Presidential system
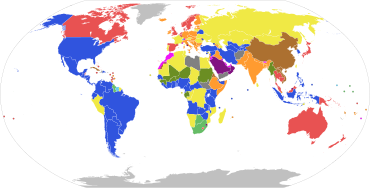
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Other systems:
Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
| Part of the Politics series |
| Politics |
|---|
|
|
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled "president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and legitimacy from a source that is separate from the legislative branch. The system was popularized by its inclusion in the Constitution of the United States.[1]
This head of government is in most cases also the head of state. In a presidential system, the head of government is directly or indirectly elected by a group of citizens and is not responsible to the legislature, and the legislature cannot dismiss the president except in extraordinary cases. A presidential system contrasts with a parliamentary system, where the head of government (usually called a prime minister) derives their power from the confidence of an elected legislature, which can dismiss the prime minister with a simple majority.
Not all presidential systems use the title of president. Likewise, the title is sometimes used by other systems. It originated from a time when such a person personally presided over the governing body, as with the President of the Continental Congress in the early United States, prior to the executive function being split into a separate branch of government. It may also be used by presidents in semi-presidential systems. Heads of state of parliamentary republics, largely ceremonial in most cases, are called presidents. Dictators or leaders of one-party states, whether popularly elected or not, are also often called presidents.
The presidential system is the dominant form of government in Latin America and is also popular in Sub-Saharan Africa. By contrast, there are very few presidential republics in Europe (with Cyprus and Turkey being the only examples). In Asia, the system is used by South Korea, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
History
Development in the Americas
The presidential system has its roots in the governance of the British colonies of the 17th century in what is now the United States. The Pilgrims, permitted to govern themselves in Plymouth Colony, established a system that utilized an independent executive branch. Each year, a governor was chosen by the colonial legislature, as well as several assistants, analogous to modern day cabinets. Additional executive officials such as constables and messengers were then appointed.[2] At the same time, the British Isles underwent a brief period of republicanism as the Protectorate, during which the Lord Protector served as an executive leader similar to a president.[3]
The first true presidential system was developed during the United States Constitutional Convention in 1787.[4] Drawing inspiration from the previous colonial governments, from English Common Law, and from philosophers such as John Locke and Montesquieu, the delegates developed what is now known as the presidential system. Most notably, James Wilson advocated for a unitary executive figure that would become the role of the president.[5] The United States became the first presidential republic when the Constitution of the United States came into force in 1789, and George Washington became the first president under a presidential system.
During the 1810s and 1820s, Spanish colonies in the Americas sought independence, and several new Spanish-speaking governments emerged in Latin America. These countries modeled their constitutions after that of the United States, and the presidential system became the dominant political system in the Americas.[4] Following several decades of monarchy, Brazil also adopted the presidential system in 1889 with Deodoro da Fonseca as its first president. Latin American presidential systems have experienced varying levels of stability, with many experiencing periods of dictatorial rule.[6][7][8]
As a global system
Following the pattern of other Spanish colonies, the Philippines established the first presidential system in Asia in 1898, but it fell under American control due to the Spanish–American War. The presidential system was restored after the United States granted the Philippines independence in 1946.[4]
The end of World War II established presidential systems in two countries. After the United States ended the Japanese occupation of Korea, it assisted South Korea in the formation of a presidential government. However, the early years of the South Korean presidency were marked by dictatorial control.[citation needed] At the same time, Indonesia declared independence from the Netherlands in 1945. While it nominally used a presidential system, it was in effect a dictatorship where the president controlled all branches of government. A true presidential system was established in 1998.[citation needed]
Decolonization in the 1950s and 1960s brought with it significant expansion of the presidential system. During this time, several new presidential republics were formed in Africa.[4] Cyprus,[9] the Maldives,[10] and South Vietnam[citation needed] also adopted the presidential system following decolonization. Pakistan and Bangladesh did so as well, but they changed their governmental systems shortly afterward.[citation needed]
Several more countries adopted the presidential system in the final decades of the 20th century. A modified version of the presidential system was implemented in Iran following constitutional reform in 1989 in which the Supreme Leader serves as the head of state and is the absolute power in this country.[11] In 1981, Palau achieved independence and adopted a presidential system.[12] When the Soviet Union was dissolved in 1991, the presidential system was adopted by the new states that were created, though most of them adopted other governmental systems over the following decades.[13]
The presidential system continues to be adopted in the 21st century. Following its independence in 2011, South Sudan adopted a presidential system.[14] In 2018, after the 2017 Turkish constitutional referendum, Turkey adopted a presidential system.[15][16][17]
Features
There are several characteristics that are unique to presidential systems or prominent in countries that use presidential systems. The defining aspect of presidential systems is the separation of powers that divides the executive and the legislature. Advocates of presidential systems cite the democratic nature of presidential elections, the advantages of separation of powers, the efficiency of a unitary executive, and the stability provided by fixed-terms. Opponents of presidential systems cite the potential for gridlock, the difficulty of changing leadership, and concerns that a unitary executive can give way to a dictatorship.
Separation of powers
The presidential system is defined by the separation of the executive branch from other aspects of government. The head of government is elected to work alongside, but not as a part of, the legislature.[18] There are several types of powers that are traditionally delegated to the president. Under a presidential system, the president may have the power to challenge legislation through a veto,[19] the power to pardon crimes, authority over foreign policy, authority to command the military as the Commander-in-chief, and authority over advisors and employees of the executive branch.[citation needed]
Checks and balances
Separation of powers is sometimes held up as an advantage, in that each branch may scrutinize the actions of the other. This is in contrast with a parliamentary system, where the majority party in the legislature that also serves as the executive is unlikely to scrutinize its own actions. Writing about the Watergate scandal, former British MP Woodrow Wyatt said "don't think a Watergate couldn't happen here, you just wouldn't hear about it."[20] The extent of this effect is debated. Some commentators argue that the effect is mitigated when the president's party is in power, while others note that party discipline is not as strictly enforced in presidential systems.[21]
Another stated benefit of the separation of powers is the ability of the legislature to enforce limits on the powers of the executive. In a parliamentary system, if important legislation proposed by the incumbent prime minister and his cabinet is "voted down" by a majority of the members of parliament then it is considered a vote of no confidence. The presidential system has no such mechanism, and the legislature has little incentive to appease the president beyond saving face.[citation needed]
Efficiencies and inefficiencies
When an action is within the scope of a president's power, a presidential system can respond more rapidly to emerging situations than parliamentary ones. A prime minister, when taking action, needs to retain the support of the legislature, but a president is often less constrained. In Why England Slept, future U.S. president John F. Kennedy argued that British prime ministers Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain were constrained by the need to maintain the confidence of the Commons.[22]
James Wilson, who advocated for a presidential system at the constitutional convention, maintained that a single chief executive would provide for greater public accountability than a group and thereby protect against tyranny by making it plain who was responsible for executive actions. He also submitted that a singular chief executive was necessary to ensure promptness and consistency and guard against deadlock, which could be essential in times of national emergency.[23]
Conversely, a presidential system can produce gridlock when the president and the legislature are in opposition. This rarely happens in a parliamentary system, as the prime minister is always a member of the party in power. This gridlock is common occurrence, as the electorate often expects more rapid results than are possible from new policies and switches to a different party at the next election.[24] Critics such as Juan Linz, argue that in such cases of gridlock, presidential systems do not offer voters the kind of accountability seen in parliamentary systems, and that this inherent political instability can cause democracies to fail, as seen in such cases as Brazil and Allende's Chile.[25]
It is easy for either the president or the legislature to escape blame by shifting it to the other. Describing the United States, former Treasury Secretary C. Douglas Dillon said "the president blames Congress, the Congress blames the president, and the public remains confused and disgusted with government in Washington".[26] Years before becoming president, Woodrow Wilson famously wrote "how is the schoolmaster, the nation, to know which boy needs the whipping?"[27] Walter Bagehot said of the American system, "the executive is crippled by not getting the law it needs, and the legislature is spoiled by having to act without responsibility: the executive becomes unfit for its name, since it cannot execute what it decides on; the legislature is demoralized by liberty, by taking decisions of which others [and not itself] will suffer the effects".[28]
A 2024 meta-analytical review found that presidential systems were associated with more corruption than parliamentary systems.[29]
Presidential elections
In a presidential system, the president is elected independently of the legislature. This may be done directly through a popular vote or indirectly such as through the electoral college used in the United States. This aspect of presidential systems is sometimes touted as more democratic, as it provides a broader mandate for the president. Once elected, a president typically remains in office until the conclusion of a term.[30]
Fixed-terms
Presidential systems are typically understood as having a head of government elected by citizens to serve one or more fixed-terms. Fixed-terms are praised for providing a level of stability that other systems lack.
Proponents of the presidential system also argue that stability extends to the cabinets chosen under the system. In most parliamentary systems, cabinets must be drawn from within the legislative branch. Under the presidential system, cabinet members can be selected from a much larger pool of potential candidates. This allows presidents the ability to select cabinet members based as much or more on their ability and competency to lead a particular department as on their loyalty to the president, as opposed to parliamentary cabinets, which might be filled by legislators chosen for no better reason than their perceived loyalty to the prime minister.
Some political scientists dispute this concept of stability, arguing that presidential systems have difficulty sustaining democratic practices and that they have slipped into authoritarianism in many of the countries in which they have been implemented. According to political scientist Fred Riggs, presidential systems have fallen into authoritarianism in nearly every country they've been attempted.[31][32] The list of the world's 22 older democracies includes only two countries (Costa Rica and the United States) with presidential systems.[33] Yale political scientist Juan Linz argues that:[25]
The danger that zero-sum presidential elections pose is compounded by the rigidity of the president's fixed term in office. Winners and losers are sharply defined for the entire period of the presidential mandate ... losers must wait four or five years without any access to executive power and patronage. The zero-sum game in presidential regimes raises the stakes of presidential elections and inevitably exacerbates their attendant tension and polarization.
Fixed-terms in a presidential system may also be considered a check on the powers of the executive, contrasting parliamentary systems, which may allow the prime minister to call elections whenever they see fit or orchestrate their own vote of no confidence to trigger an election when they cannot get a legislative item passed.
Limited mechanisms of removal
Unlike in parliamentary systems, the legislature does not have the power to recall a president under the presidential system.[30] However, presidential systems may have methods to remove presidents under extraordinary circumstances, such as a president committing a crime or becoming incapacitated. In some countries, presidents are subject to term limits.
The inability to remove a president early is also the subject of criticism. Even if a president is "proved to be inefficient, even if he becomes unpopular, even if his policy is unacceptable to the majority of his countrymen, he and his methods must be endured until the moment comes for a new election".[34]
The consistency of a presidency may be seen as beneficial during times of crisis. When in a time of crisis, countries may be better off being led by a president with a fixed term than rotating premierships.[citation needed] Some critics, however, argue that the presidential system is weaker because it does not allow a transfer of power in the event of an emergency. Walter Bagehot argues that the ideal ruler in times of calm is different from the ideal ruler in times of crisis, criticizing the presidential system for having no mechanism to make such a change.[28]
Heightened status
The president's status as both head of government and head of state is sometimes the subject of criticism. Dana D. Nelson criticizes the office of the President of the United States as essentially undemocratic and characterizes presidentialism as worship of the president by citizens, which she believes undermines civic participation.[35][36]
Comparative politics
The separation of the executive and the legislature is the key difference between a presidential system and a parliamentary system. The presidential system elects a head of government independently of the legislature, while in contrast, the head of government in a parliamentary system answers directly to the legislature. Presidential systems necessarily operate under the principle of structural separation of powers, while parliamentary systems do not;[18] however, the degree of functional separation of powers exhibited in each varies – dualistic parliamentary systems such as the Netherlands, Sweden and Slovakia forbid members of the legislature from serving in the executive simultaneously, while Westminster-type parliamentary systems such as the United Kingdom require it. Heads of government under the presidential system do not depend on the approval of the legislature as they do in a parliamentary system (with the exception of mechanisms such as impeachment).[30]
The presidential system and the parliamentary system can also be blended into a semi-presidential system. Under such a system, executive power is shared by an elected head of state (a president) and a legislature-appointed head of government (a prime minister or premier). The amount of power each figure holds may vary, and a semi-presidential system may lean closer to one system over the other.[30] The president typically retains authority over foreign policy in a semi-presidential system.[citation needed] A pure presidential system may also have mechanisms that resemble those of a parliamentary system as part of checks and balances. The legislature may have oversight of some of the president's decisions through advice and consent, and mechanisms such as impeachment may allow the legislature to remove the president under drastic circumstances.[citation needed]
Presidentialism metrics
Presidentialism metrics allow a quantitative comparison of the strength of presidential system characteristics for individual countries. Presidentialism metrics include the presidentialism index in V-Dem Democracy indices[37] and presidential power scores.[38] The table below shows for individual countries the V-Dem presidentialism index, where higher values indicate higher concentration of political power in the hands of one individual.
Subnational governments
Subnational governments may be structured as presidential systems. All of the state governments in the United States use the presidential system, even though this is not constitutionally required. In these cases instead of the title of President the role has the title of Governor. On a local level, a presidential system might be organized with the office of Mayor acting as the president. Some countries without a presidential system at the national level use a form of this system at a subnational or local level. One example is Japan, where the national government uses the parliamentary system.
States with a presidential system of government
Presidential republics without a prime minister
 Angola[a][39]
Angola[a][39] Argentina
Argentina Benin
Benin Bolivia[b]
Bolivia[b] Brazil
Brazil Chile
Chile Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cyprus
Cyprus Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador El Salvador
El Salvador Gambia, The
Gambia, The Ghana
Ghana Guatemala
Guatemala Honduras
Honduras Indonesia
Indonesia Liberia
Liberia Malawi
Malawi Maldives
Maldives Mexico
Mexico Nicaragua
Nicaragua Nigeria
Nigeria Palau
Palau Panama
Panama Paraguay
Paraguay Philippines
Philippines Seychelles
Seychelles Somaliland
Somaliland Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan United States
United States Uruguay[c]
Uruguay[c] Venezuela
Venezuela Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Non-UN members or observers are in italics.
Presidential republics with a prime minister
The following countries have presidential systems where the post of prime minister (official title may vary) exists alongside that of the president. The president is still both the head of state and government and the prime minister's role is mostly to assist the president.
Non-UN members or observers are in italics.Presidential system in administrative divisions
Dependencies of the United States
Special administrative regions of China
Former presidential republics
 Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004–2021)
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan (2004–2021) Armenia (1998–2013)[d]
Armenia (1998–2013)[d] Azerbaijan SSR/
Azerbaijan SSR/ Azerbaijan (1990–1991, 1992–2016)[e]
Azerbaijan (1990–1991, 1992–2016)[e] Bangladesh (1975–1991)[f]
Bangladesh (1975–1991)[f] Republic of China (1948–1991) de facto[g]
Republic of China (1948–1991) de facto[g] Cuba (1902–1959)
Cuba (1902–1959) Estonia (1938–1940)
Estonia (1938–1940) Georgia (1995–2004; 2005–2011)[h]
Georgia (1995–2004; 2005–2011)[h] Germany (1930–1933) de facto[i][failed verification]
Germany (1930–1933) de facto[i][failed verification] Greece (1822–1832,[41] 1973–1974)
Greece (1822–1832,[41] 1973–1974) Haiti (1859–1957, 1957–1986)
Haiti (1859–1957, 1957–1986) Katanga (1960–1963)
Katanga (1960–1963) Kirghiz SSR/
Kirghiz SSR/ Kyrgyzstan (1990–1993)[j]
Kyrgyzstan (1990–1993)[j] Mali (1960–1992)[k]
Mali (1960–1992)[k] Mauritania (1960–1978)[l]
Mauritania (1960–1978)[l] Niger (1960–1974, 1989–1993)[m]
Niger (1960–1974, 1989–1993)[m] Pakistan (1958–1973,1978–1985, 2001–2002)
Pakistan (1958–1973,1978–1985, 2001–2002) Poland (1935–1939)
Poland (1935–1939) RSFSR/
RSFSR/ Russia (1991–1992) de facto
Russia (1991–1992) de facto South Korea (1963–1972)[n]
South Korea (1963–1972)[n] South Vietnam (1955–1975)[citation needed]
South Vietnam (1955–1975)[citation needed] Syria (1963–2024)
Syria (1963–2024) Tajik SSR (1990–1991)
Tajik SSR (1990–1991) Togo (1960-2024)
Togo (1960-2024) Turkmen SSR (1990–1991)
Turkmen SSR (1990–1991) Ukraine (1995–1996)[o]
Ukraine (1995–1996)[o] Uzbek SSR (1990–1991)
Uzbek SSR (1990–1991)
Notes
- ^ President and legislature are elected directly by the people via double simultaneous vote.
- ^ President and legislature are elected directly by the people via double simultaneous vote.
- ^ President and legislature are elected directly by the people via double simultaneous vote.
- ^ as the Armenian SSR parliamentary in 1990–1991, Soviet age and after independence, it was a semi-presidential republic in 1991–1998, a presidential republic in 1998–2013, a semi-presidential republic in 2013–2018 and a parliamentary republic in 2018.
- ^ as the Azerbaijan SSR, it was a presidential republic in 1990–1991, a semi-presidential republic after independence in 1991–1992, a presidential republic in 1992–2016 and a semi-presidential republic in 2016. Under a hereditary dictatorship since 1993
- ^ Parliamentary in 1972–1975, presidential in 1975–1991, and parliamentary since 1991.
- ^ De facto Presidential system in 1948–1991 under a de jure parliamentary republic under the Temporary Provisions against the Communist Rebellion.
- ^ as the Georgian SSR and after independence, parliamentary in 1990–1991, semi-presidential in 1991–1995, presidential in 1995–2004, semi-presidential in 2004–2005 and presidential 2005–2011. Semi-presidential in 2011–2019 and parliamentary since 2019.
- ^ A semi-presidential republic as the Weimar Republic in 1918–1930, a presidential republic in 1930–1933, a totalitarian dictatorship under a parliamentary system in 1933–1945 as a Nazi Germany, a military occupation in 1945–1949 and a parliamentary republic in 1949.
- ^ Presidential in 1990–1993, Semi-presidential in 1993–2010 (de jure); 1993–2021 (de facto), Parliamentary in 2010–2021 (de jure), and presidential again in 2021.
- ^ A presidential republic (1960–1991, 2023-present), military dictatorship (1968–1991,1991–1992, 2012, 2020-present) single-party state (1960–1968, 1974–1991) semi-presidential republic (1991–2023).
- ^ A one-party presidential republic (1960–1978), military dictatorship (1978–1992, 2005–2007, 2008–2009) semi-presidential republic since 1992.
- ^ A single-party presidential republic (1960–1974, 1989–1993), a military dictatorship (1974–1993, 1996–1999, 1999, 2010–2011, 2023-present), a semi-presidential republic (1993–1996, 1999–2010, 2011–2023)
- ^ All South Korean constitutions since 1963 provided for a strong executive Presidency; in addition, the formally-authoritarian Yushin Constitution of the Fourth Republic established a presidential power to dissolve the National Assembly, nominally counterbalanced by a vote of no confidence. Both of these provisions were retained by the Fifth Republic's constitution but repealed upon the transition to democracy and the establishment of the Sixth Republic
- ^ An interim constitution passed in 1995 removed the President's ability to dissolve the Verkhovna Rada and the Rada's ability to dismiss the government by a vote of no confidence. Both of these provisions were restored upon the passage of a permanent constitution in 1996.
References
- ^ "Varieties of public representation". Political Representation. Cambridge University Press. 2010. ISBN 978-0521128650.
- ^ Fennell, Christopher. "Plymouth Colony Legal Structure". Histarch.uiuc.edu.
- ^ Vile, M. J. (1967). The separation of powers. In: Greene, J. P., & Pole, J. R. (Eds.). (2008). A companion to the American Revolution, Ch. 87. John Wiley & Sons.
- ^ a b c d Sundquist, James L. (1997). "The U.S. Presidential System as a Model for the World". In Baaklini, Abdo I.; Desfosses, Helen (eds.). Designs for Democratic Stability: Studies in Viable Constitutionalism. Routledge. pp. 53–72. ISBN 0765600528.
- ^ McCarthy, Daniel J. (1987). "James Wilson and the Creation of the Presidency". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 17 (4): 689–696.
- ^ Sondrol, Paul (2005). "The Presidentialist Tradition in Latin America". International Journal of Public Administration. 28 (5): 517–530. doi:10.1081/PAD-200055210. S2CID 153822718.
- ^ Mainwaring, Scott (1990). "Presidentialism in Latin America". Latin American Research Review. 25: 157–179. doi:10.1017/S0023879100023256. S2CID 252947271.
- ^ Valenzuela, Arturo (2004). "Latin American Presidencies Interrupted". Journal of Democracy. 15 (4): 5–19. doi:10.1353/jod.2004.0075. S2CID 51825804.
- ^ Ker-Lindsay, James (2006). "Presidential Power and Authority in the Republic of Cyprus". Mediterranean Politics. 11: 21–37. doi:10.1080/13629390500490379. S2CID 145444372.
- ^ Heath-Brown, Nick (2015). "Maldives". The Statesman's Yearbook 2016.
- ^ Buchta, Wilfried (2000). Who Rules Iran? The Structure of Power in the Islamic Republic. The Washington Institute for Near East Policy and the Konrad Adenauer Stiftung. p. 22. ISBN 0944029361.
- ^ Shuster, Donald R. (1983). "Elections in the Republic of Palau". Political Science. 35: 117–132. doi:10.1177/003231878303500108.
- ^ Hale, Henry E. (2012). "Two Decades of Post-Soviet Regime Dynamics". Demokratizatsiya. 20 (2): 71–77.
- ^ Diehl, Katharina; van der Horst, Judith (2013). "The New Electoral Law in South Sudan". Law and Politics in Africa, Asia and Latin America. 46 (2): 215–233.
- ^ Kirişci, Kemal; Toygür, Ilke (2019). "Turkey's new presidential system and a changing west". Brookings.
- ^ Adar, Sinem; Seufert, Günter (2021). "Turkey's Presidential System after Two and a Half Years". Stiftung Wissenschaft und Politik.
- ^ "Turkey elections: How powerful will the next Turkish president be?". BBC News. 2018-06-25. Retrieved 2022-03-01.
- ^ a b von Mettenheim, Kurt (1997). Presidential Institutions and Democratic Politics. The Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 2–15. ISBN 0801853133.
- ^ Tsebelis, George (1995). "Decision Making in Political Systems: Veto Players in Presidentialism, Parliamentarism, Multicameralism and Multipartyism". British Journal of Political Science. 25 (3): 289–325. doi:10.1017/S0007123400007225. S2CID 18060081.
- ^ Schlesinger, Arthur (1974). "No Way to Curb the Executive". The New Republic.
- ^ Depauw, Sam; Martin, Shane (2008). "Legislative party discipline and cohesion in comparative perspective". In Giannetti, Daniela; Benoit, Kenneth (eds.). Intra-Party Politics and Coalition Governments. Routledge.
- ^ Kennedy, John F. (1940). Why England Slept. Wilfred Funk, Inc.
- ^ Yoo 2019, pp. 55–57
- ^ George, Edwards; Warrenberg, Martin (2016). Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy, AP* Edition – 2016 Presidential Election, 17th Edition. Pearson Higher Education. p. 16. ISBN 9780134586571.
- ^ a b Linz, Juan (1990). "The perils of presidentialism". The Journal of Democracy. 1: 51–69. doi:10.1353/jod.2005.0026.
- ^ Sundquist, James (1992). Constitutional Reform and Effective Government. Brookings Institution Press. p. 11.
- ^ Wilson, Congressional Government (1885), pp. 186–187.
- ^ a b Balfour. "The Cabinet". The English Constitution.
- ^ Dawson, Stephen; Schwenk, Jana; Xezonakis, Georgios (2024-10-04). "The Distribution of Executive Power and Corruption: A Meta-Analytical Review". Comparative Political Studies. doi:10.1177/00104140241290213. ISSN 0010-4140.
- ^ a b c d Sargentich, Thomas O. (1993). "The Presidential and Parliamentary Models of National Government". American University International Law Review. 8 (2): 579–592.
- ^ Riggs, Fred W. (1997). "Presidentialism versus Parliamentarism: Implications for Representativeness and Legitimacy". International Political Science Review. 18 (3): 258. doi:10.1177/019251297018003003. JSTOR 1601343. S2CID 145450791.
- ^ "Conceptual homogenization of a heterogeneous field: Presidentialism in comparative perspective". Comparing Nations: Concepts, Strategies, Substance: 72–152. 1994.
- ^ Dahl, Robert A. (2001). How Democratic Is the American Constitution?. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-09218-0.
- ^ Balfour. "Introduction". The English Constitution.
- ^ Nelson, Dana D. (2008). Bad for Democracy: How the Presidency Undermines the Power of the People. Minneapolis, Minnesota: University of Minnesota Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0-8166-5677-6.
- ^ Sirota, David (August 22, 2008). "Why cult of presidency is bad for democracy". San Francisco Chronicle. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ a b Sigman, Rachel; Lindberg, Staffan I. (2017). "Neopatrimonialism and Democracy: An Empirical Investigation of Africa's Political Regimes". V-Dem Working Paper 2017:56. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3066654. hdl:2077/54296. S2CID 158437511.
- ^ Doyle, David; Elgie, Robert (2016). "Maximizing the Reliability of Cross-National Measures of Presidential Power". British Journal of Political Science. 46 (4): 731–741. doi:10.1017/S0007123414000465.
- ^ "CONSTITUIÇÃO DA REPÚBLICA DE ANGOLA" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 3 August 2011.
- ^ Chen, Albert Hung Yee (n.d.). "The Executive Authorities and the Legislature in the Political Structure of the Hong Kong SAR" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-03-29.
- ^ "Κεφάλαιον Ε' – Περὶ συντάξεως τῆς Ἑλληνικῆς πολιτείας" [Chapter 5 – Concerning the organisation of the Hellenic state]. Πολιτικὸν Σύνταγμα τῆς Ἑλλάδος [Political Constitution of Greece] (PDF) (in Greek). Troezen: Third National Assembly. 5 May 1827. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 July 2011. Retrieved 29 December 2024 – via the Hellenic Parliament.
Ἡ νομοτελεστικὴ [ἐξουσία] ἀνήκει εἰς ἕνα μόνον ὀνομαζόμενον Κυβερνήτην, ἔχοντα διαφόρους ὑπ' αὐτὸν γραμματεῖς τῆς ἐπικρατείας.
[The Executive [power] belongs to solely one [individual] titled Governor, who has under him state secretaries.]
External links
- The Great Debate: Parliament versus Congress
- Castagnola, Andrea/Pérez-Liñán, Aníbal: Presidential Control of High Courts in Latin America: A Long-term View (1904-2006), in Journal of Politics in Latin America, Hamburg 2009.
