Moravian Indian Grants

Moravian Indian Grants were three tracts of land in Tuscarawas County, Ohio granted by the federal government in the eighteenth century to a group of Christian Indians. In the nineteenth century, these natives moved west, and the government sold the land to white people.
Background
In 1772, Moravian missionaries established communities in the Tuscarawas River valley in present-day Tuscarawas County, Ohio. Three communities of Christian converts from the Delaware and Mohican Indian peoples were established.[1] In May, 1772 came Schoenbrunn, followed by Gnadenhutten in October that year and Salem (south of modern-day Port Washington, Ohio in 1780.[2] During the American Revolutionary War, they found themselves between British-allied Indian tribes to their west and American settlers to their east. On March 8, 1782, American militiamen came to Gnadenhutten, rounded up the Indians and executed 96 men, women and children in the Gnadenhutten massacre.[3] When it was learned in the East that these victims had not participated in massacres on settlers as previously thought, Congress acted to provide reparations to them.[4][5]
Legislative action
The Land Ordinance of 1785 established a procedure for sale of government land in what is now Ohio. It read in part:
And be it further ordained, That the towns of Gnadenhutten, Schoenbrun, and Salem, on the Muskingum, and so much of the lands adjoining to the said towns, with the buildings and improvements thereon, shall be reserved for the sole use of the Christian Indians, who were formerly settled there, or the remains of that society, as may, in the judgment of the geographer, be sufficient for them to cultivate.[6]
The surveys never made it west to the Tuscarawas Valley, so this act had no practical consequence.
In September 1788, the congress modified the ordinance to direct that a town of 666 and 2/3 acres in a tract of 4000 acres around each of the three towns should be surveyed as quickly as possible and then title should be vested in the Society of the United Brethren in trust for propagating the faith among the Indians.[7] Again nothing happened.
The Act of June 1, 1796 established the United States Military District in the Tuscarawas Valley and elsewhere. It also provided in section 5
That the said Surveyor General be, and he is hereby, required to cause to be surveyed three several tracts of land, containing four thousand acres each, at Shoenbrun, Gnadenhutten, and Salem; being the tracts formerly set apart ... for the society of the United Brethren for the propagation of the gospel among the heathen; and to issue a patent or patents for the said three tracts to the said society, in trust ...[8]
Retrocession
On February 24, 1798, a patent was issued to the Society for the tracts, but few Indians chose to live there.[7][5] The Moravians also expended large sums on improvements.[9] In March, 1823, Congress directed that arrangements should be made to purchase the title from the Indians.[10] On August 4, 1823 at Gnadenhutten, Lewis Cass for the United States, and Lewis David de Schweinitz for the Moravians reached agreement on a sale.[9] Cass also made agreement with a number of Indians at Detroit on November 8, 1823.[11] Congress accepted the agreements on May 26, 1824, and directed the tracts be divided into lots and sold.[12] The lots were surveyed in 1825 by F. Wampler, Deputy Surveyor.[11]
The lots were sold at the courthouse in New Philadelphia, Ohio, and unsold lots later sold at the land office in Zanesville, Ohio. The Christian Indians received $400 per year, and the Moravians received enough to repay their debts from improvements.[13]
Surveys
The tracts were not surveyed with the usual rectangular survey system of the Public Land Survey System. They were independent of the survey of the surrounding United States Military District.
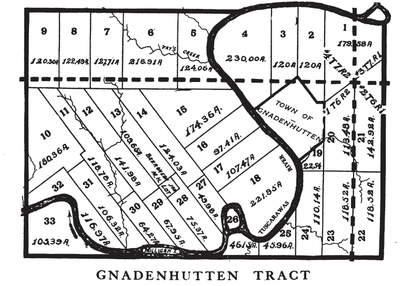 |
 |
 |
Notes
References
- "Land Ordinance of 1785". Wikisource.
- Knepper, George W (2002). The Official Ohio Lands Book (PDF). Auditor of the State of Ohio.
- Peters, William E (1918). Ohio Lands and Their Subdivision. W.E. Peters.

