2007 Peru earthquake
 Piles of rubble, one week after the shock | |
 Map of the Peru coastline, showing location and strength of quake. Star marks epicenter. | |
| UTC time | 2007-08-15 23:40:57 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 12804735 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | August 15, 2007 |
| Local time | 18:40:57 |
| Duration | 2 minutes |
| Magnitude | 8.0 Mw |
| Depth | 39 km (24 mi) |
| Epicenter | 13°21′14″S 76°30′32″W / 13.354°S 76.509°W |
| Type | Megathrust |
| Areas affected | Ica Region (Pisco, Ica and Chincha Alta) and Lima Region (San Vicente de Cañete) |
| Max. intensity | MMI XI (Extreme)[1] |
| Tsunami | flooded part of Lima's Costa Verde highway, and much of Pisco's shore |
| Casualties | 595 dead, 2,291 injured[2][3] |
The 2007 Peru earthquake, which measured 8.0 on the moment magnitude scale,[4] hit the central coast of Peru on August 15 at 23:40:57 UTC (18:40:57 local time) and lasted two minutes.[4][5] The epicenter was located 150 km (93 mi) south-southeast of Lima at a depth of 39 km (24 mi).[4] At least 595 people died and over 2,290 people were injured.[2]
Earthquake
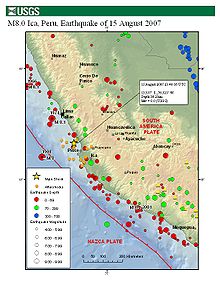
This earthquake occurred at the boundary between the Nazca and South American tectonic plates, which are converging at a rate of 78 mm (3.1 in) per year.[6] The earthquake occurred as thrust faulting on the interface between the two plates, with the South American plate moving up and seaward over the Nazca plate. Experts say this kind of earthquake is produced about once every 100 years.[7] The earthquake had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity (MMI) of XI (Extreme) assigned at two areas of the Pan-American Highway which was severely damaged at 30 km (19 mi) and 190 km (120 mi) from the epicenter, respectively.[1] MMI IX (Violent) assigned to the Pisco-Chincha Alta area.[8]
Coastal Peru has a history of very large earthquakes. The August 15th shock originated near the source of two previous earthquakes, both in the magnitude 8 range, which occurred in 1908 and 1974. This earthquake is south of the source of a magnitude 8.2 earthquake that occurred in northern Peru on October 17, 1966, and north of a magnitude 8.4 earthquake that occurred in 2001 near Arequipa in southern Peru. The largest earthquake along the coast of Peru was a magnitude 9 that occurred in 1868 in Arica. It produced a tsunami that killed several thousand people along the Peruvian coast and also caused damage in Hawaii.[4]
Damage
The cities of Pisco, Ica and Chincha Alta in the Ica Region, and San Vicente de Cañete in the Lima Region were most affected. The earthquake was also felt in the capital Lima, where the quake broke windows in downtown sectors of the city, as well as various other Peruvian cities, including Pucallpa, Iquitos, Contamana, Trujillo and Cajamarca. Some people were attending mass at the time the earthquake started. The city of Pisco, which is 260 km (160 mi) southeast of Lima, suffered the most damage, with its buildings about 85% destroyed and as many as 430 residents died; 148 of those deaths occurred when the cathedral collapsed in the city's main square.[9]
On August 16, the government reported 510 deaths.[10][11] The final losses were the following in total:
- 595 people dead;[2]
- 2,291 injured;[2]
- 58,581 houses destroyed according to Peruvian Government preliminary assessments;
- 13,585 houses affected;
- 103 hospitals affected; and
- 14 hospitals destroyed according to Peruvian Government preliminary assessments.[12]
Aftershocks
A magnitude 5.8 aftershock occurred at 19:02 local time, centered 113 km (70 mi) northeast of Chincha Alta.[13] At 19:19 local time, another 5.9 magnitude aftershock occurred, centered 48 km (30 mi) south-southwest of Ica.[13] At least a dozen aftershocks of magnitude 5.0 or greater have been recorded.[14][15]
The day after, survivors who could not be accommodated in local hospitals in Pisco were taken to Lima by airplane, arriving there later that night. On Sunday, August 19, the President of Colombia, Álvaro Uribe, arrived in Ica.[citation needed]
Tsunami warnings

A tsunami warning was issued for Peru, Ecuador, Chile, Colombia and even as far as Hawaii following the earthquakes, but was later cancelled.[16] Some areas of the port city of Callao were evacuated. Tsunami warnings were also made for Panama and Costa Rica, and a tsunami watch was posted for Nicaragua, Guatemala, El Salvador, Mexico and Honduras. All alerts were cancelled after a 25-centimetre (10 in) wave came ashore.[17] A tsunami did occur on the Peruvian coast. It flooded part of Lima's Costa Verde highway, and much of Pisco's shore. It has been reported that the tsunami reached as high as 5 m (16 ft) in the zone of Lagunillas in Pisco neighbourhood's town Paracas, with a maximum height of 10.05 m (33.0 ft) in Yumaque. The fishing village of Lagunilla was completely destroyed by the tsunami, resulting in 3 deaths out of 7 inhabitants; however, survivors reported no significant earthquake damage.[18][5]
The Japan Meteorological Agency issued a tsunami warning, projecting that waves higher than 20 cm (7.9 in) could reach Japan's northern island, Hokkaidō, on Thursday, August 16, around 19:00 UTC (Friday, 04:00 JST).[19]
Response
The Government of Peru led the response to the earthquake through the National Institute of Civil Defence (INDECI). It was supported by the military, the private sector (local, national and international) and by contributions from civil society and the international community, including governments, international NGOs and UN agencies. The initial response entailed searching for survivors, evacuating the injured, removing rubble, ensuring security and meeting the needs of affected people. Shelter was provided for those that had lost their homes, latrines were installed, clean water and medical services were established, food aid was distributed and education and psychosocial support was offered, especially to children. A Consolidated Appeals Process (CAP) in the wake of the earthquake raised approximately $37 million, $9.5m of which was provided by the Central Emergency Response Fund (CERF).
Despite the considerable relief effort, the initial response was chaotic, marked by a lack of coordination and inadequate information on the needs of people on the ground. It was hindered by a lack of capacity at the regional level and consequent political wrangling (particularly between the local, regional and national governments).[20] Many local authorities were personally attacked for the earthquake, as survivors tried to find close relatives or overcome the traumatic shock of losing so many family members. As time passed the response became better organised, particularly once an OCHA coordination office was established in Pisco and a UN Disaster Assessment and Coordination (UNDAC) team arrived to support coordination and provide technical advice.
Aftermath
Several years on, Pisco is still feeling the effects of the earthquake and is struggling to recover. Many families who lost their homes are still living in temporary housing or tents. The social/economic impacts of the quake may take many years to heal.[21]
See also
References
- ^ a b Panjamani Anbazhagan; Sushma Srinivas; Deepu Chandran (2011). "Classification of road damage due to earthquakes". Nat Hazards. 60. Springer Science: 425–460. doi:10.1007/s11069-011-0025-0. Retrieved 16 June 2024.
- ^ a b c d "Hoy, hace seis años, Pisco fue sacudido por un terremoto de 7.9 grados" (in Spanish). 15 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017.
- ^ "Peru Civil Defense Updates Damages". 2007-09-14. Retrieved 2007-09-14.
- ^ a b c d "Magnitude 8.0 – Near the Coast of Central Peru". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on 18 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
- ^ a b "Preliminar Report" (PDF). Peruvian Geophysics Institute. 2007-08-15. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-08.
- ^ Alex K. Tang, P.E. and Jorgen Johansson, ed. (2008). Pisco, Peru, Earthquake of August 15, 2007: Lifeline Performance. Reston, VA: ASCE, Technical Council on Lifeline Earthquake Engineering. ISBN 9780784410615. Archived from the original on November 14, 2012. Retrieved July 18, 2012.
- ^ Europa Press. "Perú.- Un terremoto de gran intensidad podría registrar en breve algún punto de la geografía peruana, según un experto" (in Spanish). Lukor. Archived from the original on 26 September 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
- ^ "M 8.0 – 41 km SW of San Vicente de Cañete, Peru". United States Geological Survey. 15 August 2007. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Barrionuevo, Alexei (2007-08-25). "Quake Orphan reflects Peru's Loss and Anger". The New York Times. Retrieved 2007-08-24.
- ^ "Earthquake in Peru kills hundreds". Reuters. 2007-08-16. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ "Scores killed by Peru earthquake". BBC News. 2007-08-16. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ ""Earthquake in Peru: Situation Report No. 20," United Nations Country Team Peru". Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
- ^ a b "Deadly Earthquake Strikes Peru". CNN. 2007-08-15. Archived from the original on 16 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ "Earthquake List for Map of South America". United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on 26 August 2007. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ "Instituto Geofísico informó de unas 70 réplicas tras el terremoto" (in Spanish). Peru21. Retrieved 2007-08-15. [dead link]
- ^ "Tsunami warnings issued after earthquake in Peru". Reuters. 2007-08-16. Retrieved 2007-08-15.
- ^ "Death toll from Peru earthquake rises to at least 330". Belfast Telegraph. 2007-08-16. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ "Tsunami Event: PISCO, PERU". NGDC.
- ^ "Tsunamis caused by Peru earthquake might reach Japan". Japan News Review. Archived from the original on 2007-10-16. Retrieved 2007-08-16.
- ^ Elhawary and Castillo. "The role of the affected state: a case study on the Peruvian earthquake response". Overseas Development Institute. Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2008-08-14.
- ^ "Report" Archived 2019-08-20 at the Wayback Machine, Pisco Sin Fronteras Website
External links
- Perú earthquake: Videos Archived 2018-12-16 at the Wayback Machine
- The International Seismological Centre has a bibliography and/or authoritative data for this event.
- ReliefWeb's main page for this event.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
