Kalaw Lagaw Ya
| Kalau Lagau Ya | |
|---|---|
| Western Torres Strait | |
| Mabuiag | |
| Region | Western and Central Torres Strait Islands, Queensland |
| Ethnicity | Badu Island, Mabuiag, Kaurareg, Mualgal, Saibai Island, Boigu, Dauan Island, Kulkalgal, Maluigal (Torres Strait Islanders) |
Native speakers | 888 (2021 census)[1] |
Pama–Nyungan
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Western Torres Strait Islander Sign Language | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | mwp |
| Glottolog | kala1377 |
| AIATSIS[2] | Y1 |
| ELP | Kalaw Kawaw Ya |
| Linguasphere | 29-RG(A-a) |
 Range of Kalau Lagau Ya (orange) in the Torres Strait | |
Kalau Lagau Ya, Kalaw Lagaw Ya, Kala Lagaw Ya ([kala(u) laɡau ja]), or the Western Torres Strait language (also several other names, see below) is the language indigenous to the central and western Torres Strait Islands, Queensland, Australia. On some islands, it has now largely been replaced by Torres Strait Creole.
Before colonization in the 1870s–1880s, the language was the major lingua franca of the Torres Strait cultural area of Northern Cape York Australia, Torres Strait and along the coast of the Western Province/Papua New Guinea. It is still fairly widely spoken by neighbouring Papuans and by some Aboriginal Australians. How many non-first language speakers it has is unknown. It also has a 'light' (simplified/foreigner) form, as well as a pidginised form. The simplified form is fairly prevalent on Badu and neighbouring Moa.
Names
The language is known by several names besides Kalaw Lagaw Ya, most of which (including Kalaw Lagaw Ya) are names of dialects, spelling variants, dialect variants and the like — and include translations of the English terms, Western Island Language and Central Island Language:
| Language name (with regional and spelling variants) | English | Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Kalaw Lagaw Ya / Kalau Lagau Ya / Kala Lagaw Ya |
Western Island Language | |
| Lagaw Ya / Lagau Ya | Home Island Language | |
|
Langgus |
Language, Lingo | |
| Kaywalgaw Ya / Kaiwaligau Ya / Kawalgaw Ya | Islanders' Language | |
| Kowrareg (Kaurareg) | Islander | |
| Kulkalgau Ya | Blood-Peoples' Language | kulka 'blood' was an important Central Islands cult figure, and brother to Malo-Bumai of Mer. |
| Mabuiag/Mabuyag | Mabuiag Island and Badu Island[3] | |
|
Westen |
Western Torres Strait | |
|
Dhadhalagau Ya |
Mid-Island, Central Island Language |
One term used by Eastern Islanders and neighbouring Papuans for Kala Lagaw Ya is Yagar Yagar, from the word yagar (yá 'speech, etc.' + gár 'sympathy clitic' ('dear', 'please', etc.), often used by Western and Central Islanders in speech to show a sympathetic or nostalgic frame of mind.
In literature on the language the abbreviations KLY (Kalaw Lagaw Ya), KKY (Kalau Kawau Ya), KulY (Kulkalgau Ya), MY (Muwalgau Ya) and KY (Kaiwaligau Ya) are often used as abbreviations. The name Mabuiag /mabujaɡ/, in English pronounced /ˈmoʊbiæɡ/, is fairly widespread as a name for the language, this having been established by the Cambridge Expedition to Torres Strait, whose main research on the language was with Mabuiag material. Though the preferred term in English in Academia for some time was Kala Lagaw Ya,[4] according to Ober, the form was always regarded as "colloquial" by native speakers.[citation needed] In a High Court decision on 7 August 2013, the decision was taken to officially term the language Kalau Lagau Ya, using the formal form.[citation needed]
When speaking to each other, speakers generally refer to the language as Langgus 'language' or use phrases such as KLY/KulY ngalpudh muli, MY-KY ngalpudh/ngalpadh muli, KKY ngalpadh muliz "speak(s) our language", e.g. KLY/KulY ngalpudh muuli, thanamunungu tidailai!, MY-KY ngalpudh/ngalpadh muuli, thanamuningu tidailai!, KKY ngalpadh muli, thanamulngu tidaile! 'Speak in our language so they don't understand!'. Ngalpudh/ngalpadh literally means 'like us'. The construction X-dh mula+i- 'speak X-like' is used to refer to speaking in a language, e.g. KKY markaidh muliz 'speak [in] English', zapanisadh muliz 'speak [in] Japanese', dhaudhalgadh muliz 'speak [in] Papuan', mœyamadh muliz 'speak [in] Meriam Mìr', thanamudh muliz 'speak like them, speak [in] their language'. It is otherwise common for speakers to use nominal phrases like KLY/KulY ngalpun ya, MY-KY ngalpun/ngalpan ya, KKY ngalpan ya 'our language' to refer to the language when speaking to each other.
Geographic distribution
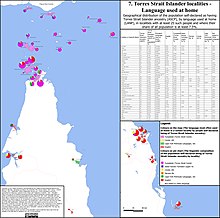
Kalau Lagau Ya is spoken on the western and central islands of Torres Strait, between Papua New Guinea (Naigay Dœgam Dhaudhai "North-side Mainland/Continent", also called Mœgi Dhaudhai "Small Mainland/Continent", KKY Mœgina Dhaudhai) and the Australian mainland (Zey Dœgam Dhaudhai "South-side Mainland/Continent", also known as Kœi Dhaudhai "Big Mainland/Continent"), though on some islands it has now been largely replaced by Brokan (Torres Strait Creole).
There is some folk history evidence that the language was spoken as a first language in a few villages neighbouring Torres Strait in Papua. It was also formerly spoken by the Hiámo (Hiámu, Hiáma) of Daru (Dhaaru) to the north-east of Torres Strait, who were originally settlers from Yama [Yam Island] in Torres Strait, Hiámu/Hiámo/Hiáma being a Kiwai pronunciation of Yama. The main body of the Hiámo moved to the Thursday Island group to escape the Kiwai colonisation of Daru some centuries ago.
Classification and external comparison
The language is classified as being part of the Pama–Nyungan languages. Mitchell regard it as a mixed language with an Australian core (Pama–Nyungan) and Papuan and Austronesian overlays,[6] while Capell and Dixon classify it among the Papuan languages. The personal pronouns are typically Australian, most kin terms are Papuan, and significant sea/canoe and agricultural vocabulary is Austronesian.[7]
Kalaw Lagaw Ya has only 6% cognation with its closest Australian neighbour, Urradhi, with a further 5% 'common' vocabulary (loans of various origins) — and about 40% common vocabulary with its Papuan neighbour, Meriam Mìr.[8] Of 279 Proto-Paman forms only 18.9% have definite realisations in Kalaw Lagaw Ya, with a further 2.5% which may be present.[9] One word that illustrates the problems of 'may-be' relationship is kùlbai (KKY kùlba) 'old', which may be a metathetic realisation of CA *bulgan 'big; old'. Potentially 80% of the vocabulary of the language is non-Australian, and includes Papuan and Austronesian items.[citation needed] Bouckaert, Bowern and Atkinson (2018) found that Kalaw Lagaw Ya had the highest number of 'unique' (that is, non-Pama-Nyungan) forms of any Australian language in their sample.[10]
| Australian (Common Australian) |
Papuan (Proto–East Trans-Fly) |
Austronesian (Proto–Central District) |
|---|---|---|
| *nya-ga 'look' nagai-/nage-/nagi- id. |
*nyily 'name' nel id. |
*gamo 'belly' gamu 'body' |
| *jana 'they' thana id. |
*p[ae]- 'that, there' pi-/pe- 'specifically yonder' |
*[w]aura 'trade wind, south-east trades' wœur(a) id. |
| *ganyarra 'reptile' kœnara 'k.o. tree snake' |
*gabo 'cold' gabu id. |
*boro-ma 'pig' bùrùm(a) id. |
| *galga 'spear' kœlak(a) id. |
*biro 'side' bero 'rib; side of boat, hillside, river bank, etc.' |
*pu[lr]i 'magic' puy(i) (older puuři) 'magic, plant' |
Oral tradition and cultural evidence recorded by Haddon and Laade,[11] backed by archaeological evidence[citation needed] and linguistic evidence, shows that Austronesian trade and settlement in South-West Papua, Torres Strait and Cape York occurred; the languages have significant Austronesian vocabulary content,[citation needed] including items such as the following:
| Kalaw Lagaw Ya | meaning | Meriam Mìr | meaning | Bine (Papua) |
meaning | Proto-Oceanic Austronesian |
meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| maapu | heavy | (beberbeber) | id. | mæpu | id. | *mapa | id. |
| maalu | deep, deep water, sea, deep water beyond edge of reef~shallows | malo | id. | malu | id. | *mwaloq | submerged rock~reef (where it disappears into sea depths) |
| laba- | cut, hack, strike (human) | --- | --- | --- | --- | *la(m)pak | strike (as with sword or flat weapon), slam something down, slap |
| wœiwi | mango | waiwi | id. | wiwi | id. | *waiwai | id. |
| waaku | mat; sail | papék | id. | waaku | id. (Kalaw Lagaw Ya loan) |
*paqu | id. |
| waaru | turtle | (nam) | id. | waaru | id. (Kalaw Lagaw Ya loan) |
*ponu | id. |
Some of the Austronesian content is clearly South-East Papuan Austronesian:
| word | Kalaw Lagaw Ya | Gudang (Australia) |
Kiwai (Papua) |
Motu (Central District, Papua) |
Proto–SE Papuan | Proto-Oceanic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nacre, mother-of-pearl | maay(i) (OKY maaři) |
maari | mari | mairi | *mwa[lr]i | ? |
| outrigger | sayim(a) OKY sařima |
charima | sarima SE Kiwai harima |
darima | *nsarima | *saRaman |
| pig | bùrùm(a) | — | boroma | boroma | *boro-ma | *mporok |
| rope, cord | wœru KKY wœrukam(i) |
uuru | waro | varo | *waro | *waro |
| head, origin, base of tree, etc. | kuik(u) KLY kuiiku |
--- | — | PCD *quiqui id. | *kulikuli | *kulukulu 'head-end, upper part' |
The linguistic history of the Torres Strait area is complex, and interaction of well over 2500 years has led to many layers of relationship between the local languages, including many words that are obviously common, such as the following 'trade' words in Torres Strait area languages.
| Kalaw Lagaw Ya | Meriam Mìr | Kiwai (Papua) |
Agöb (Papua) |
Gudang (Australia) |
Urradhi (Australia) |
Anguthimri (Australia) |
Mpakwithi (Australia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gii tusk, knife, tusk/knife-life formation |
gir tusk/knife-life formation |
giri tusk, knife, tusk/ knife-life formation |
? | ? | kiri/ghiri knife |
kiri knife |
kiri knife |
| sœguba tobacco |
sogob tobacco |
suguba tobacco |
? | —[a] | tyughubha tobacco |
tyughubhu tobacco |
? |
| yœuth(a) long house, hall; church |
ìut (alt- eut) church |
— | ? | ? | yutha house |
— | — |
| mœruka any strange four-legged animal |
— | — | ? | ? | murruku horse |
? | marruku horse |
| mœrap(i) bamboo |
marep | marabo | ? | marrapi | marrapi | ? | marrapi |
| eso thanks |
esoau | ? | eso | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| paaudh(a) peace |
paud | ? | piuda | paaudha | ? | ? | ? |
| warup(a) drum |
warup | warupa | (w)arapa | warrupa | (w)arrupa | (w)arrupa | (w)arrupa |
| thuurik(a) cutting tool |
tulik | turika | turika Bine turi/turikæ |
? | thurriya crowbar |
thurriya crowbar |
thurriya crowbar |
- ^ The only Gudang word recorded in the mid-1800s by Europeans was choki, from the Malay-based English Pidgin English used by the British (and other) sailors of the time. The Malay word is variously coki or cuki.
However, the question of external relationships of Kalaw Lagaw Ya is also complicated by resemblances between both the Paman (Pama-Nyungan, Australian languages) and the Trans-Fly (Papuan) languages. Though few, these may be significant, and include forms such as those noted below, not all of which appear in Kalaw Lagaw Ya. Such resemblances could point to a deep-level relationship dating back to before the flooding of Torres Strait at the end of the last age, as claimed by Mitchell[8] or they could point to genetic inheritance and subsequent language contact, as discussed by Alpher, Bowern, and O'Grady 2009.[12]
| Proto-Paman (or a specific North Cape York language) |
meaning | Proto-Trans-Fly | meaning | Kalaw Lagaw Ya | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *kaalu | ear | *Vtkuru | hear | kaura; kùrusai- (compounds only) |
ear |
| *ŋaa(na) | who | *ŋana | id. | ngaa | id. |
| *mini | good | *mi:nji | id. | miina | real, true, very |
| anha Urradhi, Gudang |
breath | *ŋana | id. | ngœna | id. |
| wintamwintama Urradhi |
star | *mpintom | id. | (thithuy(i) OKY thithuri) |
id. |
| *nyupun | one | *[ni/yi/dVr]ponV | id. | wœrapùn(i) ùrapùn (wara 'one of a group') |
id. |
| *pama | man, person | *pyama | id. | (mabaig lit. 'walker') | id. |
Personal pronouns
A comparison of the Kalaw Lagaw Ya, Meriam Mìr, Kiwai and Uradhi personal pronouns show similarities and differences in typology. In comparison to Uradhi, Kalaw Lagaw Ya has an archaic typology — or, rather, Uradhi has innovated, having lost the Common Australian 1, 2 and 3 plurals. Kiwai does not have 1–2 pronouns, while Meriam Mìr does not have a dual and trial/paucal set of pronouns which correspond to its verb system. The Kalaw Lagaw Ya system, like that of Uradhi, is Australian:
| singular | dual | plural | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | ngai | ngalbe | ngœi | |
| 1st–2nd person | — | ngœba | ngalpa | |
| 2nd person | ngi | ngipel | ngitha | |
| 3rd person | masc | nui | palai | thana |
| fem | na | |||
| singular | non-singular | |
|---|---|---|
| 1st person | ka | ki |
| 1st–2nd person | — | mi |
| 2nd person | ma | wa |
| 3rd person | e | wi, i |
Note that except for Meriam Mìr, the Trans Fly languages also have two-gender masculine-feminine systems, though not marked on the pronouns themselves.[13]
| singular | dual | trial | plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | mai | nimoto | nimoibi | nimo |
| 2nd person | rai | rigoto | rigoibi | rigo |
| 3rd person | nowai | neito | neibi | nei |
| singular | dual | plural | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person | ayu(va) | ampu(la) | |
| 1st–2nd person | — | ali(va) | ana(va) |
| 2nd person | antu(va) | ipu(la) | |
| 3rd person | ulu(va) | ula(va) | |
However, even though the system has no real surprises for Australian linguistics, it is clear that Kalaw Lagaw Ya has innovated in the 1st and 2nd pronouns, which have the following CA origins:
- CA *ngali 'we, inclusive' > ngœy [stem: ngœlmu- (old style singing ngalimu-, ngalemu-), ngœimu-] 'we, exclusive'; and with stem extensions ngalpa 'you and I/we' (old-style singing ngalipa/ngalepa), ngalbai/ngalbe 'we dual (exclusive)', (old style singing ngalebai/ngalibai)
- CA *ngana+pulV 'we, exclusive dual' > ngœba 'you and I'.
The 2nd person dual and plural pronouns are based on forms that literally mean 'you dual' (ngipel) and 'you-they' (ngitha[na]), in much the same way as the demonstratives mark the dual and plural (see further below in Nominal Morphology).
| English | KLY | KulY | KY | KKY | Old KY (Kowrareg) |
Proto-Pama–Nyungan origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ngay stem: nga- |
ngai stem: nga- |
ngai stem: nga- |
ngai stem: nga- |
ngai stem: nga- |
*ngayi |
| you and I | ngœba | ngœba | ngœba | ngœba | ngœba | *ngana+pulV 'we dual, exclusive' |
| we dual (exclusive)[a] | ngalbay | ngalbai | ngalbai/ngalbe | ngalbe | ngalbai/ngalbe | *ngali+[?] 'you and me, you and us' |
| we (inclusive)[a] | ngalpa stem: ngalpu- |
ngalpa stem: ngalpu- |
ngalpa stem: ngalpu- |
ngalpa stem: ngalpa- |
ngalpa stem: ngalpa- |
*ngali+[?] 'we inclusive' |
| we (exclusive)[a] | ngœy stem: ngœlmu- |
ngœi stem: ngœlmu- |
ngœyi stem: ngœymu- |
ngœi stem: ngœimu- |
ngœři stem: ngœři(mu)- |
*ngali 'we inclusive' |
| you sing | ni | ni | ngi/ni | ngi | ngi | *NHiin |
| you dual | nipel stem: nipe- |
nipel stem: nipe- |
ngipel stem: ngipe- |
ngipel/nipel stem: ngipe-/nipe- |
ngipel stem: ngipe- |
*NHiin+pulV 'you dual' |
| you pl | nitha stem: nithamu- |
nitha stem: nithamu- |
ngitha stem: ngithamu- |
ngitha/nitha stem: ngithamu-/nithamu- |
ngithana stem: ngithana(mu)- |
*NHiin + *DHana 'they plural' |
| he | nuy stem: nu- |
nui stem: nu- |
nui stem: nu- |
nui stem: nu- |
nui stem: nu- |
*NHu- |
| she | na | na | na | na | na | *NHaan |
| they dual | palay stem: palamu- |
palai stem: palamu- |
pale stem: palamu- |
palai stem: palamu-, Boigu pale stem: palemu- |
pale stem: palamu- |
*pula 'they dual, two' |
| they | thana stem: thanamu- |
thana stem: thanamu- |
thana stem: thanamu- |
thana stem: thanamu- |
thana stem: thanamu- |
*DHana 'they plural' |
| who | nga | nga | nga | nga | nga | *ngaaNH |
| what [b] |
mi-, midha- (midhi-) |
mi- | mi- | mi- | mi- | *miNHa 'food; what' |
Prehistoric overview
An examination of the various sub-systems (vocabulary, syntax, morphology) suggests the following:
- Australian (Paman)
Some basic and abstract vocabulary, all personal pronouns (inc. who and what/which), some verbs. Some grammar, such as nominal and verb morphology (subject, agent, object, genitive, -l locative, -ka dative, perfective attainative, imperfective, -i/-iz(i) perfective active. These typological categories also exist in the Trans-Fly languages; the forms in Kalaw Lagaw Ya are clearly Australian.
- Papuan (Trans-Fly)
Some basic and abstract vocabulary, some verbs. Some grammar, such as verb number and different stems for different number forms of some verbs. Use of state/movement verbs as existential and stative 'be' verbs. Two non-personal pronominals: naag/naga 'how', namuith 'when' (both in KKY, the dialect of the islands off the Papuan coast).
- Austronesian
Some basic vocabulary, terminology dealing with agriculture, canoes, the weather, the sky and the sea, some abstract nouns, some verbs. Possibly some grammar in the form of function words, such as waadh (KKY waaza) 'existential emphasis' (i.e. 'it is true that ... '), Proto Oceanic Austronesian *waDa 'existential'.
The Australian word forms and structure found in Kalaw Lagaw Ya appear to be retentions, i.e. inherited; the original Australian forms appear to be unchanged at the core level. This suggests that the language is not a pidgin/creole in origin, but an Australian language which has undergone strong external lexical and grammatical influence. The language appears to be a classic case of shift,[14] whereby speakers of one language retained multilingualism over a long period of time, absorbing aspects of another language. The Austronesian and Papuan overlays modified the Australian phonology and syntax profoundly. The contrast of Australian laminal nh/ny and lh/ly and apical n and l has been lost, voicing has become phonemic and s, z, t, d, o and òò have developed. This also affected the phonology of Australian vocabulary, where these 'foreign' sounds also occur.
The non-Australian content appears to be mainly lexicon (including verbs), particularly dealing with the sea, farming, canoe and sky/weather/astrology, with possible some syntactic words. This presents a picture[14] of a typically extensive borrowing situation with much lexical borrowing and some structural borrowing with a large amount of passive bilingualism and little active bilingualism.
Laade's picture (1968) of Australian and Papuan settlement in Torres Strait supports the above scenario of Papuan and Austronesian speakers who shifted to an Australian language over a long period of time, the Austronesians being culturally a superstratum, however not in a position to impose their language. He presented folk history evidence that a few Austronesian traders (men) settled at Parema (north-east of Daru) and married local [Proto–Trans Fly speaking] women. To avoid further miscegenation, they soon moved and settled in Torres Strait, first to the Eastern Islands, then to the Central Islands, then to Moa, Badu and Mabuiag. At Mabuiag, Badu and Moa they found Aboriginal people, killed the men and kept the women (and presumably the children). Some moved on up to Saibai, Dœwan and Bœigu to avoid this new miscegenation, hence the lighter colour of many Saibai, Dœwan and Bœigu people. Bœigu folk history collected by Laade also shows direct East Austronesian genetic influence on Bœigu.[15]
The social context was that of a few Austronesian men who settled on the outskirts of an East Trans-Fly group, intermarried, and whose children were either bilingual, or speakers of their mothers' language, with some knowledge of their fathers' language. The local people did not need to speak the traders' language, who in turn had to speak the local language. The children in turn would then speak the local language, with varying ability in the fathers' language, particularly in areas that were culturally important for the fathers.
These people then shifted to Torres Strait — maintaining established ties with Papua as well as with Austronesian speakers further east (this latter being suggested by various characteristics of the Austronesian content in Kalau Lagaw Ya) — and overlaid an Australian population in such a way that the majority of women spoke an Australian language, with a significant number, mainly men, who spoke a South-East Papuan Austronesian language, accompanied by their Papuan wives and their perhaps bilingual children. Over time, the core structure of the local mothers' language dominated, with retention of the newcomers' Papuo-Austronesian content in the appropriate cultural subsystems. In essence this would have been a 'replay' of the original settlement by Austronesian traders at Parema, with the women understanding the language of the men, but not really needing to speak it while retaining parts of their language for significant areas. The children then created a new language shift to an Australian language with a Papuan-Austronesian admixture.
Kalaw Lagaw Ya is thus a mixed language in that a significant part of its lexicon, phonology and grammar is not Australian in origin. The core nominal, pronominal and verb morphology is Australian in both form and grammar — though a certain amount of the grammar is common to Trans-Fly and Paman languages in the first place. Some semantic categories, verb number morphology, and some other morphology are non-Australian in origin. Potentially 80% of its vocabulary is non-Australian. The interplay of the above within the subsystems of Kalaw Lagaw Ya lexicon, phonology and grammar points more to mixing through shift and borrowing rather than pidginisation and creolisation.
Outside influences
The language also has some vocabulary from languages outside the Torres Strait area, from the Indonesian, Malay, Philippine, English and other 'outsiders'. Where loan words from the Western Austronesian (Indonesian, etc.) loans are concerned, it is possible that some such came into the language in pre-European contact days, with the Makassans and similar fishermen/traders who visited northern Australia and Torres Strait.
Examples of post-European contact Western Austronesian loan words:
| word | Kalaw Lagaw Ya | origin |
|---|---|---|
| coconut toddy | thúba | tuba (Eastern Indonesian or Philippine language) |
| trumps (in cards) | záru | zaru/jaru (Eastern Indonesian or Philippine language) |
| mate, friend, brother | bala Boigu variants: bœra, baya |
bela/bala (Eastern Indonesian or Philippine language) |
| blachan | bœlasan | Malay: belacan |
Some words in the language, assuming that they are Western Austronesian loans, appear to be pre-contact words. This is suggested by form and use in the language and in neighbouring languages (some of these words may ultimately be from Arabic and Sanskrit).[16]
| Kalaw Lagaw Ya | meaning | possible source | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| aya (KKY) aye (KLY,KulY,KY) |
come! (singular) | Malay: ayo | come! |
| thurik(a) | cutting tool | Tetun: tudik | knife |
| ádhi |
|
Malay: adi (Sanskrit: अधि, romanized: adhi) |
huge, great (also as an honorific) |
| kœdal(a) | crocodile | Malay: kadal Makassarese: kaɖalaq |
lizard |
| pawa | deed, action, custom | Malay: paal [paʔal] (Arabic: فَعَلَ, romanized: faʿala) |
deed, action |
Loans from modern Eastern Austronesian (Polynesian and Melanesian) into the language are mainly of religious or 'academic' use. In general, such words are terms for objects that are strictly speaking European goods. One exception is the last in the following table, which is commonly used instead of the traditional words imi 'spouse's opposite-sex sibling', 'opposite sex sibling's spouse' and ngaubath 'spouse's same-sex sibling', 'same-sex sibling's spouse'. These have also similarly been replaced in common usage by the English loan woman (pronounced [woman]) in the meaning of 'sister/daughter-in-law'.
| Kalaw Lagaw Ya | meaning | source | meaning in originating language |
|---|---|---|---|
| thúsi | book, document, letter, etc. | Samoan: tusi | (same meaning) |
| laulau | table | Samoan: laulau | plaited coconut leaf used as a tray |
| wakasu | anointment oil | Drehu: wakacu | coconut oil |
| thawiyan (emotive form thawi) |
brother/son-in-law | Vanuatu: tawean | brother-in-law |
Other biblical loans are from Ancient Greek, Latin and Biblical Hebrew:
| Kalaw Lagaw Ya | meaning | source | meaning in originating language |
|---|---|---|---|
| basalaya | kingdom | Ancient Greek: βασιλείᾱ | id. |
| aretho | holy communion | Ancient Greek: ἄρτος | wheaten bread |
| Sathana | Satan | Biblical Hebrew: שטן | Satan, opponent, adversary |
| Sabadh(a), Sabadhi | Sunday | Biblical Hebrew: שבת | Saturday (Sabbath) |
Two early English loans of interest show back formation from what in the language appeared to be a plural. Most nouns (a) form the plural with an -l suffix, and (b) in the nominative-accusative singular elide the stem final vowel, thus tukuyapa- 'same-sex sibling', plural tukuyapal, nominative-accusative tukuyap. Under this model 'custard-apple' became katitap, plural katitapal, and 'mammy-apple' (pawpaw/papaya) became mamiyap, plural mamiyapal.
Dialects
There are four main dialects, two of which are on probably the verge of extinction, one (Kaiwaligau Ya) through convergence to the neighbouring Kalaw Lagaw Ya. Within the dialects there are two or more subdialects. The average mutual intelligibility rate, based on a Swadesh count, is around 97%.
- Western Torres Strait language
- Northern dialect: Kalau Kawau Ya (Kalaw Kawaw Ya)
- Saibai (Saibai Village and Aith, also Bamaga/Seisia on Cape York), Dœwan (Dauan), Bœigu (Boigu);
- Western dialect: Kalau Lagau Ya (Kalaw Lagaw Ya)
- Mabuyag (Mabuiag) and Badhu (Badu). The western dialect also has a simplified form, particularly on Badhu, where quite a few foreign men of Malay and South Sea Islander origin settled with their Island wives in the late 1800s and early 1900s;
- Eastern dialect (Central Island dialect, spoken by the Kulkulgal nation[17]): Kulkalgau Ya
- Masig, Yama, Waraber, Puruma, and associated islands, now uninhabited, such as Nagi, Tudu and Gebar;
- Southern dialect (South-West Islands): Kaiwaligau Ya [Kauraraigau Ya]
- Muralag, Ngœrupai (alt. Ngurupai) and the other islands of the Thursday Island group, Mua (alt. Moa), Muri (Mt Adolphus — now uninhabited); Muwalgau Ya / Italgau Ya — Mua. Now converging with Kalaw Lagaw Ya.
- Northern dialect: Kalau Kawau Ya (Kalaw Kawaw Ya)
The Southern dialect has certain characteristics that link it closely to the northern dialect, and folk history dealing with the Muralag group and Mua reflects this, in that the ancestors of the Kowrareg (the Hiámo) originally came from Dharu (Daru, to the north east of Torres Strait) — and who had previously settled on Dharu from Yama in Central Torres Strait.[18]
Samples of the dialects
They cut down a big tree earlier today to make a canoe.
- Kalau Kawau Ya: Thana kayb kœi puy pathanu gulpa aymœipa.
- Kalaw Lagaw Ya: Thana kayib kœi puuyi pathanu gulka ayimka.
- Kulkalgau Ya: Thana kayb kœi puy pathanu[l] gulka aymœika.
- Kaiwaligau Ya/Muwalgau Ya: Thana kayib kœi puy pathanu[l] gulpa aymaipa.
- Old Kaiwaligau Ya (Kowrareg): Thana kayiba kœi puuři pathanulai gulpa[ri] ayimařipa[ri].
- Simplified Kalaw Lagaw Ya: Thana kaib kœi puy pathai gulka aymaik.
Underlying form:
Thana+∅
They PL+NOM
kayiba∅
today
kœi
big
puuRi+∅
tree+ACC
patha+∅+∅+nulai
chop+ATT+SG+today PST
gul+ka/pari
canoe+DAT
ayima+[R]i+ka/pari
make+VN+DAT
They cut down a big tree earlier today to make a canoe.
Some isolect markers of the four dialects of Kalaw Lagaw Ya:
| Kalau Kawau Ya | Kaiwaligau Ya | Kalaw Lagaw Ya | Kulkalgau Ya | Kauraraigau Ya (Kowrareg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| you sing | ngi | ngi | ni | ni | ngi |
| house | laag | laag, mùdh |
mùùdha | mùdh | laaga, mùdha |
| thunder | gigi | dhuyum | dhuyum | dhuyum | dhuyuma |
| end, finish | muasi- (B muyasi-) |
muasi- | minasi- | minasi- | moasi- |
| heat | kom | kœmàn | kœmààna | kom | kœmàna |
| steam | kœman | kœmàn | kœmààna | kœmàn | kœmàna |
| Dative | -pa | -pa (-ka) |
-ka (-pa) |
-ka (-pa) |
-pa, -pari (-ka) |
| Ablative | -ngu(z), -z(i) |
-ngu, -z(i) |
-ngu, -zi |
-ngu, -z(i) |
-nguzi, -zi |
| Present Perfective Active Singular |
-iz, -izi, -izin |
-i (Badhu -in), -izi (Badhu -izin) |
-i, -izi |
-i, -izi |
-izi, -iziři |
Dialectal differences
Phonology
Phonological differences between the dialects are rare, and in general sporadic. The only regular differences are the following:
Colloquial final unstressed vowel elision
Found in Kulkalgau Ya and Kaiwalgau Ya:
- maalu 'sea' > maal’
- waapi 'fish' > waap’
- thathi 'father' > thath’
- waaru 'turtle' > waar’
- ngadha 'appearance, looks' > ngadh’
- mœràpi 'bamboo' (à shows the stressed syllable) > mœràp’
- bera 'rib' > ber’
- kaaba 'dance performance, knot in bamboo (etc.)' > kaab’
- kaba 'oar, paddle' > 'kab’
Such elision is rare or sporadic in Kalau Kawau Ya.
Final unstressed vowel devoicing
In Kalaw Lagaw Ya, such final vowels in correct language are devoiced, and deleted in colloquial language, except in a small class of words which include bera 'rib', where there is a short vowel in the stem and in which the final vowel is permanently deleted, with compensatory lengthening of the final consonant (thus berr).
Strictly speaking, the process is not final vowel devoicing, but rather stressed vowel lengthening accompanied by final vowel devoicing — except in the case of words such as bera 'rib' > berr, where the process is final consonant lengthening by the final vowel being 'incorporated' into the consonant. Note that in the following the word-final capital letter represents a devoiced vowel:
- maalu 'sea' > maalU > maal’
- waapi 'fish' > waapI > waap’
- thaathi 'father' > thaathI > thaath’ (Badhu variant thath’)
- waaru 'turtle' > waarU > waar’
- ngadha 'appearance, looks' > ngaadhA > ngaadh’
- mœràpi 'bamboo' > mœrààpI > mœrààp’
- bera 'rib' > berr
- kaba 'dance performance, knot in bamboo (etc.)' > kaabA > kaab
- kaba 'oar, paddle' > kabb
In declined forms of such words, the long vowel is shortened, and the final vowel voiced, and in words like ber 'rib' the final vowel often reappears:
- maalU 'sea' + -ka 'dative' > maluka
- waapI 'fish' > wapika
- thaathI 'father' > thathika
- waarU 'turtle' > waruka
- ngaadhA 'appearance, looks' > ngadhaka
- mœrààpI 'bamboo' > mœràpika
- ber 'rib' > beraka, berka
- kaabA 'dance performance, knot in bamboo (etc.)' > kabaka
- kab 'oar, paddle' > kabaka, kabka
This vowel shortening in affixed/modified forms exists in all dialects, however the other dialects have retained contrastive length to some extent, whereas Kalaw Lagaw Ya has largely lost it for 'morphophonological' length, where the stressed vowel in non-emotive words (see below) of one or two syllables is automatically lengthened in the nominative-accusative; this also applies to words of three syllables with second syllable stress (as in mœrààpI 'bamboo').
One of the very few length contrasts in the Kalaw Lagaw Ya dialect is kaaba 'dance performance, knot in bamboo etc.' vs kaba, kab 'paddle, oar' (Old Kaiwaligaw Ya [Kauraraigau Ya] kœRaba; œRa has regularly given short a in Kalaw Lagaw Ya in kaba, kab). Such length contrasts are more widespread in the other dialects.
The exceptions are (1) the small class or words that include ber 'rib' and kab 'oar, paddle', and (2) emotive words. Emotive words are those that equate to a certain extent to diminutives in languages such as Irish, Dutch and German, where specific suffixes are added to show 'diminutive' status (-ín, -je and -chen/-el/-lein respectively). Emotive words include familiar kinship terms [the equivalent of English Mum, Dad and the like] and words used in emotive contexts such as singing/poetry.
| Word | Non-Emotive | Emotive |
|---|---|---|
| Mum | (apuuwa, apùù, àpu — mother) | Ama |
| Dad | (thaathi, thaath — father) | Baba |
| child | kaazi, kaaz | kazi |
| wife | iipi, iip | ipi |
| home (island) | laaga, laag | laga |
| dust, spray | pœœya, pœœy | pœya, paya |
| bamboo | mœrààpi, mœrààp | mœràpi, marapi |
| head | kuwììku, kuwììk | kuwìku, kuiku |
Final i-glide deletion
A small class of words in Kalau Kawau Ya do not have the final i-glide found in the other dialects, including the following:
- banana plant: KLY/KulY/KY dawai, KKY dawa
- spot, stain: KLY/KulY/KY burkui (bœrkui), KKY bœrku (burku)
- blank skink: KLY/KulY/KY mogai, KKY Saibai/Dœwan mogo, Bœigu moga
- old: KLY/KulY/KY kulbai, KKY kulba
- a short while, first before doing something else: KLY/KulY/KY mamui, KKY mamu
- birth cord: KLY/KulY/KY kùpai, KKY kùpa
Word forms in neighbouring languages as well in the Kauraraigau Ya (Kowrareg) of the mid-to-late 19th century, such as the Meriam Mìr kopor and Kauraraigau Ya kupar/kopar 'birth cord' show that in such words the final -i/Ø are the modern forms of older *ɾ.
Syntax
The main syntactic differences are:
Verb negative construction
In all dialects except Kalau Kawau Ya, the verb negative is the nominalised privative form of the verbal noun. As this form in itself a noun, its subject and direct object are cast in the genitive:
- Ngath waapi purthanu 'I ate a fish'
- Ngai stuwaka uzarima 'I went to the store'
- Ngau wapiu purthaiginga 'I didn't eat a fish'
- Ngau stuwaka uzaraiginga 'I didn't go to the store'
The Kalau Kawau Ya dialect uses the verbal noun privative form as an invariable verb negative:
- Ngath waapi purthanu 'I ate a fish'
- Ngai stuwapa uzarima 'I went to the store'
- Ngath waapi purthaiginga 'I didn't eat a fish'
- Ngai stuwapa uzaraiginga 'I didn't go to the store'
Verb tenses/aspects
The Kalau Kawau Ya dialect has the tenses and aspects listed in the section on verb morphology. The other dialects have largely lost the remote future tense, using the habitual instead; the remote future in the other dialects is retained most commonly as a 'future imperative', where the imperative refers to a vague period in the future. The Kalaw Lagaw Ya dialect also has a 'last night' tense, where the adverb bungil/bungel (reduced form bel) 'last night' has become a verb postclitic, following the model of the adverb ngùl 'yesterday', which had previously become grammaticalised as a 'recent past' tense marker in all dialects, with reduction to -ngu in Kalau Kawau Ya. In the other dialects bongel 'last night' is a fully functioning temporal adverb used in conjunction with either the today past or the recent past.
The dialects differ in the forms of the following affixes:
- present imperfective/near future perfective/verbal noun dative:
- KKY/KY -pa, KLY/KulY -ka
- Recent past
- KKY -ngu, KLY/KY/KulY -ngul
- Today past
- KKY/KLY/KulY -nu, KY -nul (older -nulai)
- Habitual
- KKY -paruig/paruidh/-parui/-paru/-pu (-pu most commonly on stems of two or more syllables, and the bi-syllabic forms on stems of one syllable [the consonant final forms are emphatic forms])
- KLY/KulY -kuruig
- KY -kurui
Nominal affixes
The main nominal affix difference is the dative ending, which has the following forms in the various dialects:
- KLY/KulY -ka; -pa with kipa 'to here', sipa 'to there', paipa 'to ahead', pawupa 'to behind, off to one side'; -pa (sometimes in poetry/singing)
- KY -pa; -ka in ngaikika 'to/for/towards me'; -ka (often in poetry/singing)
- KKY -pa in all cases; -ka (often in poetry/singing)
The plural/HAVE suffix -LAI (underlying form) also shows a small amount of dialect variation with stems of two syllables, where Kulkalgau Ya differs from the other dialects in retaining the full form of the suffix -lai, reduced to -l in the other dialects. In stems of three or more syllables, the suffix is reduced to -l in all dialects, while retained as -lai (variants according to noun sub-class -thai, -ai, -dai) with stems of one syllable.
- Three+ syllable stem
burum 'pig', stem: buruma-, plural burumal
- Bisyllabic stem
lag, KLY laaga 'place, home, home island', stem: laga-, plural lagal, KulY lagalai
- Monosyllabic stems
- Regular vowel final: ma 'spider', plural malai
- Regular -i glide final: mui 'fire', plural muithai, KLY muithail
- Regular -l final: pel 'fish tail', plural pelai
- Regular -r final: wœr/wur/uur 'water', plural wœlai/wulai/ulai, KKY wœrai
- Irregular vowel final stem: ya 'speech, word(s), message, language, etc.', plural yadai, KLY yadail
Vocabulary
The main differences between the dialects are to do with vocabulary, as can be seen in the following examples:
- house/building: KLY mùùdha (laaga), KulY mùdh (laag), KY laag (mùdh), KKY laag
- mud: KLY/KulY/KY berdhar (sœœya 'sandy mud/silt'), KKY sœœi (berdhar 'softness of food, mud, etc.')
- grandad: KLY/KulY/KY athe, KKY pòpu
- frog: KLY/KulY kœtube, kœtak, kaata, KY kat, KLY (Saibai-Dœwan) kat, (Bœigu) kœtuke, kat
- axe: KLY/KulY/KY aga, KKY agathurik (thurik 'cutting tool')
- namesake: KLY/KulY natham, KKY/KY nasem
- small, little: KLY/KulY/KY mœgi, Saibai/Dœwan mœgina, Bœigu mœgina, kœthuka
- woman, female: KKY yipkaz/yœpkaz [stem yipkazi-/yœpkazi-], KLY/KulY ipikaz (KLY variant iipka) [stem ipkazi-], KY ipkai/ipikai [stem ipkazi-/ipikazi-]
- man, male: KKY garkaz [stem garkazi-], KLY/KulY garka [stem garkazi-], KY garkai [stem garkazi-]
- unmarried young/teenage woman: KKY ngawakaz [stem ngawakazi-], KLY/KulY ngawka/ngoka [stem ngawkazi-/ngokazi-], KY ngawakaz [stem ngawakazi-]
- song: KLY naawu (plural nawul), KulY nawu (plural nawulai), KY nawu (plural nawul), KKY na (plural nathai)
- moon, month: KLY kisaayi, poetry mœlpal, KulY/KY kiisay, poetry mœlpal, KKY mœlpal, poetry kiisay
Phonology
Consonants
Kala Lagaw Ya is the only Australian language to have the alveolar fricatives /s/ and /z/. However, these have allophonic variants /tʃ/ and /dʒ/, which are the norm in Australian languages (usually /c/ and /ɟ/ but non-contrasting). These latter two are allophones in that in all environments /s/ and /z/ can appear, while /tʃ/ and /dʒ/ can not appear at the end of a word; note that this allophony is very similar to that of the neighbouring Papuan language Bine. All the stops, except for the alveolars ⟨t⟩ and ⟨d⟩, have fricative allophones, thus ⟨p⟩ can be [p] or [ɸ], ⟨k⟩ can be [k] or [x], ⟨b⟩ [b] or [β], and so on. Furthermore, it is one of the few Australian languages with fully functioning voiced-voiceless distinctions (⟨p/b⟩, ⟨t/d⟩, ⟨s/z⟩, ⟨k/g⟩, ⟨th/dh⟩) — and one of the few without retroflex stops.
The language is also one of the few Australian languages with only one rhotic, one ⟨l⟩ and one ⟨n⟩. The earliest recorded dialect, Kaiwalgau Ya (Kauraraigau Ya [Kowrareg]), however, did have two rhotics, the tap and the glide; the rhotic glide has in general become /j/, /w/ or zero in the other dialects (and Modern Kaiwaligau Ya), rarely /r/. Neighbouring languages retain an /r/ in related words, such as:
- sayima, sayim, sayma 'outrigger' - Kauraraigau Ya sařima, Kiwai (Papua) harima, Gudang (Australia) charima
- babath 'opposite-sex sibling' - Kauraraigau Ya bœřabatha 'opposite-sex sibling', Meriam Mìr berbet 'sibling'
- kupai, KKY kupa 'birth cord' - Kauraraigau Ya kupař, MM kopor
However, in singing, /s/, /z/ and /r/ are pronounced [s], [z], and [ɹ], are virtually never as [tʃ], [dʒ] and [r].
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Palato-alveolar | Velar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m ⟨m⟩ | n̪ ⟨n⟩ | ŋ ⟨ng⟩ | |||
| Obstruent | voiceless | p ⟨p⟩ | t̪ ⟨th⟩ | t ⟨t⟩ | s/tʃ ⟨s⟩ | k ⟨k⟩ |
| voiced | b ⟨b⟩ | d̪ ⟨dh⟩ | d ⟨d⟩ | z/dʒ ⟨z⟩ | ɡ ⟨g⟩ | |
| Sonorant | w ⟨w⟩ | l̪ ⟨l⟩ | r ⟨r⟩ | j ⟨y⟩ | ||
Note:
- The consonant /d/ varies to some extent with /r/, particularly in KKY/KY kadai-/karai-, KLY/KulY kad[a]/kad[a]/kadai/karai 'upwards'.
Vowels
| Unrounded | Rounded | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| short | long | short | long | |
| Close | i ⟨i⟩ | iː ⟨ii⟩ | u ⟨u⟩ | uː ⟨uu⟩ |
| Close-mid | e ⟨e⟩ | eː ⟨ee⟩ | ʊ ⟨ù⟩ | ʊː ⟨ùù⟩ |
| Open-mid | ə ⟨œ⟩ | əː ⟨œœ⟩ | o ⟨o⟩ | oː ⟨oo⟩ |
| Open | a ⟨a⟩ | aː ⟨aa⟩ | ɔ ⟨ò⟩ | ɔː ⟨òò⟩ |
Notes:
- The long vowel ⟨ùù⟩ is only found in Kala Lagaw Ya.
- Length is to a certain extent contrastive, and partly allophonic.
- The +/-round contrast is reminiscent of Papuan phonology.
- The mid long vowels are allophonic variants of the mid short vowels that are in the process of developing phonemic status, while the short vowel ⟨ò⟩ is similarly in origin an allophone of ⟨òò⟩.
Internal reconstruction and comparison with neighbouring languages suggests an underlying four vowel structure with contrasting vowel length, where underlying *i typically gives surface ⟨i⟩ and ⟨e⟩, underlying *a typically gives surface a and œ, underlying *ò typically gives surface ⟨o⟩ and ⟨ù⟩, and underlying *u typically gives surface ⟨ù⟩ and ⟨u⟩ (there are other realisations as well, depending on rules of assimilation etc.):
| Underlying Vowels | -round | +round |
|---|---|---|
| +high | *i,*ii | *u,*uu |
| -high | *a,*aa | *o,*oo |
The language undergoes low-level vowel shifts, caused by stress domination within words and phrases. Long vowels are shortened, and short vowels raise when the word is preceded by morphemes such as adjectives, demonstrative articles, prefixes and the like; the changes also occur within words when these are suffixed:
- laag 'place' — senabi lag 'that place'
- lagal 'places' — sethabi lœgal 'those places' (also sethabi lagal)
- mœrap 'bamboo' — mœrœpil 'bamboo plants/poles/sticks' (also mœrapil)
- guul 'sailing canoe' — senaubi gul 'that canoe'
- thonaral 'times' — sethabi thunaral 'those times' (also sethabi thonaral)
- zageth 'work' — zagithapa 'to/for work [dative]' (also zagethapa) (compound of za 'thing' + geth 'hand')
The processes are low-level in that they are not 'automatic' — the changes do not have to occur and can be consciously 'blocked'. In normal speech, vowel shortening and the change of a to œ normally occur, while the changes of e to i and o to u are sporadic, and most common in unstressed syllables.
Assimilation of vowels to other vowels in the vicinity and consonants is also widespread, particularly of the vowel œ:
- wœrab 'coconut' — wurab — urab
- yœlpai 'lead' [verbal noun] — yilpai — ilpai
- ngœnu 'whose' — ngunu
- kœu 'belonging to here' — kou
- ngœba 'you and I' — ngaba
Kauřařaigau Ya phonology
The following summary of the phonology of Old Kauraregau Ya is compiled from MacGillivray (1852), Brierly (in Moore 1978), Ray and Haddon (1897) and Ray (1907). In general, there does not to appear to have been any great phonological difference between OKY and the modern dialects of Kalau Lagau Ya (apart from the retention of ř).
Stress
Stress appears to have been similar to that of the modern dialects, with stress patterns being most similar to that of modern Bœigu and Ngœrupai speech, the most conservative dialects in this respect. In the following the standardised forms are in bold.
Bisyllabic forms
Stress is initial:
- baba, baba, bapa: baba 'dad'
- kawp: kaapu 'seed'
- buai, bua, bue, booi, boy, boi, booee, boye: buwai 'clan; prow'
A few forms (such as gru: gœrú 'sugar cane') show that contrastive stress existed in bisyllabic words.
Multisyllabic forms
Stress is either on the initial or second syllable:
(1) initial:
- gugure: gagaři 'bow'
- myrabada: ngœiřabatha 'father's sister'
- tukiapalli: tukuyapalai 'same sex sibling pl'
(2) second:
- bobata: bœbàtha 'grandparent'
- murrag: mœřààga 'sweat'
Shifted stress also appears to have occurred as in the modern dialects:
- purteipa: pùrthàipa 'eat' (attainative imperfective present singular / perfective today future)
- pratipa: pùràthipa 'eat' (active imperfective present singular / perfective today future)
Vowels and diphthongs
These appear to have been the same as in the modern language. Vowel length in general appeared in the same environments as in KKY, though some amount of vowel lengthening under the KLY model is evident, as in kawp: kaapu 'seed', Kalau Kawau Ya / Kulkalgau Ya kapu, Kalau Lagau Ya kaapu.
The exact extent of retention of underlying vowel length and the development of variant forms is difficult to measure, as the spelling systems used by Brierly and MacGillivray did not always mark vowel length. Further, as they obtained words through elicitation (which has a common 'lengthening effect' on vowels when words are 'slowed down'), there are a few cases where they marked vowel length wrongly. Ray marked vowel shortness in stressed syllables.
The various sound changes that the vowels and diphthongs undergo in the modern language also occurred in OKY. One change that occurred much more than in the modern dialects was that of ai monophthongisation to e. The resulting e then often raised to i in open unstressed syllables.
No change:
- alai: alai 'husband', amai: amai 'earth oven'
Change:
- buai, bua, bue, booi, boy, boi, booee, boye: buwai, buwe, buwi 'clan, prow'
- palai, pale: palai, pale 'they dual'
- kowraraiga, kowrarega: kauřařaiga ~ kauřařega 'islander'
- kowraraigali, kowraregale, kowrarigali: kauřařaigalai ~ kauřařegale ~ kauřařegali ~ kauřařigali 'islanders'
- wapi, wawpi': waapi 'fish': plural/proprietive wapilai, wapile, wapili
In the modern dialects, these forms are:
- clan, prow: buwai
- they dual: KLY,KulY,S-D palai, B,KY pale
- islander:KLY,KulY,KY-MY kaiwalaig, plural kaiwaligal / kaiwalgal, KKY kawalaig, plural kawalgal
- fish: waapi, plural wapil, KulY wapilai
The change of ai to ei appears to have been very common elsewhere in the dialect:
- adaipa, adeipa: adhaipa 'go/put out' attainative perfective today future
- amaipa, ameipa: amayipa 'crawl' imperfective present
- angaipa, angeipa: angaipa 'carry' perfective today future
- batainga, bateinga: bathainga 'tomorrow'
- baidama, beidama: baidhama 'shark'
One form shows optional i insertion:
gassumu-, gassima-: gasama- ~ gasœma- ~ gasima- 'catch, get', modern dialects gasama- ~ gasœma-
Development of ř
OKY[clarification needed what does this abbreviation stand for?] had one more consonant than modern WCL[clarification needed what does this abbreviation stand for?], transcribed ř. Though the actual pronunciation of this sound and its difference from r was not given by any early writer, it most likely was a rhotic glide [ɹ], perhaps with a palatal 'hue'. The loss of this sound in the other dialects (and in modern KY) occurred in the following rules; the changes were beginning to be evident already in OKY:
Ř between like vowels or in [ə]__V deletes.
- OKY burugo (bùřùga) > modern dialects bùg, KLY bùùga 'marsh fly'
- OKY sřinge, singe > modern dialects singe 'fish/head carrying loop'
- OKY murrag (mœřaaga) > modern dialects maag, KLY maaga 'sweat, film'
- OKY dura (dœřàà) > modern dialects daa 'chest'
Ř sporadically becomes [+hi] when in ə__a and the following syllable is stressed.
- OKY wœřàtha: KY wœyath, KLY wiyeth/wœyeth, KulY uyeth, KKY wath 'year'
- OKY norat (nœřàtha): KY nœyath/nath, KLY niyath, KulY niyath, KKY nath 'platform'
- OKY waraaba (wœřaba): KY uwiba, KLY wiiba, KulY wiiba, KKY waba 'green dove'
- OKY karrabie (kœřaba): KY kab(a) , KLY kab, KulY kœyaba, KKY kab 'paddle, oar'
Ř becomes a [+V] glide when between [-hi] and [+hi] vowels, and between [+bak] and [-bak] vowels.
- OKY mari (maaři): KLY maayi, KKY maay 'pearl shell'
- OKY sarima (sařima): KLY sayim(a), KKY sayima/sayma 'outrigger float'
- OKY puri, prui (puuři, pœřuui): KLY puuyi, KKY puuy 'tree, plant, magic'
- OKY mekari (mekaři): KLY mekey, KKY mekay 'almond'
- OKY tituri (thithuři): KLY thithúúyi, KKY thithuy 'star'
- OKY Giralaga (Giřalaga): KLY Giyalaaga, KKY Giyalag 'Friday Island'
- OKY Mora (Muřa~Mořa): KLY Muwa, KKY Muwa~Mowa
Vuř becomes /w/ when intervocalic.
- OKY Maurari (Mauřaři): modern dialects Maway(i) 'Wednesday Island'
- OKY tura (thuřa~thœuřa): modern dialects thœwa ~ thuwa 'shortness'
Ř optionally becomes /i/ when syllable final and following [-hi] vowels; in at least two words metathesis first occurred.
- OKY kopar (kùpařa): KY,KLY,KulY kùpai, KKY kùpa 'umbilical cord'
- OKY kaura (kauřa): KKY kawa, KY > *kařua > kawa~kaiwa, KLY,KulY kaiwa 'island'
- OKY wauri (wauři): KKY wawi, KY,KLY,KulY > *wařua > waiwi 'arm-band shell'
Ř deletes when syllable final following high vowels and non-final.
- OKY burkera (buřkera): KY bùker 'hot coal'
Ř disappears when followed by unstressed i and more than one syllable.
- OKY ngörimuni (ngœřimùni): KKY,KY ngœimùn, KLY,KulY ngœlmùn 'our EXC PL'
- OKY myrabat (ngœiřabatha): modern dialects ngœibath 'fathers sister'
- OKY görigar, göriga (gœřigař[i]): modern dialects gœiga 'sun, day'
- OKY kariki (kařiki): modern dialects kaiki 'here non-specific locative'
- OKY tyariki (seřiki): modern dialects seiki 'there non-specific locative'
Early spellings (e.g. möaga [məaga] 'sweat' and neet/naat/nöat/niet [nejat], [nat], [nəat], [nijet] 'platform' show that ř disappeared first, leaving a hiatus (except in those cases where ř > y~i), with reduction of [V1-V1] and [ə-V1] to [V1], and [ə-VV] to [VV].
OKY underwent the same allophony and sound changes as the modern dialects, though z ~ dh and s ~ th variation appears to have been more general in OKY, as in the following (perhaps evidence of older allophony in the language which is now levelling out):
- zaazi 'grass skirt': Brierly juagee, djaajie, djaajie, dadjee, dadji, dadje, dadjie, MacGillivray daje, OKY zaazi, dhaazi
- sagul adhamadha ~ azamadha 'be putting put on a dance!': Brierly sagool adzamada, OKY sagul adhamadha ~ azamadha
- wœsul 'dirty water': Brierly ootzoo, oodthool, OKY uusul, uuthul
- ngœzu 'my fem': Brierly udthu, oldzoo, udzoo, MacGillivray udzu, udz, OKY ngœzu, ngœdhu
An instance of optional r deletion before s is also attested in the following example, unless the first i in myaichipp is a misprint or misreading of *myarchipp:
maayi-arsipa 'wail, keen, weep': Brierly myaichipp, MacGillivray maierchipa, OKY mayarsipa, mayasipa
Various forms in OKY showed metathesis of ř and r in the environment of u, i and au:
- ngauřakai ~ ngauřakazi > naroka, nerawkaji 'maiden' (unmarried girl), cf. KKY ngawakaz
- gœřiga ~ gœřigař > gyrriegi, gurrigi, goraigor 'day, sun', cf. KKY gœiga
- puuři > uperia, oopeere, ooperie, uperi, prui, upiri 'magic gear/charms/produce', cf. KKY puuy, KLY puuyi.
- rigaboo, rugabu (rugœbaw) > modern dialects wœrugœbaw, urugœbaw, Bœigu wœrigœbaw, urigœbaw 'sweet potato', lit. wœru-gabaw 'cord/string-cultivated yam'
Syllabification
Syllabification occurred as in the modern dialects, with the addition of ř also attested as a syllable final consonant. One word was recorded by Brierly and MacGillivray with a [+nas][-son] cluster, namely enti 'spider', however this appears to be a confusion; enti is probably Gudang (Australia) ant[h]i 'sore'.
Syllables were vowel final or end in r, ř, l, glide i or glide u. Otherwise surface syllable final consonants have an underlying following vowel, in which case all consonants could be syllable initial.
Orthography
There is no strict standard spelling, and three slightly different orthographies (and often mixes of them) are in use.
Mission Spelling
The Mission Spelling (established at first by Loyalty Islands missionaries in the 1870s, then modified by Polynesian missionaries in the 1880s): a, b, d, e, g, i, j, k, l, m, n, ng, o, ö, p, r, s, t, u, z, sometimes also th, dh, dth, tr, dr, oe, ë, w, y, j, and sometimes double vowels to show length. This spelling system was based on that used for the Drehu (Lifu) language, though later with the change to Polynesian mission staff, as well as the growing number of indigenous Torres Strait missionaries, the overtly Drehu forms tr, dr and ë were lost; these had no phonological basis in Kalaw Lagaw Ya. The mission system is used in the Reports of the Cambridge Expedition to the Torres Strait (Haddon et al., 1898 and on, University of Cambridge) and in Myths and Legends of Torres Strait (Lawrie, University of Queensland, 1971). Ray, the linguist of the Cambridge Expedition, also used various diacritics to represent short vowels and vowel quality.
Klokheid and Bani
Established in the 1970s: a, aa, b, d (alveolar), dh (dental), e, ee, g, i, ii, k, l, m, n, ng, o, oo,oe (/ə/), ooe (/əː/), p, r, s, t (alveolar), th (dental), u, uu, w, y, z
Saibai, Boigu, Dauan students
Established in the late 1970s: a, b, d (alveolar), dh (dental), e, g, i, k, l, m, n, ng, o, oe (/ə/), p, r, s, t (alveolar), th (dental), u, w, y, z (vowel length, though it exists, is rarely represented).
People not only use these three slightly differing spelling systems, but also write words more or less as they pronounce them. Words are therefore often spelt in various ways, for example sena/sina 'that, there', kothai/kothay/kothei/kothey/kothe 'back of head, occiput'. Such variation depends on age, family, island, village and other factors such as poetic speech. It can be difficult at times to decide which is most correct — different people have different opinions (and sometimes have very strong opinions).
In general the pronunciation of older people has priority; however, some people can actually get quite offended if they think the language is written the 'wrong' way. Some insist that the mission spelling should be used, others the Bani spelling, and still others the KKY (Saibai etc.) spelling, and still again others use mixes of two or three, or adaptations thereof. Some writers of the Mabuiag-Badhu dialect (Kalaw Lagaw Ya), for example, write mainly in the Mission system, sometimes use the digraphs oe, th, dh (variant dth) and sometimes use capital letters at the ends of words to show devoiced vowels, such as ngukI 'fresh water/drinking water, fruit juice' /ŋʊːki̥/. In the Bani/Klokheid orthograophy nguki is written nguuki, and in the other dialects the final vowel is either fully voiced, nguki /ŋʊki/), or elided, nguk /ŋʊk/).
The biggest bone of contention between the advocates of the 'modern' orthographies and the 'traditionalist' orthographies is the use of w and y to show the semi-vowels. In general native speakers in literacy classes seem to find y and w very difficult to learn, and that u and i are the 'logical' letters to use. Syllabification of words by untrained speakers suggests that u and i are really the underlying sounds. Thus, a word like dhaudhai/dhawdhay 'mainland, continent' syllabifies as dha-u-dha-i, not dhau-dhai. In songs, the glide-u/i can also be given full syllable status. Historical considerations also point to the semi-vowels often being vocalic rather than consonantal. Thus, lagau, the genitive of laag[a] 'place' is in underlying form <laaga+ngu>; the full form of the genitive ending -ngu is only retained where the nominal has a monosyllabic stem (see the section on Nominal Morphology). Similarly, verbal nouns end in -i, e.g. lumai, stem luuma- 'search, look for, seek, hunt'. The mid-19th century to early 20th century records of Kauaraigau Ya show that the verbal noun ending was previously -ri (thus lumari), where the -r- was presumably the rhotic glide rather than the rhotic tap/trill.
A dictionary now in preparation (Mitchell/Ober) uses an orthography based on detailed study of the surface and underlying phonology of the language, as well as on observation of how people write in real life situations. It is a mix of the Mission and Kalau Kawau Ya orthographies with the addition of diacritics (the letters in brackets) to aid correct pronunciation, since many of the people who will use this dictionary will not be speakers of the language:
a (á), b, d, dh, e (é), g, i (í), k, l, m, n, ng, o (ó, ò, òò), œ (œ'), r, s, t, th, u (ú, ù), w, y, z
Within this orthography, w and y are treated as consonants — this is their phonological status in the language — while u and i are used as the glides where phonological considerations show that the 'diphthong' combination has vocalic status.
The typewritten forms of œ and œœ are oe and ooe.
Pronunciation of the letters
The English pronunciations given in the list below are those of Australian English, and are only meant as a guide. The letters in square brackets ([]) are the IPA.
- a (short) [a]: 'u' as in 'hut' — gath 'shallow, shallows', mathaman 'hit, kill'
- a, á (long) (aa in the Bani orth.) [aː] 'a' as in father — áth 'bottom turtle shell' ('plastron'), ma 'spider', lág, laaga 'place'
- b [b] as in English — Báb 'Dad', bibir 'power, authority'
- d [d] as in English — da 'chest', idi 'oil, grease, fat, dead-calm sea'
- dh [d̪] similar to d, but with the tip of the tongue put against the top teeth- dha 'ladder, stairs', adhal 'outside', Bádhu 'Badu'
- e (short) [e] 'e' as in bed — bero 'rib, side of boat, river bank, etc.', nge 'then', tete 'animal/bird leg'
- e, é (long) (ee in the Bani orth.) [eː] 'are' as in bared — gér 'sea snake', dhe 'slime', sei 'there'
- g [ɡ] as in English get, never as in general — gigi 'thunder', gugu 'owl'
- i (short) [i] short 'ee' as in feet — midh 'how', sisi 'gecko', ipi 'wife'
- i, í (long) (ii in the Bani orth.) [iː] 'ee' as in feed — síb 'liver, centre', gi 'knife', ígil 'life'
- k [k] as in English — kikiman 'hurry up', kakayam 'bird-of-paradise
- l [l] similar to English 'l' in lean, but with the tip of the tongue against the top teeth; never as in English kneel — lág 'place, home', li 'basket', gúl 'double-outrigger sailing canoe'
- m [m] as in English — mám 'love, affection', Ama 'Mum, Aunty', ma 'spider'
- n [n] similar to English 'n' in nun, but with the tip of the tongue against the top teeth — naawu, KKY na 'song', nan 'her, it', nanu 'her(s), its'
- ng [ŋ] as in English sing; never as in English finger — ngai 'I, me', ngœrang 'armpit'
- o (short) [o] more or less 'o' as is in got, though more rounded — sob 'slowness', mogai, Bœigu moga, Saibai-Dœwan mogo 'blank skink'
- o (long) (oo in the Bani orth.) [oː] more or less 'o' as in god, though more rounded — gor 'tie-hole', so 'show'
- ò (short) [ɔ] short version of 'oa' in broad — mòdhabil 'costs, prices', gòyal 'bald'
- ò (long) (oo in the Bani orth.) [ɔː] 'oa' in broad — mòs 'lung, spittle', gòy 'baldness'
- œ (short) [ə] 'a' as in about — bœtœm 'lean (animals)', bœga 'mallard'
- œ (long) (ooe in the Bani orth.) [əː] more or less like 'er' in herd — wœr 'water', Wœy 'Venus', bœi 'coming'
- p [p] as in English — papi 'noose, trap', áp 'garden', KKY Pòpu 'Grandad'
- r [r] similar to 'tt' in better when said fast (that is to say, when said as bedder). Before another consonant and at the end of a word, it is often trilled (like in 'stage' Scottish English or 'rr' in Spanish). In singing, however, it is normally pronounced much like the American English 'r' — ári 'rain, louse', rùg 'rag, piece of cloth', ár 'dawn'
- s [s] most commonly like English 's' in sister; sometimes like English 'ch' in chew when at the beginning of a word or in the middle of a word; never like 's' in 'as' (which is a 'z' sound) — sas 'style, showing off', sisi 'gecko', sagul 'game, fun, dance'
- t [t] as in English — tádu 'sand-crab', tídan 'return, understand', ít 'rock oyster'
- th [t̪] similar to t, but with the tip of the tongue put against the top teeth — tha 'crocodile tail', thathi 'father', geth 'hand'
- u (short) [u] short 'u' as in lute — buthu 'sand', gulai, KLY gulal 'sailing canoes'
- u, ú (long) (uu in the Bani orth.) [uː] 'oo' in woo — búzar 'fat, blubber', thu 'smoke'
- ù [ʊ] 'u' as in put — mùdh 'shelter, haven, back-yard, camp', kùt 'late afternoon, early evening', kùlai 'first, before'
- w [w] not as strong as English 'w' in we ; for most speakers of the language the only difference between w and short u is that w is shorter — wa 'yes', kawa 'island', báw 'wave'
- y [j] not as strong as English 'y' in yes; for most speakers of the language the only difference between y and short i is that y is much shorter — ya 'speech, talk, language', aye, KKY aya 'come!', máy 'well, spring; tears; pearl-shell, nacre'
- z [z] most commonly like English 'z' in zoo, or English 's' in has; sometimes like English 'j' in jump, or 'dg' in budge when at the beginning or in the middle of a word — zázi 'grass skirt', za 'thing, object', zizi 'crackle, crack, rustling noise'
Combinations of vowels ('diphthongs', such as ai, au, œi, eu etc.) are pronounced as written. Thus, for example, ai is a-i (basically very similar to 'i' in 'mine' with a posh accent). In singing and sometimes in slow speech, such vowel combinations can be said separately. In the Bani and Saibai (etc.) orthographies, the last elements can be written as y and w instead of i and u. The diphthongs are:
- ei/ey — sei, sey 'there'
- iu/iw — biuni, biwni 'kookoobuura, kingfisher'
- œi/œy — bœi, bœy 'coconut frond'
- eu/ew — seu, sew 'belonging to there'
- ai/ay — Saibai, Saybay 'Saibai'
- œu/œw — kœubu, kœwbu 'battle, war'
- òi/oy — òi, oy 'hoy!, hey!' (reply to a call, vocative particle)
- au/aw — kaub, kawb 'tiredness'
- ui/uy — mui, muy 'fire'
- ou/ow — berou, berow 'of a/the rib'
Grammar
Nominal morphology
Where the morphology is concerned, the language is somewhere along the continuum between agglutinative and fusional. Nominals have the following cases: nominative, accusative, instrumental (subsumes ergative), dative (subsumes allative, purposive), ablative (subsumes elative, avoidative), specific locative, nonspecific locative (subsumes perlative and comitative) and global locative. Nominals also have the following derived forms: privative, similative, resultative and proprietive, which also forms the noun nominative-accusative plural. All stems end in a vowel or a semi-vowel, except for a few monosyllables ending in -r and -l (which includes the very few reduplicated words, like tharthar 'boiling, seething', as well as ngipel 'you dual' [a compound of ngi 'you singular' and -pal 'two']). For many nouns the surface nominative(-accusative) undergoes a final stem-vowel deletion rule; in the Kalaw Lagaw Ya dialect the rule results in final devoiced vowels accompanied by main vowel lengthening. There are three numbers, singular, dual and plural. Singular and dual are the same form in all nominals except the personal pronouns. Furthermore, the plural is only distinguished in the nominative-accusative — except for the personal pronouns, where the difference in number is shown by the stem.
There are two nominal classes, Common Nominals (common nouns, demonstratives, locative/temporal/etc. adverbs) and Proper Nominals (Proper names [personal names, boat names, emotive kinship terms], pronouns). The major difference between the two classes are 1) semantic — Proper nominals have pronominal characteristics, and, 2) declensional, for example Proper Nominals have one locative case rather than the three of Common Nominals.
Common nominal declensions
Note that the following are in the Kalau Kawau Ya dialect.
| Case/Suffix | Hoe/Adze | Place/Home | Knife | Water | Mud | Middle | looking | giving, getting, being, moving, doing, etc. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stem type | multisyllabic -u final |
multisyllabic | monosyllabic vowel final |
monosyllabic -r/-l final |
monosyllabic -i glide final |
locative nominal (adverb) |
multisyllabic verbal noun |
monosyllabic verbal noun | |
| stem | pábu- | lága- | gi- | wœr- | sái- | dhadha- | naga+i- | má+i- | |
| NOM-ACC | SG-DU | pábu | lág | gi | wœr | sái | dhadh[a] | nœgai | mái |
| PL | pabul | lagal | gilai | wœrai | saithai | dhadhal[a] | — | — | |
| INST | pabun | lagan | ginu/gín | wœrnu/wœran | saithu | dhadhan | nœgain | main | |
| GEN | pabu | lagau | gingu | wœrngu | saingu | dhadhau | nœgai | mai (maingu) | |
| DAT | pabupa | lagapa | gipa | wœrpa | saipa | dhadhapa | nœgaipa | maipa | |
| ABL | pabungu | lagangu | gingu | wœrngu | saingu | dhadhaz | nœgaile | maithaile | |
| LOC | SP | pabunu, pabu' | laganu, laga' | gilai, ginu | wœrai, wœrnu | saithai, saithe | dhadhal, dhadha' | nœgainu | mainu |
| N-SP | pabuya | lagaya | giya | wœriya | saiya | dhadhaya | nœgaiya | maiya | |
| GL | pabuyab | lagayab | gipu | wœrab, wœrpu | saiyab, saipu | dhadhayab | nœgaiya | maiya | |
| PROP | pabul(ai) | lagal(ai) | gilai | wœrai | saithai, saithe |
dhadhal(ai)[a] | nœgail(ai) | maithai | |
| PRIV | pabugi | lagagi | gigi | wœrgi | saigi | dhadhagi[a] | nœgaigi | maigi | |
| SIM | pabudh(a) | lagadh(a) | gidha | wœrdha/wœradh | saidh(a) | dhadhadh(a) [a] |
nœgaidh(a) | maidh(a) | |
| RES | pabuzi | lagazi | gizi | wœrzi | saizi | dhadhazi[a] | nœgaizi | maizi | |
Irregular nouns
There are few irregular nouns, the most common being:
- ai 'food', ya 'speech, language, message, etc.', li 'basket', lu 'mound, bump, hump' (instrumental aidu, yadu, lidu, ludu; specific locative/proprietive-plural aidai/aide, yadai, lidai, ludai)
- KKY na, KLY naawu, KulY/KY nawu 'song'; KKY yu 'drying rack, cooking rack' (other dialects nuuwa, nu); specific locative/proprietive-plural KKY nathai, KLY/KY nawul, KulY nawlai; KKY yuthai (other dialects nuwanu, nuwa; nuwal, KulY nuwalai))
- za 'thing, object, matter, etc.' This word has a fuller stem form, zapu-, which appears in certain forms: instrumental zapun; genitive zapu; proprietive-plural zapul. In the locative forms both stems (za- and zapu-) appear: specific locative zanu, zapunu, etc.
- gœiga 'sun, day'; bireg/bereg 'shelf'. The stems of these words have different forms to the nominative-accusative: gœiga — stem: gœigœyi-, gœigi-; bireg/bereg — stem: bœreigi-, biregi-
- dœgam, KLK dœgaamu 'side, direction, point of compass, aspect'. This word has two stem forms, in free variation: dœgamu-, daguma-
Demonstratives
The language has a closed class of demonstrative morphemes with special morphological characteristics:
- Prefixes
- pi-, pe- 'there in the distance in a specific position'
- kai- 'there in the distance in a non-specific position'
- Stems
- ka-, kawu-/kawa- (non-specific), í- (specific) 'here, this'
- se-, si-, sewu-/sewa- 'there, that (not too far away)'
- -gu, KKY -gui, -mulu (KKY -ngùl in combined forms) 'down there'
- -ka, -karai/-kadai 'up there' (variant forms of the one underlying stem)
- -ngapa 'there beyond', 'there on the other side'
- -pai, -pa, -paipa 'ahead there, up close there' (variant forms of the one underlying stem -pai), MY -kupai, KY also -kudhai
- -pun[i], -puwa 'off from there, back from there, back over there, back there' (possibly variant forms of the one underlying stem)
The Kauřařaigau Ya forms recorded are the same as in the modern dialects, with the exception of ka-/kařu- 'non-specific here, this', se-/si-/seřu- 'there, that', kařa- 'non-specific yonder', modern dialects kai-, %ka- and -puwai 'ahead there', modern dialects -pai/-pa.
These demonstratives can take masculine, feminine and non-singular morphology (as such are pronominal) as well as case forms. Í- 'here, this' and se/si- 'there, that (not too far away)' take the gender/number morphemes as suffixes, and the other demonstratives take them as prefixes. Note that ka- 'non-specifically here' and kai- 'there in the distance in a non-specific position' cannot appear with the gender/number morphemes, these latter being specific. Í- and se/si- also take an article forming affix -bi to become demonstrative articles (e.g. KLY senuubi kaazi, KKY senaubi kaz 'that boy', KLY senaabi kaazi, KKY senabi kaz 'that girl', KLY sepalab kaazi, KKY sepalbi kaz 'those two children', sethabi kœzil 'those children'); kedha 'like this/that, thus' can also take this suffix (e.g. kedhabi puy 'such a tree').
| Case/Suffix | here | there | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| non-specific | specific | non-specific | specific | |||
| NOM-ACC | MASC | kai | in | sei, sí |
senau | |
| FEM | ina | sena/sina | ||||
| DU | ipal | sepal/sipal | ||||
| PL | itha | setha/sitha | ||||
| INST | kedha | — | kedha | — | ||
| GEN | kœu, kœwau | — | seu, sewau | — | ||
| DAT | kœpa, kœwupa | — | sepa/sipa, sewupa | — | ||
| ABL | kœzi, kœwuzi | — | seizi/sizi, sewuzi | — | ||
| LOC | SP | MASC | kai, kœwa | in | sei, sí, sewa |
senau |
| FEM | ina | sena/sina | ||||
| DU | ipal | sepal/sipal | ||||
| PL | itha | setha/sitha | ||||
| N-SP | MASC | kaiki, kawuki/kœwuki | inuki | seiki/siki, sewuki | senauki | |
| FEM | inaki | senaki/sinaki | ||||
| DU | ipalki | sepalki/sipalki | ||||
| PL | ithaki | sethaki/sithaki | ||||
| SIM/GL | kedha | kedha | kedha | kedha | ||
| article | MASC | (simulative article) kedhabi |
inubi | (simulative article) kedhabi |
senaubi | |
| FEM | inabi | senabi/sinabi | ||||
| DU | ipalbi | sepalbi/sipalbi | ||||
| PL | ithabi | sethabi/sithabi | ||||
| Case/Suffix | gui | ka(rai) | ngapa | pai/pa | pun/pawa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOM-ACC-INST-LOC | SP[a] | MASC | (pi)nugui | (pi)nuka | (pi)nungap | (pi)nupai | (pi)nupun |
| FEM | (pi)nagui | (pi)naka | (pi)nangap | (pi)napai | (pi)napun | ||
| DU | (pi)palgui | (pi)palka | (pi)palngap | (pi)palpai | (pi)palpun | ||
| PL | (pi)thagui | (pi)thaka | (pi)thangap | (pi)thapai | (pi)thapun | ||
| N-SP | kaigui | kaika | kaingap | kaipai/kaipaipa | kaipun, kaipawapa | ||
| DAT | SP[a] | MASC | (pi)numulupa | (pi)nukaripa | (pi)nungapapa | (pi)nupaipa | (pi)nupawapa |
| FEM | (pi)namulupa | (pi)nakaripa | (pi)nangapapa | (pi)napaipa | (pi)napawapa | ||
| DU | (pi)palmulupa | (pi)palkaripa | (pi)palngapapa | (pi)palpaipa | (pi)palpawapa | ||
| PL | (pi)thamulupa | (pi)thakaripa | (pi)thangapapa | (pi)thapaipa | (pi)thapawapa | ||
| N-SP | mulupa | karaipa/kadaipa | kaingapapa | (kai)paipa | (kai)pawapa | ||
| ABL | kizigui | kizika | kizingap | kizipai | kizipun | ||
| N-SP-LOC/GL-LOC neutral[a] | MASC | (pi)nuguiki | (pi)nukaki | (pi)nungapaki | (pi)nupaiki/(pi)nupaipa | (pi)nupuniki/(pi)nupawapa | |
| FEM | (pi)naguiki | (pi)nakaki | (pi)nangapaki | (pi)napaiki/(pi)napaipa | (pi)napuniki/(pi)napawapa | ||
| DU | (pi)palguiki | (pi)palkaki | (pi)palngapaki | (pi)palpaiki/(pi)palpaipa | (pi)palpuniki/(pi)palawapa | ||
| PL | (pi)thaguiki | (pi)thakaki | (pi)thangapaki | (pi)thapaiki/(pi)thapaipa | (pi)thapuniki/(pi)thapawapa | ||
| N-SP/GL-LOC | kaiguiki | kaikaki | kaingapaki | kaipaiki/kaipaipa | kaipunki, kaipawapa | ||
Pronouns
The personal pronouns are three-way nominative-ergative-accusative in declension. Note that the third person pronouns are also used as definite articles, e.g. Nuidh garkœzin nan yipkaz imadhin 'The man saw the woman'.
| Case/Suffix | I/me | you | he/it (the) |
she/it (the) |
who | what | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOM | ngai | ngi | nui | na | nga | mi- (miai, miza) | |
| ACC | ngœna | ngin | nuin | nan | ngan | mi- (miai, miza); min | |
| INST | ngath | ngidh | nuidh | nadh | ngadh | midh (miaidu/miden/midu/midun, mizœpun) | |
| GEN | MASC | ngau | nginu | nungu | nanu | ngœnu | mingu (miaingu, mizœngu) |
| FEM | ngœzu | ||||||
| DAT | ngayapa | ngibepa | nubepa | nabepa | ngabepa | mipa (miaipa, mizœpa) | |
| ABL | MASC | ngaungu(z) | nginungu(z) | nungungu(z) | nanungu(z) | ngœnungu(z) | mingu(zi) (miaingu, mizœngu) |
| FEM | ngœzungu(z) | ||||||
| LOC | SP | ngaibiya | ngibiya | nubiya | nabiya | ngabiya | miaide/miainu, mizœpunu |
| N-SP | ngaibiya | ngibiya | nubiya | nabiya | ngabiya | miaiya, mizœpuya | |
| GL | ngaibiya | ngibiya | nubiya | nabiya | ngabiya | miaiyab, mizœpuyab | |
| proprietive/plural | — | — | — | — | — | midel, mizœpul | |
| PRIV | MASC | ngaugi | nginugi | nungugi | nanugi | ngœnugi | miaigi, mizœgi |
| FEM | ngœzugi | ||||||
| SIM | MASC | ngaudh | nginudh | nungudh | nanudh | ngœnudh | midh (miaidh, mizœpudh) |
| FEM | ngœzudh | ||||||
| RES | — | — | — | — | — | miaizi, mizœzi | |
Dual pronouns
The dual and plural pronouns are nominative-accusative, the accusative being the same in form as the genitive, except in KKY, where the accusative is unmarked.
| Case/Suffix | we dual | you and I | you dual | them dual (the dual) |
who dual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOM-ACC-INST | ngalbe | ngœba | ngipel | palai (Boigu pale) |
ngawal |
| GEN | ngalben | ngœban | ngipen | palamun (Boigu palemun) |
(as for singular) |
| DAT | ngalbelpa | ngœbalpa | ngipelpa | palamulpa (Boigu palemulpa) |
(as for singular) |
| ABL | ngalbelngu | ngœbalngu | ngipelngu | palamulngu (Boigu palemulngu) |
(as for singular) |
| LOC | ngalbeniya | ngœbaniya | ngipeniya | palamuniya (Boigu palemuniya) |
(as for singular) |
| SIM | ngalbedh | ngœbadh | ngipedh | palamudh (Boigu palemudh) |
(as for singular) |
Ngawal 'who dual' is constructed from nga 'who' plus the clitic -wal 'both (dual conjunction)'.
Plural pronouns
| Case/Suffix | we (exclusive) | we (inclusive) | you | they (the) |
who |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOM-ACC-INST | ngœi | ngalpa | ngitha | thana | ngaya |
| GEN | ngœimun | ngalpan | ngithamun | thanamun | (as for singular) |
| DAT | ngœimulpa | ngalpalpa | ngithamulpa | thanamulpa | (as for singular) |
| ABL | ngœimulngu | ngalpalngu | ngithamulngu | thanamulngu | (as for singular) |
| LOC | ngœimuniya | ngalpaniya | ngithamuniya | thanamuniya | (as for singular) |
| SIM | ngœimudh | ngalpadh | ngithamudh | thanamudh | (as for singular) |
Ngaya 'who many' is constructed from nga 'who' plus the clitic -ya 'and others (plural conjunction)'.
Personal names and familiar kinship terms
Familiar kinship terms are the equivalent of English kin terms such as Dad and Mum, while non-familiar terms are the equivalent of Father and Mother; these latter are treated as common nouns in the language.
| Case/Suffix | Tom (mas.) | Anai (fem.) | Dad/Uncle (cf. father/uncle) |
Mum/Aunty (cf. mother/aunt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nom-inst | Tom | Anai | Báb (thathi) |
Ama (ápu) |
| acc-gen | Toman | Anaina | Baban (thathiu) |
Amana (apuwau) |
| dat | Tomalpa | Anailpa | Babalpa (thathipa) |
Amalpa (apuwapa) |
| abl | Tomalngu | Anailngu | Babalngu (thathingu) |
Amalngu (apuwangu) |
| loc | Tomaniya | Anainiya | Babaniya (thathiya) |
Amaniya (apuwaya) |
| proprietive/plural | — | — | babal (thathil) |
amal (apuwal) |
| priv | — | — | babagi (thathigi) |
amagi (apuwagi) |
| sim | Tomadh | Anaidh | babadh (thathidh) |
amadh (apuwadh) |
| res | — | — | babazi (thathizi) |
amazi (apuwazi) |
Kauřařaigau Ya nominal morphology
The earliest grammatical records of the language are those of the mid-1800s Kauřařaigau Ya dialect. This dialect is identical to the modern dialects, apart from having more archaic forms of some endings and suffixes as well as stem forms.
Nominal suffixes and endings
- Common Nominals
- Nominative-Accusative: unmarked
- Ergative-Instrumental: -n,-na,-nu,-Cu; demonstratives unmarked
- Genitive: monosyllable stems: -ngu, multisyllables -u
- Dative-Allative: -pa ~ -pari
- Ablative-Causative: nouns, pronouns -nguzi, verbal nouns -lai, adverbs/demonstratives -zi
- Specific Locative: monosyllabic stem nouns -lai~-dai~-thai~-ai~-řai~-rai, multisyllabic stem nouns -nulai~-nule~-nuli~-nul, adverbs -lai~-l(a) , demonstratives -ři
- Non-Specific Locative: -ya, adverbs/demonstratives -ki~-kidha
- Proprietive/Plural: monosyllabic stem nouns -lai~-dai~-thai~-ai~-řai~-rai, multisyllabic stem nouns, adverbs -lai (>-le~-li), -rai (> -re~-ri), -řai (> -ře~-ři)
- Privative: -gi
- Imitative-Similative: -dha
- Resultative: -zi
- Proper Nominals
No early writer recorded declined feminine forms, apart from the genitive. Ray (1907:20-21) implies (by default) that the OKY paradigm is basically the same as that of OKLY.
- Nominative-Ergative-Instrumental: unmarked
- Accusative-Genitive: masculine -ni, feminine -na-, dual-plural pronoun -ni~-mùni
- Dative-Allative: masculine -nipa[ri] , feminine ?-napa[ri], dual-plural pronoun -nipa[ri]~-mùnipa(ri)
- Ablative-Causative: masculine -ninguzi ~-nunguzi, feminine ?-nanguzi, dual-plural pronoun -ninguzi~-nunguzi~-mùninguzi~-mùnunguzi
- Locative: masculine -niya, feminine ? -naya, dual-plural pronoun -niya~-mùniya
- Imitative-Similative: -dha, dual-plural pronoun -dha~-mùdha
Kauřařaigau Ya pronouns
Brierly (B), MacGillivray (M) and Ray (R) recorded the following forms of the singular pronouns of OKY:
- Nominative
- 1st — Brierly gni, ngi; Macgillivray ngai; Ray ngai
- 2nd — Macgillivray ngi; Ray ngi
- 3rd masculine — Macgillivray nue; Ray nui
- 3rd feminine — Macgillivray na, nga; Ray na
- 'who' — Brierly gua; Macgillivray nga; Ray nga
- 'what' — Macgillivray []mi; Ray mi-
- Accusative
- 1st — Brierly ana; Macgillivray ana; Ray ngana
- 2nd — Brierly gin; MacGillivray ngi; Ray nginö, ngin
- 3rd masculine — Brierly nooano; MacGillivray nudu; Ray nuinö, nuin
- 3rd feminine — Ray nanö, nan
- 'who' — Ray nganö, ngan
- 'what' — not recorded
- Instrumental-Ergative
- 1st — Brierly nath, nut; Macgillivray ngatu; Ray ngata, ngatö, ngat
- 2nd — Brierly needtha, needthoo; Macgillivray ngidu; Ray ngida, ngidö, ngid
- 3rd masculine — Brierly nooide ; MacGillivray nudu; Ray nuida, nuidö, nuid
- 3rd feminine — Macgillivray nadu; Ray nada, nadö, nad
- 'who' — Macgillivray ngadu; Ray ngada, ngadö, ngad
- 'what' — Brierly meedan; Macgillivray mida; Ray mida, midö, mid
- Genitive
- 1st — Brierly ngau, gnau, ngow masculine, udthu, oldzoo, udzoo feminine; Macgillivray ngow masculine, udzu, udz feminine; Ray ngau masculine, ngazu, nguzu feminine
- 2nd — Brierly gnee, ye noo, yeenow, niu, yenoo, meeno; MacGillivray yinu; Ray nginu
- 3rd masculine — Brierly noonoo; Ray nungu
- 3rd feminine — Macgillivray nanue; Ray nanu
- 'who' — Ray ngunu
- 'what' — not recorded
Based on the above forms and the modern dialects, the OKY pronouns are reconstructed as follows:
| pronoun | Nominative | Accusative | Ergative- Instrumental |
Genitive | Dative | Ablative | Locative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | MASC | ngayi | ngœna | ngathu | ngau | ngaikika | ngaunguzi | ngaikiya |
| FEM | ngœzu | ngœzunguzi | ||||||
| 2nd | ngi | ngina | ngidhu | nginu | ngibepa[ri] | nginunguzi | ngibiya | |
| 3rd | MASC | nui | nuina | nuidhu | nungu | nubepa[ri] | nungunguzi | nubiya |
| FEM | na | nana | nadhu | nanu | nabepa[ri] | nanunguzi | nabiya | |
| 'who' | nga | ngana | ngadhu | ngœnu | ngabepa[ri] | ngœnunguzi | ngabiya | |
| 'what' | miyai | miyai | midhu | mingu | mipa[ri] | minguzi | mizapuya | |
The accusatives, the ablatives and imitatives underwent optional final vowel deletion, while the ergatives optionally transformed the final u to a or œ, or deleted it, thus ngathu > ngatha > ngathœ > ngath.
The recorded dual-plural forms are:
- Nominative-Ergative-Instrumental
- 1st Dual Exclusive — MacGillivray albei; Ray ngalbai
- 1st Dual Inclusive — MacGillivray aba; Ray ngaba
- 2nd Dual — MacGillivray ngipel; Ray ngipel
- 3rd Dual — MacGillivray pale; Ray palai
- 'who' Dual — Ray nga wal
- 1st Plural Exclusive — Brierly ari, churri; MacGillivray arri, uri; Ray ngöi
- 1st Plural Inclusive — Brierly alpa; MacGillivray alpa; Ray ngalpa
- 2nd Plural — MacGillivray ngi-tana; Ray ngita
- 3rd Plural — MacGillivray tana; Ray tana
- Accusative-Genitive
- 1st Dual Exclusive — Brierly abonnie, abuni, abani, aboni; MacGillivray N/A; Ray ngalbaini
- 1st Dual Inclusive — Brierly N/A; MacGillivray abane, abeine; Ray ngabani
- 2nd Dual — Brierly N/A; MacGillivray ngipeine; Ray ngipeni
- 3rd Dual — Brierly N/A; MacGillivray palaman; Ray palamuni
- 1st Plural Exclusive — Brierly areen; MacGillivray arrien; Ray ngöimunu
- 1st Plural Inclusive — Ray ngalpanu
- 2nd Plural — MacGillivray ngitanaman; Ray ngitamunu
- 3rd Plural — MacGillivray tanaman; Ray tanamunu
- Dative
- 1st Dual Exclusive: MacGillivray albi nipa; Ray ngalbainipa
- 1st Dual Inclusive: MacGillivray albynape; Ray ngabanipa
- 2nd Dual: Ray ngipenipa
- 3rd Dual: MacGillivray pale nipa; Ray palamunipa
- 1st Plural Exclusive: MacGillivray arri nipa; Ray ngöinipa, ngöimunipa
- 1st Plural Inclusive: Ray ngalpanipa, ngalpamunipa
- 2nd Plural: Ray ngitanipa, ngitamunipa
- 3rd Plural: MacGillivray tane nipa; Ray tananipa, tanamunipa
- Ablative
- recorded by Ray as -[mu]nunguzi
These can be reconstructed as:
| person | Nominative-Ergative-Instrumental | Accusative-Genitive | Dative | Ablative | Locative | Imitative-Similative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | dual | ngalbai | ngalbaini | ngalbainipa | ngalbainingu ngalbainungu |
ngalbainiya | ngalbainidha |
| plural | ngœři | ngœři(mù)ni | ngœři(mù)nipa | ngœři(mù)ningu ngœři(mù)nungu |
ngœři(mù)niya | ngœři(mù)nidha | |
| 1st-2nd | dual | ngaba | ngabani | ngabanipa | ngabaningu ngabanungu |
ngabaniya | ngabanidha |
| plural | ngalpa | ngalpa(mù)ni | ngalpa(mù)nipa | ngalpa(mù)ningu ngalpa(mù)nungu |
ngalpa(mù)niya | ngalpa(mù)nidha | |
| 2nd | dual | ngipel | ngipeni | ngipenipa | ngipeningu ngipenungu |
ngipeniya | ngipenidha |
| plural | ngitha(na) | ngitha(na)(mù)ni | ngitha(na)(mù)nipa | ngitha(na)(mù)ningu ngitha(na)(mù)nungu |
ngitha(na)(mù)niya | ngitha(na)(mù)nidha | |
| 3rd | dual | palai pale |
palamùni | palamùnipa | palamùningu palamùnungu |
palamùniya | palamùnidha |
| plural | thana | thana(mù)ni | thana(mù)nipa | thana(mù)ningu thana(mù)nungu |
thana(mù)niya | thana(mù)nidha | |
- 'Who' in the dual nominative-accusative (and optionally in the ergative-instrumental) had the forms ngawal (dual) and ngaya (plural).
- Mi- 'what, which' was used in much the same way as in the modern dialects.
Verb morphology
Verbs can have over 100 different aspect, tense, voice, mood and number forms. Verb agreement is with the object (i.e. 'ergative') in transitive clauses, and with the subject in intransitive clauses. Imperatives, on the other hand, agree with both subject and object in transitive clauses.
There are three aspects ('perfective', 'imperfective', 'habitual'), two telicity forms ('active', which focuses on the verb activity and subsumes many intransitives, many antipassives and some transitives, and 'attainative', which subsumes many transitives, some antipassives and some intransitives), two moods ('non-imperative' and 'imperative' [which resembles a subjunctive in some uses]), 6 tenses ('remote future', 'today/near future', 'present', 'today past', 'recent past', 'remote past' — KLY has developed a 7th tense, a 'last night' tense) and four numbers ('singular', 'dual', 'specific plural', 'animate active plural' — in form the animate active plural is the same as the singular, and is only found on certain verbs).
In most descriptions of the language the active and attainative forms have been mistermed transitive and intransitive respectively. Transitive, intransitive, passive, antipassive and 'antipassive passive' in the language are syntactic categories, and are formed by the interplay of nominal and verbal morphology, clause/sentence-level characteristics such as word-order, and semantic considerations.
Verb morphology consists of prefixes (aspect, positioning, etc.), suffixes (telicity, number, and two fossilised multiplicative/causative suffixes) and endings (tense, aspect and mood, and a very limited extent number and telicity). The structural matrix of the verb is as follows. Note that the two fossilised suffixes are mutually exclusive; if a suffix is in the A slot, a suffix cannot appear in the B slot, and vice versa:
(prefix) + (prefix) + stem (+FOSSILISED SUFFIX A) + (TELICITY) (+FOSSILISED SUFFIX B) + (number) + ending (+ending)
Examples:
- pabalkabuthamadhin 'two were laid down across something' [which would be clear in the context]
- pabalkabuthemadhin 'two lay down (laid themselves down) across something' [which would be clear in the context]
- prefix: pa- 'telic prefix'
- prefix: bal- 'positional — across'
- stem: kabutha- 'place, lay'
- telicity suffix: -Ø 'attainative', -i 'active'
- number suffix: -ma 'dual' (absolutive agreement)
- tense-aspect-mood ending: -dhin 'remote past perfective'
- garwœidhamemanu 'two met each other earlier today'
- prefix: gar- 'collective'
- stem: wœidha- 'place, put'
- Fossilised suffix: ma 'intensive'
- telicity suffix: i 'active'
- number suffix: ma 'dual'
- tense-aspect-mood ending: dhin 'remote past perfective'
Sample verb declension
The verb here is íma- 'see, observe, supervise, examine, try, test'
| Case/Suffix | Attainative | Active | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perfective | Imperfective | Perfective | Imperfective | ||
| remote future | singular | imane | imaipu (imaiparui) | imedhe | imepu (imeparui) |
| dual | imamane | imampu (imamparui) | imemadhe | imempu (imemparui) | |
| plural | imamœine | imamœipu (imamœiparui) | imemœidhe | imemœipu (imemœiparui) | |
| near future | singular | imaipa | imaipu (imaiparui) | imepa | imepu (imeparui) |
| dual | imampa | imampu (imamparui) | imempa | imempu (imemparui) | |
| plural | imamœipa | imamœipu (imamœiparui) | imemœipa | imemœipu (imemœiparui) | |
| present | singular | iman | imaipa | imiz | imepa |
| dual | imaman | imampa | imeman | imempa | |
| plural | imamœin | imamœipa | imemœin | imemœipa | |
| today past | singular | imanu | imadha | imema | imedha |
| dual | imamanu | imamadha | imemanu | imemadha | |
| plural | imamœinu | imamœidha | imemœinu | imemœidha | |
| recent past | singular | imangu | imarngu | imaingu | imairngu |
| dual | imamangu | imamarngu | imemangu | imemarngu | |
| plural | imamœingu | imamœirngu | imemœingu | imemœirngu | |
| remote past | singular | imadhin | imar | imaidhin | imai |
| dual | imamadhin | imamar | imemadhin | imemar | |
| plural | imamœidhin | imamœi (imamir) | imemœidhin | imemœi (imemir) | |
| Case/Suffix | Singular | Dual | Plural | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Habitual | Attainative | imaipu (imaiparui) | imampu (imamparui) | imamœipu (imamœiparui) | |
| Active | imepu (imeparui) | imempu (imemparui) | imemœipu (imemœiparui) | ||
| Perfective | Attainative | Singular Subject | imar | imamar | imamœi (imamir) |
| Non-Singular Subject | imau (imaziu) | imamariu | imamœi (imamœiziu, imamiu) | ||
| Active | imi | imemariu | imemœi (imemœiziu, imemiu) | ||
| Imperfective | Attainative | imadha | imamadha | imamœidha | |
| Active | imedha | imemadha | imemœidha | ||
| Case/Suffix | Verbal Noun | Proprietive | Privative | Resultative | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unmarked form | imai | imail | imaigi | imaizi | |
| impersonal (NOM-ACC) |
independent form | imai | imailnga | imaiginga | imaizinga |
| stem | imai- | imailmai- | imaigimai- | imaizimai- | |
| personal (NOM-ACC) |
independent form | — | imailaig | imaigig | imaizig |
| stem | — | imailga- | imaigiga- | imaiziga- | |
Kauřařaigau Ya verbal morphology
Prefixes
These were the same as in the modern dialects.
Suffixes
The only suffix differences with the modern dialects were in the form of the plural and verbal noun suffixes. In OKY these were maři and ři respectively. The dual was ngauma on ma- 'take, give, move etc.' and otherwise uma.
Class 1: wœidha- 'put, place, cook'
- wœidhamařinu attainative perfective present plural object
- wœidhaumanu attainative perfective present dual object
- wœidhemařinu active perfective present plural subject
- wœidheumanu active perfective present dual subject
- wœidhàři verbal noun
Class 2: ni-, niya- 'sit, stay'
- niyamařipa[ri] imperfective present plural
- niyaumapa[ri] imperfective present dual
- niyàři, niyài verbal noun
Verb endings
| ATTAINATIVE INDICATIVE | perfective | singular perfective active (where different) |
imperfective |
|---|---|---|---|
| remote future | -kœrui | — | -kœrui |
| future | -pa[ri] | — | -kœrui |
| present | -nu | -izi monosyllabic stem: -iziři |
-pa[ri] |
| today past | -nulai | -ma | -adha |
| recent past | -ngùl | — | -r(a)ngùl |
| remote past | -dhin(i) | — | -r(a) |
| ATTAINATIVE IMPERATIVE | -r(a) SgS, -u PlS, -riu Dual | -i | -adha |
On the whole, the OKY verb seems to have been declined like the Kalau Lagau Ya verb. This includes the loss of the suffix ma in the intransitive imperfective present/perfective today future singular. This loss, however, appears to have been optional in the today past equivalent:[19]
- OKY daneipa (danaipa) 'rise (sun)' (MacGillivray): KLY danaika, KKY danamipa 'rise (sun, etc.), load (self) up' present imperfective
- OKY dadeipa (dhœidhaipa) 'die' (MacGillivray): KLY dhœidhaika (base dhœidhama-) 'be dizzy, dead drunk' present imperfective
- OKY usimema, usima (usimima, usima) 'douse' (MacGillivray): KLY usima, KKY wœsimima 'douse' today past perfective
Vowel/diphthong deletion and reduction in class 1b verbs was optional in OKY where it is now optional or obligatory:
- OKY uzareuma-: KLY uzareuma-, KKY uzarma- 'go dual'
- OKY delupeipa (dœdupaipa) 'drown, sink': KLY dudupaka, KKY dœdupapa
The irregular verb yœwi- / iya- / yœuna- 'lie/slant/lean over/down' was recorded in the form iipa (eepah), indicating the stem ii- (the remote past form iir is found in modern KY, though not recorded in OKY). Otherwise, only yœuna- was recorded for OKY.
Miscellaneous paradigms
Three paradigms that have irregular morphology are:
- Si[ ]kai 'perhaps, maybe, possibly' (all dialects except Kalau Kawau Ya). This word modifies for singular gender : masculine sinukai/senukai; feminine sinakai/senakai; general (singular, dual, plural) sikai. In KKY, the word is invariable sike, sikedh (sikedh is more emphatic.)
- yawa 'goodbye, farewell, take care' (cf. yawar 'journey, travel'; yawaya- 'watch over, watch out for, etc.'). This word is only used when speaking to a single person. For two or more people, the form is yawal.
- masculine kame ~ kamedh, feminine kake ~ kakedh, non-singular kole ~ koledh 'hey!' (word used to attract someone's attention; in kamedh, kakedh and koledh (the -dh final in all these, like in sikedh above, is only found in more emphatic use.)
Sign language
The Torres Strait Islanders, neighbouring Papuans and neighbouring Australians have a common sign language,[20] though early records did not make a detailed study of this (e.g. Australian Aboriginal sign languages).[21] Simple conversations and stories can be carried out in the sign language; however, it does not attain the sophistication of a fully developed sign language. It's had some influence on Far North Queensland Indigenous Sign Language.
See also
References
- ^ "SBS Australian Census Explorer". Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ Y1 Kalau Lagau Ya at the Australian Indigenous Languages Database, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies
- ^ Crump, Des (27 July 2020). "Language of the Week: Week Nine - Mabuiag". State Library Of Queensland. Retrieved 15 December 2023.
- ^ Y1 Kalaw Lagaw Ya at the Australian Indigenous Languages Database, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies
- ^ ""2021 Census - Cultural Diversity, 2021, TableBuilder"". Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS).
- ^ Mitchell (2015)
- ^ Capell (1956), Dixon (2002)
- ^ a b Mitchell 2015.
- ^ Sommer (1969, pp. 62–66)
- ^ Bouckaert, Remco R.; Bowern, Claire; Atkinson, Quentin D. (April 2018). "The origin and expansion of Pama–Nyungan languages across Australia". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 2 (4): 741–749. doi:10.1038/s41559-018-0489-3. PMID 29531347. S2CID 4208351.
- ^ Haddon (1935), Laade (1968)
- ^ Alpher et al. 2008. Torres Strait Language Classification. in Bowern, Evans, and Miceli (eds). _Morphology and Language History_ Amsterdam: John Benjamins
- ^ Wurm 1975, pp. 333–334
- ^ a b Thomason & Kaufman 1988, p. 212
- ^ Laade 1968.
- ^ Ngajedan 1987.
- ^ "Masig calendar - Indigenous Weather Knowledge". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- ^ Lawrence 1989.
- ^ MacGillivray 1852, p. 311.
- ^ Seligman, C. G., and A. Wilkin (1907). The gesture language of the Western Islanders, in "Reports of the Cambridge Anthropological Expedition to Torres Straits." Cambridge, England: The University Press, v.3.
- ^ Kendon, A. (1988) Sign Languages of Aboriginal Australia: Cultural, Semiotic and Communicative Perspectives. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Bibliography
- Capell, Arthur (1956), A new approach to Australian linguistics, Sydney: Oceanic Linguistic Monographs, p. 108
- Dixon, R. M. W. (2002), Australian Languages: Their Nature and Development, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-47378-1
- Evans, Nicholas (June 2005), "Australian Languages Reconsidered: A Review of Dixon (2002)", Oceanic Linguistics, 44 (1): 242–286, doi:10.1353/ol.2005.0020, hdl:1885/31199, S2CID 145688642
- Ford, Kevin; Ober, Dana (1991), "A sketch of Kalaw Kawaw Ya", in Romaine, S. (ed.), Language in Australia, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 118–142
- Haddon, Alfred Cort (1935). Reports of the Cambridge Anthropological Expedition To Torres Straits: Volume 1:General Ethnography. The University Press.
- Laade, Wolfgang (January 1968). "The Torres strait islanders' own traditions about their origin". Ethnos. 33 (1–4): 141–158. doi:10.1080/00141844.1968.9981002.
- Lawrence, David (1989). "FROM THE OTHER SIDE: Recently collected oral evidence of contacts between the Torres Strait Islanders and the Papuan peoples of the southwestern coast". Aboriginal History. 13 (1/2): 94–123. JSTOR 24045613.
- MacGillivray, John (1852). Narrative of the voyage of HMS Rattlesnake. T. W. Boone.
- Mitchell, Rod (April 2015), "Ngalmun Lagaw Yangukudu: The Language of our Homeland in Goemulgaw Lagal: Cultural and Natural Histories of the Island of Mabuyag, Torres Strait", Memoirs of the Queensland Museum – Culture, 8 (1): 323–446, ISSN 1440-4788
- Ngajedan, Mohamad (1987). Kamus etimologi bahasa Indonesia. Dahara Prize.
- Sommer, Bruce A. (1969). Kunjen Phonology: Synchronic and Diachronic. Australian National Univ.
- Thomason, Sarah Grey; Kaufman, Terrence (1988). Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-07893-2.
- Wurm, S.A. (1975). "The Trans-Fly (Sub-Phylum Level) Stock". In S.A. Wurm (ed.). Papuan languages and the New Guinea linguistic scene. Vol. 1, Pacific Linguistics. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, The Australian National University. pp. 323–348.
