Littlejohn's tree frog
| Littlejohn's tree frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Hylidae |
| Genus: | Litoria |
| Species: | L. littlejohni |
| Binomial name | |
| Litoria littlejohni | |
| |
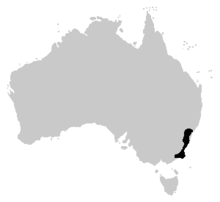
| Distribution of the Littlejohn's Tree Frog. | |
Littlejohn's tree frog (Litoria littlejohni), also called a heath frog or orange-bellied tree frog, is a species of tree frog native to eastern Australia from Wyong, New South Wales, to Buchan, Victoria.
Taxonomy
In 2020, following a taxonomic review, the species was split, with the description of a new species Litoria watsoni encompassing the southernmost populations.[1]
Description
This is a medium-sized frog reaching 60 mm (2.4 in) in length. It is normally brown or grey-brown on the dorsal surface with many scattered darker flecks and spots. Often, a faint darker patch runs down the back. A dark line runs from behind the nostril down to the shoulder. The belly is cream. The iris is golden-yellow, and it has large toe discs. The armpits and thighs are orange, this helps distinguish it from the similar Jervis Bay tree frog (Litoria jervisiensis).
Behaviour and ecology

This species is associated with swamps and dams, still creeks, and pools, mostly in heathland, but also in forest and woodland, mostly in highland areas. Males make a trilling "weep, weep, weep, weep..." from elevated areas or while floating in water around the breeding site. Males call mostly during the cooler months (April to September); however, calling has been observed in all months with a peak in February. Clusters of about 60 eggs are laid attached to submerged twigs or branches near the edge of the water body. Tadpoles are dark in colour, reaching about 65 mm and take about 120 days to develop. Metamorphs resemble the adult and measure around 20 mm.
This species of frog is one of the least encountered species in Australia. Despite a large distribution, the number of sites where this species has been recorded is low (total 75) across New South Wales and Victoria. At the majority of breeding sites, the number of calling males is also normally low (less than four) and has only rarely been recorded with more than 10 calling males, which is low for even rare species of frogs. This may be due to poor surveying techniques as a result of lack of data on the breeding habits and habitat preferences of this species.

This species does not appear to be under direct threat from habitat clearing, and appears tolerant of disturbance. More research is required of this species to determine why low numbers of individuals are being recorded. However, despite the low numbers, they appear stable and this species does not appear to be in serious decline.
As a pet
It is kept as a pet, and in Australia this animal may be kept in captivity with the appropriate permit.
References
- ^ Mahony, M; Moses, B; Mahony, SV; Lemckert, FL; Donnellan, S (2020). "A new species of frog in the Litoria ewingii species group (Anura: Pelodryadidae) from south-eastern Australia". Zootaxa. 4858 (2): 201–230. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4858.2.3. PMID 33056230.
- Frogs Australia Network-Frog call available here.
- Frogs of Australia
- Amphibian Species of the World
- Article Road: List of All Frog Breeds: Things You Can Do to Ensure Your Frog Has a Long, Happy and Healthy Life: Ornate Burrowing Frog
- Department of Environment, Climate Change and Water, New South Wales: Amphibian Keeper's Licence: Species Lists
- Anstis, M. 2002. Tadpoles of South-eastern Australia. Reed New Holland: Sydney.
- Robinson, M. 2002. A Field Guide to Frogs of Australia. Australian Museum/Reed New Holland: Sydney. (under the Jervis Bay Tree Frog)
- Lemckert, F. The Biology and Conservation Status of the Heath Frog, Litoria littlejohni. Herpetofauna Vol. 34 No. 2, December 2004.