Dorsal veins of the penis
| Superficial dorsal vein of the penis | |
|---|---|
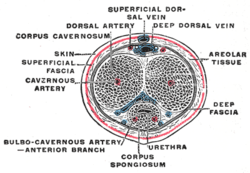 The penis in transverse section, showing the blood vessels | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Penis |
| Drains to | External pudendal vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae dorsales superficiales penis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human male anatomy, the dorsal veins of the penis are blood vessels that drain the shaft (corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum), the skin and the glans of the human penis. They are typically located in the midline on the dorsal aspect of the penis and they comprise the superficial dorsal vein of the penis, that lies in the subcutaneous tissue of the shaft, and the deep dorsal vein of the penis, that lies beneath the deep fascia.[1]
| Deep dorsal vein of the penis | |
|---|---|
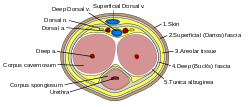 The penis in transverse section, showing the blood vessels | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Penis |
| Drains to | Prostatic venous plexus |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of the penis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena dorsalis profunda penis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
| Cavernosal veins of the penis | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Drains from | Penis |
| Drains to | Prostatic venous plexus |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of the penis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
| Para-arterial veins of the penis | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Drains from | Penis |
| Drains to | Prostatic venous plexus |
| Artery | Dorsal artery of the penis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Superficial dorsal vein
The superficial dorsal vein of the penis belongs to the superficial drainage system. It is located within the superficial dartos fascia, a continuation of the Colles' fascia, on the dorsal surface of the penis and, in contrast to the deep dorsal vein, it lies outside the deeper Buck's fascia.[2] It is formed by smaller superficial veins that merge on the dorsolateral aspect of the penis. It drains the prepuce and the skin of the shaft, and, running backward in the subcutaneous tissue, inclines to the right or left, and opens into the corresponding superficial external pudendal vein, a tributary of the great saphenous vein.[1][3]
Deep dorsal vein
The deep dorsal vein of the penis belongs to the intermediate drainage system of the penis, along with the circumflex veins and their emissary veins.[1] It runs directly beneath the superficial dorsal vein, with a layer of connective tissue, the deep fascia of the penis, separating the two vessels. It receives oxygen-depleted blood from the glans and corpora cavernosa and courses backward in the middle line accompanied by the dorsal arteries on each side.[citation needed]
Near the root of the penis, it passes between the two parts of the suspensory ligament and then through an aperture between the arcuate pubic ligament and the transverse ligament of the pelvis, and divides into two branches, which enter the vesical and prostatic plexuses. From the prostatic plexus, the deoxygenated blood travels through the venal system until it arrives at the center of the circulatory system for resupply with oxygen in the lungs and recirculation through the left side of the heart.[citation needed]
The deep vein also communicates below the pubic symphysis with the internal pudendal vein.
Clinical significance
It is possible but rare for the superficial dorsal vein to rupture during intercourse, which presents in a manner similar to penile fracture.[4]
The dorsal veins of the penis can be used for intravenous injections in rats.[5]
Additional images
- The veins of the right half of the male pelvis
- Veins of the penis
- Vertical section of bladder, penis, and urethra
- Transverse section of the penis
- Anterior abdominal wall, intermediate dissection
- Prominent superficial dorsal vein
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 676 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 676 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b c "Dorsal veins of penis". Kenhub. Retrieved 2023-06-12.
- ^ Sauerland, Eberhardt K.; Tank, Patrick W., PhD. (2005). Grant's dissector. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 101. ISBN 0-7817-5484-4.
- ^ "Male Genital Anatomy » Sexual Medicine » BUMC". www.bumc.bu.edu. Retrieved 2023-06-13.
- ^ Perlmutter AE, Roberts L, Farivar-Mohseni H, Zaslau S (2007). "Ruptured superficial dorsal vein of the penis masquerading as a penile fracture: case report". Can J Urol. 14 (4): 3651–2. PMID 17784989.
- ^ Koch, Michael A. (2006-01-01), Suckow, Mark A.; Weisbroth, Steven H.; Franklin, Craig L. (eds.), "Chapter 18 - Experimental Modeling and Research Methodology", The Laboratory Rat (Second Edition), American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine, Burlington: Academic Press, pp. 587–625, doi:10.1016/b978-012074903-4/50021-2, ISBN 978-0-12-074903-4, retrieved 2021-02-07
External links
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (maleugtriangle4)