Historical buildings and structures of Zion National Park
Multiple Resources for Zion National Park | |
 East Entrance Sign | |
| Coordinates | 37°14′7″N 112°52′7″W / 37.23528°N 112.86861°W |
|---|---|
| Architectural style | NPS-Rustic style |
| MPS | Zion National Park MRA |
| NRHP reference No. | 64000878[1] |
The historical buildings and structures of Zion National Park represent a variety of buildings, interpretive structures, signs and infrastructure associated with the National Park Service's operations in Zion National Park, Utah. Structures vary in size and scale from the Zion Lodge to road culverts and curbs, nearly all of which were designed using native materials and regional construction techniques in an adapted version of the National Park Service Rustic style. A number of the larger structures were designed by Gilbert Stanley Underwood, while many of the smaller structures were designed or coordinated with the National Park Service Branch of Plans and Designs. The bulk of the historic structures date to the 1920s and 1930s. Most of the structures of the 1930s were built using Civilian Conservation Corps labor.
The version of the National Park Service Rustic style that was adopted at Zion was less extreme in its rustic character than that employed at other parks. Compared with the Bryce Canyon Lodge, the Zion Park Lodge used smaller elements of timber and stonework, and employed milled lumber in place of rough log elements. This reflected the more settled character of the Zion area, which retained farms and irrigation systems at the time the first visitor facilities were built.[1]
Many of Zion's historical structures are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP), either as individual structures or as contributing structures in a historic district.[1] They represent an unusually homogeneous series of buildings for a national park, sharing details of composition, scale and materials. They have collectively been described as some the best work in the National Park Service Rustic style.[2] (The NRHP-listed structures are also listed in alphabetical order in National Register of Historic Places listings in Zion National Park.)
The park also preserves remnants of early Mormon settlement in Zion Canyon, which began in 1862. Two irrigation canals and a cable draw works remain.[1]
Utah Parks Company

- The Zion Lodge was designed in the rustic style by Underwood in 1924 as the centerpiece of Zion's visitor facilities.[1] A 1966 fire destroyed the facility. A temporary lodge was reconstructed in 1992 to more fully resemble Underwood's Lodge.[3]
- The Zion Lodge Historic District comprises a large group of historic lodgings and support facilities surrounding the Zion Lodge, most of which were designed by Underwood.[4] The district's National Register of Historic Places reference is 82001718.[5]
- The Zion Nature Center-Zion Inn was designed by Underwood for the Utah Parks Company as a cafeteria, gift shop and office for the tourist cabins surrounding it. The inn was built in 1934 in the National Park Service Rustic style and was used by the Utah Parks Company until 1972, when the Park Service remodeled it for use as a nature center. The structure features rubblestone pilasters at each corner with a "framing out" style infill. The roof is framed in log.[6] The Zion Inn was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1987.[5] It was recently restored to the original Underwood exterior design. The Nature Center was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003719. 37°12′19.2″N 112°58′56.75″W / 37.205333°N 112.9824306°W[5]
Transportation and infrastructure
- The Floor of the Valley Road follows the North Fork of the Virgin River through Zion Canyon. The nine-mile road was planned by the National Park Service to blend with the landscape while highlighting the canyon's features for motorists. The earliest portions were built in 1916, but the bulk of the present road and associated structures were built in the 1930s as a Depression-era public works project.
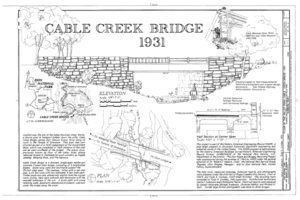
- The Cable Creek Bridge is on the Floor of the Valley Road. It is individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places for its integrity as an example of the National Park Service Rustic style of design. The single-span sandstone-faced concrete bridge was designed by the Western Office of Design and Construction of the National Park Service, and was built in 1932 with Civilian Conservation Corps labor.[7] The bridge was listed on the NRHP on February 16, 1996, with reference number 96000053,[5] and is a contributing structure on the Floor of the Valley Road. 37°16′13″N 112°56′19″W / 37.27028°N 112.93861°W[5]
- The Zion-Mount Carmel Highway was built to link Zion with Grand Canyon National Park. Completed in 1930, the road features a 5,613-foot (1,711 m) tunnel in the wall of Pine Creek Canyon.[8] The road enables visitors to do a loop tour of Grand Canyon, Zion, Bryce Canyon National Park and Cedar Breaks National Monument.
- The East Entrance Checking Station was built in 1935 by Civilian Conservation Corps labor from CCC Camp NP-2 at the eastern end of the Zion-Mt. Carmel Highway. The station was designed by the National Park Service Branch of Plans and Design in the National Park Service Rustic style, featuring rough sandstone walls.[9] It was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003710. 37°13′59.7″N 112°52′31.5″W / 37.233250°N 112.875417°W[5]

- The East and South Entrance Signs are individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The signs comprise two locally quarried red sandstone pillars flanking the east and south entrance road, with a horizontal log projecting from one pylon supporting a sign. The signs were designed by the National Park Service Branch of Plans and Designs in 1936 and was built by Civilian Conservation Corps labor from Camp NP-2. They were altered in 1940 to the design of Park Service architects H.W. Young and A.C. Kuehl.[10][11] The sign reflects a consistent design theme that was developed for many park structures in Zion.[12] The signs are individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places, with the east sign listed on July 7, 1987, with reference number 86003710 and the south sign on February 14, 1987, as 86003713. 37°14′7″N 112°52′7″W / 37.23528°N 112.86861°W (east) and 37°12′4.7″N 112°59′18.8″W / 37.201306°N 112.988556°W (south).[5]
Park Service facilities
- The Grotto Camping Ground Comfort Stations were built in the same style and material as the Grotto Residence. The south station was built in 1925, while the north station was built in 1930-31 to a design by Harry Langley. The walls are massive stepped sandstone in 15-to-18-inch courses with board-and-batten infill at the gables and 24-inch (61 cm) roof overhangs at the sides and 36-inch (91 cm) overhangs at the ends.[13][14] Both were renovated in 1959. Listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, their reference numbers are 86003704 (south) and 86003705 (north). 37°15′31″N 112°56′27″W / 37.25861°N 112.94083°W (south) and 37°15′33″N 112°56′33″W / 37.25917°N 112.94250°W (north).[5]
- The South Campground Comfort Station was designed by W.G. Carnes of the Western Division of the Branch of Plans and Design and built in 1934 using rustic design elements of preceding buildings.[15] The South Campground building was \listed on the NRHP on February 14, 1987, with reference number 86003708. 37°12′14″N 112°58′21″W / 37.20389°N 112.97250°W[5]
- The South Campground Amphitheater was built by the Civilian Conservation Corps in 1934 and 1935. The CCC work is visible in the stonework of the stage and its retaining walls, walkways and steps. Red sandstone was used in accordance with NPS Rustic design principles. The original wood benches were placed on stone blocks and were replaced with metal seats in 1956.[16] The amphitheater was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003717. 37°12′15.9″N 112°58′52.2″W / 37.204417°N 112.981167°W[17]
Employee and service facilities

- The Museum-Grotto Residence is the oldest building remaining in Zion National Park. The Grotto structure was built in 1924 as the Park Museum, then rebuilt as a residence in 1936 to a design by Harry Langler of the NPS Branch of Plans and Designs, using CCC labor. The stonework is significantly larger in scale than later work.[18] The Grotto Residence was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places, reference number 86003721 on February 14, 1987. 37°15′28″N 112°57′3″W / 37.25778°N 112.95083°W[5]

- The East Entrance Residence is a companion to the similar East Entrance Checking Station. The residence was built by the Civilian Conservation Corps in 1934 to a design in the National Park Service Rustic style by the Branch of Plans and Design. It is individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places, reference 86003712.[19] The residence was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003712. 37°13′59.7″N 112°52′35.7″W / 37.233250°N 112.876583°W[5]
- The Pine Creek Residential Historic District was designed by Thomas Chalmers Vint to house Park Service staff, setting the style for smaller buildings at Zion. Located near the original headquarters of the park,[1] the five major buildings in the complex were built in 1929-1930 using red sandstone, cedar shingles and milled lumber. The district includes the Superintendent's Residence.[20] The Pine Creek district was individually listed on the National Register on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003736. 37°12′59″N 112°58′32″W / 37.21639°N 112.97556°W[5]
- The buildings of the Oak Creek Historic District were built during the 1930s and early 1940s in what had by then become the standard National Park Service Rustic style adapted for use at Zion. The Oak Creek compound provided housing for Park Service employees as well as service and utility facilities. Most were constructed by CCC labor.[1] A number of Mission 66 buildings were constructed in the 1950s, but are not considered contributing structures. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003706. 37°12′40″N 112°59′10″W / 37.21111°N 112.98611°W[5]
Trails
- The Canyon Overlook Trail was built by Civilian Conservation Corps labor in 1933 from the east portal of the Zion-Mt. Carmel Tunnel to and overlook at the Great Arch. The design was overseen by local park officials for consistency with other trail improvements in Zion.[21] The rail was listed on the National Register on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003722. 37°12′49″N 112°56′54″W / 37.21361°N 112.94833°W[5]
- A total of 4 miles (6.4 km) long, the East Rim Trail was improved by local rancher John Winder in 1896. Originally an Indian trail, it was further improved in 1918-1919 by the National Park Service. The lower two miles of trail provided access to the Cable Mountain Draw Works. The trail improvements include rubblestone retaining walls typical of park improvements found elsewhere in Zion.[22] The East Rim Trail was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003723. 37°16′42″N 112°55′45″W / 37.27833°N 112.92917°W[5]

- The Angels Landing Trail-West Rim Trail was built in 1926 following the completion of the East Rim Trail. The Angels Landing trail climbs a sandstone spine, providing rails and chain handholds for a 300-foot (91 m) climb in .5 miles (0.80 km).[23] It joins the West Rim Trail, built in 1925-26 and extended in 1935. Both trails were planned by Thomas Chalmers Vint of the NPS Branch of Plans and Design and Walter Ruesch, the Zion Park building foreman. Ruesch lent his name to Walter's Wiggles, a series of 21 switchbacks.[24] The trails were listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003707. 37°16′6″N 112°56′58″W / 37.26833°N 112.94944°W[5]
- The Emerald Pools Trail begins at the Zion Lodge westward to Lower Emerald Pool. Built in 1932, it was created using only hand tools. An extension built the same year runs to the Grotto Campground. The first section required the construction of stone steps to a high standard of design and finish. Repairs to the stonework were carried out in 1969.[25] The 2.2-mile (3.5 km) trail was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003725. 37°14′58″N 112°57′16″W / 37.24944°N 112.95444°W[5]
- The Gateway to the Narrows Trail, also known as the Riverside Walk, is a relatively short nature trail of one mile along the Virgin River. It connects the parking area at the Temple of Sinawava with The Narrows and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The trail uses local materials such as red sandstone to blend with its surroundings, following the tenets of the National Park Service Rustic style. Survey work was carried out in 1928 by National Park Service engineer Guy D. Edwards. Construction began the following year under the supervision of Walter Ruesch.[26] On August 1, 1968, a rock slide buried a 250-foot portion of the trail with debris ranging from three to twenty feet deep. Rather than removing the rock, the trail was routed over the slide.[26] The trail was upgraded for accessibility by the handicapped in 1982.[26] The trail and kiosk were listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003726. 37°17′48″N 112°56′42″W / 37.29667°N 112.94500°W[5]
- The Grotto Trail begins at Zion Lodge, running along the floor of the valley to the Zion Museum at what is now the Grotto Picnic Area along the original path of the Floor of the Valley Road. The trail was designed by landscape architect Harry Langley and was built by the National Park Service in 1932 using only hand tools. Sandstone retaining walls and culverts were used to continue the rustic style.[1] The Grotto Trail was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1986, reference number 86003914. 37°15′1″N 112°57′26″W / 37.25028°N 112.95722°W[5]

- The Hidden Canyon Trail was built in 1928 under the guidance of Guy D. Edwards and F.A. Kittredge to provide access to a hanging canyon. The trail consists of three sections. The first section starts at the East Rim Trail and runs for 950 feet (290 m) as a horse trail with eleven switchbacks with dry-laid sandstone retaining walls. The 745-foot (227 m) section was built as a hikers-only trail along a natural shelf, with a small section of blasted passage with steps and a hand rail. The final section was blasted from a steep slope by workers hanging from ropes. The completed work was designed to blend into the landscape, while vegetation was preserved during construction.[27] The Hidden Canyon Trail was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1987, reference number 86003731. 37°16′1″N 112°55′50″W / 37.26694°N 112.93056°W[5]
Archeological sites
- Parunuweap Canyon Archeological District includes several Ancestral Puebloan ruins dating between 500-1150 AD. The sites are associated with the Virgin Anasazi peoples and consist of small masonry dwelling and granary complexes.[28] The site was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on November 7, 1996, reference number 96001235.[5]
The West Rim Trail follows along the rim with views of Phantom valley and the canyons to the south.
Other historic places
- The Cable Mountain Draw Works was built by David Flanigan beginning in 1901, although he had first proposed the system as a teenager in 1885.[29] From 1904, timber was harvested from the heights above the valley and moved from Cable Mountain down to the draw works in the valley, a vertical distance of 2,000 feet (610 m). The system fulfilled an 1863 prophecy made by Brigham Young that timber would descend from the cliffs "like a hawk flying."[1] Before the draw works were constructed, the timber on Cable Mountain was obtained only by a ten-day round trip. Flanigan sold the operation in 1906 to Alfred Stout and O.D. Gifford of Springdale, who operated it as the Cable Mountain Timber Works. The draw works were destroyed by lightning and rebuilt in 1911. Intermittent operation continued until 1926 when the system was abandoned. The cables were removed in 1930.[29] It is the oldest pre-park structure in Zion.[1] The site was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on May 24, 1978, reference number 78000281. 37°15′57″N 112°55′59″W / 37.26583°N 112.93306°W[5]
- The chief remaining structure is a wood headframe on Cable Mountain. The structures at the bottom of the cables consisted of snubbing posts to separate the cables. Nothing remains of the lower end of the draw works.[29]
- The Pine Creek Irrigation Canal was excavated around the 1890s by Mormon farmers, using water from Pine Creek to irrigate farmland for about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) on the west side of the Virgin River near Bridge Mountain. Water was drawn from Pine Creek just upstream from the creek's confluence with the Virgin River and used to feed the Flanigan Ditch distribution system. Original rock retaining walls remain visible in some sections. New headworks were built in 1934 by Civilian Conservation Corps labor from Camp NP-2 using a 15-foot (4.6 m) sandstone boulder as an anchorage,[30] to draw water directly from the Virgin River 1/4 mile upstream from Pine Creek, conveying the water over Pine Creek in a flume. Funding was provided by the Public Works Administration.[1] The Pine Creek Canal was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003734. 37°12′6″N 112°58′40″W / 37.20167°N 112.97778°W[5]
- The Oak Creek Irrigation Canal was built in 1935 by CCC labor to irrigate vegetation in the park's South Campground. Additional improvements were undertaken in 1941 to replace wood flumes and to build new concrete diversion dams. The 2-mile (3.2 km) canal diverts water from the North Fork of the Virgin River with a diversion dam that spans the river. A headgate on the west bank controls the flow. Further works executed in 1959 and 1961 provide irrigation to the visitor center and the Pine Creek residential area before laterals take off to irrigate the South Campground. The ditch then rejoins the river. The canal is largely lined with concrete. A siphon connected to the south entrance plaza.[31] The Oak Creek Canal was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places on July 7, 1987, reference number 86003738. 37°12′9″N 112°59′28″W / 37.20250°N 112.99111°W[5]
- Flanigan Ditch was constructed about 1880 by the Flanigan family, Mormon pioneers in the Zion valley. The Flanigans acquired water rights for a portion of the flow of the Virgin River in 1880 to water the family's lands along the river. The family was prominent, with the feature now known at "The Watchman" called "Flanigan Peak", while the location of the present Watchman campground was called Flanigan Field. Over time, the farmlands on the lower portion of the ditch were abandoned below the present outlet at the Watchman campground. The buried portion of the ditch is regarded as a potential archeological feature relating to the period of pioneer settlement. The lands surrounding the ditch were acquired by the Park Service from the Flanigans in 1960. Of the original 15,000 feet (4,600 m) of ditch, about 12,000 feet (3,700 m) are within the park, with the upper third largely intact but unwatered for part of its length. A portion continues to carry water for irrigation of the Watchman campground. Expansion of the park boundaries has included a buried and abandoned portion of the lower ditch. The ditch shares its headworks with the Springdale Consolidated Irrigation Company's pipeline, which provides municipal water to the town through a pipeline installed in 1988.[32] Flanigan Ditch was listed on the NRHP on January 12, 1998, reference number 97001630. 37°12′53″N 112°58′28″W / 37.21472°N 112.97444°W[5]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Jurale, Jim; Witherall, Nancy (1984). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory - Nomination Form: Multiple Resources for Zion National Park". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-03.
- ^ Kaiser, Harvey H. (2008). The National Park Architecture Sourcebook. Princeton Architectural Press. pp. 163. ISBN 978-1-56898-742-2.
- ^ Kaiser, Harvey H. (2008). The National Park Architecture Sourcebook. Princeton Architectural Press. pp. 162. ISBN 978-1-56898-742-2.
- ^ Culpin, Mary Shivers (January 12, 1982). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory - Nomination Form: Zion Lodge Historic District". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-06-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "List of Classified Structures: Zion Nature Center/Zion Inn". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-06-19.
- ^ Sontag, Robert (July 27, 1995). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Cable Creek Bridge" (pdf). National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Culbertson, Laura J.; Croteau, Todd A. (1993). "Zion-Mount Carmel Highway Tunnel 1930". Historic American Engineering Record. p. 1. Retrieved 2009-06-19.
- ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: East Entrance Checking Station" (pdf). National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: East Entrance Sign". National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "East Entrance Sign". List of Classified Structures. National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ^ "Zion National Park, Entrance Sign (1936)". Parkitecture in the Western Parks. National Park Service. 2009-09-02.
- ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: Grotto Picnic Area Comfort Station (No. 129)". National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: Grotto Picnic Area Comfort Station (No. 130)". National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: South Campground Comfort Station (No. 131)". National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Witherell, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory Report: South Campground Amphitheater". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-09.
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. April 15, 2008.
- ^ Witherall, Nancy (October 10, 1984). "Classified Struicture Field Inventory: Grotto Residence". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
- ^ Nancy Witherell (October 10, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: East Entrance Residence" (pdf). National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Jurale, James (July 6, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory: Pine Creek Residential Historic District". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-10-09.
- ^ Jurale, James (September 12, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory Report: Canyon Overlook Trail". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ Jurale, James (September 5, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory Report: East Rim Trail". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-10.
- ^ Annie, Hartman (12 July 2018). "Angels Landing Is One of the Most Dangerous Hikes in the US". Curiosity: Amazing Places. curiosity.com. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ^ Jurale, James (September 14, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory Reports: Angels Landing Trail and West Rim Trail". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-09.
- ^ Jurale (September 6, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: Emerald Pools Trail" (pdf). National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b c James Jurals (September 6, 1984). "Classified Structure Inventory: Gateway to the Narrows" (pdf). National Park Service.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Jurale, James (September 6, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory Report: Hidden Canyon Trail". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
- ^ "Parunuweap Canyon Prehistoric Structure". List of Classified Structures. National Park Service. Archived from the original on 2012-06-01. Retrieved 2009-03-02.
- ^ a b c Parkinson, Charles R. (September 1977) [January 1972]. "National Register of Historic Places Inventory - Nomination Form: Cable Mountain Draw Works". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ^ Jurale, James. "Classified Structure Field Inventory Report: Pine Creek Irrigation Canal". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ^ Jurale, James (September 29, 1984). "Classified Structure Field Inventory: Oak Creek Irrigation Canal". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-08.
- ^ Kardas, Susan; Larrabee, Edward (April 1997). "National Register of Historic Places Continuation Sheet: Flanigan Ditch, Zion National Park MRA (addendum)". National Park Service. Retrieved 2009-09-09.
External links
- Parkitecture in the Western Parks: Gateways National Park Service
- Ancestral Puebloans in Zion National Park
National Register of Historic Places photographs
- Photographs of the Zion Lodge Historic District at the National Park Service's NRHP database
- Photographs of the Zion Nature Center at the National Park Service's NRHP database (pre-renovation)
- Photographs of the Birch Creek Historic District at the National Park Service's NRHP database
- Photographs of the south Grotto Campground Comfort Station at the National Park Service's NRHP database
HABS/HAER Documentation
The Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) and the Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) have extensive documentation of park structures. A selection is provided below.
- HABS No. UT-108-F, "Zion National Park, Gateway to Narrows Interpretive Kiosk, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 1 photo, 1 photo caption page
- HABS No. UT-108-G, "Zion National Park, East Entrance Checking Station, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 10 photos, 2 photo caption pages
- HABS No. UT-108-H, "Zion National Park, East Ranger's House, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 15 photos, 2 photo caption pages
- HABS No. UT-108-I, "Zion National Park, East Entrance Sign, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 7 photos, 2 photo caption pages
- HABS No. UT-109-C, "Pine Creek Historic Complex, Chief Ranger's House, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 3 photos, 1 photo caption page
- HABS No. UT-110-A, "Oak Creek Historic Complex, Ranger's Dormitory, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 7 photos, 1 photo caption page
- HABS No. UT-110-B, "Oak Creek Historic Complex, Ranger's House, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 4 photos, 1 photo caption page
- HAER No. UT-40-D, "Zion National Park Historic Trails System, Gateway to Narrows, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 2 data pages
- HAER No. UT-72-A, "South Entrance Sign, Zion-Mt. Carmel Highway at south park boundary, Springdale, Washington County, UT", 12 photos, 1 photo caption page
- HAER No. UT-73-A, "Floor of the Valley Road, Cable Creek Bridge, Spanning Cable Creek on Floor of Valley, Springdale vicinity, Washington County, UT", 7 photos, 1 measured drawing, 1 photo caption page


