Municipal corporation (India)
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of India |
|---|
 |
|
|
A municipal corporation is a type of local government in India which administers urban areas with a population of more than one million. The growing population and urbanization of various Indian cities highlighted the need for a type of local governing body that could provide services such as healthcare, education, housing and transport by collecting property taxes and administering grants from the state government.
The Municipal corporation carries out its function through well organized divisions or departments. For example, water supply and sewage disposal Undertaking, Housing Board, Education Department and Electricity Department. Each of these Departments are looked after by experienced and qualified persons.[citation needed]
The 74th Amendment Act defined the formations of urban local governments and their activities.[1]
Other names for municipal corporations
Municipal corporations are referred to by different names in different states (due to regional language variations), all of which are translated to "municipal corporation" in English. These names include Nagar Nigam (in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, and Haryana), Nagara Nigama (in Punjab), Mahanagar Palika (in Goa and Maharashtra), Mahanagara Palike (in Karnataka), Mahanagar Seva Sadan (in Gujarat), Pouro Nigom (in Assam), Mahānagara Pālikā (in Odisha), Pouro Nigam (in West Bengal), Pur Porishod (in Tripura), Nagar Palika Nigam (in Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh), Nagara Paalaka Samstha or Mahaanagara Paalaka Samstha (in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana), Nagara Sabha (in Kerala) and Maanagaraatchi (in Tamil Nadu).[citation needed]
The Vadodara Municipal Corporation of the city of Vadodara in Gujarat is typically called by the name "Vadodara Mahanagar Seva Sadan" and the Greater Bangalore Municipal Corporation of the city of Bangalore in Karnataka is typically called "Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike". The detailed structure of these urban bodies varies from state to state, as per the laws passed by the state legislatures, but the basic structure and function is almost the same.
Composition
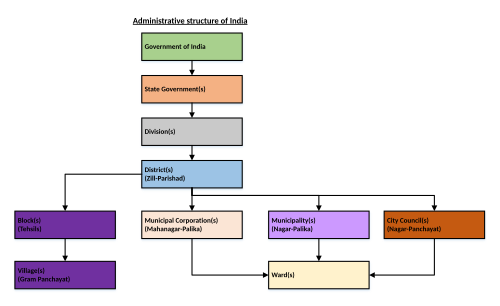
The area administered by a municipal corporation is known as a municipal area. Each municipal area is divided into territorial constituencies known as wards. A municipal corporation is made up of a wards committee. Each ward has one seat in the wards committee. Members are elected to the wards committee on the basis of adult franchise for a term of five years. These members are known as councillors or corporators. The number of wards in a municipal area is determined by the population of the city. Some seats are reserved for scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, backward classes and women.[1]
A state can choose to constitute additional committees to carry functions of urban local governance, in addition to the wards committees. In addition to the councillors elected from the wards, the legislature of a state may also choose to make provisions for the representation of persons having special knowledge or experience in municipal administration, the MPs or MLAs representing the constituencies which comprise wholly or partly the municipal area, and/or the commissioners of additional committees that the state may have constituted. If a state legislature appoints a person from the first category to a wards committee, that individual will not have the right to vote in the meetings of the municipal corporation, while MPs, MLAs and commissioners do have the right to vote in meetings.[1]
Superlatives
The largest corporations are in the ten major metropolitan cities of India, viz. Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Ahmedabad, Lucknow, Jaipur, Kanpur.
The Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) of the city of Mumbai in Maharashtra is the richest municipal corporation in India.[2][3] Greater Chennai Corporation of the city of Chennai in Tamil Nadu is the oldest municipal corporation in India and second oldest municipal corporation in the world only behind City of London Corporation in United Kingdom.[4]
Administration
Municipal Corporations are typically headed by a Mayor and Deputy Mayor (elected from among the councilors), and comprise elected councillors.[5]
The Mayor is the head of the municipal corporation, but in most states and territories of India the role is largely ceremonial as executive powers are vested in the Municipal Commissioner. The office of the Mayor combines a functional role of chairing the Corporation council meetings as well as ceremonial role associated with being the First Citizen of the city. As per the amended Municipal Corporation Act of 1888, a Deputy Mayor is appointed by the Mayor. The tenure of the Mayor, Deputy Mayor and Council is five years. However, in seven states: Haryana, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand; Mayors are directly elected by the people and thus hold the executive powers of the municipal corporations.
The administrative machinery is further supported by a Municipal Commissioner or secretary. They functions as the chief executive officer of the municipal corporation. These officials are tasked with the day-to-day operations, implementing policies, and ensuring the efficient delivery of essential services. Executive officers monitor the implementation of all the programs related to planning and development of the corporation with the coordination of mayor and councilors. The municipal corporations consists departments like health, general administration, revenue, engineering, town planning, welfare, education, etc. The officials of these departments, like health inspectors, engineers, and administrative officers, are appointed by the state government.
Functions of municipal corporations
The Twelfth Schedule of the Constitution lists the subjects that municipal corporations are responsible for. Corporations may be entrusted to perform functions and implement schemes including those in relation to the matters listed in the Twelfth Schedule.[1]
- Regulation of land-use and construction of buildings .
- Urban planning including town planning .
- Planning for economic and social development .
- Water supply for domestic, industrial and commercial purposes .
- Public health, sanitation conservancy and solid waste management .
- Fire services .
- Urban forestry, protection of the environment and promotion of ecological aspects.
- Safeguarding the interests of weaker sections of society, including the handicapped and mentally disabled
- Slum improvement and upgradation.
- Repair street lights
- Urban poverty alleviation.
- Provision of urban amenities and facilities such as parks, gardens, playgrounds.
- Promotion of cultural, educational and aesthetic aspects.
- Burials and burial grounds; cremations, cremation grounds and electric crematoriums.
- Cattle pounds; prevention of cruelty to animals.
- Vital statistics including registration of births and deaths.
- Public amenities including street lighting, parking lots, bus stops and public conveniences.
- Regulation of slaughter houses and tanneries[1]
Municipal corporation headquarters of major metropolitan cities
See also
- List of municipal corporations in India
- Municipal governance in India
- Municipal Corporation Elections
References
- ^ a b c d e "74th Amendment Act" (PDF).
- ^ "BMC to open green channel for octroi". Financialexpress.com. 3 September 2007. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ "Gold & beautiful, News - Cover Story". Mumbai Mirror. Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ Achutan, Kannal (23 September 2008). "Chennai Corporation to celebrate 320 years". The Hindu. Chennai. Archived from the original on 23 September 2008. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
- ^ "Administration | City Corporation Of Thiruvananthapuram". tmc.lsgkerala.gov.in. Retrieved 14 December 2023.







