Ijlil al-Shamaliyya
Ijlil al-Shamaliyya | |
|---|---|
| Etymology: El Jelil, meaning "illustrious/grand" (Ar), or "a district/circuit"(He)[1] | |
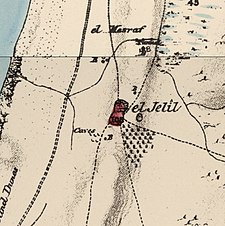
A series of historical maps of the area around Ijlil al-Shamaliyya (click the buttons) | |
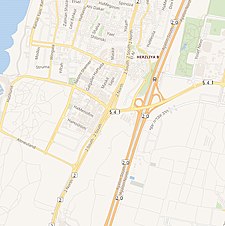
Location within Mandatory Palestine | |
| Coordinates: 32°09′36″N 34°48′42″E / 32.16000°N 34.81167°E | |
| Palestine grid | 132/174 |
| Geopolitical entity | Mandatory Palestine |
| Subdistrict | Jaffa |
| Date of depopulation | End of March- April 3, 1948[4] |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,450 dunams (2.45 km2 or 610 acres) |
| Population (1945) | |
• Total | 190[2][3] |
| Cause(s) of depopulation | Fear of being caught up in the fighting |
| Current Localities | Glil Yam[5] |
Ijlil al-Shamaliyya (Arabic: إجليل الشمالية Ijlīl aš-Šamāliyya) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Jaffa Subdistrict. Established in the 19th century, it was founded by Bani Sa'b tribesmen from the Qalqiliya area and migrants from Egypt.[6] It was depopulated during the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on April 3, 1948.
Location
Ijlil al-Shamaliyya, (meaning "Northern Ijlil"), was located on a hilltop, 15 km (9 mi) northeast of Jaffa, and about 100 meters north of its sister village, Ijlil al-Qibliyya ("Southern Jilil").[5]
History
Ijlil was one of four villages founded in the 18th century, near the coast north of the Yarkon River (along with the villages of Al-Shaykh Muwannis, Al-Haram, and Umm Khalid). According to historian Roy Marom, the establishment of Ijlil "demonstrates that the expansion of settlement in the southern Sharon was the result of the internal expansion of the core settlement by residents of the mountainous highlands of Samaria, and not by Egyptian ‘penetrators’ as previously claimed."[7]
In June 1870, the French explorer Victor Guérin visited both villages. He described them as one unit called Edjlil, situated on a hill and divided into two districts. Together, they had 380 inhabitants. The houses were built of rammed earth or with different small aggregates mixed in with kneaded and dried silt.[8] In 1870/1871 (1288 AH), an Ottoman census listed Ijlil in the nahiya (sub-district) of Bani Sa'b.[9]
In 1882, the PEF's Survey of Western Palestine described the two villages, named El Jelil, as "a mud village, with a well to the south and a second to the north. [..] A small olive-grove exists to the south-east."[10]
British Mandate era
In the 1922 census of Palestine conducted by the British Mandate authorities, the twin villages of Ijlil (spelled Jelil) had a population of 154, all Muslims,[11] increasing by the 1931 census to 305, still all Muslim.[12] In 1943 Glil Yam was founded on what was traditionally village land, to the east of the village site.[5]


In the 1945 statistics the population of Ijlil al-Shamaliyya consisted of 190 Muslims[2] and the land area was 2,450 dunams of land, according to an official land and population survey.[3] Of this land, 183 dunams were designated for citrus and bananas, 13 for plantations and irrigable land, 1,574 for cereals,[13] while seven dunams were built-up areas.[14] Also in 1945, a school was founded in the village and shared with Ijlil al-Qibliyya. It had 64 students in its first year. The village also had a mosque and several small shops.[5]
1948 war, and aftermath
In December 1947 and January 1948 the leaders of al-Shaykh Muwannis, al-Mas'udiyya, al-Jammasin al-Sharqi, al-Jammasin al-Gharbi, and the mukhtars of 'Arab Abu Kishk and the two Ijlil-villages met with Haganah representatives in Petah Tikva. These villages wanted peace, and promised not to harbor any Arab Liberation Army soldiers or local Arab militia. They further promised that, in the case they were not able to keep them out alone, they were to call on Haganah for help.[15]
By mid-March 1948, the Alexandroni Brigade had imposed isolation, dubbed "quarantine", of al-Shaykh Muwannis, 'Arab Abu Kishk and the two Ijlil-villages. However, on 12 March, the LHI kidnapped five village notables from al-Shaykh Muwannis.[16] This undermined the villagers' trust in former agreements, and many left. The people of the two Ijlil-villages also left, after asking Jewish neighbours to look after their property.[17]
In 1992, the historian Walid Khalidi found that the place was difficult to identify with precision as it was part of a large garbage dump.[5]
References
- ^ Palmer, 1881, p. 214
- ^ a b Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 27
- ^ a b c Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 52
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. xviii, village No. 196. Also gives cause of depopulation
- ^ a b c d e Khalidi, 1992, p. 243
- ^ Grossman, D. (1986). "Oscillations in the Rural Settlement of Samaria and Judaea in the Ottoman Period". in Shomron studies. Dar, S., Safrai, S., (eds). Tel Aviv: Hakibbutz Hameuchad Publishing House. p. 372
- ^ Roy Marom, "Al-Sheikh Muwannis: Transformations in the Arab Countryside between the Mountainous Interior and the City of Jaffa, 1750–1848," Cathedra 183 (February 2023), pp. 9–34.
- ^ Guérin, 1875, p. 374
- ^ Grossman, David (2004). Arab Demography and Early Jewish Settlement in Palestine. Jerusalem: Magnes Press. p. 255.
- ^ Conder and Kitchener, 1882, SWP II, p. 251
- ^ Barron, 1923, Table VII, Sub-district of Jaffa, p. 20
- ^ Mills, 1932, p. 13
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 95
- ^ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 145
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 91
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 127
- ^ Morris, 2004, p. 128
Bibliography
- Barron, J.B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Clermont-Ganneau, C.S. (1895). Études d'archéologie orientale (in French). Paris: E. Bouillon. (pp. 192−196: "Les Trois−Ponts, Jorgilia")
- Conder, C.R.; Kitchener, H.H. (1882). The Survey of Western Palestine: Memoirs of the Topography, Orography, Hydrography, and Archaeology. Vol. 2. London: Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
- Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine.
- Guérin, V. (1875). Description Géographique Historique et Archéologique de la Palestine. Vol 2 Samarie, pt. 2. Paris, Imprimé par autorisation de l'empereur à l'Impr. impériale.
- Hadawi, S. (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Center.
- Khalidi, W. (1992). All That Remains: The Palestinian Villages Occupied and Depopulated by Israel in 1948. Washington D.C.: Institute for Palestine Studies. ISBN 0-88728-224-5.
- Mills, E., ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Morris, B. (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00967-6.
- Palmer, E.H. (1881). The Survey of Western Palestine: Arabic and English Name Lists Collected During the Survey by Lieutenants Conder and Kitchener, R. E. Transliterated and Explained by E.H. Palmer. Committee of the Palestine Exploration Fund.
External links
- Welcome To Ijlil al-Shamaliyya
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 13: IAA, Wikimedia commons
- Ijlil al Shamaliyya from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
- Ijlil al-Shamaliyya, Zochrot
- Ijlil tour, 20.3.04, from Zochrot
- Ibrahim Abu-Sneineh, Ijlil, Testimony collected in preparation for Zochrot's tour and booklet of Ijlil, March 30, 2004
- Mahmoud Abu-Sneineh, Ijlil, Testimony collected in preparation for Zochrot's tour and booklet of Ijlil, March 20, 2004.
- Remembering Ijlil, Ijlil Booklet, 03/2004