Pale-rumped swift
| Pale-rumped swift | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Apodidae |
| Genus: | Chaetura |
| Species: | C. egregia |
| Binomial name | |
| Chaetura egregia Todd, 1916 | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Acanthylis egregia[2] | |
The pale-rumped swift (Chaetura egregia) is a species of bird in subfamily Apodinae of the swift family Apodidae.[3][4] It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.[5]
Taxonomy and systematics
The pale-rumped swift has at times been treated as conspecific with the grey-rumped swift (C. cinereiventris). The two of them, the band-rumped swift (C. spinicaudus), and the Lesser Antillean swift (C. martinica) were at one time placed in genus Acanthylis.[6] The pale-rumped swift is monotypic.[3]
Description
The pale-rumped swift is about 10.5 cm (4.1 in) long and weighs about 23 g (0.81 oz). It has a protruding head, a short square tail, and wings that bulge in the middle and somewhat hook at the end. The sexes are alike. Their upperparts are black with a bronze gloss and a whitish rump and uppertail coverts. Their underparts are mostly dark, with a pale throat and blackish undertail coverts.[6]
Distribution and habitat
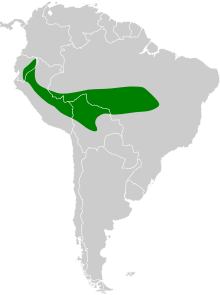
The pale-rumped swift is found in eastern Ecuador, eastern Peru, western Brazil, and northwestern Bolivia and has been recorded as a vagrant in Colombia. It principally inhabits lowland tropical evergreen forest but also occurs over more open landscapes and urban areas.[6][5]
Behavior
Movement
The pale-rumped swift is thought to be a year-round resident throughout its range.[6]
Feeding
Like all swifts, the pale-rumped is an aerial insectivore. It often feeds with other species of swift and tends to stay in the lower part of the flock. No details of its diet are known.[6]
Breeding
Nothing is known about the pale-rumped swift's breeding phenology and its nest and eggs have not been described.[6]
Vocalization
The pale-rumped swift's main vocalizations are "a single-noted 'tsee'...and more complex twittering calls such as 'tsee-titi' or 'titi-tsee-trtr'."[6]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the pale-rumped swift as being of Least Concern, though its population size is not known and is believed to be decreasing. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] It is generally thought to be one of the rarer members of genus Chaetura but at least in parts of Peru it is more common than some of the others and is abundant in parts of Ecuador.[6]
References
- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Pale-rumped Swift Chaetura egregia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22686706A93123251. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22686706A93123251.en. Retrieved 6 October 2022.
- ^ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 July 2022. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved July 24, 2022
- ^ a b Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (August 2022). "Owlet-nightjars, treeswifts, swifts". IOC World Bird List. v 12.2. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- ^ HBW and BirdLife International (2021) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 6. Available at: http://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v6_Dec21.zip retrieved August 7, 2022
- ^ a b Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 July 2022. Species Lists of Birds for South American Countries and Territories. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCCountryLists.htm retrieved July 24, 2022
- ^ a b c d e f g h Chantler, P. and P. F. D. Boesman (2020). Pale-rumped Swift (Chaetura egregia), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.parswi1.01 retrieved October 6, 2022


