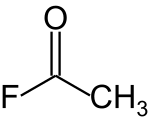
Acetyl fluoride

| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Acetyl fluoride | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Ethanoyl fluoride | |
| Other names Methylcarbonyl fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.354 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3FO | |
| Molar mass | 62.043 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.032 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −84 °C (−119 °F; 189 K) |
| Boiling point | 21 °C (70 °F; 294 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Acetyl fluoride is an acyl halide with the chemical formula CH3COF.[2] The formula is commonly abbreviated AcF. This chemical is corrosive. This chemical can be known as Acetyl fluoride, 557-99-3 or Methylcarbonyl fluouride. It carries a oxo group at position 1.[3]
Synthesis
Acetyl fluoride is synthesized using hydrogen fluoride and acetic anhydride. Acetic acid is produced as a byproduct.[4]
- HF + (CH
3CO)
2O → CH
3CO
2H + CH
3COF
See also
References
- ^ "Acetyl fluoride". Archived from the original on 2014-03-28. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
- ^ "Acetyl Fluoride". NIST. Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 7 March 2012.
- ^ PubChem. "Acetyl fluoride". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2023-11-14.
- ^ Tanaka, Mutsuo; Fujiwara, Masahiro; Ando, Hisanori (1995). "Dual Reactivity of the Formyl Cation as an Electrophile and a Bransted Acid in Superacids". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 60 (12): 3846–3850. doi:10.1021/jo00117a041.
