Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn | |
 1856 drawing showing Fort Dearborn as it appeared in 1831[1] | |
| Location | Chicago, Illinois |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 41°53′17″N 87°37′26″W / 41.88806°N 87.62389°W |
| Built | 1803 |
| Architect | U.S. Army |
| Architectural style | log-built fort enclosed in a double stockade |
| Part of | American frontier, Michigan–Wacker Historic District (ID78001124) |
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort, first built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by U.S. troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War. The original fort was destroyed following the Battle of Fort Dearborn during the War of 1812, and a replacement Fort Dearborn was constructed on the same site in 1816 and decommissioned by 1837.
Parts of the fort were lost to the widening of the Chicago River in 1855, and a fire in 1857. The last vestiges of Fort Dearborn were destroyed in the Great Chicago Fire of 1871. The site of the fort is now a Chicago Landmark, located in the Michigan–Wacker Historic District, at the southern end of the DuSable Michigan Avenue Bridge.
Background
Historic events
Human activity in the Chicago area prior to the arrival of European explorers is mostly unknown. In 1673, an expedition headed by Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette was the first recorded to have crossed the Chicago Portage and traveled along the Chicago River.[2] Marquette returned in 1674, and camped for a few days near the mouth of the river. He moved to the portage, where he camped through the winter of 1674–75. Joliet and Marquette did not report any Native Americans living near the Chicago River area at that time.[3] Archaeologists, however, have discovered numerous historic Indian village sites dating to that time elsewhere in the Chicago region.[4]
In 1682, René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle had claimed a large territory (including the Chicago area), for France.[5] Two of de La Salle's men built a stockade at the portage in the winter of 1682/1683.[6]
In 1763, following defeat in the French and Indian War, the French ceded this area to Great Britain. It became a region within their Province of Quebec. Great Britain later ceded the area to the United States (at the end of the American Revolutionary War), although the Northwest Territory remained under de facto British control until about 1796.[7]
Following defeat of several Native American tribes in the Northwest Indian War of 1785–1795, the Treaty of Greenville was signed between the US and several chiefs at Fort Greenville (now Greenville, Ohio), on August 3, 1795. As part of the terms of this treaty, a coalition of Native Americans and Frontiers men, known as the Western Confederacy, ceded to the United States large parts of modern-day Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Wisconsin, and Illinois. This included "six miles square" centered from the mouth of the Chicago River.[8][9]
Local events
A French-Jesuit mission, the Mission of the Guardian Angel, was founded somewhere in the vicinity in 1696, but was abandoned around 1700.[10] The Fox Wars effectively closed the area to Europeans in the first part of the 18th century. The first non-native to re-settle in the area may have been a trader named Guillory, who might have had a trading-post near Wolf Point on the Chicago River around 1778.[11]
Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, a French-speaking colonist of African descent, built a prosperous farm and trading post near the mouth of the Chicago River in the 1780s, at a site directly across the river from the future fort.[12] A settlement developed there and he is widely regarded as the founder of Chicago.[13][14] Antoine Ouilmette is the next recorded resident of Chicago; he claimed to have settled at the mouth of the Chicago River in July 1790.[15]
First Fort Dearborn

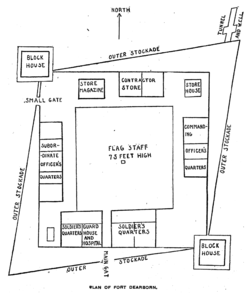
On March 9, 1803, Henry Dearborn, the Secretary of War, wrote to Colonel Jean Hamtramck, the commandant of Detroit, instructing him to have an officer and six men survey the route from Detroit to Chicago, and to make a preliminary investigation of the situation at Chicago.[16] Captain John Whistler was selected as commandant of the new post, and set out with six men to complete the survey. The survey completed, on July 14, 1803, a company of troops set out to make the overland journey from Detroit to Chicago. Whistler and his family made their way to Chicago on a schooner called the Tracy. The troops reached their destination on August 17.[17] The Tracy was anchored about half a mile offshore, unable to enter the Chicago River due to a sandbar at its mouth. Julia Whistler, the wife of Captain Whistler's son, Lieutenant William Whistler, later related that 2000 Indians gathered to see the Tracy.[18][19] The troops had completed the construction of the fort by the summer of 1804;[20] it was a log-built fort enclosed in a double stockade, with two blockhouses (see diagram above).[17] The fort was named Fort Dearborn, after U.S. Secretary of War Henry Dearborn, who had commissioned its construction.

A fur trader, John Kinzie, who bought the old Du Sable property, arrived in Chicago in 1804, and rapidly became the civilian leader of the small settlement that grew around the fort.[17] In 1810, Kinzie and Whistler became embroiled in a dispute over Kinzie supplying alcohol to the Indians. In April, Whistler and other senior officers at the fort were removed; Whistler was replaced as commandant of the fort by Captain Nathan Heald.[22]
Battle of Fort Dearborn
During the War of 1812, General William Hull ordered the evacuation of Fort Dearborn in August 1814. Captain Heald oversaw the evacuation, but on August 15, the evacuees were ambushed along the trail by about 500 Potawatomi Indians in the Battle of Fort Dearborn. The Potawatomi captured Heald and his wife, Rebekah, and ransomed them to the British. Of the 148 soldiers, women, and children who evacuated the fort, 86 were killed in the ambush. The Potawatomi burned the fort to the ground the next day.
Second Fort Dearborn


Following the war, a second Fort Dearborn was built (1816). This fort consisted of a double wall of wooden palisades, officer and enlisted barracks, a garden, and other buildings. The American forces garrisoned the fort until 1823, when peace with the Indians led the garrison to be deemed redundant. The temporary abandonment lasted until 1828, when it was re-garrisoned following the outbreak of war with the Winnebago Indians.[23] In her 1856 memoir, Wau Bun, Juliette Kinzie described the fort as it appeared on her arrival in Chicago in 1831:
The fort was inclosed [sic] by high pickets, with bastions at the alternate angles. Large gates opened to the north and south, and there were small portions here and there for the accommodation of the inmates. ... Beyond the parade-ground which extended south of the pickets, were the company gardens, well filled with currant-bushes and young fruit-trees. The fort stood at what might naturally be supposed to be the mouth of the river, yet it was not so, for in these days the latter took a turn, sweeping round the promontory on which the fort was built, towards the south, and joined the lake about half a mile below...[24]
The fort was closed briefly before the Black Hawk War of 1832 and by 1837, the fort was being used by the Superintendent of Harbor Works. In 1837, the fort and its reserve, including part of the land that became Grant Park, was deeded to the city by the Federal Government.[25] In 1855, part of the fort was demolished so that the south bank of the Chicago River could be dredged, straightening the bend in the river and widening it at this point by about 150 feet (46 m);[26] and in 1857, a fire destroyed nearly all the remaining buildings in the fort. The remaining blockhouse and few surviving outbuildings were destroyed in the Great Chicago Fire of 1871.
Legacy and monuments

The southern perimeter of Fort Dearborn was located at what is now the intersection of Wacker Drive and Michigan Avenue in the Loop community area of Chicago along the Magnificent Mile. Part of the fort outline is marked by plaques, and a line embedded in the sidewalk and road near the Michigan Avenue Bridge and Wacker Drive. A few boards from the old fort were retained and are now in the Chicago History Museum in Lincoln Park.
First Presbyterian Church (Chicago), the longest continuously-operating institution in Chicago was founded in the carpentry shop of Fort Dearborn on June 26, 1833 and today is located in Woodlawn, Chicago[27]
On March 5, 1899, the Chicago Tribune publicized a Chicago Historical Society replica of the original fort.[28]
In 1933, at the Century of Progress Exhibition, a detailed replica of Fort Dearborn was erected as a fair exhibit.[29][30][31] As part of the celebration, both a United States one-cent postage stamp and a souvenir sheet (containing 25 of the stamps) were issued, showing the fort. The individual stamp and sheet were reprinted when Postmaster General James A. Farley gave imperforated examples of these, and other stamps, to his friends. Because of the ensuing public outcry, millions of copies of "Farley's Follies" were printed and sold.
In 1939, the Chicago City Council added a fourth star to the city flag to represent Fort Dearborn. This star is depicted as the left-most, or first, star of the flag.[32]
The site of the fort was designated a Chicago Landmark on September 15, 1971.[33]
An elementary school in the Chicago Public Schools system is named after Fort Dearborn.[34]
Gallery
- Modern Commemorations
- Fort Dearborn 1808 layout
- London Guarantee Building with large relief above the entrance commemorating Fort Dearborn
- A plaque on Michigan avenue
- A marker showing the fort's southern perimeter
See also
References
- ^ Kinzie 1856; p. 182.
- ^ Quaife 1913, pp. 22–24
- ^ Quaife 1933, p. 18
- ^ Swenson, John F. "Chicago: Meaning of the Name and Location of Pre-1800 European Settlements". Early Chicago. Early Chicago Inc. Retrieved September 13, 2010.
- ^ Worth, Richard (2006). Louisiana, 1682-1803. National Geographic Books. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-7922-6544-3.
- ^ Mason, Edward (1901). Chapters from Illinois History. Chicago: Herbert S. Stone and Company. p. 144. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ^ Quaife 1933, pp. 63–64
- ^ Charles J. Kappler (1904). "Treaty With the Wyandot, etc., 1795". U.S. Government treaties with Native Americans. Oklahoma State University Library. Archived from the original on November 8, 2010. Retrieved April 17, 2011.
- ^ "Fort Dearborn"; Encyclopedia of Chicago online; accessed August 8, 2009]
- ^ Briggs, Winstanley (2005). "Mission of the Guardian Angel". The Electronic Encyclopedia of Chicago. Chicago Historical Society. Retrieved August 6, 2010.
- ^ Meehan, Thomas A. (1963). "Jean Baptiste Point du Sable, the First Chicagoan". Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society. 56 (3): 439–453. JSTOR 40190620.
- ^ Pacyga 2009, p. 12
- ^ Baumann, Timothy E. (December 2005). "The Du Sable Grave Project in St. Charles, Missouri". The Missouri Archaeologist. 66: 59–76.
- ^ Graham, Shirley (1953). Jean Baptiste Pointe De Sable Founder of Chicago. Julian Messner. Retrieved April 16, 2011.
- ^ Letter of Antoine Ouilmette to John H. Kinzie, June 1, 1839; reproduced in Blanchard, Rufus (1898). Discovery and Conquests of the Northwest, with the History of Chicago (volume 1). R. Blanchard and Company. p. 574. Retrieved September 7, 2010.
- ^ Quaife 1933, pp. 65–66
- ^ a b c Pacyga 2009, p. 13
- ^ Currey 1912, p. 24
- ^ Quaife 1933, p. 72
- ^ Quaife 1933, p. 75
- ^ Lossing, Benson (1868). The Pictorial Field-Book of the War of 1812. Harper & Brothers, Publishers. p. 303.
- ^ Pacyga 2009, p. 14
- ^ Currey 1912, p. 188
- ^ Kinzie 1856, pp. 183–184
- ^ "United States v. Illinois Cent. R. CO., 154 U.S. 225 (1894)". Retrieved 15 May 2011.
- ^ Andreas, Alfred T. (1884). History of Chicago, Volume 1. A. T. Andreas. p. 238. Retrieved September 19, 2010.
- ^ Eyre, Ethel. A History of the First Presbyterian Church of Chicago, 1933-1941. Works Progress Administration
- ^ ""Replica of the Original Fort Dearborn," Chicago Tribune, 5 March 1899". Encyclopedia of Chicago. Chicago Historical Society. Retrieved 2011-12-30.
- ^ Lohr, Lenox R. (1952). Fair Management. The Story of a Century of Progress. The Cuneo Press.
- ^ "Rebuilding Old Fort Tests Engineers' Skill". Popular Mechanics. 55 (1): 48–49. January 1931. Retrieved 2011-04-18.
- ^ "Reproduction of Fort Dearborn at the Century of Progress Exposition, 1933". Encyclopedia of Chicago. Chicago Historical Society. Retrieved 2011-12-30.
- ^ "Municipal Flag of Chicago". Chicago Public Library. 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-04.
- ^ "Site of Fort Dearborn". City of Chicago Department of Planning and Development, Commission on Chicago Landmarks. 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2022.
- ^ "School Details Page | Chicago Public Schools".
Bibliography
- Currey, J. Seymour (1912). The Story of Old Fort Dearborn. Chicago: A. C. McClurg & Co.
- Helm, Linai T. (1912). Gordon, Nellie Kinzie (ed.). The Fort Dearborn Massacre. Rand McNally.
- Kinzie, Juliette (1856). Wau-Bun, the "Early Day" in the North-West. Derby and Jackson. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- Pacyga, Dominic A. (2009). Chicago: A Biography. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-64431-8.
- Quaife, Milo Milton (1913). Chicago and the Old Northwest, 1673-1835. The University of Chicago Press. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- Quaife, Milo Milton (1933). Checagou From Indian Wigwam To Modern City 1673-1835. The University of Chicago Press. Retrieved August 26, 2010.
External links
- "Site of Fort Dearborn". City of Chicago Department of Planning and Development, Commission on Chicago Landmarks.