Mu Arietis
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 02h 42m 21.93980s[1] |
| Declination | +20° 00′ 41.2612″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.74[2] (6.38/8.38/6.72/12.2)[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0 Vp + F2 V + A1 V[3] |
| U−B color index | –0.03[4] |
| B−V color index | –0.02[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –6.0[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +27.68[1] mas/yr Dec.: –47.64[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.64 ± 0.88 mas[1] |
| Distance | 340 ± 30 ly (104 ± 9 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.41[6] |
| Orbit[7] | |
| Period (P) | 8.845 ± 0.046 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 0.0563 ± 0.0008″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.337 ± 0.023 |
| Inclination (i) | 71.2 ± 1.1° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 101.0 ± 1.0° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | B 1981.099 ± 0.063 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 92.3 ± 1.7° |
| Details | |
| Mass | 3.4 ± 1.7 (Aa) / 2.1 ± 1.7 (Ab)[7] M☉ |
| Luminosity | 71.7[6] L☉ |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 175[8] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
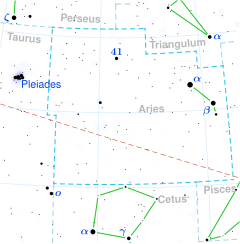
Mu Arietis, Latinized from μ Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a star system in the northern constellation of Aries. It is approximately 340 light-years (100 parsecs) distant from Earth, give or take a 30 light-year margin of error, and has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.74.[2] According to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, this means it is faintly visible to the naked eye from dark suburban skies.
At the heart of this system is a close orbiting pair consisting of a magnitude 6.38 A-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of A0 Vp and a magnitude 8.38 F-type main sequence companion with a classification of F2 V. These two components have an angular separation of 0.04 arcseconds. A third component, consisting of a magnitude 6.72 star with a classification of A1 V, is orbiting the inner pair with a period of 8.845 years and an eccentricity of 0.34. A smaller fourth component, at an angular separation of 19.1 arcseconds, has a magnitude of 12.2.[3]
References
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b Oja, T. (August 1991). "UBV photometry of stars whose positions are accurately known. VI". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 89 (2): 415–419. Bibcode:1991A&AS...89..415O.
- ^ a b c Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ^ a b Osawa, K.; Hata, S. (1960), "Three colour photometry of B8-A2 stars.", Annals of the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory, 6: 148, Bibcode:1960AnTok...6..148O.
- ^ Palmer, D. R.; et al. (1968), "The radial velocities spectral types and projected rotational velocities of 633 bright northern A stars", Royal Observatory Bulletin, 135: 385, Bibcode:1968RGOB..135..385P.
- ^ a b Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b Mason, Brian D. (1997). "Binary Star Orbits from Speckle Interferometry. XI. Orbits of Twelve Lunar Occultation Systems". The Astronomical Journal. 114: 808. Bibcode:1997AJ....114..808M. doi:10.1086/118514.
- ^ Royer, F.; Zorec, J.; Gómez, A. E. (February 2007), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. III. Velocity distributions", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 463 (2): 671–682, arXiv:astro-ph/0610785, Bibcode:2007A&A...463..671R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224, S2CID 18475298.
- ^ "mu. Ari". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2012-08-07.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)