Nethercross
Nethercross An Chrois Íochtarach (Irish) | |
|---|---|
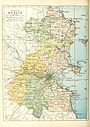
 Barony map of County Dublin, 1900; Nethercross barony is in the north. | |
| Coordinates: 53°29′13″N 6°16′12″W / 53.487°N 6.27°W | |
| Sovereign state | Ireland |
| Province | Leinster |
| County | Fingal |
| Area | |
• Total | 88.3 km2 (34.1 sq mi) |
Nethercross (Irish: An Chrois Íochtarach) is a feudal title of one of the baronies of Ireland. Originally part of the Lordship of Meath, it was then constituted as part of the County Dublin. Today, is in the modern county of Fingal.[1]
The barony was created by Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath as his own feudal barony, held directly from himself in capite, and so once constituted a feudal title. His vassals were commonly called "De Lacy's Barons".[2]
Name
The placename derives from "Crosslands" (Latin: Croceae), a term applied to lands that were owned by the Catholic Church. County Dublin's crosslands were divided into two portions, designated "Nethercross" and "Upper Cross." The baronies do not precisely match the old crossland boundaries; for example, Holmpatrick, Lambay and Ireland's Eye were part of the northern crosslands but Holmpatrick was transferred to Balrothery East and the islands to Coolock barony.[3]
The barony is also said to be named from the cross of the abbey said to have been founded by St. Cainnech in AD 560; this cross was most likely used to mark the boundary. The cross may today be seen in the old graveyard of the ecclesiastical parish of St Canice in Finglas.[4]
Location
It is one of seven and a half baronies that used to comprise the old county of Dublin.[5] It stretches from Portrane to the M2 motorway (from east to west) and from Belinstown on the M1 motorway to Swords (from north to south). It is located between the baronies of Balrothery West and Balrothery East to the north, Castleknock to the south-west and Coolock to the east. To the west lies the county of Meath with the Irish Sea lying to the east. The whole of the barony is contained within the modern county of Fingal and it is subject to Fingal County Council.
Legal context
Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as subdivisions of counties and were used for administration. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they are no longer used for many administrative purposes. While they have been administratively obsolete since 1898, they continue to be used in land registration, and specification such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic túath which had submitted to the Crown. In the case of Nethercross, it was probably under the sway of the Danish kings of Dublin immediately prior to the invasion.
Geography
- Lambay Island, which is the easternmost point of the Republic of Ireland.
- Blue flag beaches (Portrane strand and Donabate strand)
- Watercourses (Broadmeadow Water or River, and its major tributary the Ward, and other elements of the Broadmeadow system)
- Estuaries (Rogerstown Estuary and Broadmeadow, along with the Broadmeadow viaduct
- Donabate railway station
- Public parks (Newbridge Estate)
- Dublin Airport covers several townlands in the barony[6]
Civil parishes
There are seven civil parishes in the barony:
- Kilsallaghan, the most western part of the barony which forms the border with County Meath and with the barony of Castleknock at the parish of Ward.
- Killeek, along with Killossery, it forms the central section of the barony.
- Killossery, along with Killeek, it forms the central section of the barony.
- Donabate, along with Portrane, it forms the coastal part of the barony.
- Portrane, along with Donabate, it forms the coastal part of the barony.
- Swords, which is the largest parish and is also the location of the county seat of Fingal.
- Finglas - this is an enclave of five townlands that are separated from the parish proper which lies in the neighbouring Barony of Castleknock.
Cross
The Nethercross or Lowercross was carved in granite at St Canice's abbey sometime between the 7th and 9th centuries. The original height of the cross is not known as it was dismantled by the clergy during the Cromwellian invasion of Ireland and hidden to prevent its desecration by the Roundheads. In 1806, Rev. Robert Walsh was appointed curate of the Church of Ireland parish of Finglas. Following his literary and antiquarian pursuits, he came to hear the story of the cross.[7] He tracked down an old man whose grandfather, as a boy, had been present at the burial of the cross in a corner of one of the glebe fields. Rev. Walsh unearthed the cross from its hiding place, as described by the old man, and had it erected in the south-east corner of the parish graveyard, where it now stands.
Following its recovery (circa 1809 - 1816) and restoration, it now stands at more than two metres tall.[8]). There are spiral designs on the underside of the cross. The cross was the northern boundary marker of the parish from early times at a place which is still called Watery Lanes, north of Mellows Road.[9]
See also
References
- ^ Placenames Database of Ireland - Nethercross barony
- ^ Vicissitudes of Families by Sir Bernard Burke, Ulster King of Arms, Longman Green Longman and Roberts, Paternoster Row, London, 1861 (pages 363-364)
- ^ Dublin Historical Record. (1960:37). Ireland: Old Dublin Society.
- ^ Parish of St. Canice - The Cross of Nethercross Archived 2013-02-08 at archive.today
- ^ According to the "Local Government Act, 2001", section 10(2): "The State continues to stand divided into local government areas to be known as counties and cities which are the areas set out in Parts 1 and 2, respectively, of Schedule 5." It is clear from SCHEDULE 5, Local Government Areas (Counties and Cities, PART 1, that "Dublin" is defined only as a city (as distinct from a county).
- ^ Irish Statute Book AIR NAVIGATION AND TRANSPORT ACT, 1950. SECOND SCHEDULE, PART I, 3
- ^ Walsh, Robert, "Fingal and its Churches: A Historical Sketch of the Foundation and Struggles of the Church of Ireland in that Part of the County Dublin which Lies to the North of the River Tolka", W. McGee, 1888
- ^ Church of Ireland - parish of Santry
- ^ Finglas The Nethercross
External links
- Local Government Act, 2001
- Placenames Database of Ireland
- Walsh, Dennis (2003). "Barony Map of Ireland". Archived from the original on 15 January 2007. Retrieved 13 February 2007. Source given is "Ordnance survey".