Sistema Ibérico
| Iberian System | |
|---|---|
| Sistema Ibérico (Spanish) Sistema Iberico (Aragonese) Sistema Ibèric (Valencian) | |
 View of the Moncayo Massif from Alcalá de Moncayo | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Moncayo |
| Elevation | 2,313 m (7,589 ft) |
| Coordinates | 41°44′45″N 01°46′53″W / 41.74583°N 1.78139°W |
| Geography | |
| Country | Spain |
| Communities | Aragon, Castile and León, La Rioja, Valencian Community, Catalonia and Castile-La Mancha |
| Geology | |
| Orogeny | Alpine |
| Rock age | Tertiary |
| Rock type(s) | Nummulite limestone, marble and sandstone |





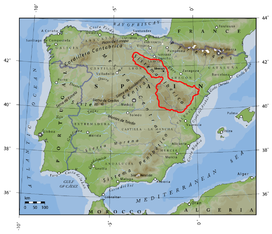
The Iberian System[a] is one of the major systems of mountain ranges in Spain. It consists of a vast and complex area of mostly relatively high and rugged mountain chains and massifs located in the central region of the Iberian Peninsula, but reaching almost the Mediterranean coast in the Valencian Community in the east.
The system is hydrographically important, as it separates the watersheds of most of the major rivers in Spain and Portugal, including the Ebro basin to the east from the basins of the Douro, Tagus, Guadiana (Záncara-Gigüela), Júcar and Turia to the west and south.
There are important mining areas in some of the ranges such as Sierra Menera, Sierra de Arcos and Sierra de San Just, making the system one of the chief mining regions in Spain since ancient times.[1][2] One of the comarcas of Aragon located in the Iberian System was given the name of Cuencas Mineras, lit. 'Mining Basins', since mining is the main activity in the comarca.[3]
Location and description
The Sistema Ibérico mountain range borders the Meseta Central on its eastern end and separates the Meseta Central from the Ebro valley and from the Mediterranean coast.
This system runs northwest-southeast between the Ebro plain and the Meseta Central for over 500 km, from the La Bureba corridor in Burgos Province close to the Cordillera Cantábrica to the Mediterranean sea close to Valencia in the south and close to Tortosa and the Ebro Delta in the east. The bulk of the Sistema Ibérico is located in the southern half of Aragon. The Prebaetic System rises south of the southernmost end of the Iberian System.
The geology of the Iberian System is complex, for it can hardly be defined as a homogeneous system. It is composed of a haphazard and motley series of mountain ranges, massifs, plateaus and depressions without a definite common petrologic composition and overall structure. Nummulite limestone, marble and sandstone are common throughout the area. Some of the parts of the system stand geologically isolated, interrupting the continuity of the whole, linked to the other parts through high plateaus of varying altitudes.[4]
Ecology and human activity
Population decline
Large zones of the mountainous Iberian System have undergone heavy depopulation since the early 20th century. There are many ghost towns and abandoned villages scattered across different parts of the Iberian System, especially in Teruel Province.[5] Currently a great number of surviving towns have only a residual population. In some cases, many of the inhabitants are not natives anymore but immigrants from Romania or the Maghreb working as contract laborers in agricultural activities.[6]
The exodus from the rural mountainous areas in Spain rose after General Franco's Stabilization Plan in 1959. The population declined steeply as people emigrated towards the industrial areas of the large cities and the coastal towns where the tourism industry was growing. Other causes of high emigration have been the abandonment by the local youth of traditional agricultural practices that were the mainstay of the village economy, such as sheep and goat rearing, as well as the lifestyle changes that swept over rural Spain during the second half of the 20th century.[7]
Fauna
The heavy depopulation has favored wildlife so that one of the last colonies of griffon vultures in Europe is in the Iberian System. Wolves and eagles (Aquila chrysaetos, Hieraaetus fasciatus, Hieraaetus pennatus, Circaetus gallicus) are also relatively common in the lonely heights. Among the mammals, the Spanish ibex, roe deer, wild boar, European badgers, common genets, among others, have their habitat in many of these desolate mountain ranges.[8]
The most common reptiles in the Iberian System are Lacerta lepida, Psammodromus algirus, Psammodromus hispanicus, Podarcis muralis and Podarcis hispanicus. Chalcides chalcides, Chalcides bedriagai and Anguis fragilis, are relatively rarer. The snakes present in these mountains are Natrix maura, Natrix natrix, Malpolon monspessulanus, Elaphe scalaris, Coronella girondica, Coronella austriaca and Vipera latastei.
Some amphibians are abundant in or near ponds and rivulets throughout the whole system, such as Rana perezi, Bufo bufo, Bufo calamita, Alytes obstetricans, Triturus marmoratus and Lissotriton helveticus, the latter also at high altitude, whether in intermittent or permanent bodies of water. Hyla arborea and Salamandra salamandra are somewhat rarer, but still having a wide distribution, especially in humid forested zones. The Iberian ribbed newt (Pleurodeles waltl), however, is rarely found in the mountainous areas. Aquatic invertebrates, including the Austropotamobius pallipes crayfish, and certain fishes, such as Salaria fluviatilis and Cobitis paludica are common in the upper course of the Sistema Ibérico rivers.[9] Some mountain streams have been stocked with trout.[10]
Traditional cattle rearing activities, formerly so important in central Iberia, still survive on dry grasslands in certain villages around the system. There are also many hunters visiting some of the ranges, mainly those that are relatively closer to the urban areas and especially on weekends.[11]
Vegetation
Some ranges have forested patches, consisting mainly of Pinus pinaster, Pinus sylvestris and Pinus uncinata pines and Quercus rotundifolia, Quercus pyrenaica and Quercus faginea oaks, even Fagus sylvatica beeches and Betula pendula birches grow in some humid slopes, where Pteridium aquilinum, Polypodium vulgare ferns may also be found.
Other ranges are rocky and quite bare with heath (Erica arborea, Erica vagans, Calluna vulgaris), broom as well as thyme and Festuca and Nardus stricta grasslands. Thin forest or shrubland may include Juniperus communis, Juniperus thurifera, Cytisus purgans, Erinacea anthyllis and Calluna vulgaris shrub. Often the southern slopes are drier than the northern ones and may be subject to wildfires in periods of prolonged drought, especially in the summer.
Bogs are not common in the Iberian Peninsula, but high altitude bogs form in the few areas of the Sistema Ibérico where the water remains stagnant, such as near Orihuela del Tremedal, Bronchales and in the place known as Fuente del Hierro, at an altitude between 1.400 and 1.550 m. The plants growing in these bogs are mainly Polytrichum mosses, Potentilla erecta, Pinguicula vulgaris, Vaccinium myrtillus, Calluna vulgaris, and also Drosera rotundifolia, a carnivorous plant that does not grow further south in Western Europe.
Centaurea pinnata is an endangered species of plant present in the Sierra de Vicort and Sierra de Santa Cruz mountain ranges.[12]
Mountain ranges
The Sistema Ibérico comprises several mountain ranges and massifs:
- Northern: Sierra de Mencilla, Sierra de la Demanda, Sierra de Neila, Mesa de Cebollera and the Picos de Urbión in the northwest, the Sierra de Alcarama, Sierra de Peñalmonte, Sierra de Moncalvillo and the isolated Moncayo Massif in the north, always crested with snow in the winter, with its eastern prolongation the Sierra de Nava Alta.
- Western: Smaller and drier mountain ranges close to the transition area with the Sistema Central, such as Sierra de Perdices, Sierra Ministra, Sierra de Caldereros (Águila 1,443 m), Sierra de Pardos, Sierra de Miñana, Sierra de Solorio, Sierra de Selas (Aragoncillo 1,517 m) and Parameras de Molina (Mojón Alto 1,408 m).
- Central: Numerous mountain ranges located at the heart of the system, such as Sierra de la Virgen, Sierra de Vicort, Sierra de Algairén, Sierra de Santa Cruz, Sierra de Cucalón, Sierra de Herrera, Sierra de San Just, Sierra de Lidón and Sierra Palomera, among others.
- Southwestern: Serranía de Cuenca, Sierra Menera, Sierra de Albarracín, Montes de Picaza (Colmenarejo 1,426 m), Montes Universales and Sierra de Mira.
- Southeastern: Sierra de Javalambre, Sierra del Toro, Sierra de Gúdar, Sierra de Mayabona, Sierra de Camarena, Sierra de Sollavientos, Sierra del Rayo, and Sierra de Pina.
- Eastern: A succession of ranges that reaches the Mediterranean Sea, including the Maestrat or Maestrazgo with the Penyagolosa Massif, Sierra de la Lastra, Sierra de los Caballos, Sierra de Garrocha, Sierra de la Cañada, Sierra Carrascosa, the Ports de Morella, Serra de la Creu, Serra d'En Segures, Serra d'en Galceran, Serra d'Esparreguera, Serra de Vallivana, Serra d'En Celler, Serra del Turmell, Serra de l'Espadella and the Moles de Xert, as well as the Talaies d'Alcalà, Serra de la Vall d'Àngel, the Cervera Mountains, Serra de Sant Pere, Serra Calderona and Serra d'Espadà foothills at the eastern end.
- Northeastern: A complex mountainous area connecting with the Catalan Pre-Coastal Range, which includes the Ports de Tortosa-Beseit[13][14] and the Benifassà Mountains.
Main subranges and features
- The arid Sierra de los Caballos range rises behind Molinos
- The main peaks of the Moncayo Massif rising behind Cueva de Agreda
- Sierra del Bollón, foothills of the Moncayo Massif, near Fuendejalón
- The massive Roques de Benet in the western side of the Ports de Beseit
- The Laguna Negra in the Picos de Urbión area
- Sierra de San Just above Ejulve
- Waterfall in the Monasterio de Piedra Natural Park
- Sierra de Algairén towering behind Almonacid de la Sierra
- Rugged Sierra de Albarracín
- La Modorra, highest peak in the Sierra de Cucalón system
- Sierra de la Virgen behind Gotor
- View of Morella
- Calatayud with the Sierra de Vicort in the background
- Purujosa from the Cabezo
- The Penyagolosa summit
- Sierra de Alcarama in La Rioja
- "Pico Palomera", part of the central-uplift chain in the Rubielos de la Cérida impact structure in Sierra Palomera
- Cabezo del Santo, Sierra de Castejón, Brieva de Cameros, La Rioja
- Los Callejones de Las Majadas in the Serranía de Cuenca
- View of Calmarza with the Sierra de Solorio cliffs above the town
- Ranera Peak in Sierra de Mira
- Northeastern end of Sierra Carrascosa with the "Guerrero Romano" rock formation
- Monegre peak in Sierra de Nava Alta
- South face of Isasa Peak, Sierra de Peñalmonte
- Laguna de Gallocanta, located in an endorheic basin within the Iberian System
- Hill in the Sierra de Arcos area with unusual rock formations on top
- Vistabella de Huerva below Sierra de Herrera range
- Paridera cave, in the Piedra river, next to Monasterio de Piedra, Spain
- Montenegro de Cameros, typical village in the northern part of the range
Peaks
The main peaks of the system are: Moncayo (2,313 m), Monte San Lorenzo (2,262 m), Pico de Urbión (2,228 m), Pico San Millán (2,131 m), Peña Cebollera (2,129 m), Javalambre (2,020 m) and Peñarroya (2,019 m). Other locally important summits are Cerro Calderón (1,837 m), Mont Caro (1,441 m), Tossal d'Orenga (1,144 m) and Montegordo (837 m),
Rivers
The Sistema Ibérico is not as high as other mountain systems in Spain. It is, however, very significant from the hydrographic point of view for important rivers of the Iberian Peninsula have their source in its mountains, which divide the Atlantic from the Mediterranean watershed. The following rivers rise in the Sistema Ibérico:
- The Douro and the Tagus, flowing westwards across the Meseta Central towards Portugal
- The Jalón River, one of the main tributaries of the Ebro, flowing northwards, as well as the Huerva and the Aranda River
- The Turia, the Júcar and the Cabriel flowing eastwards across the Valencian Community towards the Mediterranean Sea
See also
- List of mountains in Aragon
- List of mountains in the Valencian Community
- List of mountains in Catalonia
- Monasterio de Piedra
- Laguna de Gallocanta
- Forests of the Iberian Peninsula
Notes
- ^ Spanish: Sistema Ibérico [sisˈtema jˈβeɾiko]; Aragonese: Sistema Iberico [sisˈtema jβeˈɾiko]; Valencian: Sistema Ibèric [sisˈtema jˈbɛɾik]
References
- ^ "Recursos minerales de España - Universidad de Zaragoza". Archived from the original on 2011-08-10. Retrieved 2011-06-05.
- ^ Luis Diego Arribas, Contemporary Art and Opencast Mining, University of Zaragoza, 2009
- ^ Comarcas de Aragón - Cuencas Mineras
- ^ Natura Xilocae - Entre la sierra de Caldereros y el Maestrazgo de Teruel
- ^ Pueblos deshabitados - Collado de la Grulla (Teruel)
- ^ Un pueblo de Teruel, salvado por la inmigración
- ^ Despoblación en Aragon Archived 2012-08-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Walking In Spain
- ^ "Número de especies y endemismos". Archived from the original on 2013-06-19. Retrieved 2011-06-20.
- ^ Mapa de la trucha del Sistema Ibérico Archived 2012-03-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ MARM / Biodiversidad - Sierra de Vicort Archived 2011-08-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ De Rutas - Sierra de Vicor Archived 2011-05-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Country Studies
- ^ Montipedia - Spanish Archived 2012-09-05 at archive.today
External links
- Spain - The Valley Of The Ebro, Aragon And Catalonia
- Enciclopedia Aragonesa (in Spanish)
- Aragonese part of the Sistema Ibérico[permanent dead link]
- Sierra de la Demanda, Burgos, Sistema Ibérico
- Sierra de Cucalón
- Mendikat - Moncayo Archived 2014-07-28 at the Wayback Machine
- Ascensión a el Bollón (1036 m) Archived 2020-10-01 at the Wayback Machine