Yemen
Republic of Yemen ٱلْجُمْهُورِيَّةُ ٱلْيَمَنِيَّةُ (Arabic) al-Jumhūriyyatu l-Yamaniyyatu (formal) al-Jumhūriyyah l-Yamaniyyah (informal) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: ٱللَّهُ، ثُمَّ ٱلْوَطَنُ، ٱلثَوْرَةُ، ٱلْوَحْدَةُ Allāhu, thumma l-Waṭanu, ath-Thawratu, al-Waḥdatu "God, then Country, Revolution, Unity" | |
| Anthem: الجمهورية المتحدة al-Jumhūriyyatu l-Muttaḥidatu "United Republic" | |
| Status | |
| Capital and largest city | Sanaa[n 1] 15°20′54″N 44°12′23″E / 15.34833°N 44.20639°E |
| Capital-in-exile | Aden[n 2] |
| Official language and national language | Arabic[2] |
| Ethnic groups (2000)[3] | 92.8% Arabs 3.7% Somalis 3.5% other |
| Religion (2020),[4] also see Religion in Yemen | |
| Demonym(s) | Yemeni Yemenite |
| Government | Unitary provisional republic |
• Chairman of the Presidential Leadership Council | Rashad al-Alimi (disputed)[n 3] |
| Ahmad Awad bin Mubarak (disputed)[n 4] | |
| Sultan al-Barakani | |
| Ahmed Obaid Bin Dagher | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Shura Council | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
| 22 May 1990 | |
| 16 May 1991 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 455,503[5] km2 (175,871 sq mi) (49th) |
• Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | 34,449,825[6] |
• Density | 65.0/km2 (168.3/sq mi) (152nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2014) | 36.7[8] medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | low (186th) |
| Currency | Yemeni rial (YER) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Drives on | right[10] |
| Calling code | +967 |
| ISO 3166 code | YE |
| Internet TLD | .ye, اليمن. |
Yemen,[a] officially the Republic of Yemen,[b] is a country in West Asia.[11] Located in southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to the north, Oman to the northeast, the Red Sea to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south, sharing maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia across the Horn of Africa. Covering roughly 455,000 square kilometres (176,000 square miles),[5] with a coastline of approximately 2,000 kilometres (1,200 miles), Yemen is the second largest country on the Arabian Peninsula.[12] Sanaa is its constitutional capital and largest city. Yemen's estimated population is 34.7 million, mostly Arab Muslims.[13] It is a member of the Arab League, the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Owing to its geographic location, Yemen has been at the crossroads of many civilisations for over 7,000 years. In 1200 BCE, the Sabaeans formed a thriving commercial kingdom that included parts of modern Ethiopia and Eritrea.[14][15][16] In 275 CE, it was succeeded by the Himyarite Kingdom, which spanned much of Yemen's present-day territory and was heavily influenced by Judaism.[17] Christianity arrived in the fourth century, followed by the rapid spread of Islam in the seventh century. Yemenite troops played a crucial role in early Islamic conquests.[18] Various dynasties emerged between the 9th and 16th centuries.[19] During the 19th century, the country was divided between the Ottoman and British empires. After World War I, the Kingdom of Yemen was established, which in 1962 became the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen) following a coup. In 1967, the British Aden Protectorate became the independent People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (South Yemen), the first and only officially socialist state in the Arab world. In 1990, the two Yemeni states united to form the modern Republic of Yemen, with Ali Abdullah Saleh serving as the first president until his resignation in 2012 in the wake of the Arab Spring.[20][21]
Since 2011, Yemen has been enduring a political crisis, marked by street protests against poverty, unemployment, corruption, and President Saleh's plan to amend Yemen's constitution and eliminate the presidential term limit.[22] By 2015, the country became engulfed by an ongoing civil war with multiple entities vying for governance, including the Presidential Leadership Council of the internationally recognized government, and the Houthi movement's Supreme Political Council. This conflict, which has escalated to involve various foreign powers, has led to a severe humanitarian crisis.[23][24][25][26][27][28]
Yemen is one of the least developed countries in the world,[29] facing significant obstacles to sustainable development,[30] and is one of the poorest countries in the Middle East and North Africa.[31] In 2019, the United Nations reported that Yemen had the highest number of people in need of humanitarian aid, amounting to about 24 million individuals, or nearly 75% of its population.[32] As of 2020, Yemen ranked highest on the Fragile States Index[33] and second-worst on the Global Hunger Index, surpassed only by the Central African Republic.[33] Additionally, it has the lowest Human Development Index out of all non-African countries.
Etymology
The term Yamnat was first mentioned in the Old South Arabian inscriptions on the title of one of the kings of the second Himyarite Kingdom known as Shammar Yahri'sh. The term probably referred to the southwestern coastline of the Arabian Peninsula and the southern coastline between Aden and Hadhramaut.[34][35] Historical Yemen included much greater territory than the current nation, stretching from northern 'Asir in southwestern Saudi Arabia to Dhofar in southern Oman.[36][37]
One etymology derives Yemen from ymnt, meaning literally "South [of the Arabian Peninsula]", and significantly plays on the notion of the land to the right (𐩺𐩣𐩬).[38] Other sources claim that Yemen is related to yamn or yumn, meaning "felicity" or "blessed", as much of the country is fertile, in contrast to the barren land of most of Arabia.[39][40] The Romans called it Arabia Felix ("happy" or "fortunate" Arabia"), as opposed to Arabia Deserta ("deserted Arabia"). Latin and Greek writers referred to ancient Yemen as "India", which arose from the Persians calling the Abyssinians whom they came into contact with in South Arabia by the name of the black-skinned people who lived next to them.[41][42]
History
Yemen has existed at the crossroads of its civilisations for more than 7,000 years. The country was home to figures such as the Queen of Sheba who brought a caravan of gifts for King Solomon. For centuries, it became a primary producer of coffee exported in the port of Mocha. From its conversion to Islam in the 7th century, Yemen became a center of Islamic learning, and much of its architecture survived until modern times.
Ancient history

With its long sea border between eastern and western civilizations, Yemen has long existed at a crossroads of cultures with a strategic location in terms of trade on the west of the Arabian Peninsula. Large settlements for their era existed in the mountains of northern Yemen as early as 5000 BC.[43] The Sabaean Kingdom came into existence in at least the 12th century BC.[44] The four major kingdoms or tribal confederations in South Arabia were Saba, Hadhramaut, Qataban, and Ma'in.
Sabaʾ (Arabic: سَـبَـأ)[45][46] is thought to be biblical Sheba and was the most prominent federation.[47] The Sabaean rulers adopted the title Mukarrib generally thought to mean unifier,[48] or a priest-king,[49] or the head of the confederation of South Arabian kingdoms, the "king of the kings".[50] The role of the Mukarrib was to bring the various tribes under the kingdom and preside over them all.[51] The Sabaeans built the Great Dam of Marib around 940 BC.[52] The dam was built to withstand the seasonal flash floods surging down the valley.
By the third century BC, Qataban, Hadhramaut, and Ma'in became independent from Saba and established themselves in the Yemeni arena. Minaean rule stretched as far as Dedan,[53] with their capital at Baraqish. The Sabaeans regained their control over Ma'in after the collapse of Qataban in 50 BC. By the time of the Roman expedition to Arabia Felix in 25 BC, the Sabaeans were once again the dominating power in Southern Arabia.[54] Aelius Gallus was ordered to lead a military campaign to establish Roman dominance over the Sabaeans.[55]
The Romans had a vague and contradictory geographical knowledge about Arabia Felix. A Roman army of 10,000 men was defeated before reaching Marib.[56] Strabo's close relationship with Aelius Gallus led him to attempt to justify his friend's defeat in his writings. It took the Romans six months to reach Marib and 60 days to return to Egypt. The Romans blamed their Nabataean guide and executed him for treachery.[57] No direct mention in Sabaean inscriptions of the Roman expedition has yet been found.
After the Roman expedition (perhaps earlier) the country fell into chaos, and two clans, namely Hamdan and Himyar, claimed kingship, assuming the title King of Sheba and Dhu Raydan.[58] Dhu Raydan, i.e., Himyarites, allied themselves with Aksum in Ethiopia against the Sabaeans.[59] The chief of Bakil and king of Saba and Dhu Raydan, El Sharih Yahdhib, launched successful campaigns against the Himyarites and Habashat, i.e., Aksum. El Sharih took pride in his campaigns and added the title Yahdhib to his name, which means "suppressor"; he used to kill his enemies by cutting them to pieces.[60] Sana'a came into prominence during his reign, as he built the Ghumdan Palace as his place of residence.


The Himyarites annexed Sana'a from Hamdan around 100 AD.[61] Hashdi tribesmen rebelled against them and regained Sana'a around 180.[62] Shammar Yahri'sh had conquered Hadhramaut, Najran, and Tihamah by 275, thus unifying Yemen and consolidating Himyarite rule.[63][64] The Himyarites rejected polytheism and adhered to a consensual form of monotheism called Rahmanism.[65]
In 354, Roman Emperor Constantius II sent an embassy headed by Theophilos the Indian to convert the Himyarites to Christianity.[66] According to Philostorgius, the mission was resisted by local Jews.[67] Several inscriptions have been found in Hebrew and Sabaean praising the ruling house in Jewish terms for "...helping and empowering the People of Israel."[68]
According to Islamic traditions, King As'ad the Perfect mounted a military expedition to support the Jews of Yathrib.[69] Abu Kariba As'ad, as known from the inscriptions, led a military campaign to central Arabia or Najd to support the vassal Kingdom of Kinda against the Lakhmids.[70] However, no direct reference to Judaism or Yathrib was discovered from his lengthy reign. Abu Kariba died in 445, having reigned for almost 50 years.[71] By 515, Himyar became increasingly divided along religious lines and a bitter conflict between different factions paved the way for an Aksumite intervention. The last Himyarite king Ma'adikarib Ya'fur was supported by Aksum against his Jewish rivals. Ma'adikarib was Christian and launched a campaign against the Lakhmids in southern Iraq, with the support of other Arab allies of Byzantium.[72] The Lakhmids were a bulwark of Persia, which was intolerant to a proselytizing religion like Christianity.[73]
After the death of Ma'adikarib Ya'fur around 521, a Himyarite Jewish warlord called Dhu Nuwas rose to power. Emperor Justinian I sent an embassy to Yemen. He wanted the officially Christian Himyarites to use their influence on the tribes in inner Arabia to launch military operations against Persia. Justinian I bestowed the "dignity of king" upon the Arab sheikhs of Kindah and Ghassan in central and northern Arabia.[74] From early on, Roman and Byzantine policy was to develop close links with the powers of the coast of the Red Sea. They were successful in converting[clarification needed] Aksum and influencing their culture. The results concerning to Yemen were rather disappointing.[74]
A Kendite prince called Yazid bin Kabshat rebelled against Abraha and his Arab Christian allies. A truce was reached once the Great Dam of Marib had suffered a breach.[75] Abraha died around 570. The Sasanid Empire annexed Aden around 570. Under their rule, most of Yemen enjoyed great autonomy except for Aden and Sana'a. This era marked the collapse of ancient South Arabian civilization, since the greater part of the country was under several independent clans until the arrival of Islam in 630.[76]
Middle Ages
Advent of Islam and the three dynasties

Muhammad sent his cousin Ali to Sana'a and its surroundings around 630. At the time, Yemen was the most advanced region in Arabia.[77] The Banu Hamdan confederation was among the first to accept Islam. Muhammad sent Muadh ibn Jabal, as well to Al-Janad, in present-day Taiz, and dispatched letters to various tribal leaders.[78] Major tribes, including Himyar, sent delegations to Medina during the "year of delegations" around 630–631. Several Yemenis accepted Islam before 630, such as Ammar ibn Yasir, Al-Ala'a Al-Hadrami, Miqdad ibn Aswad, Abu Musa Ashaari, and Sharhabeel ibn Hasana. A man named 'Abhala ibn Ka'ab Al-Ansi expelled the remaining Persians and claimed he was a prophet of Rahman. He was assassinated by a Yemeni of Persian origin called Fayruz al-Daylami. Christians, who were mainly staying in Najran along with Jews, agreed to pay jizyah (Arabic: جِـزْيَـة), although some Jews converted to Islam, such as Wahb ibn Munabbih and Ka'ab al-Ahbar.
Yemen was stable during the Rashidun Caliphate. Yemeni tribes played a pivotal role in the Islamic expansion into Egypt, Iraq, Persia, the Levant, Anatolia, North Africa, Sicily, and Andalusia.[79][80][81] Yemeni tribes who settled in Syria contributed significantly to the solidification of Umayyad rule, especially during the reign of Marwan I. Powerful Yemenite tribes such as Kinda were on his side during the Battle of Marj Rahit.[82][83]
Muhammad ibn Abdullah ibn Ziyad founded the Ziyadid dynasty in Tihamah around 818. The state stretched from Haly (in present-day Saudi Arabia) to Aden. They nominally recognized the Abbasid Caliphate but ruled independently from Zabid.[84] By virtue of its location, they developed a special relationship with Abyssinia. The chief of the Dahlak islands exported slaves, as well as amber and leopard hides, to the ruler of Yemen.[85] They controlled only a small portion of the coastal strip in Tihamah along the Red Sea, and never exercised control over the highlands and Hadhramaut.[86] A Himyarite clan called the Yufirids established their rule over the highlands from Saada to Taiz, while Hadhramaut was an Ibadi stronghold and rejected all allegiance to the Abbasids in Baghdad.[84]
The first Zaidi imam, Yahya ibn al-Husayn, arrived in Yemen in 893. He was a religious cleric and judge who was invited to come to Saada from Medina to arbitrate tribal disputes.[87] Yahya persuaded local tribesmen to follow his teachings. The sect slowly spread across the highlands, as the tribes of Hashid and Bakil, later known as "the twin wings of the imamate", accepted his authority.[88] He founded the Zaidi imamate in 897. Yahya established his influence in Saada and Najran. He also tried to capture Sana'a from the Yufirids in 901 but failed miserably.
Sulayhid dynasty (1047–1138)
The Sulayhid dynasty was founded in the northern highlands around 1040; at the time, Yemen was ruled by different local dynasties. In 1060, Ali ibn Muhammad Al-Sulayhi conquered Zabid and killed its ruler Al-Najah, founder of the Najahid dynasty. His sons were forced to flee to Dahlak.[89] Hadhramaut fell into Sulayhid hands after their capture of Aden in 1162.[90]
By 1063, Ali had subjugated Greater Yemen.[91] He then marched toward Hejaz and occupied Makkah.[92] Ali was married to Asma bint Shihab, who governed Yemen with her husband.[93] The Khutba during Friday prayers was proclaimed in both her husband's name and hers. No other Arab woman had this honor since the advent of Islam.[93]
Ali al-Sulayhi was killed by Najah's sons on his way to Mecca in 1084. His son Ahmed Al-Mukarram led an army to Zabid and killed 8,000 of its inhabitants.[94] He later installed the Zurayids to govern Aden. al-Mukarram, who had been afflicted with facial paralysis resulting from war injuries, retired in 1087 and handed over power to his wife Arwa al-Sulayhi.[95] Queen Arwa moved the seat of the Sulayhid dynasty from Sana'a to Jibla, a small town in central Yemen near Ibb. She sent Ismaili missionaries to India, where a significant Ismaili community was formed that exists to this day.[96]
Queen Arwa continued to rule securely until her death in 1138.[96] She is still remembered as a great and much-loved sovereign, as attested in Yemeni historiography, literature, and popular lore, where she is referred to as Balqis al-sughra ("the junior queen of Sheba").[97] Shortly after Arwa's death, the country was split between five competing petty dynasties along religious lines.[98] The Ayyubid dynasty overthrew the Fatimid Caliphate in Egypt. A few years after their rise to power, Saladin dispatched his brother Turan Shah to conquer Yemen in 1174.[99]
Ayyubid conquest (1171–1260)
Turan Shah conquered Zabid from the Mahdids in 1174, then marched toward Aden in June and captured it from the Zurayids.[100] The Hamdanid sultans of Sana'a resisted the Ayyubid in 1175, and the Ayyubids did not manage to secure Sana'a until 1189.[101] The Ayyubid rule was stable in southern and central Yemen, where they succeeded in eliminating the ministates of that region, while Ismaili and Zaidi tribesmen continued to hold out in several fortresses.[101]
The Ayyubids failed to capture the Zaydis stronghold in northern Yemen.[102] In 1191, Zaydis of Shibam Kawkaban rebelled and killed 700 Ayyubid soldiers.[103] Imam Abdullah bin Hamza proclaimed the imamate in 1197 and fought al-Mu'izz Ismail, the Ayyubid Sultan of Yemen. Imam Abdullah was defeated at first but was able to conquer Sana'a and Dhamar in 1198,[104] and al-Mu'izz Ismail was assassinated in 1202.[105]
Abdullah bin Hamza carried on the struggle against the Ayyubid until his death in 1217. After his demise, the Zaidi community was split between two rival imams. The Zaydis were dispersed, and a truce was signed with the Ayyubid in 1219.[106] The Ayyubid army was defeated in Dhamar in 1226.[106] Ayyubid Sultan Mas'ud Yusuf left for Mecca in 1228, never to return.[107] Other sources suggest that he was forced to leave for Egypt instead in 1223.[108]
Rasulid dynasty (1229–1454)

The Rasulid dynasty was established in 1229 by Umar ibn Rasul, who was appointed deputy governor by the Ayyubids in 1223. When the last Ayyubid ruler left Yemen in 1229, Umar stayed in the country as caretaker. He subsequently declared himself an independent king by assuming the title "al-Malik Al-Mansur" (the king assisted by Allah).[108]
Umar first established himself at Zabid, then moved into the mountainous interior, taking the important highland centre Sana'a. However, the Rasulid capitals were Zabid and Taiz. He was assassinated by his nephew in 1249.[107] Omar's son Yousef defeated the faction led by his father's assassins and crushed several counterattacks by the Zaydi imams who still held on in the northern highland. Mainly because of the victories he scored over his rivals, he assumed the honorific title "al-Muzaffar" (the victorious).[109]
After the fall of Baghdad to the Mongols in 1258, al-Muzaffar Yusuf I appropriated the title of caliph.[109] He chose the city of Taiz to become the political capital of the kingdom because of its strategic location and proximity to Aden.[110] The Rasulid sultans built numerous Madrasas to solidify the Shafi'i school of thought, which is still the dominant school of jurisprudence amongst Yemenis today.[111] Under their rule, Taiz and Zabid became major international centres of Islamic learning.[112] The kings were educated men in their own right, who not only had important libraries but also wrote treatises on a wide array of subjects, ranging from astrology and medicine to agriculture and genealogy.[110]

They had a difficult relationship with the Mamluks of Egypt because the latter considered them a vassal state.[110] Their competition centred over the Hejaz and the right to provide kiswa of the Ka'aba in Mecca.[110] The dynasty became increasingly threatened by disgruntled family members over the problem of succession, combined with periodic tribal revolts, as they were locked in a war of attrition with the Zaydi imams in the northern highlands.[112] During the last 12 years of Rasulid rule, the country was torn between several contenders for the kingdom. The weakening of the Rasulid provided an opportunity for the Banu Taher clan to take over and establish themselves as the new rulers of Yemen in 1454 AD.[111]
Tahirid dynasty (1454–1517)

The Tahirids were a local clan based in Rada'a. They built schools, mosques, and irrigation channels, as well as water cisterns and bridges in Zabid, Aden, Rada'a, and Juban. Their best-known monument is the Amiriya Madrasa in Rada' District, which was built in 1504.[113] The Tahirids were too weak either to contain the Zaydi imams or to defend themselves against foreign attacks.
Realizing how rich the Tahirid realm was, the Mamluks decided to conquer it.[114] The Mamluk army, with the support of forces loyal to Zaydi Imam Al-Mutawakkil Yahya Sharaf ad-Din, conquered the entire Tahirid realm but failed to capture Aden in 1517. The Mamluk victory was short-lived. The Ottoman Empire conquered Egypt, hanging the last Mamluk Sultan in Cairo.[114] The Ottomans had not decided to conquer Yemen until 1538. The Zaydi highland tribes emerged as national heroes[115] by offering stiff, vigorous resistance to the Turkish occupation.[116] The Mamluks tried to attach Yemen to Egypt and the Portuguese led by Afonso de Albuquerque, occupied the island of Socotra and made an unsuccessful attack on Aden in 1513.[117]
Portuguese
Starting in the 15th century, Portugal intervened, dominating the port of Aden for about 20 years and maintaining a fortified enclave on the island of Socotra during this period. From the 16th century, the Portuguese posed an immediate threat to Indian Ocean trade. The Mamluks therefore sent an army under Hussein al-Kurdi to fight the intruders [118] The Mamluk sultan went to Zabid in 1515 and entered into diplomatic talks with the Tahiri sultan 'Amir bin Abdulwahab for money that would be needed for the jihad against the Portuguese. Instead of confronting them, the Mamluks, who were running out of food and water, landed on the coast of Yemen and began harassing the villagers of Tihamah to obtain the supplies they needed.
The interest of Portugal on the Red Sea consisted on the one hand of guaranteeing contacts with a Christian ally in Ethiopia and on the other of being able to attack Mecca and the Arab territories from the rear, while still having absolute dominance over trade of spices, the main intention was to dominate the commerce of the cities on the coast of Africa and Arabia.[119] To this end, Portugal sought to influence and dominate by force or persuasion all the ports and kingdoms that fought among themselves. It was common for Portugal to keep under its influence the Arab allies that were interested in maintaining independence from other Arab states in the region.[120]
Modern history
The Zaydis and Ottomans

The Ottomans had two fundamental interests to safeguard in Yemen: The Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, and the trade route with India in spices and textiles—both threatened, and the latter virtually eclipsed, by the arrival of the Portuguese in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea in the early 16th century.[121] Hadım Suleiman Pasha, the Ottoman governor of Egypt, was ordered to command a fleet of 90 ships to conquer Yemen. The country was in a state of incessant anarchy and discord as Pasha described it by saying:[122]
Yemen is a land with no lord, an empty province. It would be not only possible but easy to capture, and should it be captured, it would be master of the lands of India and send every year a great amount of gold and jewels to Constantinople.
Imam al-Mutawakkil Yahya Sharaf ad-Din ruled over the northern highlands including Sana'a, while Aden was held by the last Tahiride Sultan 'Amir ibn Dauod. Pasha stormed Aden in 1538, killing its ruler, and extended Ottoman authority to include Zabid in 1539 and eventually Tihamah in its entirety.[123] Zabid became the administrative headquarters of Yemen Eyalet.[123] The Ottoman governors did not exercise much control over the highlands. They held sway mainly in the southern coastal region, particularly around Zabid, Mocha, and Aden.[124] Of 80,000 soldiers sent to Yemen from Egypt between 1539 and 1547, only 7,000 survived.[125] The Ottoman accountant-general in Egypt remarked:[125]
We have seen no foundry like Yemen for our soldiers. Each time we have sent an expeditionary force there, it has melted away like salt dissolved in water.

The Ottomans sent yet another expeditionary force to Zabid in 1547, while Imam al-Mutawakkil Yahya Sharaf ad-Din was ruling the highlands independently. Yahya chose his son Ali to succeed him, a decision that infuriated his other son al-Mutahhar ibn Yahya.[126] Al-Mutahhar was lame, so he was not qualified for the imamate.[126] He urged Oais Pasha, the Ottoman colonial governor in Zabid, to attack his father.[127] Indeed, Ottoman troops supported by tribal forces loyal to Imam al-Mutahhar stormed Taiz and marched north toward Sana'a in August 1547. The Turks officially made Imam al-Mutahhar a Sanjak-bey with authority over 'Amran. Imam al-Mutahhar assassinated the Ottoman colonial governor and recaptured Sana'a, but the Ottomans, led by Özdemir Pasha, forced al-Mutahhar to retreat to his fortress in Thula. Özdemir Pasha effectively put Yemen under Ottoman rule between 1552 and 1560. Özdemir died in Sana'a in 1561 and was succeeded by Mahmud Pasha.
Mahmud Pasha was described by other Ottoman officials as a corrupt and unscrupulous governor, and he was displaced by Ridvan Pasha in 1564. By 1565, Yemen was split into two provinces, the highlands under the command of Ridvan Pasha and Tihamah under Murad Pasha. Imam al-Mutahhar launched a propaganda campaign in which he claimed that the prophet Mohammed came to him in a dream and advised him to wage jihad against the Ottomans.[128] Al-Mutahhar led the tribes to capture Sana'a from Ridvan Pasha in 1567. When Murad tried to relieve Sana'a, highland tribesmen ambushed his unit and slaughtered all of them.[129] Over 80 battles were fought. The last decisive encounter took place in Dhamar around 1568, in which Murad Pasha was beheaded and his head sent to al-Mutahhar in Sana'a.[129][130] By 1568, only Zabid remained under the possession of the Turks.[130]


In 1632, Al-Mu'ayyad Muhammad sent an expeditionary force of 1,000 men to conquer Mecca.[131] The army entered the city in triumph and killed its governor.[131] The Ottomans sent an army from Egypt to fight the Yemenites.[131] Seeing that the Turkish army was too numerous to overcome, the Yemeni army retreated to a valley outside Mecca.[132] Ottoman troops attacked the Yemenis by hiding at the wells that supplied them with water. This plan proceeded successfully, causing the Yemenis over 200 casualties, most from thirst.[132] The tribesmen eventually surrendered and returned to Yemen.[133] Al-Mu'ayyad Muhammad died in 1644. He was succeeded by Al-Mutawakkil Isma'il, another son of al-Mansur al-Qasim, who conquered Yemen in its entirety.[134][135][136][137]
Yemen became the sole coffee producer in the world.[138] The country established diplomatic relations with the Safavid dynasty of Persia, Ottomans of Hejaz, Mughal Empire in India, and Ethiopia, as well. In the first half of the 18th century, the Europeans broke Yemen's monopoly on coffee by smuggling coffee trees and cultivating them in their own colonies in the East Indies, East Africa, the West Indies, and Latin America.[139] The imamate did not follow a cohesive mechanism for succession, and family quarrels and tribal insubordination led to the political decline of the Qasimi dynasty in the 18th century.[140]
Great Britain and the nine regions

The British were looking for a coal depot to service their steamers en route to India. It took 700 tons of coal for a round-trip from Suez to Bombay. East India Company officials decided on Aden. The British Empire tried to reach an agreement with the Zaydi imam of Sana'a, permitting them a foothold in Mocha, and when unable to secure their position, they extracted a similar agreement from the Sultan of Lahej, enabling them to consolidate a position in Aden.[141] The British managed to occupy Aden and evicted the Sultan of Lahej from Aden and forced him to accept their "protection".[141] In November 1839, 5,000 tribesmen tried to retake the town but were repulsed and 200 were killed.
With emigrants from India, East Africa, and Southeast Asia, Aden grew into a world city. In 1850, only 980 Arabs were registered as original inhabitants of the city.[142] The English presence in Aden put them at odds with the Ottomans. The Turks asserted to the British that they held sovereignty over the whole of Arabia, including Yemen as the successor of Mohammed and the Chief of the Universal Caliphate.[143]
Ottoman return

The Ottomans were concerned about the British expansion from the British ruled subcontinent to the Red Sea and Arabia. They returned to the Tihamah in 1849 after an absence of two centuries.[144] Rivalries and disturbances continued among the Zaydi imams, between them and their deputies, with the ulema, with the heads of tribes, as well as with those who belonged to other sects. Some citizens of Sana'a were desperate to return law and order to Yemen and asked the Ottoman Pasha in Tihamah to pacify the country.[145] The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 strengthened the Ottoman decision to remain in Yemen.[146] By 1873, the Ottomans succeeded in conquering the northern highlands. Sana'a became the administrative capital of Yemen Vilayet.
The Ottomans learned from their previous experience and worked on the disempowerment of local lords in the highland regions. They even attempted to secularize the Yemeni society, while Yemenite Jews came to perceive themselves in Yemeni nationalist terms.[147] The Ottomans appeased the tribes by forgiving their rebellious chiefs and appointing them to administrative posts. They introduced a series of reforms to enhance the country's economic welfare. However, corruption was widespread in the Ottoman administration in Yemen. This was because only the worst of the officials were appointed because those who could avoid serving in Yemen did so.[148] The Ottomans had reasserted control over the highlands for a temporary duration.[144] The so-called Tanzimat reforms were considered heretic by the Zaydi tribes. In 1876, the Hashid and Bakil tribes rebelled against the Ottomans; the Turks had to appease them with gifts to end the uprising.[149]
The tribal chiefs were difficult to appease and an endless cycle of violence curbed Ottoman efforts to pacify the land. Ahmed Izzet Pasha proposed that the Ottoman army evacuate the highlands and confine itself to Tihamah, and not unnecessarily burden itself with continuing military operation against the Zaydi tribes.[148] Imam Yahya Hamidaddin led a rebellion against the Turks in 1904; the rebels disrupted the Ottoman ability to govern.[150] The revolts between 1904 and 1911 were especially damaging to the Ottomans, costing them as many as 10,000 soldiers and as much as 500,000 pounds per year.[151] The Ottomans signed a treaty with imam Yahya Hamidaddin in 1911. Under the treaty, Imam Yahya was recognized as an autonomous leader of the Zaydi northern highlands. The Ottomans continued to rule Shafi'i areas in the mid-south until their departure in 1918.
Mutawakkilite Kingdom

Imam Yahya hamid ed-Din al-Mutawakkil was ruling the northern highlands independently from 1911, from which he began a conquest of the Yemen lands. In 1925 Yahya captured al-Hudaydah from the Idrisids.[152] In 1927, Yahya's forces were about 50 km (30 mi) away from Aden, Taiz, and Ibb, and were bombed by the British for five days; the imam had to pull back.[153] Small Bedouin forces, mainly from the Madh'hij confederation of Marib, attacked Shabwah but were bombed by the British and had to retreat.
The Italian Empire was the first to recognize Yahya as the king of Yemen in 1926. This created a great deal of anxiety for the British, who interpreted it as recognition of Imam Yahya's claim to sovereignty over Greater Yemen, which included the Aden protectorate and Asir.[154] The Idrisis turned to Ibn Saud seeking his protection from Yahya. However, in 1932, the Idrisis broke their accord with Ibn Saud and went back to Yahya seeking help against Ibn Saud, who had begun liquidating their authority and expressed his desire to annex those territories into his own Saudi domain.[155][156] Yahya demanded the return of all Idrisi dominion.[155]
Negotiations between Yahya and Ibn Saud proved fruitless. After the 1934 Saudi-Yemeni war, Ibn Saud announced a ceasefire in May 1934.[157] Imam Yahya agreed to release Saudi hostages and the surrender of the Idrisis to Saudi custody. Imam Yahya ceded the three provinces of Najran, Asir, and Jazan for 20 years.[158] and signed another treaty with the British government in 1934. The imam recognized the British sovereignty over Aden protectorate for 40 years.[159] Out of fear for Hudaydah, Yahya did submit to these demands.
Colonial Aden

Starting in 1890, hundreds of Yemeni people from Hajz, Al-Baetha, and Taiz migrated to Aden to work at ports, and as labourers. This helped the population of Aden once again become predominantly Arab after, having been declared a free zone, it had become mostly foreigners. During World War II, Aden had increasing economic growth and became the second-busiest port in the world after New York City.[160] After the rise of labour unions, a rift was apparent between the sectors of workers and the first signs of resistance to the occupation started in 1943.[160] Muhammad Ali Luqman founded the first Arabic club and school in Aden, and was the first to start working towards a union.[161]
The Colony of Aden was divided into an eastern colony and a western colony. Those were further divided into 23 sultanates and emirates, and several independent tribes that had no relationships with the sultanates. The deal between the sultanates and Britain detailed protection and complete control of foreign relations by the British. The Sultanate of Lahej was the only one in which the sultan was referred to as His Highness.[162] The Federation of South Arabia was created by the British to counter Arab nationalism by giving more freedom to the rulers of the nations.[163]
The North Yemen Civil War inspired many in the south to rise against the British rule. The National Liberation Front (NLF) of Yemen was formed with the leadership of Qahtan Muhammad Al-Shaabi. The NLF hoped to destroy all the sultanates and eventually unite with the Yemen Arab Republic. Most of the support for the NLF came from Radfan and Yafa, so the British launched Operation Nutcracker, which completely burned Radfan in January 1964.[164]
Two states

Arab nationalism had an influence in some circles who opposed the lack of modernization efforts in the Mutawakkilite monarchy. This became apparent when Imam Ahmad bin Yahya died in 1962. He was succeeded by his son, but army officers attempted to seize power, sparking the North Yemen Civil War.[165] The Hamidaddin royalists were supported by Saudi Arabia, Britain, and Jordan (mostly with weapons and financial aid, but also with small military forces), whilst the military rebels were backed by Egypt. Egypt provided the rebels with weapons and financial assistance, but also sent a large military force to participate in the fighting. Israel covertly supplied weapons to the royalists to keep the Egyptian military busy in Yemen and make Nasser less likely to initiate a conflict in the Sinai. After six years of civil war, the military rebels formed the Yemen Arab Republic.[166]

The revolution in the north coincided with the Aden Emergency, which hastened the end of British rule in the south. On 30 November 1967, the state of South Yemen was formed, comprising Aden and the former Protectorate of South Arabia. This socialist state was later officially known as the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen and a programme of nationalisation was begun.[167]
Relations between the two Yemeni states fluctuated between peaceful and hostile. The South was supported by the Eastern bloc. The North, however, was not able to get the same connections. In 1972, the two states fought a war. The war was resolved with a ceasefire and negotiations brokered by the Arab League, where it was declared that unification would eventually occur. In 1978, Ali Abdullah Saleh was named as president of the Yemen Arab Republic.[168] After the war, the North complained about the South's help from foreign countries. This included Saudi Arabia.[169]
In 1979, fresh fighting between the two states resumed and efforts were renewed to bring about unification.[168] Thousands were killed in 1986 in the South Yemen Civil War. President Ali Nasser Muhammad fled to the north and was later sentenced to death for treason. A new government formed.[168]
Unification and civil war

In 1990, the two governments reached a full agreement on the joint governing of Yemen, and the countries were merged on 22 May 1990, with Saleh as president.[168] The president of South Yemen, Ali Salim al-Beidh, became vice president.[168] A unified parliament was formed and a unity constitution was agreed upon.[168] In the 1993 parliamentary election, the first held after unification, the General People's Congress won 122 of 301 seats.[170]: 309
After the invasion of Kuwait crisis in 1990, Yemen's president opposed military intervention from non-Arab states.[171] As a member of the United Nations Security Council for 1990 and 1991, Yemen abstained on a number of UNSC resolutions concerning Iraq and Kuwait[172] and voted against the "...use of force resolution." The vote outraged the U.S.,[173] and Saudi Arabia expelled 800,000 Yemenis in 1990 and 1991 to punish Yemen for its opposition to the intervention.[174]
In the absence of strong state institutions, elite politics in Yemen constituted a de facto form of collaborative governance, where competing tribal, regional, religious, and political interests agreed to hold themselves in check through tacit acceptance of the balance it produced.[175] The informal political settlement was held together by a power-sharing deal among three men: President Saleh, who controlled the state; major general Ali Mohsen al-Ahmar, who controlled the largest share of the Yemeni Armed Forces; and Abdullah ibn Husayn al-Ahmar, figurehead of the Islamist al-Islah party and Saudi Arabia's chosen broker of transnational patronage payments to various political players,[176] including tribal sheikhs.[177][178][179][180] The Saudi payments have been intended to facilitate the tribes' autonomy from the Yemeni government and to give the Saudi government a mechanism with which to weigh in on Yemen's political decision-making.[181]
Following food riots in major towns in 1992, a new coalition government made up of the ruling parties from both the former Yemeni states was formed in 1993. However, Vice President al-Beidh withdrew to Aden in August 1993 and said he would not return to the government until his grievances were addressed. These included northern violence against his Yemeni Socialist Party, as well as the economic marginalization of the south.[182] Negotiations to end the political deadlock dragged on into 1994. The government of Prime Minister Haydar Abu Bakr Al-Attas became ineffective due to political infighting.[183]
An accord between northern and southern leaders was signed in Amman, Jordan on 20 February 1994, but this could not stop the civil war.[184] During these tensions, both the northern and southern armies (which had never integrated) gathered on their respective frontiers.[185]
Contemporary Yemen

Ali Abdullah Saleh became Yemen's first directly elected president in the 1999 presidential election, winning 96% of the vote.[170]: 310 The only other candidate, Najeeb Qahtan Al-Sha'abi, was the son of Qahtan Muhammad al-Sha'abi, a former president of South Yemen. Though a member of Saleh's General People's Congress (GPC) party, Najeeb ran as an independent.[187]
In October 2000, 17 U.S. personnel died after an al-Qaeda suicide attack on the U.S. naval vessel USS Cole in Aden. After the September 11 attacks on the United States, President Saleh assured U.S. President George W. Bush that Yemen was a partner in his War on Terror. In 2001, violence surrounded a referendum, which apparently supported extending Saleh's rule and powers.
The Houthi insurgency in Yemen began in June 2004 when dissident cleric Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, head of the Zaidi Shia sect, launched an uprising against the Yemeni government. The Yemeni government alleged that the Houthis were seeking to overthrow it and to implement Shī'ite religious law. The rebels countered that they were "defending their community against discrimination" and government aggression.[188] In 2005, at least 36 people were killed in clashes across the country between police and protesters over rising fuel prices. In the 2006 presidential election, Saleh won with 77% of the vote. His main rival, Faisal bin Shamlan, received 22%.[189][190] Saleh was sworn in for another term on 27 September.[191]
A suicide bomber killed eight Spanish tourists and two Yemenis in the Marib Governorate in July 2007. A series of bomb attacks occurred on police, official, diplomatic, foreign business, and tourism targets in 2008. Car bombings outside the U.S. embassy in Sana'a killed 18 people, including six of the assailants in September 2008. In 2008, an opposition rally in Sana'a demanding electoral reform was met with police gunfire.[192]
Social hierarchy
There is a system of social stratification in Yemen that was officially abolished at the creation of the Yemen Arab Republic in 1962, but in practice this system has not disappeared and Yemeni society is still organized around hierarchical ranks. The difference between ranks is manifested by descent and occupation and is consolidated by marriages between people of the same ranks.
There are five status groups. At the top of hierarchy, there are the religious elites, also called sada. These are then followed by the strata of judges (quad). The third hierarchical status is the qaba’il, who are the peasants who belong to tribes and who live mainly from agriculture and trading. The fourth group is called the mazayanah. This group is composed of people who had no land and provide different kinds of services such as butchers and craftsmen. Finally, at the bottom of the hierarchy are the slaves (a’bid) and even further below them Al-Akhdam, which means servants.[193]
Revolution and aftermath
The 2011 Yemeni revolution followed other Arab Spring mass protests in early 2011. The uprising was initially against unemployment, economic conditions, and corruption, as well as against the government's proposals to modify the constitution of Yemen so that Saleh's son could inherit the presidency.
In March 2011, police snipers opened fire on a pro-democracy camp in Sana'a, killing more than 50 people. In May, dozens were killed in clashes between troops and tribal fighters in Sana'a. By this point, Saleh began to lose international support. In October 2011, Yemeni human rights activist Tawakul Karman won the Nobel Peace Prize, and the UN Security Council condemned the violence and called for a transfer of power. On 23 November 2011, Saleh flew to Riyadh, in neighbouring Saudi Arabia, to sign the Gulf Co-operation Council plan for political transition, which he had previously spurned. Upon signing the document, he agreed to legally transfer the office and powers of the presidency to his deputy, Vice President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi.[194]
Hadi took office for a two-year term upon winning the uncontested presidential elections in February 2012.[195] A unity government—including a prime minister from the opposition—was formed. Al-Hadi would oversee the drafting of a new constitution, followed by parliamentary and presidential elections in 2014. Saleh returned in February 2012. In the face of objections from thousands of street protesters, parliament granted him full immunity from prosecution. Saleh's son, General Ahmed Ali Abdullah Saleh, continues to exercise a strong hold on sections of the military and security forces.
AQAP claimed responsibility for a February 2012 suicide attack on the presidential palace that killed 26 Republican Guards on the day that President Hadi was sworn in. AQAP was also behind a suicide bombing that killed 96 soldiers in Sana'a three months later. In September 2012, a car bomb attack in Sana'a killed 11 people, a day after a local al-Qaeda leader Said al-Shihri was reported killed in the south.
By 2012, there was a "small contingent of U.S. special-operations troops"—in addition to CIA and "unofficially acknowledged" U.S. military presence—in response to increasing terror attacks by AQAP on Yemeni citizens.[196] Many analysts have pointed out the former Yemeni government role in cultivating terrorist activity in the country.[197] Following the election of President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, the Yemeni military was able to push Ansar al-Sharia back and recapture the Shabwah Governorate.

The central government in Sana'a remained weak, staving off challenges from southern separatists and Houthis as well as AQAP. The Houthi insurgency intensified after Hadi took power, escalating in September 2014 as anti-government forces led by Abdul-Malik al-Houthi swept into the capital and forced Hadi to agree to a "unity" government.[198] The Houthis then refused to participate in the government,[199] although they continued to apply pressure on Hadi and his ministers, even shelling the president's private residence and placing him under house arrest,[200] until the government's mass resignation in January 2015.[201] The following month, the Houthis dissolved parliament and declared that a Revolutionary Committee under Mohammed Ali al-Houthi was the interim authority in Yemen. Abdul-Malik al-Houthi, a cousin of the acting president, called the takeover a "glorious revolution". However, the "constitutional declaration" of 6 February 2015 was widely rejected by opposition politicians and foreign governments, including the United Nations.[26]
Hadi managed to flee from Sana'a to Aden, his hometown and stronghold in the south, on 21 February 2015. He promptly gave a televised speech rescinding his resignation, condemning the coup, and calling for recognition as the constitutional president of Yemen.[202] The following month, Hadi declared Aden Yemen's "temporary" capital.[203][204] The Houthis, however, rebuffed an initiative by the Gulf Cooperation Council and continued to move south toward Aden. All U.S. personnel were evacuated, and President Hadi was forced to flee the country to Saudi Arabia. On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia announced Operation Decisive Storm and began airstrikes and announced its intentions to lead a military coalition against the Houthis, who they claimed were being aided by Iran and began a force buildup along the Yemeni border. The coalition included the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, Jordan, Morocco, Sudan, Egypt, and Pakistan. The United States announced that it was assisting with intelligence, targeting, and logistics. After Hadi troops took control of Aden from Houthis, jihadist groups became active in the city, and some terrorist incidents were linked to them such as Missionaries of Charity attack in Aden on 4 March 2016. In February 2018, Aden was seized by the UAE-backed separatist Southern Transitional Council.[205]
Yemen has been suffering from a famine since 2016 as a result of the civil war. More than 50,000 children in Yemen died from starvation in 2017.[206][207] Numerous commentators have condemned the Saudi-led coalition's military campaign, including its blockade of Yemen, as genocide.[208][209][210] The famine is being compounded by an outbreak of cholera that has affected more than one million people.[211] The Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen and blockade of Yemen have contributed to the famine and cholera epidemic.[212][213] The UN estimated that by the end of 2021, the war in Yemen would have caused over 377,000 deaths, and roughly 70% of deaths were children under age 5.[214][215]
On 4 December 2017, deposed strongman and former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, accused of treason, was assassinated by Houthis whilst attempting to flee clashes near rebel-held Sana'a between Houthi and pro-Saleh forces.[216] After losing the support of the Saudi-led coalition, Yemen's President Abd Rabbuh Mansur Hadi resigned, and the Presidential Leadership Council took power in April 2022.[217]
Following the outbreak of the 2023 Israel–Hamas war, the Houthis began to fire missiles at Israel and attack ships off Yemen's coast in the Red Sea, which they say is in solidarity with the Palestinians and aiming to facilitate entry of humanitarian aid into the Gaza Strip.[218][219]
In June 2024, the UAE-backed STC were putting pressure to lease the Aden International Port to Abu Dhabi Ports. The move was opposed by the Parliament and the public. A joint statement by 24 members of Shura Council expressed categorical rejection of the lease agreement. Economists said the Emirates was attempting to control the Aden Port and limit its activities, in order to keep its own ports active. Governor of Aden, Tariq Salam also said the lease attempt aims to devalue the Aden Port and take its international maritime status.[220][221][222] Aden International Port had ended its agreement to manage two container terminals with Dubai Ports World in 2012, due to economic decline and failure to fulfill commitments.[223]
Geography

Yemen covers 455,000 km2 (175,676 sq mi)[5] and is located at the southern part of the Arabian Peninsula.[224] It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, the Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel to the south, and Oman to the east.
Several Red Sea islands, including the Hanish Islands, Kamaran, and Perim, as well as Socotra in the Arabian Sea, belong to Yemen; the largest of these is Socotra. Many of the islands are volcanic; Jabal al-Tair Island had volcanic eruptions in 1883 and 2007. Although mainland Yemen is in the southern Arabian Peninsula and thus part of Asia, and its Hanish Islands and Perim in the Red Sea are associated with Asia, the archipelago of Socotra, which lies east of the horn of Somalia and is much closer to Africa than to Asia, is geographically and biogeographically associated with Africa.[225]
Regions and climate

Yemen can be divided geographically into four main regions: the coastal plains in the west, the western highlands, the eastern highlands, and the Rub' al Khali in the east. The Tihamah ("hot lands" or "hot earth") form a very arid and flat coastal plain along Yemen's entire Red Sea coastline. Despite the aridity, the presence of many lagoons makes this region very marshy and a suitable breeding ground for malaria-borne mosquitos. Extensive crescent-shaped sand dunes are present. The evaporation in the Tihamah is so great that streams from the highlands never reach the sea, but they do contribute to extensive groundwater reserves. Today, these are heavily exploited for agricultural use.
Near the village of Madar about 50 km (30 mi) north of Sana'a, dinosaur footprints were found, indicating that the area was once a muddy flat. The Tihamah ends abruptly at the escarpment of the western highlands. This area, now heavily terraced to meet the demand for food, receives the highest rainfall in Arabia, rapidly increasing from 100 mm (3.9 in) per year to about 760 mm (29.9 in) in Taiz and over 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in Ibb. Temperatures are warm in the day but fall dramatically at night.
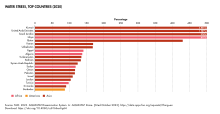
The central highlands are an extensive high plateau over 2,000 m (6,562 ft) in elevation. This area is drier than the western highlands because of rain-shadow influences, but still receives sufficient rain in wet years for extensive cropping. Water storage allows for irrigation and the growing of wheat and barley. Sana'a is in this region. The highest point in Yemen and Arabia is Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb, at about 3,666 m (12,028 ft).[224][227]
Yemen's portion of the Rub al Khali desert in the east is much lower, generally below 1,000 m (3,281 ft), and receives almost no rain. It is populated only by Bedouin herders of camels.
Biodiversity
Yemen contains six terrestrial ecoregions: Arabian Peninsula coastal fog desert, Socotra Island xeric shrublands, Southwestern Arabian foothills savanna, Southwestern Arabian montane woodlands, Arabian Desert, and Red Sea Nubo-Sindian tropical desert and semi-desert.[228] The flora is a mixture of the tropical African, Sudanian plant geographical region and the Saharo-Arabian region. The Sudanian element—characterized by relatively high rainfall—dominates the western mountains and parts of the highland plains. The Saharo-Arabian element dominates in the coastal plains, eastern mountain, and the eastern and northern desert plains.
A high percentage of Yemen plants belong to tropical African plants of Sudanian regions. Among the Sudanian element species, the following may be mentioned: Ficus spp., Acacia mellifera, Grewia villosa, Commiphora spp., Rosa abyssinica, Cadaba farinosa and others.[229] Among the Saharo-Arabian species, these may be mentioned: Panicum turgidum, Aerva javanica, Zygophyllum simplex, Fagonia indica, Salsola spp., Acacia tortilis, A. hamulos, A. ehrenbergiana, Phoenix dactylifera, Hyphaene thebaica, Capparis decidua, Salvadora persica, Balanites aegyptiaca, and many others. Many of the Saharo-Arabian species are endemic to the extensive sandy coastal plain (the Tihamah).[230]
Among the fauna, the Arabian leopard, which would inhabit the mountains, is considered rare here.[231]
Politics
Yemen is a republic with a bicameral legislature. Under the 1991 constitution, an elected president, an elected 301-seat Assembly of Representatives, and an appointed 111-member Shura Council share power. The president is the head of state, and the prime minister is the head of government. In Sana'a, a Supreme Political Council (not recognized internationally) forms the government.
The 1991 constitution provides that the president be elected by popular vote from at least two candidates endorsed by at least 15 members of the Parliament. The prime minister, in turn, is appointed by the president and must be approved by two-thirds of the Parliament. The presidential term of office is seven years, and the parliamentary term of elected office is six years. Suffrage is universal for people aged 18 and older, but only Muslims may hold elected office.[232]
President Ali Abdullah Saleh became the first elected president in reunified Yemen in 1999 (though he had been president of unified Yemen since 1990 and president of North Yemen since 1978). He was re-elected to office in September 2006. Saleh's victory was marked by an election that international observers judged was "partly free", though the election was accompanied by violence, violations of press freedoms, and allegations of fraud.[233] Parliamentary elections were held in April 2003, and the General People's Congress maintained an absolute majority. Saleh remained almost uncontested in his seat of power until 2011, when local frustration at his refusal to hold another round of elections, as combined with the consequences of the 2011 Arab Spring, resulted in mass protests.[195] In 2012, he was forced to resign from power, though he remained an important factor in Yemeni politics, allying with the Houthis during their takeover in the mid-2010s.[234]
The constitution calls for an independent judiciary. The former northern and southern legal codes have been unified. The legal system includes separate commercial courts and a Supreme Court based in Sana'a. Sharia is the main source of laws, with many court cases being debated according to the religious basis of law and many judges being religious scholars as well as legal authorities. The Prison Authority Organization Act, Republican decree no. 48 (1981), and Prison Act regulations, provide the legal framework for management of the country's prison system.[235]
Foreign relations
Yemen is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and also participates in the nonaligned movement. Yemen has acceded to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons.

Since the end of the 1994 civil war, tangible progress has been made on the diplomatic front in restoring normal relations with Yemen's neighbors. In the summer of 2000, Yemen and Saudi Arabia signed an International Border Treaty settling a 50-year-old dispute over the location of the border between the two countries.[236] Yemen's northern border had been undefined; the Arabian Desert prevented any human habitation there. The Saudi – Yemen barrier was constructed by Saudi Arabia against an influx of illegal immigrants and against the smuggling of drugs and weapons.[237] The Independent headed an article with "Saudi Arabia, one of the most vocal critics in the Arab world of Israel's "security fence" in the West Bank, is quietly emulating the Israeli example by erecting a barrier along its porous border with Yemen."[238][unreliable source?]
In March 2020, the Trump administration and key U.S. allies, including Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, cut off tens of millions of dollars for health care programs and other aid to the United Nations' appeal for Yemen. As a result of funding cuts, the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs stated that the UN agencies were forced to either close or reduce more than 75 per cent of its programs that year alone, affecting more than 8 million people. Saudi Arabia had been leading a Western-backed military coalition, including the United Arab Emirates as a key member, which intervened in Yemen in 2015, in a bid to restore the government ousted from power by the Houthi movement. The United Nations described the situation in Yemen, where the war killed tens of thousands of people and left millions on the brink of famine, as the world's worst humanitarian crisis.[239]
In January 2024, President Joe Biden announced that the United States, Britain and allies Australia, Bahrain, Canada and the Netherlands had launched a military assault on Houthi militant targets in Yemen.[240]
Military

The armed forces of Yemen include the Yemen Army (includes Republican Guard), Navy (includes Marines), Yemeni Air Force (Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Yamaniya; includes Air Defense Force). A major reorganization of the armed forces continues. The unified air forces and air defenses are now under one command. The navy has concentration in Aden. Total armed forces manning numbers about 401,000 active personnel, including moreover especially conscripts.
The number of military personnel is relatively high; in sum, Yemen has the second largest military force on the Arabian Peninsula after Saudi Arabia. In 2012, total active troops were estimated as follows: army, 390,000; navy, 7,000; and air force, 5,000. In September 2007, the government announced the reinstatement of compulsory military service. Yemen's defense budget, which in 2006 represented approximately 40 percent of the total government budget, is expected to remain high for the near term, as the military draft takes effect and internal security threats continue to escalate. By 2012, Yemen had 401,000 active personnel.
Human rights
Corruption in Yemen is such that it ranked 176 out of 180 countries in the 2022 Corruption Perceptions Index.[241] The government and its security forces have been responsible for torture, inhumane treatment, and extrajudicial executions. There are arbitrary arrests of citizens, especially in the south, as well as arbitrary searches of homes. Prolonged pretrial detention is a serious problem, and judicial corruption, inefficiency, and executive interference undermine due process. Freedom of speech, the press, and religion are all restricted.[242] Journalists critical of the government are often harassed and threatened by the police.[172] Homosexuality is illegal, punishable by death.[243]
Yemen is ranked last of 135 countries in the 2012 Global Gender Gap Report.[244] Human Rights Watch reported on discrimination and violence against women as well as on the abolition of the minimum marriage age of 15 for women. The onset of puberty (interpreted by some to be as low as the age of nine) was set as a requirement for marriage instead.[245] Publicity about the case of ten-year-old Yemeni divorcee Nujood Ali brought the child marriage issue to the forefront worldwide.[246][247][248]
In 2017, the UN Human Rights Council voted to create a team of experts to investigate suspected breaches of humanitarian law and human rights in Yemen.[249] In December 2021, The Guardian revealed, Saudi Arabia used "incentives and threats" as part of a pressure campaign to end a UN inquiry into human rights infringements in Yemen.[250] In June 2020, a human rights group revealed the scale of torture and deaths in Yemen's unofficial detention centres. UAE and Saudi forces were responsible for some of the most shocking treatment of prisoners, including being hung upside down for hours and sexual torture such as the burning of genitals.[251]
According to 2020 United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) estimates, 6.1 million girls and women were in need of gender-based violence services. The UNFPA also reported a rise in gender-based violence cases amid COVID-19 pandemic, increase in rate of child marriages, most acutely among internally displaced persons (IDPs). One in five girls aged 10 to 19 were married in IDP camps, compared to 1 in 8 in host communities.[252]
The United States Department of State 2013 Trafficking in Persons report classified Yemen as a Tier 3 country,[253] meaning that its government does not fully comply with the minimum standards against human trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so.[254] Yemen officially abolished slavery in Yemen in 1962,[255] but it is still being practiced.[256] On 22 June 2020, Human Rights Watch wrote an open letter to the UN Secretary-General on "Children and Armed Conflict" report to improve the protection of children in Yemen and in Myanmar.[257] Amnesty said, United Nations Security Council must urgently fix its monitoring and reporting mechanism for children affected by armed conflict.[258] On 14 September 2020, Human Rights Watch demanded an end to the interference caused by Houthi rebels and other authorities in Yemen aid operations, as millions of lives dependent on the aid operations were being put at risk.[259]
Administrative divisions
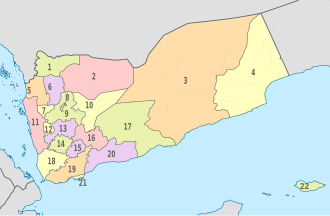
Yemen is divided into twenty-one governorates (muhafazat) plus one municipality called "Amanat Al-Asemah" (the latter containing the constitutional capital, Sana'a).[260] An additional governorate (Soqatra Governorate) was created in December 2013 comprising Socotra Island, previously part of Hadramaut Governorate.[261] The governorates are subdivided into 333 districts (muderiah), which are subdivided into 2,210 sub-districts, and then into 38,284 villages (as of 2001).
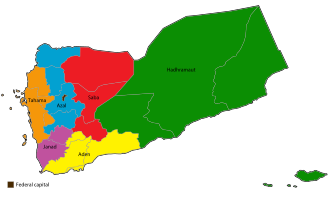
In 2014, a constitutional panel decided to divide the country into six regions—four in the north, two in the south, and capital Sana'a outside of any region—creating a federalist model of governance.[262] This federal proposal was a contributing factor toward the Houthis' subsequent coup d'état against the government.[263][264][265]
Economy

Since its unification in 1990, Yemen has been one of the poorest countries in the Middle East.[266] As of 2013 Yemen had a GDP (PPP) of US$61.63 billion, with an income per capita of $2,500. Services are the largest economic sector (61.4% of GDP), followed by the industrial sector (30.9%), and agriculture (7.7%). Of these, petroleum production represents around 25% of GDP and 63% of the government's revenue.[4] After the start of the civil war in 2014, its GDP dropped rapidly by over 50%,[267][268] thanks to the blockade led by Saudi Arabia and an effective embargo on oil exports imposed by the Houthis.[269]
Agriculture

Principal agricultural commodities produced include grain, vegetables, fruits, pulses, qat, coffee, cotton, dairy products, fish, livestock (sheep, goats, cattle, camels), and poultry.[4] Most Yemenis are employed in agriculture. However, the role of agricultural sector is limited by the relatively low share of the sector in GDP and the large share of net food-buying households (97%).[270] Sorghum is the most common crop. Cotton and many fruit trees are also grown, with mangoes being the most valuable.
A big problem in Yemen is the cultivation of Khat (or qat), a psychoactive plant that releases a stimulant when chewed, and accounts for up to 40 percent of the water drawn from the Sana'a Basin each year, and that figure is rising. Some agricultural practices are drying the Sana'a Basin and displaced vital crops, which has resulted in increasing food prices. Rising food prices, in turn, pushed an additional six percent of the country into poverty in 2008 alone,[271] and led to food riots starting in 2008 in poorer cities.[272] Efforts are being made by the government and Dawoodi Bohra community at northern governorates to replace qat with coffee plantations.[273]
Industry
The industrial sector is centred on crude oil production and petroleum refining, food processing, handicrafts, small-scale production of cotton textiles and leather goods, aluminum products, commercial ship repair, cement, and natural gas production. In 2013, Yemen had an industrial production growth rate of 4.8%.[4] It also has large proven reserves of natural gas.[274] Yemen's first liquified natural gas plant began production in October 2009.
Export and import
In 2013, exports totaled $6.694 billion. The main export commodities are crude oil, coffee, dried and salted fish, liquefied natural gas. These products were mainly sent to China (41%), Thailand (19.2%), India (11.4%), and South Korea (4.4%). Imports totaled $10.97 billion. The main imported commodities are machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, livestock, and chemicals. These products were mainly imported from the EU (48.8%), UAE (9.8%), Switzerland (8.8%), China (7.4%), and India (5.8%).[4]
State budget

As of 2013, the government's budget consisted of $7.769 billion in revenues and $12.31 billion in expenditures. Taxes and other revenues constituted roughly 17.7% of the GDP, with a budget deficit of 10.3%. The public debt was 47.1% of GDP. Yemen had reserves of foreign exchange and gold of around $5.538 billion in 2013. Its inflation rate over the same period based on consumer prices was 11.8%. The external debt totaled $7.806 billion.[4] Yemen is missing some international support because, as of 2024, it is one of three countries which have not ratified the Paris Agreement to limit climate change.[275]
Water supply and sanitation
A key challenge is severe water scarcity, especially in the Highlands, prompting The Times, in 2009, to write "Yemen could become first nation to run out of water."[276] A second key challenge is a high level of poverty, making it difficult to recover the costs of service provision. Access to water supply sanitation is low. Yemen is both the poorest country and the most water-scarce country in the Arab world. Third, the capacity of sector institutions to plan, build, operate and maintain infrastructure remains limited. Last but not least the security situation makes it even more difficult to improve or even maintain existing levels of service.
The average Yemeni has access to only 140 cubic meters of water per year (101 gallons per day) for all uses, while the Middle Eastern average is 1,000 m3/yr, and the internationally defined threshold for water stress is 1,700 cubic meters per year.[277] Groundwater is the main source of water in the country, but the water tables have dropped severely leaving Yemen without a viable source of water. For example, in Sana'a, the water table was 30 metres (98 feet) below surface in the 1970s but had dropped to 1,200 metres (3,900 feet) below the surface by 2012. The groundwater has not been regulated by Yemen's governments.[278]
Even before the revolution, Yemen's water situation had been described as increasingly dire by experts who worried that Yemen would be the first country to run out of water.[279] In part due to the 2015 Yemeni civil war, the infrastructure required to build better access to water has been delayed in construction. It is estimated that as many as 80% of the population struggles to access water to drink and bathe. Bombing has forced many Yemenis to leave their homes for other areas, leaving wells in the new areas under increasing demands.[280]
Together with partners, UNICEF has advanced its efforts and provided access to safe and sustained drinking water to 8.8 million people (5.3 million children). It scaled up its emergency WASH assistance in Yemen to ensure sustainable WASH services through capacity building of local WASH authorities, solarisation of water systems and rainwater harvesting.[281]
Demographics

Yemen's population is 33 million by 2021 estimates,[282][283] with 46% of the population being under 15 years old and 2.7% above 65 years. In 1950, it was 4.3 million.[284][285] By 2050, the population is estimated to increase to about 60 million.[286] Yemen has a high total fertility rate, at 4.45 children per woman.[287] Sana'a's population has increased rapidly, from roughly 55,000 in 1978[288] to nearly 1 million in the early 21st century.[289]
People

When the states of North and South Yemen were established, most resident minority groups departed.[290] Yemen is a largely tribal society.[291] There are also hereditary caste groups in urban areas such as Al-Akhdam.[292] There are also Yemenis of Persian origin. According to Muqaddasi, Persians formed the majority of Aden's population in the 10th century.[293][294]
Yemenite Jews once formed a sizable minority with a distinct culture from other Jewish communities in the world.[295] Most emigrated to Israel in the mid-20th century, following the Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries and Operation Magic Carpet. An estimated 100,000 people of Indian origin are concentrated in the southern part of the country, around Aden, Mukalla, Shihr, Lahaj, Mokha and Hodeidah.[296]
Most of the prominent Indonesians, Malaysians, and Singaporeans of Arab descent are Hadhrami people with origins in southern Yemen in the Hadhramaut coastal region.[297] Today there are almost 10,000 Hadramis in Singapore.[298] The Hadramis migrated to Southeast Asia, East Africa and the Indian subcontinent.[299]
The Maqil were a collection of Arab Bedouin tribes of Yemeni origin who migrated westwards via Egypt. Several groups of Yemeni Arabs turned south to Mauritania, and by the end of the 17th century, they dominated the entire country. They can also be found throughout Morocco and in Algeria as well as in other North African countries.[300]
Yemen is the birthplace of the Arabs and the language; Qahtanite Arabs —the original Arabs — originated in Yemen. According to Arab tradition, Ishmael son of Abraham married a woman from the Jurhum tribe.[301]
Yemen is the only country in the Arabian Peninsula that is signatory to two international accords dating back to 1951 and 1967 governing the protection of refugees.[302] Yemen hosted a population of refugees and asylum seekers numbering approximately 124,600 in 2007. Refugees and asylum seekers were predominantly from Somalia (110,600), Iraq (11,000), Ethiopia (2,000),[303] and Syria.[304] Additionally, more than 334,000 Yemenis have been internally displaced by conflict.[302] The Yemeni diaspora is largely concentrated in neighbouring Saudi Arabia, where between 800,000 and 1 million Yemenis reside,[305] and the United Kingdom, home to between 70,000 and 80,000 Yemenis.[306]
Languages
Modern Standard Arabic is the official language, while Yemeni Arabic is used as the vernacular. In al Mahrah Governorate in the far east and the island of Socotra, several non-Arabic languages are spoken.[307][308] Yemeni Sign Language is used by the deaf community.
Yemen is part of the homeland of the South Semitic languages. Mehri is the largest South Semitic language spoken in the nation, with more than 70,000 speakers. The ethnic group is called Mahra. Soqotri is another South Semitic language, with speakers on the island of Socotra isolated from the pressures of Arabic on the Yemeni mainland. According to the 1990 census, the number of speakers was 57,000.[309] Yemen was home of the Old South Arabian languages. The Razihi language appears to be the only remaining Old South Arabian language.
English is the most important foreign language, being widely taught and spoken mostly in the south, a former British protectorate.[310]
Religion
Islam is the state religion. Religion in Yemen consists primarily of two Islamic religious groups. According to a UNHCR report, the Shia "Zaydis make up about 45 percent of the population, Sunnis 53 percent and there are also tiny minorities of other Shia groups—the Ismaili and Twelver communities."[312] Sunnis are primarily Shafi'i but also include significant groups of Malikis and Hanbalis. Shias are primarily Zaydi and also have significant minorities of Ismaili[313] and Twelver[313][314] Shias.
The Sunnis are predominantly in the south and southeast which traditionally have less population. The Zaidis/Shias are predominantly in the north and northwest where the vast majority of the Yemeni population traditionally lives whilst the Ismailis are in the main centres such as Sana'a and Ma'rib. There are mixed communities in the larger cities.[315][316] According to WIN/Gallup International polls, Yemen has the highest share of the population identifying as religious among Arab countries, and one of the highest in the world.[317]
About .05 percent of Yemenis are non-Muslim—adhering to Christianity, Judaism, or Hinduism or having no religious affiliation. Yemen is number five on Open Doors' 2022 World Watch List, an annual ranking of the 50 countries where Christians face the most extreme persecution.[318] Estimates of the number of Christians in Yemen range from 25,000[319] to 41,000.[320] A 2015 study estimates 400 Christians from a Muslim background reside in the country.[321] There are approximately 50 or fewer Jews left in Yemen. Some 200 Yemeni Jews were brought to Israel by the Jewish Agency c. 2016.[322] According to a 2020 estimate, as few as 26 Jews remain in Yemen.[323] However, in 2022 it was estimated that only one Yemeni Jew remained according to a United Nations report about the treatment of religious minorities in conflict zones; however, there are reportedly a handful of "hidden Jews" who have converted to Islam but secretly continue to practice Judaism.[324]
Education

The adult literacy rate in 2010 was 64%.[325] The government has committed to reduce illiteracy to less than 10% by 2025.[326] Although the government provides for universal, compulsory, free education for children ages six through 15, the U.S. Department of State reports that compulsory attendance is not enforced. The government developed the National Basic Education Development Strategy in 2003 that aimed at providing education to 95% of children between the ages of six and 14 years and also at decreasing the gap between males and females in urban and rural areas.[327]
A seven-year project to improve gender equity and the quality and efficiency of secondary education, focusing on girls in rural areas, was approved by the World Bank in March 2008. Following this, Yemen has increased its education spending from 5% of GDP in 1995 to 10% in 2005.[172]
According to the Webometrics Ranking of World Universities, the top-ranking universities in the country are the Yemeni University of Science & Technology (6532nd worldwide), Al Ahgaff University (8930th) and Sanaa University (11043rd).[328] Yemen was ranked 131st in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 129th in 2019.[329][330][331][332]
Health
Despite the significant progress the government has made to expand and improve its health care system over the past decade, the system remains severely underdeveloped. Total expenditures on health care in 2002 constituted 3.7 percent of GDP.[333] In that same year, the per capita expenditure for health care was very low, as compared with other Middle Eastern countries—US$58 according to United Nations statistics and US$23 according to the World Health Organization.
According to the World Bank, the number of doctors rose by an average of more than 7 percent between 1995 and 2000, but as of 2004, there were still only three doctors per 10,000 persons. In 2003, Yemen had only 0.6 hospital beds available per 1,000 persons.[333] Health care services are particularly scarce in rural areas. Only 25 percent of rural areas are covered by health services, as compared with 80 percent of urban areas. Emergency services, such as ambulance service and blood banks, are non-existent.[333]
Culture



Media
Radio broadcasting in Yemen began in the 1940s.[334] After unification in 1990, the government reformed its corporations and founded some additional radio stations that broadcast locally. However, it drew back after 1994, due to destroyed infrastructure resulting from the 1994 civil war.
Television is the most significant media platform. Given the low literacy rate in the country, television is the main source of news. There are six free-to-air channels currently headquartered in Yemen, of which four are state-owned.[335] The Yemeni film industry is in its early stages; only eight Yemeni films have been released as of 2023.
Theatre
Yemeni theatre dates to the early 20th century. Both amateur and professional (government-sponsored) theatre troupes perform in the country's major urban centres. Many significant poets and authors, like Ali Ahmed Ba Kathir, Muhammad al-Sharafi, and Wajdi al-Ahdal, have written dramatic works; poems, novels, and short stories by Yemeni authors like Mohammad Abdul-Wali and Abdulaziz Al-Maqaleh have also been adapted for the stage.
There have been Yemeni productions of plays by Arab authors such as Tawfiq al-Hakim and Saadallah Wannous and by Western authors, including Shakespeare, Pirandello, Brecht, and Tennessee Williams. Historically speaking, Aden is the cradle of Yemeni theatre; in recent decades Sana'a has hosted numerous theatre festivals, often in conjunction with World Theatre Day.
Sport
Football is the most popular sport. The Yemen Football Association is a member of FIFA and AFC. The Yemeni national football team participates internationally. The country also hosts many football clubs. They compete in the national and international leagues.
Yemen's mountains provide many opportunities for outdoor sports, such as biking, rock climbing, trekking, hiking, and other more challenging sports, including mountain climbing. Mountain climbing and hiking tours to the Sarawat Mountains, including peaks of 3,000 m (9,800 ft) and above, particularly that of An-Nabi Shu'ayb,[224][227] are seasonally organized by local and international alpine agencies. The coastal areas and Socotra provide many opportunities for water sports, such as surfing, bodyboarding, sailing, swimming, and scuba diving. Socotra is home to some of the best surfing destinations in the world.
Camel jumping is a traditional sport that is becoming increasingly popular among the Zaraniq tribe on the west coast. Camels are placed side to side and victory goes to the competitor who leaps, from a running start, over the most camels. Tribesmen (women may not compete) tuck their robes around their waists for freedom of movement while running and leaping.[336]
Yemen's biggest sports event was hosting the 20th Arabian Gulf Cup in Aden and Abyan in 2010. Yemen was defeated in the first three matches of the tournament.[337]
World Heritage sites

Among its natural and cultural attractions are four World Heritage sites.[338][339] The Old Walled City of Shibam in Wadi Hadhramaut, inscribed by UNESCO in 1982, two years after Yemen joined the World Heritage Committee, is nicknamed "Manhattan of the Desert" because of its skyscrapers. Surrounded by a fortified wall made of mud and straw, the 16th-century city is one of the oldest examples of urban planning based on the principle of vertical construction.[340]
The Old City of Sana'a, at an altitude of more than 2,100 metres (7,000 ft), has been inhabited for over two and a half millennia, and was inscribed in 1986. Sana'a became a major Islamic centre in the seventh century, and the 103 mosques, 14 hammams (traditional bathhouses), and more than 6,000 houses that survive all date from before the 11th century.[341]
Close to the Red Sea coast, the historic town of Zabid, inscribed in 1993, was Yemen's capital from the 13th to the 15th century, and is an archaeological and historical site. It played an important role for many centuries because of its university, which was a centre of learning for the whole Arab and Islamic world.[342]
The latest addition to Yemen's list of World Heritage Sites is the Socotra Archipelago. Mentioned by Marco Polo in the 13th century, this remote and isolated archipelago consists of four islands and two rocky islets delineating the southern limit of the Gulf of Aden. The site has a rich biodiversity. Nowhere else in the world do 37% of Socotra's 825 plants, 90% of its reptiles and 95% of its snails occur. It is home to 192 bird species, 253 species of coral, 730 species of coastal fish, and 300 species of crab and lobster,[343] as well as the Dragon's Blood Tree (Dracaena cinnabari).[344] The cultural heritage of Socotra includes the unique Soqotri language.
See also
Notes
- ^ Constitutional capital under Houthi movement control
- ^ Claimed by the Presidential Leadership Council as its provisional capital[1]
- ^ Disputed by Mahdi al-Mashat of the Supreme Political Council. Despite not holding an official position in the government, Houthi movement leader Abdul-Malik al-Houthi controls the SPC.
- ^ Disputed by Abdel-Aziz bin Habtour of the Supreme Political Council
References
- ^ Al-Sakani, Ali (19 April 2022). "Yemen inaugurates new presidential council". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 8 May 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
Yemen's Prime Minister Maeen Abdulmalik Saeed, along with other senior government officials, had also arrived in Aden, which serves as Yemen's temporary capital, before the swearing-in ceremony.
- ^ "Yemen's Constitution of 1991 with Amendments through 2015" (PDF). Constitute Project. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2020.
- ^ "Yemen – Flora, Fauna, Ecosystems". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 5 February 2024. Retrieved 8 September 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f "Yemen". Central Intelligence Agency. CIA World Factbook. 6 December 2013. Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 24 January 2021.
- ^ a b c "THE NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY 2005-2015 AND NATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL ACTION PLAN 2005-2010" (PDF). Republic of Yemen Ministry of Water and Environment Environment Protection Agency. p. 6.
The area of Yemen is 455,503 sq. km. most of which is rocky land
- ^ "Yemen population". Yemen population 2023 Estimate based on UN World Bank. World Population Review. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Yemen)". International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2023. Archived from the original on 22 October 2023. Retrieved 16 October 2023.
- ^ "GINI index (World Bank estimate)". World Bank. Archived from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24". United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived from the original on 19 March 2024. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- ^ "Yemen". International News Safety Institute. Archived from the original on 5 May 2010. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- ^ "Yemen | History, Map, Flag, Population, Capital, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ^ McLaughlin, Daniel (1 February 2008). Yemen. Bradt Travel Guides. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-84162-212-5. Archived from the original on 2 July 2020. Retrieved 11 March 2017.
- ^ "Yemen Population (2023) - Worldometer". www.worldometers.info. Archived from the original on 11 May 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2023.
- ^ Burrowes, Robert D. (2010). Historical Dictionary of Yemen. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 319. ISBN 978-0-8108-5528-1.
- ^ St. John Simpson (2002). Queen of Sheba: treasures from ancient Yemen. British Museum Press. p. 8. ISBN 0-7141-1151-1.
- ^ Kenneth Anderson Kitchen (2003). On the Reliability of the Old Testament. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 116. ISBN 0-8028-4960-1.
- ^ Yaakov Kleiman (2004). DNA & Tradition: The Genetic Link to the Ancient Hebrews. Devora Publishing. p. 70. ISBN 1-930143-89-3.
- ^ Marta Colburn (2002). The Republic of Yemen: Development Challenges in the 21st Century. CIIR. p. 13. ISBN 1-85287-249-7.
- ^ Karl R. DeRouen; Uk Heo (2007). Civil Wars of the World: Major Conflicts Since World War II, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. p. 810. ISBN 978-1-85109-919-1.
- ^ Laura Etheredge (2011). Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 137. ISBN 978-1-61530-335-9.
- ^ Burrowes, Robert. "Why Most Yemenis Should Despise Ex-president Ali Abdullah Saleh". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 16 June 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2015.
- ^ James L. Gelvin (2012). The Arab Uprisings: What Everyone Needs to Know. Oxford University Press. p. 68. ISBN 978-0-19-989177-1.
- ^ Mareike Transfeld (2014). "Capturing Sanaa: Why the Houthis Were Successful in Yemen". Muftah. Archived from the original on 21 October 2014. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ Steven A. Zyck (2014). "Mediating Transition in Yemen: Achievements and Lessons" (PDF). International Peace Institute. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ Silvana Toska (26 September 2014). "Shifting balances of power in Yemen's crisis". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ a b "Houthi leader vows to defend 'glorious revolution'". Al Jazeera. 8 February 2015. Archived from the original on 8 February 2015. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ Aboueldahab, Noha. "Yemen's fate was sealed six years ago". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 31 August 2020. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ^ Borger, Julian (5 June 2015). "Saudi-led naval blockade leaves 20 m Yemenis facing humanitarian disaster". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 5 June 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- ^ "LDCs at a Glance | Department of Economic and Social Affairs". Economic Analysis & Policy Division | Dept of Economic & Social Affairs | United Nations. 25 May 2008. Archived from the original on 29 March 2022. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- ^ "Least Developed Countries (LDCs) | Department of Economic and Social Affairs". Economic Analysis & Policy Division | Dept of Economic & Social Affairs | United Nations. 23 September 2010. Archived from the original on 20 June 2019. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- ^ "Overview". Archived from the original on 26 April 2024. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ "Yemen: 2019 Humanitarian Needs Overview [EN/AR]". ReliefWeb. United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA). 14 February 2019. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- ^ a b "Global Data | Fragile States Index". fragilestatesindex.org. Archived from the original on 15 July 2019. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- ^ Jawād ʻAlī (1968) [Digitized 17 February 2007]. الـمـفـصـّل في تـاريـخ العـرب قبـل الإسـلام [Detailed history of Arabs before Islam] (in Arabic). Vol. 1. Dār al-ʻIlm li-l-Malāyīn. p. 171.
- ^ Neuwirth, Angelika; Sinai, Nicolai; Marx, Michael (2010). The Qur??n in Context: Historical and Literary Investigations Into the Qur??nic Milieu. BRILL. ISBN 9789004176881.
- ^ Burrowes (2010), p. 145
- ^ Smith, William Robertson. Kinship and Marriage in Early Arabia. p. 193. ISBN 1-117-53193-7.
He was worshiped by the Madhij and their allies at Jorash (Asir) in Northern Yemen
- ^ Beeston, A.F.L.; Ghul, M.A.; Müller, W.W.; Ryckmans, J. (1982). Sabaic Dictionary. University of Sanaa, YAR. p. 168. ISBN 2-8017-0194-7.
- ^ Vladimir Sergeyevich Solovyov (2007). Enemies from the East?: V. S. Soloviev on Paganism, Asian Civilizations, and Islam. Northwestern University Press. p. 149. ISBN 978-0-8101-2417-2.
- ^ Edward Balfour (1873). Cyclopædia of India and of Eastern and Southern Asia, Commercial, Industrial and Scientific: Products of the Mineral, Vegetable and Animal Kingdoms, Useful Arts and Manufactures, Band 5. Printed at the Scottish & Adelphi presses. p. 240.
- ^ Bell, Richard (20 October 1926). "Origin Of Islam In Its Christian Environment" – via Internet Archive.
- ^ Nöldeke, Theodor (1879). T. Nöldeke, Geschichte der Perser und Araber zur Zeit der en aus der arabischen Chronik des Tabari: Übersetzt und mit ausführlichen Erläuterungen und ergänzungen Versehn. Leiden: E.J. Brill. pp. 222.
- ^ McLaughlin (2008), p. 4
- ^ Kenneth Anderson Kitchen (2003). On the Reliability of the Old Testament. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 594. ISBN 0-8028-4960-1.
- ^ Quran 27:6-93
- ^ Quran 34:15-18
- ^ Geoffrey W. Bromiley (1979). The International Standard Bible Encyclopedia. Vol. 4. Wm. B. Eerdmans. p. 254. ISBN 0-8028-3784-0.
- ^ Nicholas Clapp (2002). Sheba: Through the Desert in Search of the Legendary Queen. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 204. ISBN 0-618-21926-9.
- ^ P. M. Holt; Peter Malcolm Holt; Ann K. S. Lambton; Bernard Lewis (21 April 1977). The Cambridge History of Islam. Cambridge University Press. p. 7.
- ^ Korotayev, Andrey (1995). Ancient Yemen: some general trends of evolution of the Sabaic language and Sabaean culture. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-922237-1. Archived from the original on 29 November 2023. Retrieved 21 May 2017.
- ^ McLaughlin (2008), p. 5
- ^ Jerry R. Rogers; Glenn Owen Brown; Jürgen Garbrecht (1 January 2004). Water Resources and Environmental History. ASCE Publications. p. 36. ISBN 0-7844-7550-4.
- ^ Negev, Avraham; Gibson, Shimon, eds. (2001). Dedan. New York and London: Continuum. p. 137. ISBN 0-8264-1316-1. Archived from the original on 23 September 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2021.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) (Snippet view). - ^ Lionel Casson (2012). The Periplus Maris Erythraei: Text with Introduction, Translation, and Commentary. Princeton University Press. p. 150. ISBN 978-1-4008-4320-6.
- ^ Peter Richardson (1999). Herod: King of the Jews and Friend of the Romans. Continuum. p. 230. ISBN 0-567-08675-5.
- ^ Hârun Yahya (1999). Perished Nations. Global Yayincilik. p. 115. ISBN 1-897940-87-4.
- ^ Jan Retso (2013). The Arabs in Antiquity: Their History from the Assyrians to the Umayyads. Routledge. p. 402. ISBN 978-1-136-87282-2.
- ^ Clifford Edmund Bosworth (1989). The Encyclopedia of Islam. Vol. 6. Brill Archive. p. 561. ISBN 9004090827.
- ^ Stuart Munro-Hay (2002). Ethiopia, the Unknown Land: A Cultural and Historical Guide. I. B. Tauris. p. 236. ISBN 1-86064-744-8.
- ^ G. Johannes Botterweck; Helmer Ringgren (1979). Theological Dictionary of the Old Testament. Vol. 3. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 448. ISBN 0-8028-2327-0.
- ^ Jawād ʻAlī (1968) [Digitized 17 February 2007]. الـمـفـصـّل في تـاريـخ العـرب قبـل الإسـلام [Detailed history of Arabs before Islam] (in Arabic). Vol. 2. Dār al-ʻIlm lil-Malāyīn. p. 482.
- ^ Albert Jamme (1962). Inscriptions From Mahram Bilqis (Marib). Baltimore. p. 392.
- ^ Dieter Vogel; Susan James (1990). Yemen. APA Publications. p. 34.
- ^ Klaus Schippmann (2001). Ancient South Arabia: from the Queen of Sheba to the advent of Islam. Markus Wiener Publishers. pp. 52–53. ISBN 1-55876-236-1.
- ^ Francis E. Peters (1994). Muhammad and the Origins of Islam. SUNY Press. p. 48. ISBN 0-7914-1875-8.
- ^ Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 265. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Shlomo Sand (2010). The Invention of the Jewish People. Verso. p. 193. ISBN 978-1-84467-623-1.
- ^ Y. M. Abdallah (1987). "The Inscription CIH 543: A New Reading Based on the Newly-Found Original". In C. Robin & M. Bafaqih (eds.). Sayhadica: Recherches Sur Les Inscriptions De l'Arabie Préislamiques Offertes Par Ses Collègues Au Professeur A.F.L. Beeston. Paris: Librairie Orientaliste Paul Geuthner S.A. pp. 4–5.
- ^ Raphael Patai; Jennifer Patai (1989). The Myth of the Jewish Race. Wayne State University Press. p. 63. ISBN 0-8143-1948-3.
- ^ Uwidah Metaireek Al-Juhany (2002). Najd before the Salafi reform movement: social, political and religious conditions during the three centuries preceding the rise of the Saudi state. Ithaca Press. p. 171. ISBN 0-86372-401-9.
- ^ Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 266. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 282. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Irfan Shahîd (1989). Byzantium and the Arabs in the 5th Century. Dumbarton Oaks. p. 65. ISBN 0-88402-152-1.
- ^ a b Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 293. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Scott Johnson (1 November 2012). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. p. 298. ISBN 978-0-19-533693-1.
- ^ Sabarr Janneh. Learning From the Life of Prophet Muhammad. AuthorHouse. p. 17. ISBN 1-4678-9966-6.
- ^ Abd al-Muhsin Madʼaj M. Madʼaj The Yemen in Early Islam (9–233/630–847): A Political History p. 12 Ithaca Press, 1988 ISBN 0863721028
- ^ Wilferd Madelung The Succession to Muhammad: A Study of the Early Caliphate p. 199 Cambridge University Press, 15 October 1998 ISBN 0521646960
- ^ Ṭabarī The History of al-Tabari Vol. 12: The Battle of al-Qadisiyyah and the Conquest of Syria and Palestine A.D. 635–637/A.H. 14–15 pp. 10–11 SUNY Press, 1992 ISBN 0791407330
- ^ Idris El Hareir The Spread of Islam Throughout the World p. 380 UNESCO, 2011 ISBN 9231041533
- ^ Nejla M. Abu Izzeddin The Druzes: A New Study of Their History, Faith, and Society BRILL, 1993 ISBN 9004097058
- ^ Hugh Kennedy The Armies of the Caliphs: Military and Society in the Early Islamic State p. 33 Routledge, 17 June 2013 ISBN 1134531133
- ^ a b Paul Wheatley The Places Where Men Pray Together: Cities in Islamic Lands, Seventh Through the Tenth Centuries p. 128 University of Chicago Press, 2001 ISBN 0226894282
- ^ Paul Lunde, Alexandra Porter (2004). Trade and travel in the Red Sea Region: proceedings of Red Sea project I held in the British Museum, October 2002. Archaeopress. p. 20. ISBN 1-84171-622-7.
in 976–77 AD[...] the then ruler of Yemen received slaves, as well as amber and leopard skins from the chief of the Dahlak islands (off the coast from Massawa).
- ^ Kamal Suleiman Salibi A History of Arabia p. 108 Caravan Books, 1980 OCLC Number: 164797251
- ^ Stephen W. Day Regionalism and Rebellion in Yemen: A Troubled National Union p. 31 Cambridge University Press, 2012 ISBN 1107022150
- ^ Gerhard Lichtenthäler Political Ecology and the Role of Water: Environment, Society and Economy in Northern Yemen p. 55 Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. 2003 ISBN 0754609081
- ^ J. D. Fage, Roland Anthony Oliver The Cambridge History of Africa, Volume 3 p. 119 Cambridge University Press,1977 ISBN 0521209811
- ^ William Charles Brice (1981), An Historical Atlas of Islam [cartographic Material], BRILL, p. 338, ISBN 9004061169
- ^ Farhad Daftary Ismailis in Medieval Muslim Societies: A Historical Introduction to an Islamic Community p. 92 I. B. Tauris, 2005 ISBN 1845110919
- ^ Farhad Daftary The Isma'ilis: Their History and Doctrines p. 199 Cambridge University Press, 2007 ISBN 1139465783
- ^ a b Fatima Mernissi The Forgotten Queens of Islam p. 14 U of Minnesota Press, 1997 ISBN 0816624399
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدو المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 237.
- ^ Farhad Daftary Ismailis in Medieval Muslim Societies: A Historical Introduction to an Islamic Community p. 93 I. B. Tauris, 2005 ISBN 1845110919
- ^ a b Steven C. Caton Yemen p. 51 ABC-CLIO, 2013 ISBN 159884928X
- ^ Bonnie G. Smith (2008). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Women in World History (in Arabic). Vol. 4. Oxford University Press. p. 163. ISBN 978-0-19-514890-9.
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدو المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 303.
- ^ Alexander Mikaberidze (2011). Conflict and Conquest in the Islamic World: A Historical Encyclopedia: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 159. ISBN 978-1-59884-337-8.
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدو المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 311.
- ^ a b Farhad Daftary (2007). The Isma'ilis: Their History and Doctrines. Cambridge University Press. p. 260. ISBN 978-1-139-46578-6.
- ^ Josef W. Meri (2004). Medieval Islamic Civilization. Psychology Press. p. 871. ISBN 0-415-96690-6.
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدول المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 350.
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدول المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 354.
- ^ Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدول المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 371.
- ^ a b Mohammed Abdo Al-Sururi (1987). الحياة السياسية ومظاهر الحضارة في اليمن في عهد الدول المستقلة [political life and aspects of civilization in Yemen during the reign of Independent States] (in Arabic). University of Sana'a. p. 407.
- ^ a b Alexander D. Knysh (1999). Ibn 'Arabi in the Later Islamic Tradition: The Making of a Polemical Image in Medieval Islam. SUNY Press. p. 230. ISBN 1-4384-0942-7.
- ^ a b Abdul Ali (1996). Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization During the Later Medieval Times. M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd. p. 84. ISBN 8175330082.
- ^ a b Abdul Ali (1996). Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization During the Later Medieval Times. M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd. p. 86. ISBN 8175330082.
- ^ a b c d Josef W. Meri; Jere L. Bacharach (2006). Medieval Islamic Civilization: L-Z, index. Taylor & Francis. p. 669. ISBN 0-415-96692-2.
- ^ a b David J Wasserstein; Ami Ayalon (2013). Mamluks and Ottomans: Studies in Honour of Michael Winter. Routledge. p. 201. ISBN 978-1-136-57917-2.
- ^ a b Alexander D. Knysh (1999). Ibn 'Arabi in the Later Islamic Tradition: The Making of a Polemical Image in Medieval Islam. SUNY Press. p. 231. ISBN 1-4384-0942-7.
- ^ "Yemen Tourism Promotion Board – The Mosque and School of Al-Amiryah". www.yementourism.com. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 16 April 2023.
- ^ a b Steven C. Caton Yemen p. 59 ABC-CLIO, 2013 ISBN 159884928X
- ^ Abdul Ali (1996). Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization During the Later Medieval Times. M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd. p. 94. ISBN 8175330082.
- ^ Bernard Haykel (2003). Revival and Reform in Islam: The Legacy of Muhammad Al-Shawkani. Cambridge University Press. p. 30. ISBN 0-521-52890-9.
- ^ Halil İnalcık; Donald Quataert (1994). An Economic and Social History of the Ottoman Empire, 1300–1914. Cambridge University Press. p. 320. ISBN 0-521-34315-1.
- ^ Zurcher, Erik Jan (1 January 1996). "An Economic and Social History of the Ottoman Empire, 1300–1914. Ed. by Halil Inalcik, with Donald Quataert". International Review of Social History. Archived from the original on 27 February 2024. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ Silva, António Dinis da Cruz e (1817). Poesias de Antonio Diniz da Cruz e Silva: Segunda parte das Odes pindaricas (in Brazilian Portuguese). Typografia Lacerdina. Archived from the original on 4 January 2024. Retrieved 26 January 2024.
- ^ Barros, Joao de (1628). Asia ... Dos feitos que os Portugueses fezerao no descobrimento e conquista dos mares e terras do Oriente (in Brazilian Portuguese). Jorge Rodriguez.
- ^ Nahrawālī, Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad (6 September 2002). البرق اليماني في الفتح العثماني [Lightning Over Yemen: A History of the Ottoman Campaign in Yemen, 1569–71]. Translated by Smith, Clive. I. B. Tauris. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-86064-836-6.
- ^ Giancarlo Casale (2010). The Ottoman Age of Exploration. Oxford University Press. p. 43. ISBN 978-0-19-979879-7.
- ^ a b Nahrawālī (2002), p. 88
- ^ Jane Hathaway (2012). A Tale of Two Factions: Myth, Memory, and Identity in Ottoman Egypt and Yemen. SUNY Press. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-7914-8610-8.
- ^ a b Robert W. Stookey (1978). Yemen: the politics of the Yemen Arab Republic. Westview Press. p. 134. ISBN 0-89158-300-9.
- ^ a b Nahrawālī (2002), p. 95
- ^ R. B. Serjeant; Ronald Lewcock (1983). Sana: An Arabian Islamic City. World of Islam Festival Pub. Co. p. 70. ISBN 0-905035-04-6.
- ^ Nahrawālī (2002), p. 134
- ^ a b Nahrawālī (2002), p. 180
- ^ a b Abdul Ali (1996). Islamic Dynasties of the Arab East: State and Civilization During the Later Medieval Times. M.D. Publications Pvt. Ltd. p. 103. ISBN 8175330082.
- ^ a b c Accounts and Extracts of the Manuscripts in the Library of the King of France. Vol. 2. R. Faulder. 1789. p. 75. Archived from the original on 28 October 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ a b Accounts and Extracts of the Manuscripts in the Library of the King of France. Vol. 2. R. Faulder. 1789. p. 76. Archived from the original on 28 October 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ Accounts and Extracts of the Manuscripts in the Library of the King of France. Vol. 2. R. Faulder. 1789. p. 78. Archived from the original on 28 October 2023. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- ^ Kjetil Selvik; Stig Stenslie (2011). Stability and Change in the Modern Middle East. I. B. Tauris. p. 90. ISBN 978-1-84885-589-2.
- ^ Anna Hestler; Jo-Ann Spilling (2010). Yemen. Marshall Cavendish. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-7614-4850-1.
- ^ Richard N. Schofield (1994). Territorial foundations of the Gulf states. UCL Press. p. 90. ISBN 1-85728-121-7.
- ^ Burrowes (2010), p. 295
- ^ Nelly Hanna (2005). Society and Economy in Egypt and the Eastern Mediterranean, 1600–1900: Essays in Honor of André Raymond. American Univ in Cairo Press. p. 124. ISBN 9774249372.
- ^ Marta Colburn (2002). The Republic of Yemen: Development Challenges in the 21st Century. CIIR. p. 15. ISBN 1-85287-249-7.
- ^ Ari Ariel (2013). Jewish-Muslim Relations and Migration from Yemen to Palestine in the Late Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries. BRILL. p. 24. ISBN 978-9004265370.
- ^ a b Caesar E. Farah (2002). The Sultan's Yemen: 19th-Century Challenges to Ottoman Rule. I. B. Tauris. p. 120. ISBN 1-86064-767-7.
- ^ R. J. Gavin (1975). Aden Under British Rule, 1839–1967. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 60. ISBN 0-903983-14-1.
- ^ Caesar E. Farah (2002). The Sultan's Yemen: 19th-Century Challenges to Ottoman Rule. I. B. Tauris. p. 132. ISBN 1-86064-767-7.
- ^ a b Caesar E. Farah (2002). The Sultan's Yemen: 19th-Century Challenges to Ottoman Rule. I. B. Tauris. p. 120. ISBN 1-86064-767-7.
- ^ Reeva S. Simon; Michael Menachem Laskier; Sara Reguer (2013). The Jews of the Middle East and North Africa in Modern Times. Columbia University Press. p. 390. ISBN 978-0-231-50759-2.
- ^ B. Z. Eraqi Klorman (1993). The Jews of Yemen in the Nineteenth Century: A Portrait of a Messianic Community. BRILL. p. 11. ISBN 9004096841.
- ^ Ari Ariel (2013). Jewish-Muslim Relations and Migration from Yemen to Palestine in the Late Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries. BRILL. p. 37. ISBN 978-9004265370.
- ^ a b Doğan Gürpınar (2013). Ottoman/Turkish Visions of the Nation, 1860–1950. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 71. ISBN 978-1-137-33421-3.
- ^ Caesar E. Farah (2002). The Sultan's Yemen: 19th-Century Challenges to Ottoman Rule. I. B. Tauris. p. 96. ISBN 1-86064-767-7.
- ^ B. Z. Eraqi Klorman (1993). The Jews of Yemen in the Nineteenth Century: A Portrait of a Messianic Community. BRILL. p. 12. ISBN 9004096841.
- ^ Eugene L. Rogan (2002). Frontiers of the State in the Late Ottoman Empire: Transjordan, 1850–1921. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-89223-6.
- ^ Bernard Reich (1990). Political Leaders of the Contemporary Middle East and North Africa: A Biographical Dictionary. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 509. ISBN 0-313-26213-6.
- ^ Paul Dresch (2000). A History of Modern Yemen. Cambridge University Press. p. 34. ISBN 0-521-79482-X.
- ^ Massimiliano Fiore (2010). Anglo-Italian Relations in the Middle East, 1922–1940. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-7546-9747-3.
- ^ a b Madawi al-Rasheed (2002). A History of Saudi Arabia. Cambridge University Press. p. 101. ISBN 0-521-64412-7.
- ^ Bernard Reich (1990). Political Leaders of the Contemporary Middle East and North Africa: A Biographical Dictionary. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 509. ISBN 978-0-313-26213-5.
- ^ Madawi al-Rasheed (April 2010). A History of Saudi Arabia. Cambridge University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-521-76128-4.
- ^ Raymond A. Hinnebusch; Anoushiravan Ehteshami (2002). The Foreign Policies of Middle East States. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 262. ISBN 1-58826-020-8.
- ^ Glen Balfour-Paul (1994). The End of Empire in the Middle East: Britain's Relinquishment of Power in Her Last Three Arab Dependencies. Cambridge University Press. p. 60. ISBN 0-521-46636-9.
- ^ a b Kiren Aziz Chaudhry The Price of Wealth: Economies and Institutions in the Middle East p. 117
- ^ Ulrike Freitag Indian Ocean Migrants and State Formation in Hadhramaut: Reform
- ^ Don Peretz The Middle East Today p. 490
- ^ The Middle East Today By Don Peretz p. 491
- ^ Human Rights Human Wrongs By M. S. Gill p. 48
- ^ F. Gregory Gause (1990). Saudi-Yemeni Relations: Domestic Structures and Foreign Influence. Columbia University Press. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-231-07044-7. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Dresch, Paul (2000). A History of Modern Yemen. Cambridge University Press. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-521-79482-4. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Schmitthoff, Clive Macmillan, Clive M. Schmitthoff's select essays on international trade law p. 390
- ^ a b c d e f "Yemen profile (timeline)". BBC. 26 October 2013. Archived from the original on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
1978 – Ali Abdullah Saleh named as president of YAR.
- ^ Dresch, Paul (2000). A History of Modern Yemen. Cambridge University Press. pp. 120–124.
- ^ a b Nohlen, Dieter; Grotz, Florian; Hartmann, Christof, eds. (2001). Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume I. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 309–310. ISBN 978-0-19-924958-9. Archived from the original on 15 February 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
- ^ "Persian Gulf War, Desert Storm – War with Iraqi". Laughtergenealogy.com. Archived from the original on 22 January 2004. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ a b c "Country Profile: Yemen" (PDF). Library of Congress – Federal Research Division. August 2008. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2010.
- ^ "Fighting al-Qaeda: The Role of Yemen's President Saleh". Realclearworld.com. 17 December 2009. Archived from the original on 9 February 2010. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Ginny Hill (1 April 2009). "Yemen's point of no return". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 7 September 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Ginny Hill; Peter Salisbury; Léonie Northedge; Jane Kinninmont (2013). "Yemen: Corruption, Capital Flight and Global Drivers of Conflict". Chatham House. Archived from the original on 30 March 2015. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "The Islah Party". Islamopedia Online. 13 December 2012. Archived from the original on 7 April 2015. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- ^ Peter W. Wilson (1994). Saudi Arabia:The Coming Storm. M.E. Sharpe. p. 129. ISBN 978-0-7656-3347-7.
- ^ Ginny Hill; Peter Salisbury; Léonie Northedge; Jane Kinninmont (2013). "Yemen: Corruption, Capital Flight and Global Drivers of Conflict". Chatham House. Archived from the original on 30 March 2015. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ John R. Bradley (2012). After the Arab Spring: How Islamists Hijacked The Middle East Revolts. Macmillan. p. 113. ISBN 978-0-230-39366-0.
- ^ Bernard Haykel (14 June 2011). "Saudi Arabia's Yemen Dilemma:How to Manage an Unruly Client State". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 28 July 2011. Retrieved 24 October 2014.
- ^ Sarah Phillips (2008). Yemen's Democracy Experiment in Regional Perspective. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-230-61648-6.
- ^ "Civil war". Yca-sandwell.org.uk. Yemeni Community Association in Sandwell. Archived from the original on 16 June 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- ^ U.S. Department of State. Background Notes: Mideast, March 2011. InfoStrategist.com. ISBN 978-1-59243-126-7.
- ^ "News", Policemen killed in south Yemen in clash with rebels, UK: BBC, 1 March 2010, archived from the original on 7 February 2022, retrieved 9 May 2022
- ^ "Yemen timeline". BBC. 28 November 2012. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- ^ "Time running out for solution to Yemen's water crisis". The Guardian, IRIN, quoting Jerry Farrell, country director of Save the Children in Yemen, and Ghassan Madieh, a water specialist for UNICEF in Yemen. 26 August 2012.
- ^ "In eleventh-hour reversal, President Saleh announces candidacy". IRIN. 25 June 2006. Archived from the original on 5 January 2008. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ "Deadly blast strikes Yemen mosque". BBC News. 2 May 2008. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2008.
- ^ "President Ali Abdullah Saleh Web Site". Presidentsaleh.gov.ye. Archived from the original on 19 December 2010. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- ^ "Saleh re-elected president of Yemen". Al Jazeera. 23 September 2006. Archived from the original on 20 February 2011. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ "Yemeni president takes constitutional oath for his new term". News.xinhaunet.com. Xinhua. 27 September 2006. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 14 December 2010.
- ^ "Car bombs at U.S. embassy in Yemen kill 16". Reuters. 17 September 2008. Archived from the original on 9 May 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2022.
- ^ Hall, Bogumila. "Subaltern Rightful Struggles, Comparative ethnographies of the Bedouin villagers in the Naqab, and the akhdam slum dwellers in Sana’a". Ph.D. diss., European University Institute, 2016.
- ^ "Yemen's Ali Abdullah Saleh resigns – but it changes little | Brian Whitaker". the Guardian. 24 November 2011.
- ^ a b Lewis, Alexandra (May 2012). "Changing Seasons: The Arab Spring's Position Within the Political Evolution of the Yemeni State" (PDF). Post-war Reconstruction and Development Unit Working Paper Series. 3.[dead link]
- ^ Ghosh, Bobby (17 September 2012). "The End of Al-Qaeda?". Time. New York. Archived from the original on 6 September 2012. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- ^ "Whose Side Is Yemen On?". Foreign Policy. Washington, D.C. 29 August 2012. Archived from the original on 30 May 2013. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Yemeni Parties, Houthi Rebels Form Unity Government". Voice of America. 21 September 2014. Archived from the original on 9 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Yemen Swears In New Government Amid Crisis". The Huffington Post. 9 November 2014. Archived from the original on 23 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Shiite rebels shell Yemen president's home, take over palace". Newsday. 20 January 2015. Archived from the original on 23 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Here is what's happening in Yemen". The Washington Post. 22 January 2015. Archived from the original on 22 January 2015. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ Rohan, Brian (22 February 2015). "Hadi, a once-quiet leader of a fractious Yemen, strikes defiant pose by reclaiming presidency". U.S. News & World Report. Archived from the original on 22 February 2015. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Yemen's President Hadi declares new 'temporary capital'". Deutsche Welle. 21 March 2015. Archived from the original on 5 June 2015. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ "President Hadi says Aden is Yemen's 'capital'". Al Arabiya. 7 March 2015. Archived from the original on 9 March 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ^ "Yemen's Prime Minister Is Preparing to Flee as Separatists Reach Gates of the Presidential Palace". Time. 30 January 2018. Archived from the original on 2 February 2018. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ Patrick Wintour (16 November 2017). "Saudis must lift Yemen blockade or "untold" thousands will die, UN agencies warn". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 December 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ "50,000 children in Yemen have died of starvation and disease so far this year, monitoring group says". Chicago Tribune. Associated Press. 16 November 2017. Archived from the original on 1 November 2018. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ Kentish, Benjamin (9 October 2016). "Saudi-led coalition in Yemen accused of "genocide" after airstrike on funeral hall kills 140". The Independent. Archived from the original on 7 May 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ Bachman, Jeff (26 November 2018). "US complicity in the Saudi-led genocide in Yemen spans Obama, Trump administrations". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 13 January 2020. Retrieved 13 January 2020.
As a scholar of genocide and human rights, I believe the destruction brought about by these attacks combined with the blockade amounts to genocide.
- ^ Taves, Harold (23 February 2019). Genocide in Yemen-Is the West Complicit? (Essay).
Is there a genocide in Yemen? Based on the definition of genocide: The deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group or nation. The answer is an unequivocal YES.
- ^ "Suspected cholera cases in Yemen surpass one million, reports UN health agency". UN. 22 December 2017. Archived from the original on 4 April 2018. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ Kristof, Nicholas (31 August 2017). "The Photos the U.S. and Saudi Arabia Don't Want You to See". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 17 May 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ "Saudi de facto blockade starves Yemen of food and medicine". Reuters. 11 October 2017. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 10 June 2018.
- ^ "Yemen war will have killed 377,000 by year's end: UN". France 24. 23 November 2021. Archived from the original on 9 December 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- ^ "Yemen war deaths will reach 377,000 by end of the year: UN". Al Jazeera. 23 November 2021. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 30 May 2022.
- ^ "Ali Abdullah Saleh, Yemen's former leader, killed in Sanaa". BBC News. 4 December 2017. Archived from the original on 8 April 2019. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- ^ "Yemen's President Hadi has effectively been sacked by Saudi Arabia". Middle East Monitor. 20 April 2022. Archived from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- ^ "US warship intercepts missiles fired from Yemen 'potentially towards Israel'". BBC News. 20 October 2023. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
- ^ "Who are the Houthis, the group attacking ships in the Red Sea?". The Economist. 12 December 2023. Archived from the original on 12 January 2024. Retrieved 13 January 2024.
Since the bombardment of Gaza began, the Houthis, a Yemeni rebel group, have launched a series of attacks on cargo ships. The insurgents, who are backed by Iran, say they are acting in solidarity with Palestinians. They have threatened to attack any ship bound for or leaving Israel without delivering humanitarian aid to Gaza.
- ^ "UAE's Return to Aden Port Sparks Anger among Yemeni Officials". 21 June 2024.
- ^ "UAE's Bid to Acquire Aden Port Faces Backlash from Public and Parliament". 24 June 2024.
- ^ "Aden Governor warns of UAE occupation's efforts to destroy Aden port". 22 June 2024.
- ^ "Yemen's Aden port to cancel DP World deal -official". Reuters.
- ^ a b c Robert D. Burrowes (2010). Historical Dictionary of Yemen. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 5–340. ISBN 978-0-8108-5528-1.
- ^ "Islands east of the Horn of Africa and south of Yemen". WorldWildlife.org. World Wildlife Fund. Archived from the original on 5 February 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- ^ Peel, M. C.; Finlayson, B. L.; McMahon, T. A. (2007). "Updated world map of the Köppen–Geiger climate classification". Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 11 (5): 1633–1644. Bibcode:2007HESS...11.1633P. doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007. ISSN 1027-5606. Archived from the original on 10 February 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2020. (direct: Final Revised Paper Archived 3 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ a b McLaughlin (2008), p. 3.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Abdul Wali A. al-Khulaidi, Flora of Yemen, Sustainable Environmental Management Program (YEM/97/100), Republic of Yemen, June 2000, p. 7
- ^ Hepper, F.N. (July 1978). "Were There Forests in the Yemen?". Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies. 9 (1979): 65–71. JSTOR 41223217.
- ^ Spalton, J. A.; Al Hikmani, H. M. (2006). "The Leopard in the Arabian Peninsula – Distribution and Subspecies Status" (PDF). Cat News (Special Issue 1): 4–8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 December 2020. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
- ^ "Yemen". State.gov. 8 November 2005. Archived from the original on 16 February 2023. Retrieved 17 October 2010.
- ^ "Freedom in the World – Yemen (2007)". Freedomhouse.org. 2007. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 17 October 2010.
- ^ "Yemen's Saleh declares alliance with Houthis". Al Jazeera. 10 May 2015. Archived from the original on 28 May 2015. Retrieved 5 January 2016.
- ^ Mangan, Fiona (March 2015). Prisons in Yemen. Washington, DC: United States Institute of Peace. p. 9. Retrieved 21 June 2015.
- ^ "The Yemeni-Saudi Border Treaty". Theestimate.com. June 2000. Archived from the original on 15 April 2001. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Saudi authorities erect barriers on Yemeni border". 20 January 2008. Archived from the original on 20 January 2008. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- ^ Bradley, John (11 February 2004). "Saudi Arabia enrages Yemen with fence". The Independent. London. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2007.
- ^ "The hardest part is when we lose a child". CNN. 15 September 2020. Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- ^ "U.S. and U.K. strike Houthi targets in Yemen". NPR. 11 January 2024. Archived from the original on 1 March 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ Lewis, Alexandra (14 May 2013). "Violence in Yemen: Thinking About Violence in Fragile States Beyond the Confines of Conflict and Terrorism". Stability: International Journal of Security and Development. 2 (1): 13.
- ^ "Human Rights in Yemen". Derechos – Human Rights. January 2001. Archived from the original on 9 August 2014. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Here are the 10 countries where homosexuality may be punished by death". The Washington Post. 24 February 2014. Archived from the original on 29 June 2014. Retrieved 3 September 2017.
- ^ "The Global Gender Gap Report 2012" (PDF). World Economic Forum. 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 September 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "World Report 2001 on Yemen". Human Rights Watch. 2001. Archived from the original on 15 June 2010. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ Daragahi, Borzou (11 June 2008). "Yemeni bride, 10, says I won't". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 18 February 2010. Retrieved 16 February 2010.
- ^ Walt, Vivienne (3 February 2009). "A 10-Year-Old Divorcée Takes Paris". Time/CNN. Archived from the original on 5 February 2009. Retrieved 16 February 2010.
- ^ Madabish, Arafat (28 March 2009). "Sanaa's first woman lawyer". Asharq Alawsat English edition. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013. Retrieved 16 February 2010.
- ^ Refugees, United Nations High Commissioner for. "Refworld | UN: Breakthrough resolution establishes expert group to investigate violations in Yemen". Refworld. Archived from the original on 14 September 2023. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Saudis used "incentives and threats" to shut down UN investigation in Yemen". the Guardian. 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Scale of torture and deaths in Yemen's unofficial prisons revealed". The Guardian. 30 June 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- ^ "2020 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Yemen". Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. Archived from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 9 May 2022.
- ^ "Trafficking in Persons Report: Country Narratives T – Z and Special Case" (PDF). U.S. Department of State. 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ^ "Tiers: Placement, Guide, and Penalties for Tier 3 Countries". U.S. Department of State. 2011. Archived from the original on 10 May 2020. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ^ Mohaiemen, N. (27 July 2004). "Slaves in Saudi". The Daily Star. Archived from the original on 11 August 2004.
- ^ "Slaves in impoverished Yemen dream of freedom". Al Arabiya. 21 July 2010. Archived from the original on 12 January 2012.
- ^ "Open Letter to the UN Secretary-General on Children and Armed Conflict". HRW. Archived from the original on 23 July 2020. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- ^ "UN: Children in war must never be a political bargaining chip". Amnesty. 23 June 2020. Archived from the original on 23 June 2020. Retrieved 23 June 2020.
- ^ "Deadly Consequences Obstruction of Aid in Yemen During Covid-19". Human Rights Watch. 14 September 2020. Archived from the original on 22 September 2020. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- ^ Ministry of Public Health & Population, Yemen.
- ^ "Law establishing province of Socotra Archipelago issued". Presidenthadi-gov-ye.info. 18 December 2013. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- ^ "Yemen to Become Six-Region Federation". Al-Jazeera. 10 February 2014. Archived from the original on 27 May 2018. Retrieved 10 February 2014.
- ^ Al-Haj, Ahmed (3 January 2015). "Yemen's Shiite rebels reject plan for federal system". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ "Yemeni government quits in protest at Houthi rebellion". The Guardian. 22 January 2015. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ Greenfield, Danya (22 January 2015). "Yemen crisis: A coup in all but name". BBC News. Archived from the original on 31 January 2023. Retrieved 21 March 2015.
- ^ Tharoor, Ishaan (1 November 2010). "A Brief History of Yemen: Rich Past, Impoverished Present". Time. ISSN 0040-781X. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Basic Data Selection - amaWebClient". unstats.un.org. Archived from the original on 20 September 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Yemen Overview". World Bank. Archived from the original on 26 April 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "The Houthis' embargo on Yemen's oil exports". Middle East Institute. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ Breisinger, C., Diao, X., Collion, M. H., & Rondot, P. (2011). Impacts of the triple global crisis on growth and poverty: The case of Yemen. Development Policy Review, 29(2), 155–184
- ^ Adam Heffez (23 July 2013). "Water Problem due to cultivation of Qat". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 28 December 2013. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- ^ "Conflict in Yemen: From Ethnic Fighting to Food Riots". New England Complex Systems Institute. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 25 February 2024.
- ^ "Entrepreneur tries to get Yemenis buzzing about coffee, not qat". CSMonitor.com. 27 October 2012. Archived from the original on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- ^ "Yemen". Encyclopaedia Britannica. 23 April 2013. Archived from the original on 25 April 2021. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Climate Change: A New Battlefield in Yemen's Ongoing Conflict". Arab Center Washington DC. 3 October 2024. Retrieved 29 October 2024.
- ^ Evans, Judith (21 October 2009). "Yemen could become first nation to run out of water". The Times. Archived from the original on 11 March 2017. Retrieved 11 March 2017.
- ^ "Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability". Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- ^ "YEMEN: Time running out for solution to water crisis". IRIN. 13 August 2012. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ^ Mahr, Krista (14 December 2010). "What If Yemen Is the First Country to Run Out of Water?". TIME Magazine. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
- ^ al-Mujahed, Ali; Naylor, Hugh (23 July 2015). "In Yemen's grinding war, if the bombs don't get you, the water shortages will". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 18 October 2015. Retrieved 20 September 2015.
- ^ "Water, Sanitation and Hygiene". www.unicef.org. Archived from the original on 27 November 2021. Retrieved 25 April 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "The General Census of Population 2004". Sabanews. 29 December 2004 [Updated 13 December 2013]. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "The population explosion on Europe's doorstep". Times (London). London. 18 May 2008. Archived from the original on 24 June 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Yemen: Government planning to curb population growth". IRIN Middle East. 14 July 2008. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2013. (for Arabic, read it here: [1].)
- ^ "Country Comparison: Total fertility rate". Central Intelligence Agency. CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- ^ Eric Hansen (January 2006). "Sana'a Rising". Saudi Aramco World. Archived from the original on 27 November 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Sanaa | History, Population, & Facts | Britannica". 17 June 2023. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- ^ "U.S. Relations With Yemen". U.S. Department of State. 28 August 2013. Archived from the original on 4 June 2019. Retrieved 21 May 2019.
- ^ Flamand, Annasofie; Macleod, Hugh (5 December 2009). "The children of Yemen's tribal war". The Herald Scotland. Glasgow. Archived from the original on 25 November 2010. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Lehmann, Hermann (1954). "Distribution of the sickle cell trait". Eugenics Review. 46 (2): 101–121. PMC 2973326. PMID 21260667.
- ^ Lawrence G. Potter (2009). The Persian Gulf in History. Springer. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-230-61845-9.
- ^ Pirouz Mojtahed-Zadeh (2013). Security and Territoriality in the Persian Gulf: A Maritime Political Geography. Routledge. p. 64. ISBN 978-1-136-81717-5.
- ^ "Yemen". Jewish Virtual Library. 22 May 2012. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Indian Diaspora in Yemen". Indian Embassy in Sanaa. Archived from the original on 12 March 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ^ "The world's successful diasporas". Management Today. London. 3 April 2007. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ Ameen Ali Talib (November 1995). "Hadramis in Singapore". Al-bab.com. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "African connections in Yemeni music". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 22 February 2013. [dead link]
- ^ "Mauritania – Arab invasions". Library of Congress Country Studies. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Story of the Prophet Ismail (Ishmael) – Ishmael's Wives | Islamic History". Alim.org. Retrieved 29 September 2022.
- ^ a b Jonathan Fowler (18 October 2014). "Red Sea drownings of Yemen-bound migrants hit new high". Your Middle East. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- ^ "World Refugee Survey 2008". U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants. 19 June 2008. Archived from the original on 19 October 2014. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Poor and desperate, Syrian refugees beg on Yemen's streets". Reuters. 26 September 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ Black, Ian (2 April 2013). "Saudi Arabia expels thousands of Yemeni workers". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ^ "History of Islam in the UK". BBC. 7 September 2009. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ Woodard, Roger D. (10 April 2008). The Ancient Languages of Asia and the Americas. Cambridge University Press. p. 228. ISBN 978-0-521-68494-1. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ^ "Ethnologue entry for South Arabian languages". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ "Yemen – Languages". Ethnologue. 19 February 1999. Retrieved 23 December 2015.
- ^ "Wikimedia Traffic Analysis Report – Wikipedia Page Views Per Country – Breakdown". stats.wikimedia.org.
- ^ "Yemen Ethno Religious summary". www.gulf2000.columbia.edu.
- ^ "Yemen: The conflict in Saada Governorate – analysis". UNHCR. Archived from the original on 20 November 2012.
- ^ a b "Yemen: The conflict in Saada Governorate – analysis". UN High Commissioner for Refugees. 24 July 2008. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ Al-Zaidi, Hassan (22 October 2007). "The Twelve-Imam Shiite Sect". Yemen Times. Archived from the original on 22 October 2007.
- ^ "Yemen 2012 International Religious Freedom Report" (PDF). United States Secretary of State. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- ^ "Yemen". Institut MEDEA. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 14 December 2013.
- ^ Smith, Oliver (15 April 2017). "Mapped: The world's most (and least) religious countries". The Telegraph. Digital Travel Editor. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2020.
- ^ "Serving Persecuted Christians Worldwide – Yemen – Open Doors UK & Ireland". Opendoorsuk.org. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ Department Of State. The Office of Electronic Information, Bureau of Public Affairs (19 September 2008). "Yemen". 2001-2009.state.gov. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- ^ "Guide: Christians in the Middle East". BBC News. 11 October 2011.
- ^ Johnstone, Patrick; Miller, Duane Alexander (2015). "Believers in Christ from a Muslim Background: A Global Census". IJRR. 11: 17. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ Ben Zion, Ilan (21 March 2016). "17 Yemenite Jews secretly airlifted to Israel in end to 'historic mission'". Times of Israel. Retrieved 21 March 2016.
- ^ "A Final Push to Free Yemen's Remaining Jews". Tablet Magazine. 6 November 2020.
- ^ "History of the Jews of Yemen". 10 May 2022.
- ^ "National adult literacy rates (15+), youth literacy rates (15–24) and elderly literacy rates (65+)". UNESCO Institute for Statistics. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Education Report 2008. "The Development of Education in the Republic of Yemen."" (PDF). 2008. p. 3. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Education Report 2008." The Development of Education in the Republic of Yemen."" (PDF). 2008. p. 5. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "Yemen". Ranking Web of Universities. Retrieved 26 February 2013.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2021". World Intellectual Property Organization. United Nations. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2019". www.wipo.int. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "RTD – Item". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index". INSEAD Knowledge. 28 October 2013. Archived from the original on 2 September 2021. Retrieved 2 September 2021.
- ^ a b c "About this Collection | Country Studies | Digital Collections | Library of Congress". Library of Congress. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- ^ "The media in Yemen, short introduction to media in Yemen including broadcasting. Last revised on 21 February 2006". Al-bab.com. Archived from the original on 27 March 2014. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- ^ "Arab Media Outlook 2011–2015" (PDF). 2012. p. 217. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ^ "The Sport of Camel Jumping". Smithsonianmag.com. September 2010. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Yemenis open up about the Gulf Cup". Yemen Today. 7 January 2011. Archived from the original on 10 May 2011. Retrieved 8 February 2011.
- ^ "List of World Heritage in Danger: The 54 properties which the World Heritage Committee has decided to include on the List of World Heritage in danger in accordance with Article 11 (4) of the Convention". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. 2015. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- ^ Bokova, Irina (12 May 2015). "UNESCO Director-General calls on all parties to protect Yemen's cultural heritage". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
In addition to causing terrible human suffering, these attacks are destroying Yemen's unique cultural heritage, which is the repository of people's identity, history and memory and an exceptional testimony to the achievements of the Islamic Civilization.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Old Walled City of Shibam". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Old City of Sana'a". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Historic Town of Zabid". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre. "Socotra Archipelago". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ "Saving the dragon's blood: how an island refused to let a legendary tree die out". the Guardian. 12 November 2022. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
External links
Government
- National Information Center – Official Yemen Information Portal
- Presidential Leadership Council – official website of the president of Yemen
- Prime Minister – official website of the prime minister of Yemen
- Statistics – official website of Central Statistical Organization
History
- "History" – Yemeni History at National Information Center
Tourism
- Explore Yemen – Yemen's official tourism portal
Maps
 Wikimedia Atlas of Yemen
Wikimedia Atlas of Yemen Geographic data related to Yemen at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Yemen at OpenStreetMap