Acacetin
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
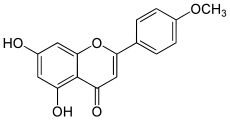
| IUPAC name 5,7-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Linarigenin Acacetine Buddleoflavonol Linarisenin 4′-Methoxyapigenin Apigenin 4′-methyl ether 5,7-Dioxy-4′-methoxyflavone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.867 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 284.26 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Acacetin is a 4′-O-methylated flavone of the parent compound apigenin, found in Robinia pseudoacacia (black locust), Turnera diffusa (damiana), Betula pendula (silver birch),[1] and in the fern Asplenium normale.[2]
In plant synthesis the enzyme apigenin 4′-O-methyltransferase uses S-adenosyl methionine and 5,7,4′-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin) to produce S-adenosylhomocysteine and 4′-methoxy-5,7-dihydroxyflavone (acacetin).
It shows moderate aromatase inhibition.[3]
See also
- Genkwanin (methoxylated apigenin)
- Thevetiaflavone (methoxylated apigenin)
References
- ^ Valkama, E; Salminen, J-P; Koricheva, J; Pihlaja, K (2004). "Changes in leaf trichomes and epicuticular flavonoids during leaf development in three birch taxa". Annals of Botany. 94 (2): 233–242. doi:10.1093/aob/mch131. PMC 4242156. PMID 15238348.
- ^ UmiKalsom, Yusuf; Harborne, Jeffrey B. (1991). "Flavonoid distribution in asplenioid ferns". Pertanika. 14 (3): 297–300.
- ^ Zhao, J; Dasmahapatra, AK; Khan, SI; Khan, IA (December 2008). "Anti-aromatase activity of the constituents from damiana (Turnera diffusa)". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 120 (3): 387–393. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2008.09.016. PMID 18948180.
