish conquest. Unfortunately the first part is only partly preserved. Other sources include a number of small pictorial manuscripts, the best known being the Lienzo de Jucutacuto.[citation needed]
Foundation and expansion
| |||||||||||||||||||
|


In the late classic, at least two non-Purépecha ethnic groups lived around Lake Pátzcuaro: Nahuatl speakers in Jarácuaro, and some Chichimecan cultures on the northern banks, with the Nahua population being the second largest.
According to the Relación de Michoacán a visionary leader of the Purépecha named Tariácuri decided to gather the communities around Lake Pátzcuaro into one strong state. Around 1300 he undertook the first conquests and installed his sons Hiripan and Tangáxuan as lords of Ihuatzio and Tzintzuntzan respectively, himself ruling from Pátzcuari city. By the death of Taríacuri (around 1350), his lineage was in control of all the major centers around Lake Pátzcuaro. His son Hiripan continued the expansion into the area surrounding Lake Cuitzeo.
Hiripan and later his brother Tangáxuan I began to institutionalize the tributary system and consolidate the political unity of the empire. They created an administrative bureaucracy and divided responsibilities of and tributes from the conquered territories between lords and nobles. In the following years, first the sierra and then the Balsas River was incorporated into the increasingly centralized state.
Under the rule of cazonci Tzitzipandáquare a number of regions were conquered, only to be lost again by rebellions or strategic retreats when confronted with Aztec expansion. In 1460 the Iréchikwa reached the Pacific coast at Zacatula, advanced into the Toluca Valley, and also, on the northern rim, reached into the present day state of Guanajuato. In the 1470s, Aztecs under Axayacatl captured a series of frontier towns and closed in on the Purepecha heartland, but were eventually defeated. This experience prompted the Purepecha ruler to further fortify the Aztec frontier with military centers along the border, such as at Cutzamala. He also allowed Otomies and Matlatzincas who had been driven out of their homelands by the Aztecs to settle in the border area under the condition that they took part in the defense of the Purepecha lands. From 1480 the Aztec ruler Ahuitzotl intensified the conflict with the Iréchikwa. He supported attacks on Purepecha lands by other ethnic groups allied with or subjugated to the Aztecs such as Matlatzincas, Chontales, and Cuitlatecs. The Purepecha, led by the cazonci Zuangua, repelled the attacks but further Purepecha expansion was halted until the arrival of the Spaniards two years into the rule of the last cazonci of an independent Iréchikwa, Tangáxuan II.
Between 1480 and 1510, the Iréchikwa occupied parts of present day Colima and Jalisco in order to secure Nitratine (Chile saltpeter) mines in the region. Throughout the occupation, the peoples of Colima, Sayula, Zapotlán, Tapalpa, and Autlán resisted Purepecha rule in the Saltpeter War. By the end of the 30 year long occupation, the Iréchikwa was forced out of the area permanently.
Religion
Like most Mesoamerican cultures, the Purépecha were polytheists who worshipped a large array of deities. Chiefly was Curicaveri/Kurikaweri, the god of the sun.[10]
Metallurgy

Historian Robert West states, "The Tarascans and their neighbors near the Pacific coast were the foremost metallurgists of pre-Conquest Mexico." This included copper, silver and gold, where Michoacán and Colima provided placer gold, Tamazula provided silver, and the La Huacana area provided copper. Copper-silver alloy artefacts found in the palaces and graves of Tzintzuntzan include rodelas, armlets, bracelets and cups. Copper bells made from lost-wax casting were used in religious ceremonies from 650 AD to at least 1200. This was followed by copper-gold and copper-silver items such as discs, bracelets, diadems and masks. Other items were made from bronze, including needles, fishhooks, tweezers, axeheads, and awls. The religious national treasures were looted by the Spanish during the Conquest from Lake Patzcuaro graves and storerooms.[13]
It has been speculated that Purepecha metallurgy was developed due to contact with South American cultures.[14]
Spanish conquest of Purepechan Empire

After hearing about the fall of the Aztec Empire, cazonci Tangáxuan II sent emissaries to the Spanish victors. A few Spaniards went with them to Tzintzuntzan where they were presented to the ruler and gifts were exchanged. They returned with samples of gold and Cortés' interest in the Iréchikwa was awakened. In 1522 a Spanish force under the leadership of Cristóbal de Olid was sent into Purepecha territory and arrived at Tzintzuntzan within days. The Purepecha army numbered many thousands, perhaps as many as 100,000[citation needed], but at the crucial moment they chose not to fight. Tangáxuan submitted to the Spanish administration, but for his cooperation was allowed a large degree of autonomy. This resulted in a strange arrangement where both Cortés and Tangáxuan considered themselves rulers of Michoacán for the following years: the population of the area paid tribute to them both. When the Spanish found out that Tangáxuan was still de facto ruler of his empire but only supplied the Spanish with a small part of the resources extracted from the population they sent the ruthless conquistador Nuño de Guzmán, who allied himself with a Purepecha noble Don Pedro Panza Cuinierángari, and the cazonci was executed on February 14, 1530.[15][16][17][18] A period of violence and turbulence began. During the next decades Purepecha puppet rulers were installed by the Spanish government, but when Nuño de Guzman had been disgraced and recalled to Spain, Bishop Vasco de Quiroga was sent to the area to clean up. He rapidly gained the respect and friendship of the natives who ceased hostilities towards the Spanish hegemony.[citation needed]
Notes
- ^ Blanford, Adam Jared (2014). "Rethinking Tarascan Political and Spatial Organization" (PDF). Anthropology Graduate Theses & Dissertations. University of Colorado Boulder: 6. S2CID 147339315. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2020-07-03.
By A.D. 1450, the Tarascan Uacúsecha were leaders of an empire that spanned 75,000 square kilometers of west Mexico
- ^ "Welcome to The Human Past – Student Study Guide Website". Archived from the original on 2014-10-20. Retrieved 2014-04-27.
- ^ "Julie Adkins, "Mesoamerican Anomaly? The Pre-Conquest Tarascan State", Robert V. Kemper, Faculty papers, Southern Methodist University. On line". smu.edu. Archived from the original on 19 December 2009. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican Cultures: The Civilizations of Mexico and Central America. Oxford University Press. 2001. p. 279. ISBN 978-0-19-510815-6.
- ^ Middleton, John (2015). World Monarchies and Dynasties. Routledge. p. 37. ISBN 978-1-317-45158-7.
- ^ Maldonado, Blanca Estela (2018). Tarascan Copper Metallurgy: A Multiapproach Perspective. Archaeopress Publishing Ltd. p. 71. ISBN 978-1-78491-626-8.
- ^ Malmstrom, Vincent H. (1 January 1995). "Geographical Origins of the Tarascans". Geographical Review. 85 (1): 31–40. doi:10.2307/215553. JSTOR 215553.
- ^ Pollard, Helen Perlstein (1980). "Central Places and Cities: A Consideration of the Protohistoric Tarascan State". American Antiquity. 45 (4): 677–696. doi:10.2307/280141. JSTOR 280141. S2CID 163246131.
This was the Tarascan state [...] peopled by ethnic groups of matlazincas, tecos, mazahuas, otomíes, chontales, nahuas and primarily tarascos
- ^ Relación de Michoacán, complete text (in Spanish)
- ^ "Tarascan Tribe Gods & Symbols". study.com.
- ^ American Museum of Natural History.
- ^ Covarrubias, p. 103.
- ^ West, Robert. Early Silver Mining in New Spain, 1531–1555 (1997). Bakewell, Peter (ed.). Mines of Silver and Gold in the Americas. Aldershot: Variorum, Ashgate Publishing Limited. pp. 45–48, 58–59.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Anawalt, Patricia Rieff. "Ancient Cultural Contacts between Ecuador, West Mexico, and the American Southwest: Clothing Similarities." Latin American Antiquity 3, no. 2 (1992): 121.
- ^ David Marley (2008). Wars of the Americas: A Chronology of Armed Conflict in the Western Hemisphere, 1492 to the Present. ABC-CLIO. p. 43. ISBN 978-1-59884-100-8.
- ^ James Krippner-Martínez (1 November 2010). Rereading the Conquest: Power, Politics, and the History of Early Colonial Michoac‡n, Mexico, 1521–1565. Penn State Press. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-271-03940-4.
- ^ Bernardino Verástique (1 January 2010). Michoacán and Eden: Vasco de Quiroga and the Evangelization of Western Mexico. University of Texas Press. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-292-77380-6.
- ^ See Gorenstein (1993, xv). According to some other sources Tangáxuan II was dragged behind a horse and then burned.
References
- Covarrubias, Miguel (1957). Indian Art of Mexico and Central America. New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Gorenstein, Shirley (1993). "Introduction". In Helen Perlstein Pollard (ed.). Taríacuri's Legacy: The Prehispanic Tarascan State. The Civilization of the American Indian series, vol. 209. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. p. xiii–xx. ISBN 978-0-8061-2497-1. OCLC 26801144.
- Pollard, Helen Perlstein (1993). Taríacuri's Legacy: The Prehispanic Tarascan State. The Civilization of the American Indian series, vol. 209. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 978-0-8061-2497-1. OCLC 26801144.
- Pollard, Helen Perlstein (2003). "El gobierno del estado tarascano prehispanico". In Carlos Paredes Martínez; Marta Terán (eds.). Autoridad y gobierno indígena en Michoacán: ensayos a través de su historia. Colección Investigaciones series (in Spanish). Vol. 1. Zamora, Mexico: Colegio de Michoacán. pp. 49–60. ISBN 978-970-679-121-4. OCLC 55237579.
- Silverstein, Jay (2001). "The southeastern extent of Tarascan imperialism". Abstract of a paper presented at the 100th Annual Meeting of the American Anthropological Association, Washington, D.C.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Warren, J. Benedict (1963). "The Caravajal Visitation: First Spanish Survey of Michoacán". Americas. 19 (4): 404–412. doi:10.2307/979507. JSTOR 979507.
- ——— (1985). The Conquest of Michoacán: The Spanish Domination of the Tarascan Kingdom in Western Mexico, 1521–1530. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
- ——— (1970–1971). "Fray Jerónimo de Alcalá: Author of the Relación de Michoacán?". 27, Americas: 307–327.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Weaver, Muriel Porter (1993). The Aztecs, Maya, and Their Predecessors: Archaeology of Mesoamerica (3rd ed.). San Diego, California: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-739065-9. OCLC 25832740.

