Sincalide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
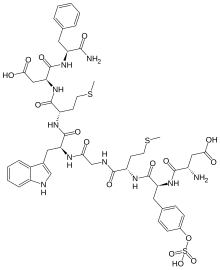
| Other names | 1-De(5-oxo-L-proline)-2-de-L-glutamine- 5-L-methioninecaerulein, 3-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[(2-amino-3-carboxy-propanoyl) amino]-3-(4-sulfooxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4- methylsulfanyl-butanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3- (1H-indol-3-yl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanyl- butanoyl]amino]-3-[(1-carbamoyl-2-phenyl-ethyl) carbamoyl]propanoic acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.384 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C49H62N10O16S3 |
| Molar mass | 1143.27 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Sincalide (INN) is a cholecystokinetic drug administered by injection to aid in diagnosing disorders of the gallbladder and pancreas. It is the 8-amino acid C-terminal fragment of cholecystokinin, and also known as CCK-8.
Common adverse effects following administration include abdominal discomfort and nausea. These effects are more pronounced following rapid infusion.
Clinical Use
Indications
Sincalide may be used to stimulate gallbladder contraction, as may be assessed by contrast agent cholecystography or ultrasonography, or to obtain by duodenal aspiration a sample of concentrated bile for analysis of cholesterol, bile salts, phospholipids, and crystals.[1] It can also be used to stimulate pancreatic secretion (especially in conjunction with secretin) prior to obtaining a duodenal aspirate for analysis of enzyme activity, composition, and cytology. In some instances it is used to accelerate the transit of a barium meal through the small bowel, thereby decreasing the time and-extent of radiation associated with fluoroscopy and x-ray examination of the intestinal tract.[2]
References
- ^ Ziessman HA (September 2019). "Sincalide: A Review of Clinical Utility, Proper Infusion Methodology, and Alternative Cholecystogogues". Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology. 47 (3): 210–212. doi:10.2967/jnmt.119.226019. PMID 31019045. S2CID 131775567.
- ^ Kinevac Package Insert
External links
- "KINEVAC (sincalide)]". DailyMed. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
