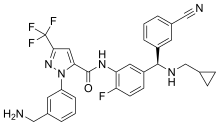
Berotralstat
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Orladeyo |
| Other names | BCX7353, BCX-7353 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Plasma kallikrein inhibitor |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H26F4N6O |
| Molar mass | 562.573 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Berotralstat, sold under the brand name Orladeyo, is a medication used to prevent attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in people aged twelve years and older.[3][5][7][8][4]
The most common side effects include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, back pain, and heartburn.[4]
Berotralstat was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2020,[3][4][9] and in the European Union in April 2021.[5]
History
Berotralstat was approved based on evidence from one clinical trial (Trial 1 /NCT03485911) of 120 participants with hereditary angioedema.[4] The trial was conducted at 40 sites in the United States, the European Union, and Canada.[4] Trial investigators evaluated participants 12 years and older[10] with hereditary angioedema for eight weeks to determine the number of attacks for each participant.[4] The trial enrolled only participants who had at least two attacks during the eight-week period.[4] Participants were assigned to receive one of two doses of berotralstat or placebo once every day for 24 weeks.[4] Neither the participants nor the investigators knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was completed.[4] All participants could use other medications for treatment of attacks.[4]
References
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision - Orladeyo". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 28 November 2022.
- ^ Product monograph hres.ca
- ^ a b c "Orladeyo- berotralstat hydrochloride capsule". DailyMed. Retrieved 25 December 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Drug Trials Snapshot: Orladeyo". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 3 December 2020. Retrieved 25 December 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c "Orladeyo EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 24 February 2021. Retrieved 12 July 2021.
- ^ "Orladeyo Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ Hwang JR, Hwang G, Johri A, Craig T (December 2019). "Oral plasma kallikrein inhibitor BCX7353 for treatment of hereditary angioedema". Immunotherapy. 11 (17): 1439–1444. doi:10.2217/imt-2019-0128. PMID 31635497.
- ^ Zuraw B, Lumry WR, Johnston DT, Aygören-Pürsün E, Banerji A, Bernstein JA, et al. (October 2020). "Oral once-daily berotralstat for the prevention of hereditary angioedema attacks: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 148 (1): 164–172.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.015. PMID 33098856.
- ^ "Orladeyo: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 25 December 2020.
- ^ "Berotralstat (Oral Route) Side Effects - Mayo Clinic". www.mayoclinic.org. Retrieved 3 March 2021.
External links
- "Berotralstat". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT03485911 for "Efficacy and Safety Study of BCX7353 as an Oral Treatment for the Prevention of Attacks in HAE (APeX-2)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
