Gömör and Kishont County
| Gömör-Kishont County | |
|---|---|
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary (1802-1923, 1938-1945) | |
 | |
| Capital | Rimaszombat; Putnok (1920-1923) |
| Area | |
| • Coordinates | 48°23′N 20°1′E / 48.383°N 20.017°E |
• 1910 | 4,279 km2 (1,652 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1910 | 188,098 |
| History | |
• Established | 1802 |
• Treaty of Trianon | 4 June 1920 |
• Merged into Borsod-Gömör County | 1923 |
• County recreated (First Vienna Award) | 1938 |
• Remerged into Borsod-Gömör County | 1945 |
| Today part of | Slovakia (3,956 km2) Hungary (323 km2) |
| Rimavská Sobota is the current name of the capital. | |
Gömör-Kishont (Hungarian: Gömör és Kishont, Slovak: Gemer a Malohont, German: Gemer und Kleinhont) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its capital was Rimaszombat (present-day Rimavská Sobota). Most of its territory is now part of Slovakia, while a smaller part belongs to Hungary.
Geography

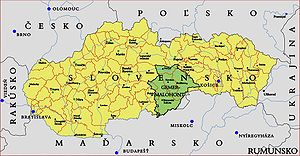
Around 1910, Gömör-Kishont county shared borders with the counties Zólyom, Liptó, Szepes, Abaúj-Torna, Borsod, Heves and Nógrád. It was situated in the Gömör–Szepesi-érchegység (present-day Slovak Ore Mountains) approximately between the present-day Slovak-Hungarian border, the towns Poltár and Rozsnyó (present-day Rožňava) and the Low Tatras (Hungarian: Alacsony-Tátra, Slovak: Nízke Tatry). The river Sajó flowed through the county. Its area was 4,279 km² around 1910.
History
The county Gömör-Kishont was a combination of the counties Gömör and Kishont formed in 1802. It existed until the end of World War I. Gömör is one of the oldest counties of the Kingdom of Hungary, and was already mentioned in the 11th century. Kishont is the territory approximately between the towns Tiszolc (present-day Tisovec) and Rimaszombat (present-day Rimavská Sobota). Counties of Gömör and Kishont was part of Ottoman Empire between 1541–1595 and 1596–1686.
In the aftermath of World War I, most of Gömör-Kishont county became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia, as recognized by the concerned states in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon. The area around Putnok became part of the newly formed Hungarian county Borsod-Gömör-Kishont (currently part of Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén) in 1923. The Czechoslovak part of the county was part of the Slovak Land (Slovenská krajina/zem).
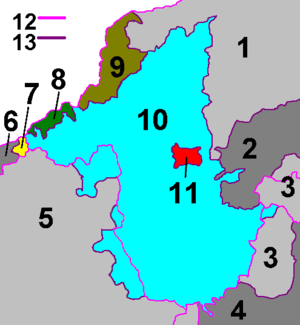
Following the provisions of the First Vienna Award, most of the Czechoslovak part became part of Hungary again in November 1938. The Gömör-Kishont county was recreated. The small northernmost part that remained in Slovak hands (a.o. the towns Dobšiná and Revúca) became part of the new Hron county (Pohronská župa). The Trianon borders were restored after World War II and the county was merged into Borsod-Gömör County. Since 1993, when Czechoslovakia was split, Gemer and Malohont have been part of Slovakia, and since 1996 divided between the Košice region and the Banská Bystrica region.
Demographics

| Census | Total | Hungarian | Slovak | German | Other or unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880[1] | 169,064 | 83,235 (50.95%) | 72,432 (44.34%) | 5,714 (3.50%) | 1,981 (1.21%) |
| 1890[2] | 174,810 | 93,695 (53.60%) | 74,731 (42.75%) | 4,770 (2.73%) | 1,614 (0.92%) |
| 1900[3] | 183,784 | 103,660 (56.40%) | 74,517 (40.55%) | 4,059 (2.21%) | 1,548 (0.84%) |
| 1910[4] | 188,098 | 109,994 (58.48%) | 72,232 (38.40%) | 2,930 (1.56%) | 2,942 (1.56%) |
| Census | Total | Roman Catholic | Lutheran | Calvinist | Jewish | Greek Catholic | Other or unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1880 | 169,064 | 68,776 (40.68%) | 60,138 (35.57%) | 32,066 (18.97%) | 4,320 (2.56%) | 3,662 (2.17%) | 102 (0.06%) |
| 1890 | 174,810 | 73,197 (41.87%) | 59,486 (34.03%) | 33,479 (19.15%) | 4,572 (2.62%) | 4,019 (2.30%) | 57 (0.03%) |
| 1900 | 183,784 | 79,838 (43.44%) | 59,459 (32.35%) | 34,707 (18.88%) | 5,339 (2.91%) | 4,344 (2.36%) | 97 (0.05%) |
| 1910 | 188,098 | 85,355 (45.38%) | 57,744 (30.70%) | 34,798 (18.50%) | 5,603 (2.98%) | 4,410 (2.34%) | 188 (0.10%) |
Subdivisions
In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Gömör-Kishont county were:

| Districts (járás) | |
|---|---|
| District | Capital |
| Feled | Feled (now Jesenské) |
| Garamvölgy | Nándorvölgy (now Vaľkovňa) |
| Nagyrőce | Jolsva (now Jelšava) |
| Putnok (from 1910) | Putnok |
| Ratkó (from 1909) | Ratkó (now Ratková) |
| Rimaszombat | Nyustya (now Hnúšťa) |
| Rozsnyó | Rozsnyó (now Rožňava) |
| Tornalja | Tornalja (now Tornaľa) |
| Urban districts (rendezett tanácsú város) | |
| Dobsina (now Dobšiná) | |
| Jolsva (now Jelšava) | |
| Nagyrőce (now Revúca) | |
| Rimaszombat (now Rimavská Sobota) | |
| Rozsnyó (now Rožňava) | |
Putnok is now in Hungary; all other named towns are now in Slovakia.

Notes
References
- ^ "Az 1881. év elején végrehajtott népszámlálás főbb eredményei megyék és községek szerint rendezve, II. kötet (1882)". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-28.
- ^ "A Magyar Korona országainak helységnévtára (1892)". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
- ^ "A MAGYAR KORONA ORSZÁGAINAK 1900". library.hungaricana.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
- ^ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2021-09-29.


