Cannone-Mitragliera da 37/54 (Breda)
| Cannone-Mitragliera da 37/54 (Breda) | |
|---|---|
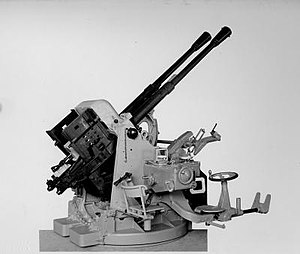 A twin 37/54 Modello 1938. | |
| Type | Anti-aircraft gun |
| Place of origin | Italy |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Kingdom of Italy Nazi Germany |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Breda |
| Produced | 1932–45 |
| Variants | Modello 32, Modello 38, Modello 39, Modello RM39 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 277 kg (611 lb) (Modello 38 without mounting) |
| Length | 3.28 m (10 ft 9 in) |
| Barrel length | 1.998 m (6 ft 7 in) (L/54) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 37 x 232mm SR[1] |
| Shell weight | 1.25–1.63 kg (2 lb 12 oz – 3 lb 9 oz) (High-explosive shell) |
| Caliber | 37 mm (1.5 in) |
| Action | Gas operated |
| Elevation | −10° to +90° (single mounts); −10° to +80° (twin mounts) |
| Traverse | 360° |
| Rate of fire | 60-90-120 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 800 m/s (2,600 ft/s) |
| Effective firing range | 4,000 m (4,400 yd) |
| Maximum firing range | 7,800 m (8,500 yd) |
| Feed system | Automatic |
The Cannone-Mitragliera da 37/54 (Breda) was a 37 mm (1.5 in) automatic anti-aircraft gun produced by the Breda company in Italy.
It was used by both the Regia Marina and the Regio Esercito during World War II, with the former using it as the standard light anti-aircraft weapon on its battleships and cruisers. Nazi Germany used captured weapons after the surrender of Italy in 1943 as the 3.7 cm Breda (i).
Design
The Model 1932 was water-cooled while Models 1938 and 1939 were air-cooled. The gun was fed by a flat magazine holding six rounds which could be loaded one after another to maintain a high rate of fire. It was possible to select alternate rates of fire, either 60, 90 or 120 rpm. The twin mountings for Models 1932 and 1938 were very heavy and required a strong supporting structure. The single Model 1939 (fitted on the Andrea Doria-class and Littorio-class battleships), was instead a single collapsible mount, which also had much less vibrations than its predecessors thanks to the addition of an equilibrator. This meant it could also fitted on smaller warships.
Ship classes that carried the Breda 37/54 include:
- Capitani Romani-class cruiser
- Conte di Cavour-class battleship
- Giussano-class cruiser
- Navigatori-class destroyer
- Oriani-class destroyer
- San Giorgio-class cruiser
- Soldati-class destroyer
- Trento-class cruiser
- Zara-class cruiser
The Breda 37/54 was also fitted in the CANSA FC.20bis ground attack aircraft prototype in its variant Model 39 37/45.
Performance
Although appreciated in the Regia Marina, overall this gun was of limited efficacy because of its gas-operated action (which reduced its rate of fire[citation needed]) and its substantial vibrations (due to their non-recoiling mounting) which impaired accuracy. Instead the single collapsible model, which largely eliminated the latter issue, was seen as a definite improvement, while still being rather heavy and with its production being insufficient to satisfy the needs.[2][3]
Comparison of anti-aircraft guns
| Country | Gun Model | RPM | Projectile Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cannone-Mitragliera da 37/54 (Breda) | 60-120 | 0.82 kg (1.8 lb)[4] | |
| 3.7 cm SK C/30 | 30 | 0.74 kg (1.6 lb)[5] | |
| Canon de 37 mm Modèle 1925 | 15-21 | 0.72 kg (1.6 lb)[6] | |
| 37 mm Gun M1 | 120 | 0.87 kg (1.9 lb) | |
| 3.7 cm Flak 18/36/37/43 | 150 | 0.64 kg (1.4 lb)[7] | |
| 37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K) | 80[8] | 0.73 kg (1.6 lb)[9] | |
| QF 2-pounder naval gun | 115 | 0.91 kg (2.0 lb)[10] | |
| Bofors 40 mm gun | 120 | 0.9 kg (2.0 lb)[11] |
References
- ^ "31-37 MM CALIBRE CARTRIDGES". www.quarryhs.co.uk. Archived from the original on 13 January 2021. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ^ "Italy 37 mm/54 (1.5") Models 1932, 1938 and 1939". NavWeaps. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ Bagnasco, p. 85
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "Kingdom of Italy 37 mm/54 (1.5") Models 1932, 1938 and 1939 - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "Germany 3.7 cm/83 SK C/30 - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "France 37 mm/50 (1.46") Model 1925 and CAIL Model 1933 - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "Germany 3.7 cm/57 (1.5") Flak M43 - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ Foss, Christopher (1977). Jane's pocket book of towed artillery. New York: Collier. p. 27. ISBN 0020806000. OCLC 911907988.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "Russia / USSR 37 mm/67 (1.5") 70-K - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "United Kingdom / Britain 2-pdr QF Mark VIII - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ DiGiulian, Tony. "USA Bofors 40 mm/60 Model 1936 - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
Bibliography
- Bagnasco, Erminio. Le armi delle navi italiane nella Seconda Guerra Mondiale. Parma, Albertelli, 1978 (2007 ed.) ISBN 88-87372-40-3
- Campbell, John (1985). Naval Weapons of World War II. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-459-4.
- Gander, Terry and Chamberlain, Peter. Weapons of the Third Reich: An Encyclopedic Survey of All Small Arms, Artillery and Special Weapons of the German Land Forces 1939-1945. New York: Doubleday, 1979 ISBN 0-385-15090-3
