Magsaysay, Palawan
Magsaysay | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Magsaysay | |
 Map of Palawan with Magsaysay highlighted | |
Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 10°52′N 121°03′E / 10.87°N 121.05°E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Mimaropa |
| Province | Palawan |
| District | 1st district |
| Founded | January 1, 1964 |
| Barangays | 11 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Rommel L. dela Torre |
| • Vice Mayor | Aloysius M. Quejano |
| • Representative | Edgardo Salvame |
| • Municipal Council | Members |
| • Electorate | 8,046 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
• Total | 49.48 km2 (19.10 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 20 m (70 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 255 m (837 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | −2 m (−7 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[3] | |
• Total | 12,603 |
| • Density | 250/km2 (660/sq mi) |
| • Households | 2,973 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 5th municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 26.32 |
| • Revenue | ₱ 78.09 million (2020), 31.67 million (2012), 34.84 million (2013), 40.7 million (2014), 45.05 million (2015), 50.03 million (2016), 57.52 million (2017), 60.84 million (2018), 63.97 million (2019), 77.19 million (2021) |
| • Assets | ₱ 187.8 million (2020), 35.15 million (2012), 43.53 million (2013), 52.9 million (2014), 76.52 million (2015), 93.56 million (2016), 127.1 million (2017), 167.8 million (2018), 178.6 million (2019), 213.8 million (2021) |
| • Expenditure | ₱ 81.36 million (2020), 25.92 million (2012), 29.6 million (2013), 30.79 million (2014), 34.13 million (2015), 37.08 million (2016), 39.07 million (2017), 42.29 million (2018), 52.41 million (2019), 61.96 million (2021) |
| • Liabilities | ₱ 60.63 million (2020), 7.702 million (2012), 13.04 million (2013), 12.2 million (2014), 27.46 million (2015), 31.77 million (2016), 48.41 million (2017), 77.24 million (2018), 38.65 million (2019), 73.4 million (2021) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | Palawan Electric Cooperative (PALECO) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 5319 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)48 |
| Native languages | Cuyonon Palawano Tagalog |
Magsaysay, officially the Municipality of Magsaysay (Tagalog: Bayan ng Magsaysay), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,603 people.[3]
It is the easternmost of the three municipalities of the Cuyo Archipelago, and its territory includes the eastern half of Cuyo Island, as well as Alcoba, Canipo, Cocoro, Patunga, Paya, Putic, Siparay, Tacbubuc, and Tagauanian islands.
Geography
Barangays
Magsaysay is politically subdivided into 11 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks and some have sitios.
- Alcoba
- Balaguen
- Canipo
- Cocoro
- Danawan (Poblacion)
- Emilod
- Igabas
- Lacaren
- Los Angeles
- Lucbuan – one of the oldest barangays in Magsaysay. The Saint Michael Archangel Parish Church, where the town fiesta is celebrated, and Cuyo Airport are both located in Lucbuan.
- Rizal
Climate
| Climate data for Magsaysay, Palawan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
30 (85) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 45 (1.8) |
34 (1.3) |
62 (2.4) |
64 (2.5) |
127 (5.0) |
159 (6.3) |
172 (6.8) |
147 (5.8) |
167 (6.6) |
182 (7.2) |
172 (6.8) |
88 (3.5) |
1,419 (56) |
| Average rainy days | 12.1 | 9.4 | 13.0 | 14.3 | 22.7 | 26.9 | 28.0 | 26.4 | 27.0 | 27.0 | 22.7 | 17.8 | 247.3 |
| Source: Meteoblue[5] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[6][7][8][9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2020 census, the population of Magsaysay, Palawan, was 12,603 people,[3] with a density of 250 inhabitants per square kilometre or 650 inhabitants per square mile.
Economy
Poverty incidence of Magsaysay
10 20 30 40 2006 34.80 2009 17.64 2012 15.91 2015 17.25 2018 11.90 2021 26.32 Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17] |
History
Spanish Era
The modern-day municipality traces back its origins to the town of Cuyo. Cuyo, which included the entire island of Cuyo, was founded as a Spanish settlement in 1622.[18]
In 1762, one of the British ships that invaded Manila fired at the Cuyo fort but it was not damaged at all.[19] Another fort was started at Lucbuan seven kilometres away on the east side of Cuyo island, but it was never finished.
Lucbuan Republic
Revolutionary Dictatorial Government of Lucbuan Republic of Lucbuan | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1899–1902 | |||||||||
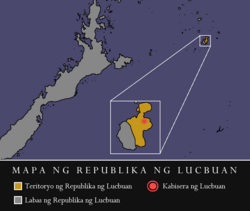 Map of the territory of the Republic of Lucbuan from 1899 to 1902 under Don Casiano Padon. | |||||||||
| Capital | Lucbuan | ||||||||
| Common languages | Cuyonon, Tagalog and Spanish | ||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism | ||||||||
| Government | Revolutionary Dictatorial Government | ||||||||
• Governor | Don Casiano Padon | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established by Don Casiano Padon | 1899 | ||||||||
• Arrival of American Forces | 1902 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Revolutionary Dictatorial Government of Lucbuan, often referred to as the “Lucbuan Republic” was a state on the island of Cuyo (now Magsaysay, Palawan) that briefly existed during the Philippine-American War. It was established to break away from the administration of President Emilio Aguinaldo and his central administration.
Even before the establishment of the Republic of Lucbuan, Don Casiano Padon, a native of Molo, Iloilo, began organizing a government in August 1898 due to the persuasion of the people of Lucbuan.
After the arrival of the representative of the Province of Calamianes from Bulacan in the last days of 1898, there was not much change in leadership in the entire archipelago of Cuyo and Palawan. This affected the livelihood of the people of Lucbuan as well as the inability to rule by the rulers of Calamianes. By this time the Spaniards had fled throughout Palawan to Borneo to return to Spain.
Very few knew Aguinaldo, and that is why the people of Lucbuan did not like to be ruled by Tagalog representatives under Aguinaldo which was the reason the Republic of Lucbuan was founded by Don Casiano Padon on 30 May 1899 and he himself as Governor of the government.[20]
All went well for the government until Padon decided to build a church which was strongly opposed by the legislature and the people. Thus, Padon and his family fled back to Iloilo and thus for the second time the attempt to join the state and the church was frustrated.[21]
American Era
This republic was not long in coming when the Province of Calamianes was organized by the Americans on 23 June 1902 under Philippine Commission Act No. 422. This was also accompanied by the conquest of the island of Lucbuan by American soldiers. This is also when the Lucbuan Republic ended.[20]
A marker of Don Casiano Padon currently exists on the municipality of Magsaysay in commemoration of the foundation of the Lucbuan Republic.[22]
Modern Era
On June 18, 1961, the barrios of Balaguen, Canipo, Cocoro, Danawan, Igabas, Imilod, Los Angeles, Lucbuan, Patonga, Rizal, Siparay Island, and Tagawayan Island were separated from the municipality of Cuyo and constituted into a new municipality known as Magsaysay, by virtue of Republic Act No. 3426.[23] The law took effect on January 1, 1964, when its first municipal officials were elected in the November 1963 local elections.[24]
References
- ^ Municipality of Magsaysay | (DILG)
- ^ "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ a b c Census of Population (2020). "Mimaropa". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ "PSA Releases the 2021 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 2 April 2024. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ "Magsaysay, Palawan: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 17 November 2019.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). "Region IV-B (Mimaropa)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-B (Mimaropa)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region IV-B (Mimaropa)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- ^ "Province of Palawan". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ^ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 29 November 2005.
- ^ "2003 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 23 March 2009.
- ^ "City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates; 2006 and 2009" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 3 August 2012.
- ^ "2012 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. 31 May 2016.
- ^ "Municipal and City Level Small Area Poverty Estimates; 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. 10 July 2019.
- ^ "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- ^ "PSA Releases the 2021 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 2 April 2024. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ "Cuyunon Island by Lydia Mary De Leon". Archived from the original on 2010-03-04. Retrieved 2010-04-03.
- ^ "Cuyo Island, Palawan, Philippines". Ako Cuyonon. Retrieved 9 November 2012.
- ^ a b "Palawan History Excerpt". Pdfslide.net. Retrieved 2021-05-03.
- ^ Bewley, Luther B. (January 1961). 1961: Rizal Centennial Year. Manila: The Grand Lodge of the Philippines. p. 71.
- ^ Tupaz, Harry (14 February 2015). "Magsaysay, Palawan: Lucbuan Republic". Viajero.
- ^ Republic Act No. 3426 (June 18, 1961), An Act Creating the Municipality of Magsaysay in the Province of Palawan, The Corpus Juris, retrieved September 22, 2023
- ^ "Executive Summary (Magsaysay)" (PDF). Commission on Audit. Retrieved September 22, 2023.




